KP221- Final Exam
1/462
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
463 Terms
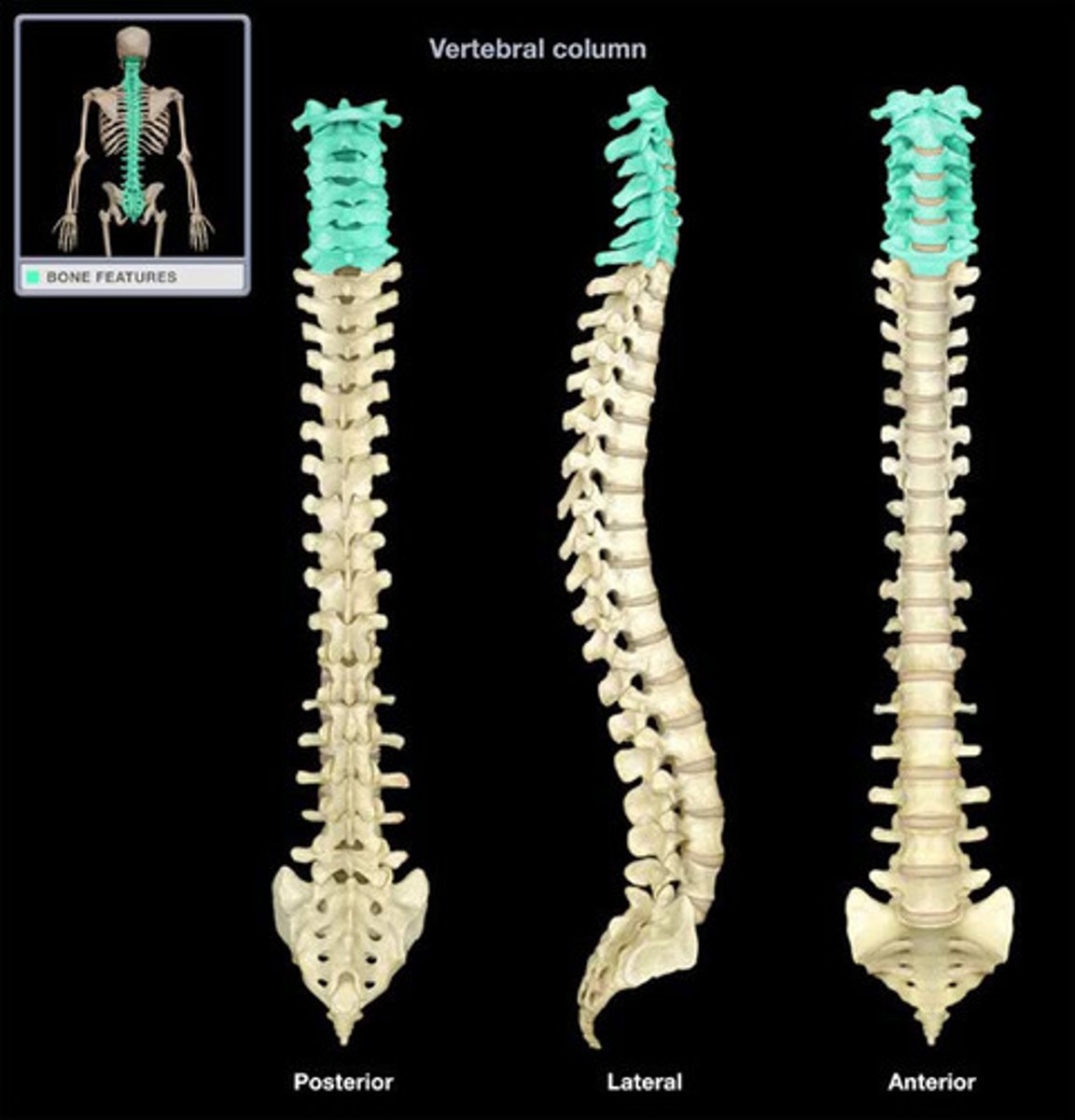
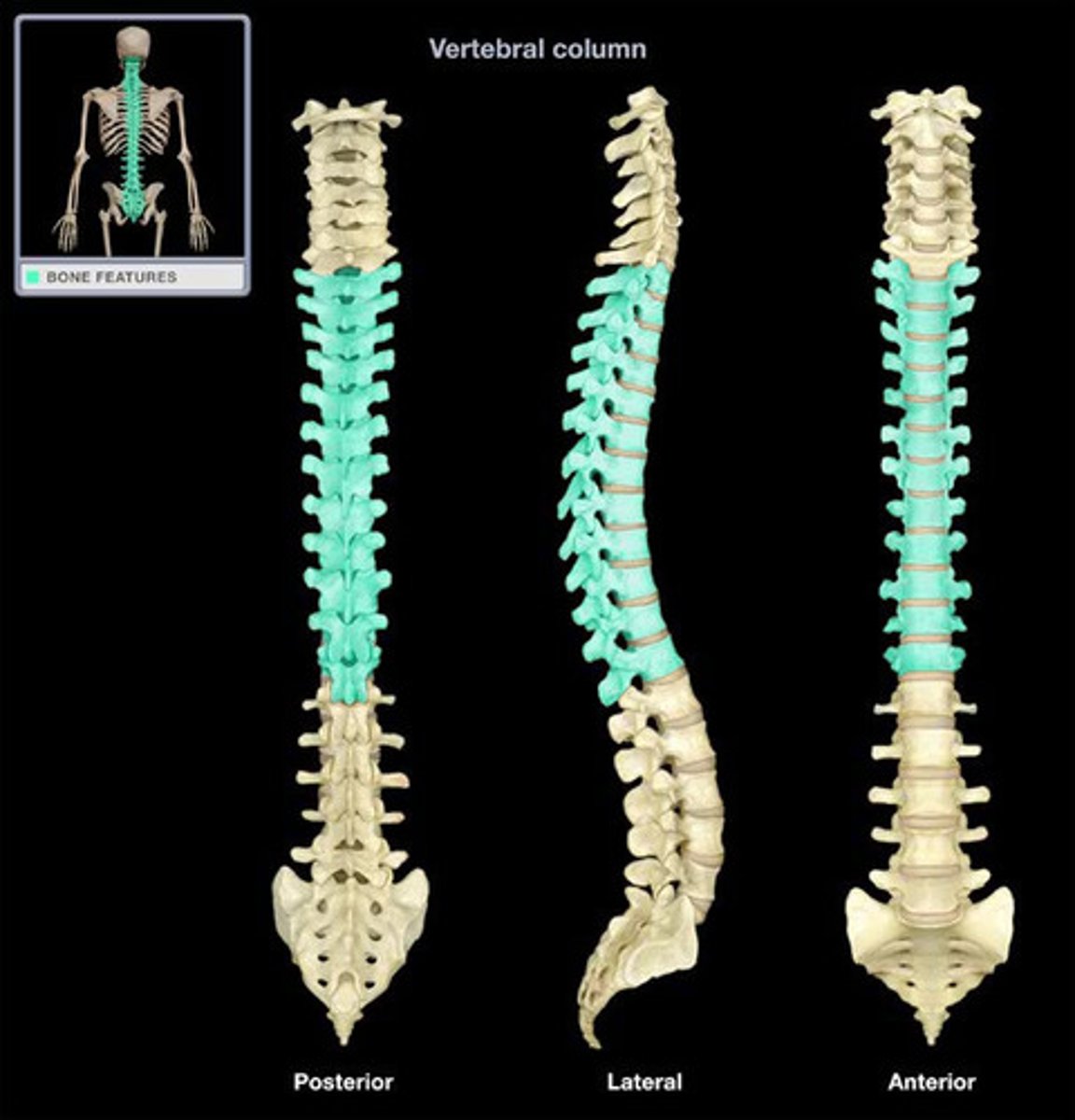
The Vertebral Column
Also known as the spine or the spinal column
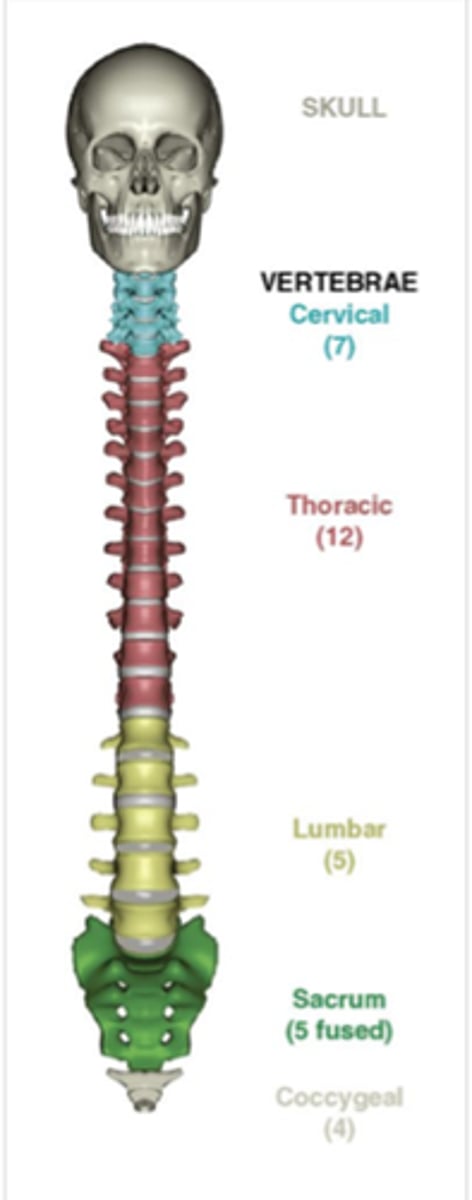
How many vertebrae in the vertebral column?
33 vertebrae
Movements of the Vertebral Column
Flexion, Extension, Lateral Flexion, Rotation
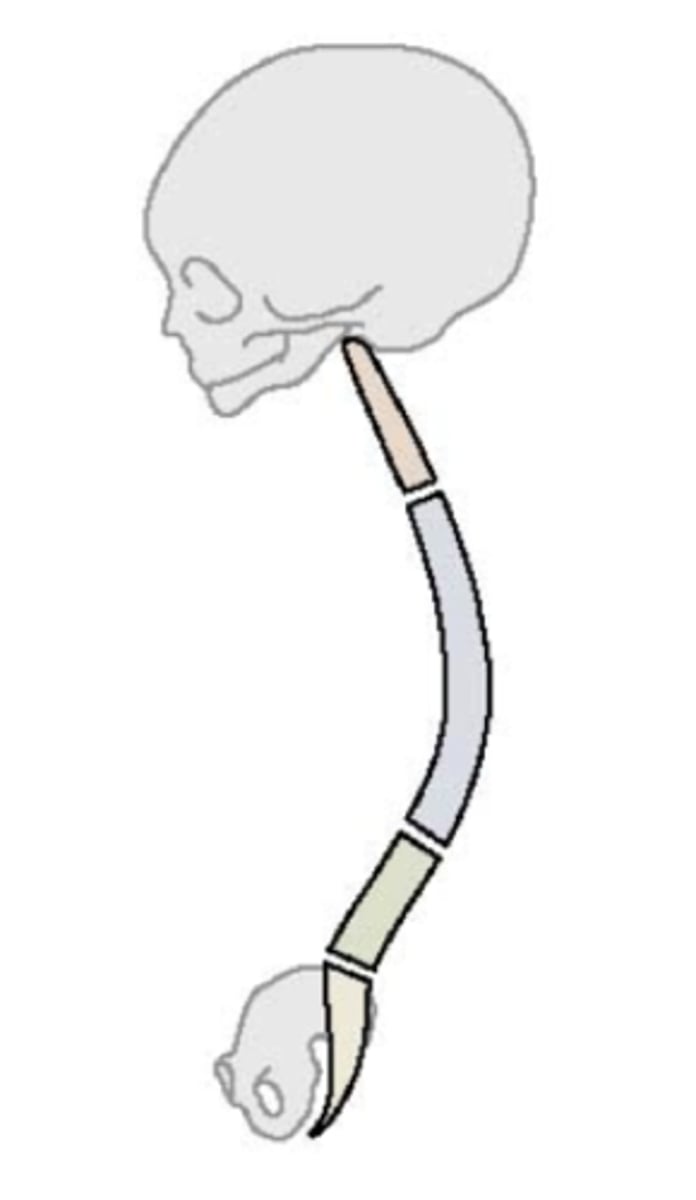
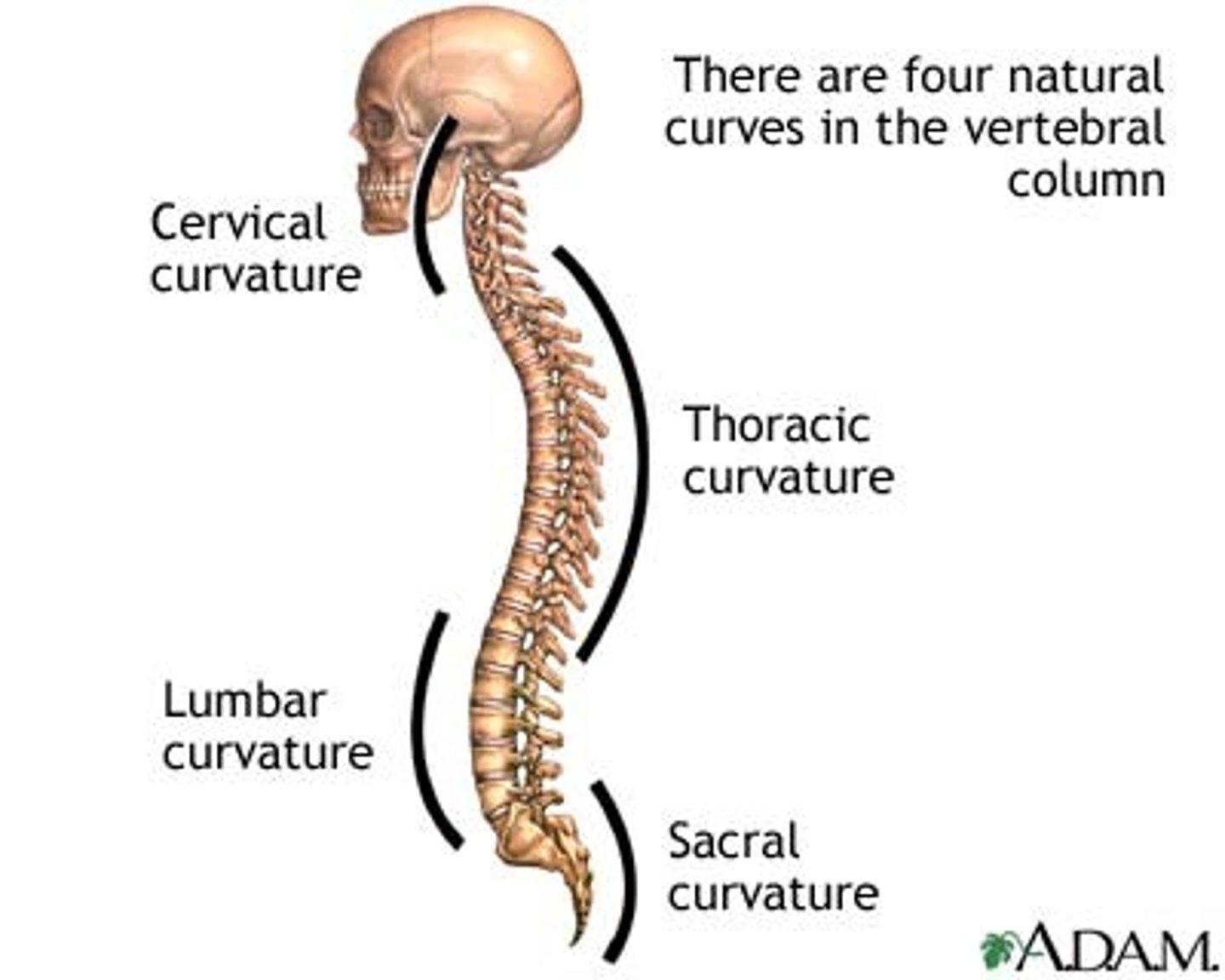
Fetal Spinal Curvature
Vertebral column is C-shaped
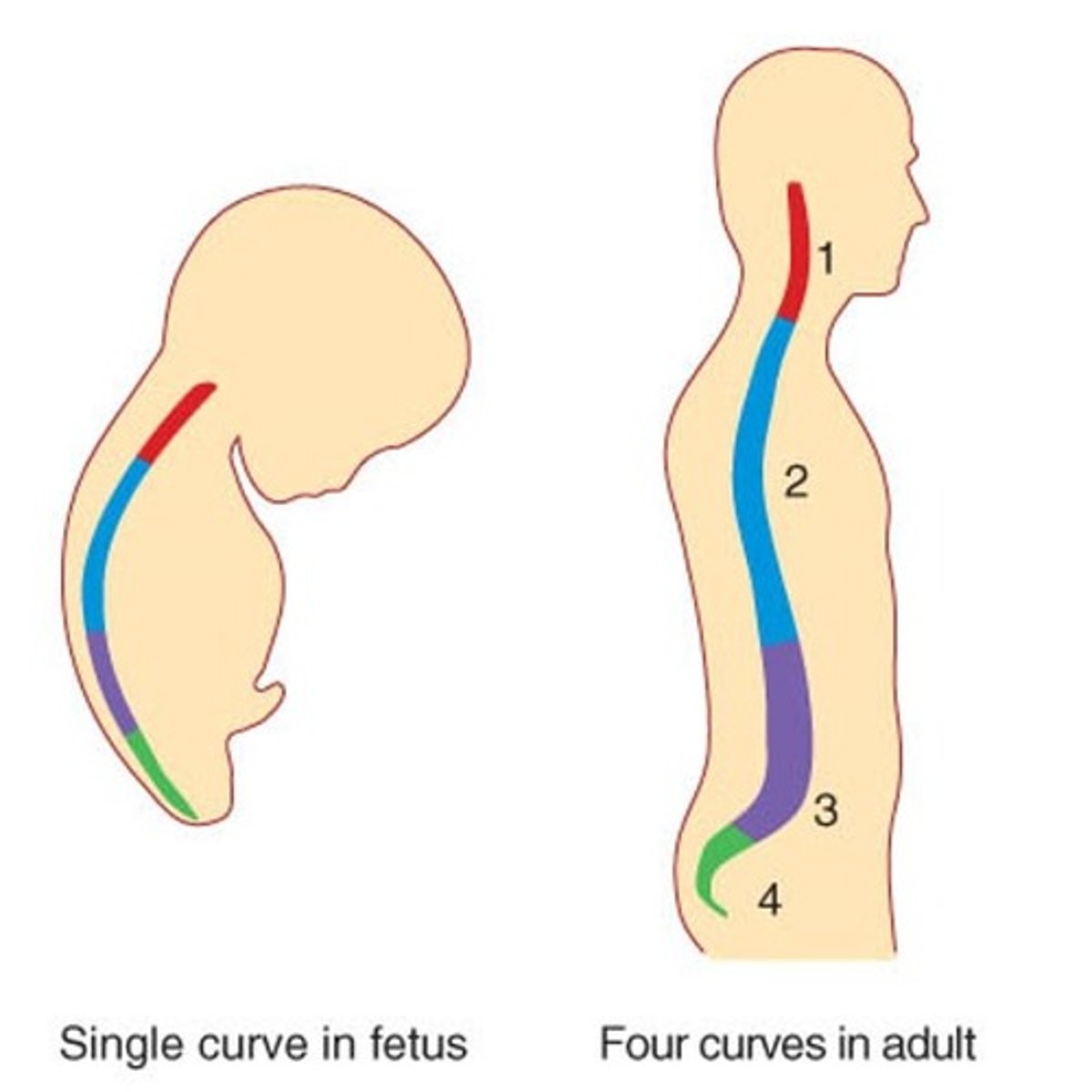
Newborn Spinal Curvature
Slight flexes present between lumbar and sacral areas
Adult Spinal Curvature
Thoracic & Sacral curvatures represent the remains of the original curve
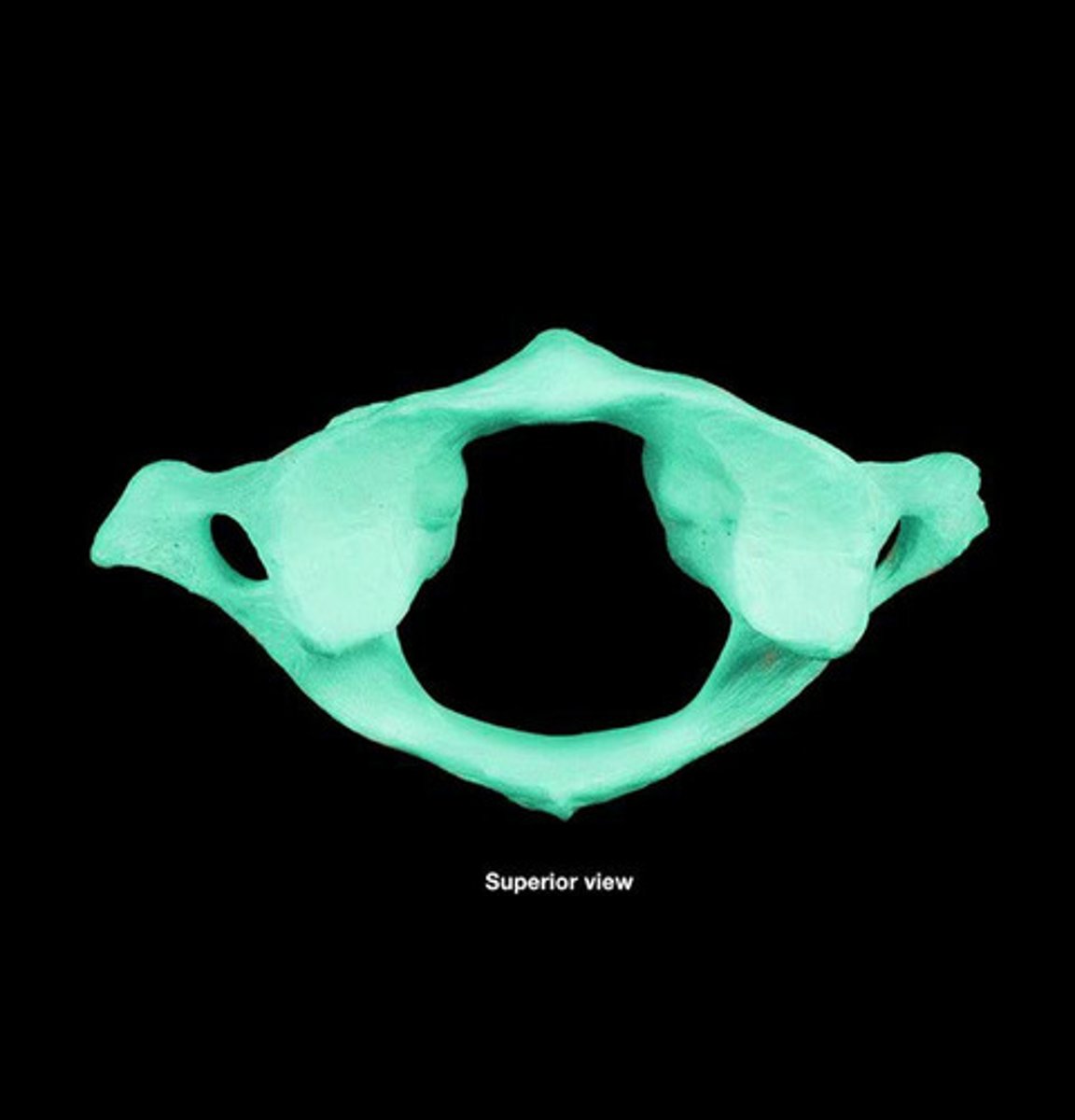
Typical Vertebra Body
Cylindrical & heavy made of spongy bone and covered by thin layer of cortical bone
Vertebral Pedicles
2, on posterior side, extend posteriorly & connect to laminae

What makes up the vertebral arch?
Vertebral foramen & Vertebral canal
Vertebral Foramen
Between vertebral arch & body
Vertebral Canal
Successive vertebral foramina, where spinal cord lies
Transverse process of vertebra
Project laterally at point of union of pedicle & laminae

Function of Transverse Process
Allow for muscle attachment & articulation with ribs
Zygapophyses(Z joints)
Junction of pedicle & lamina
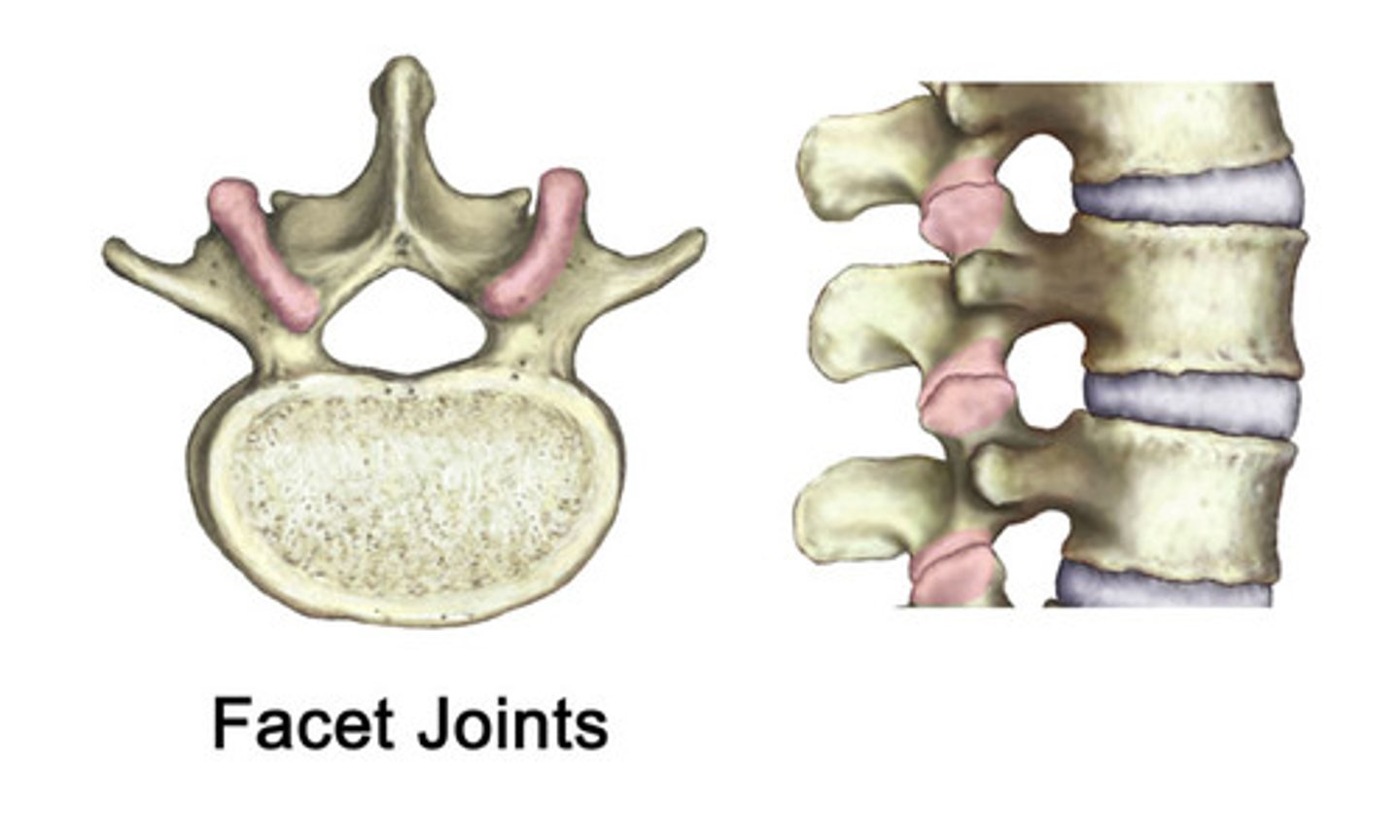
Function of Z joints
Facets for articulation with vertebrae above & below
Spinous Process
Midline posterior projection from laminae
Function of Spinous process
Allow for attachment of muscles
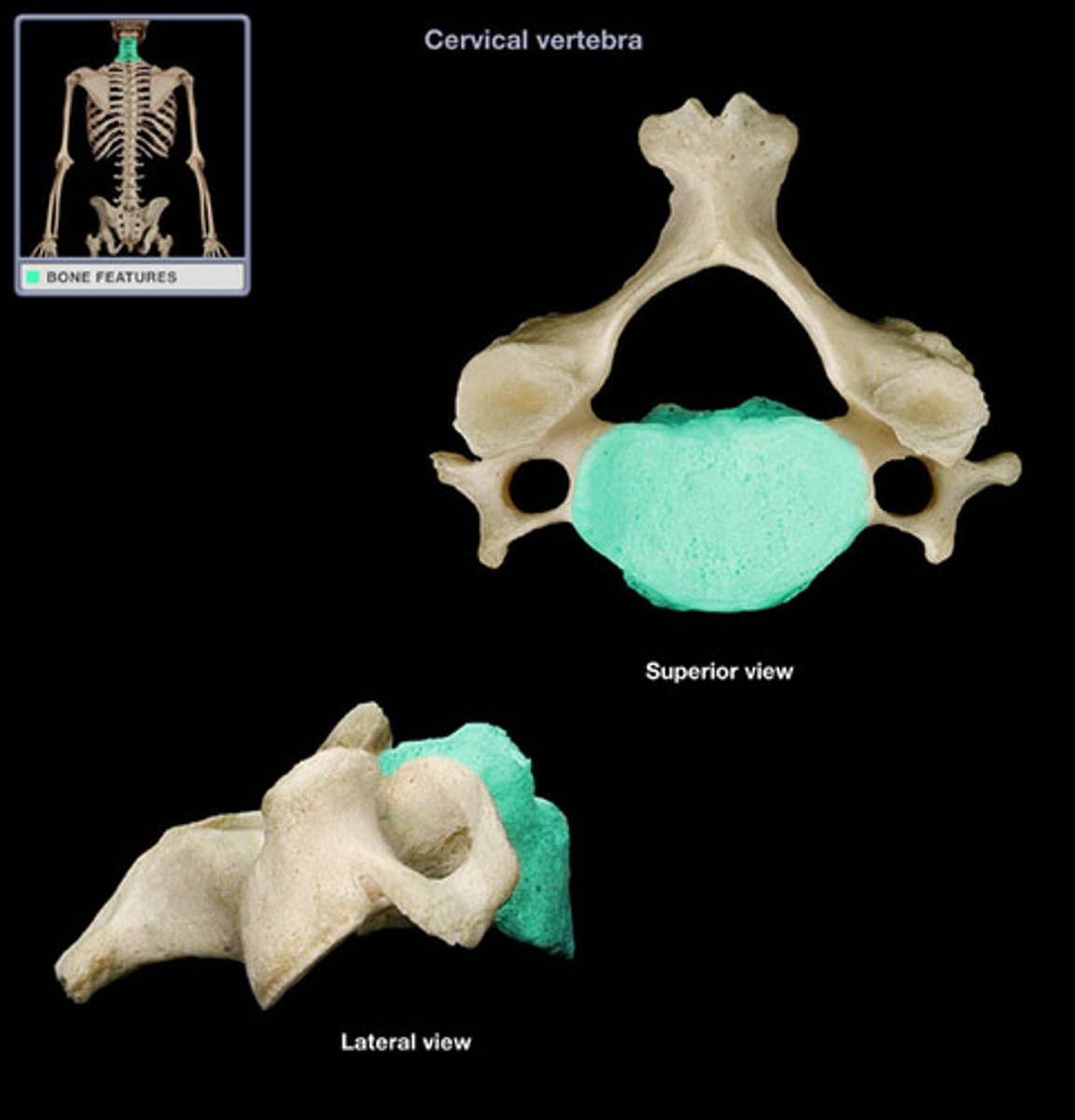
Cervical Vertebrae
Get increasingly larger caudally, C7 transition between cervical & thoracic vertebrae, C1-C7
Atlas(C-1)
-Superior articular facets are concave & articulate with occipital consults of skull
-Inferior articular faces are flatter & articulate with axis
Axis(C-2)
-Dens articulate with anterior arch of atlas & held in position by ligament
-Dens act like a pivot around which the atlas rotates
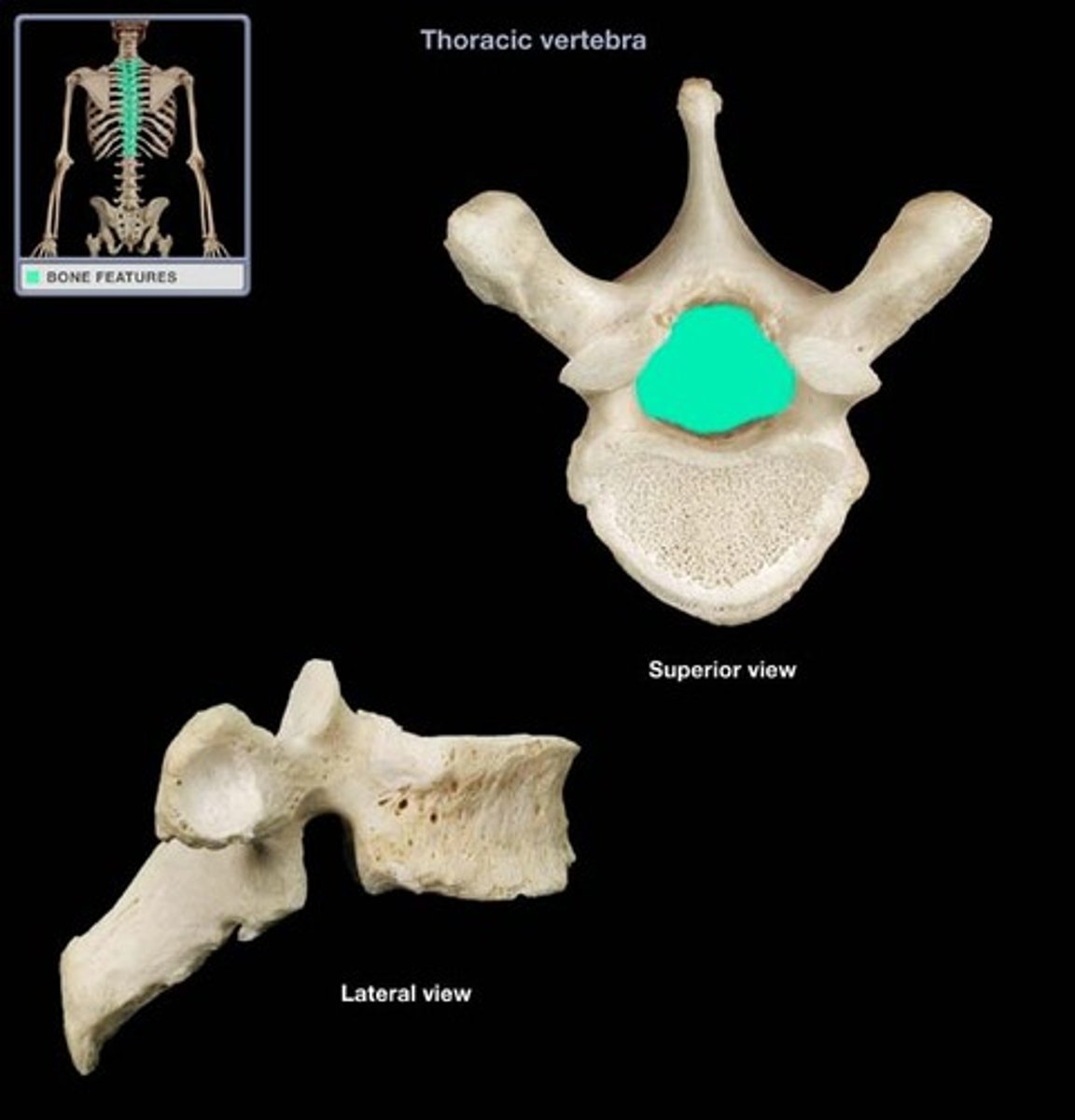
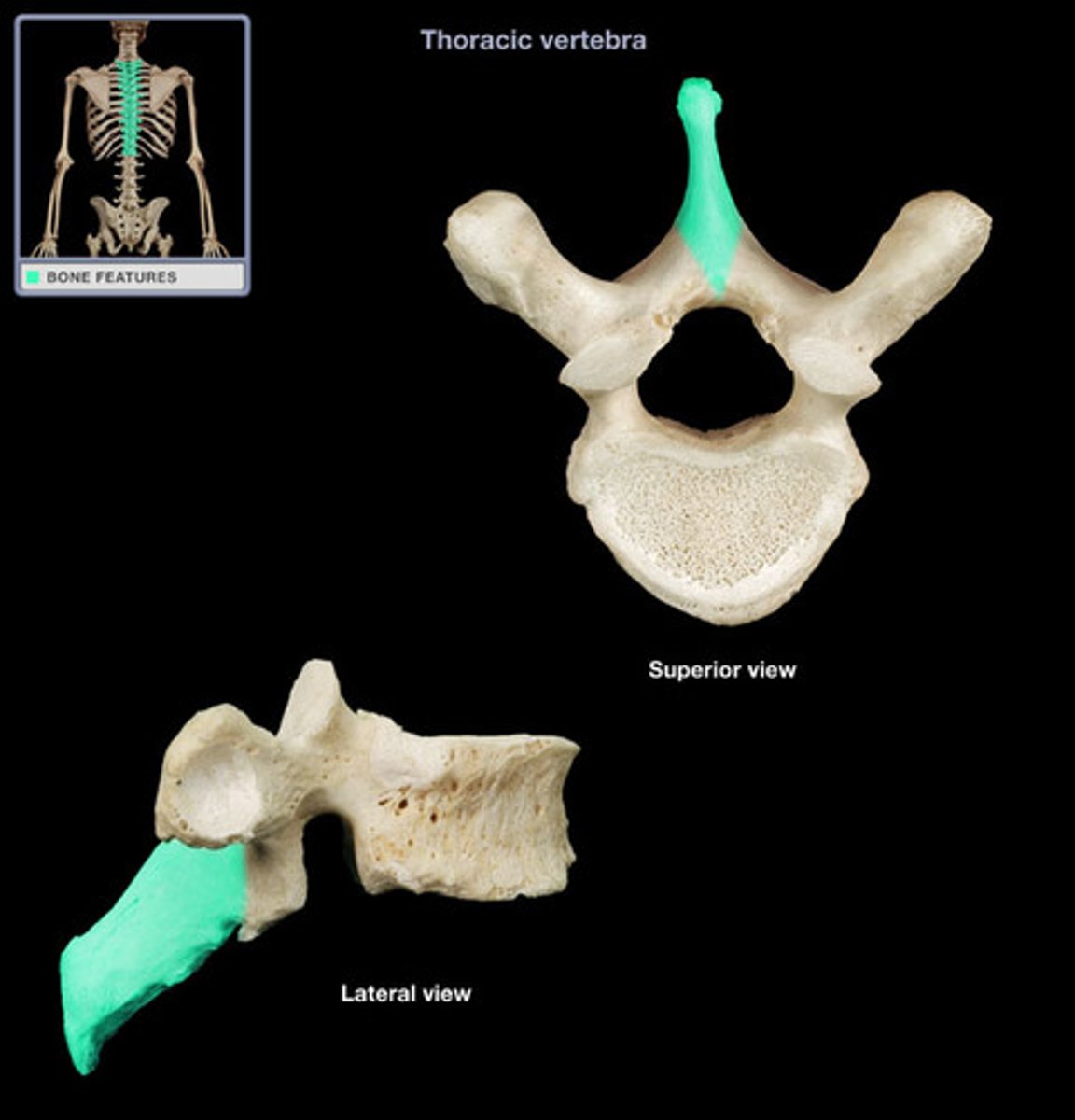
Thoracic Vertebrae
Superior & inferior articular facets almost in frontal plane, no foramina, costal facets articulate with ribs, spinous processes are long, slender, directed downward & overlap each other, T1-T12
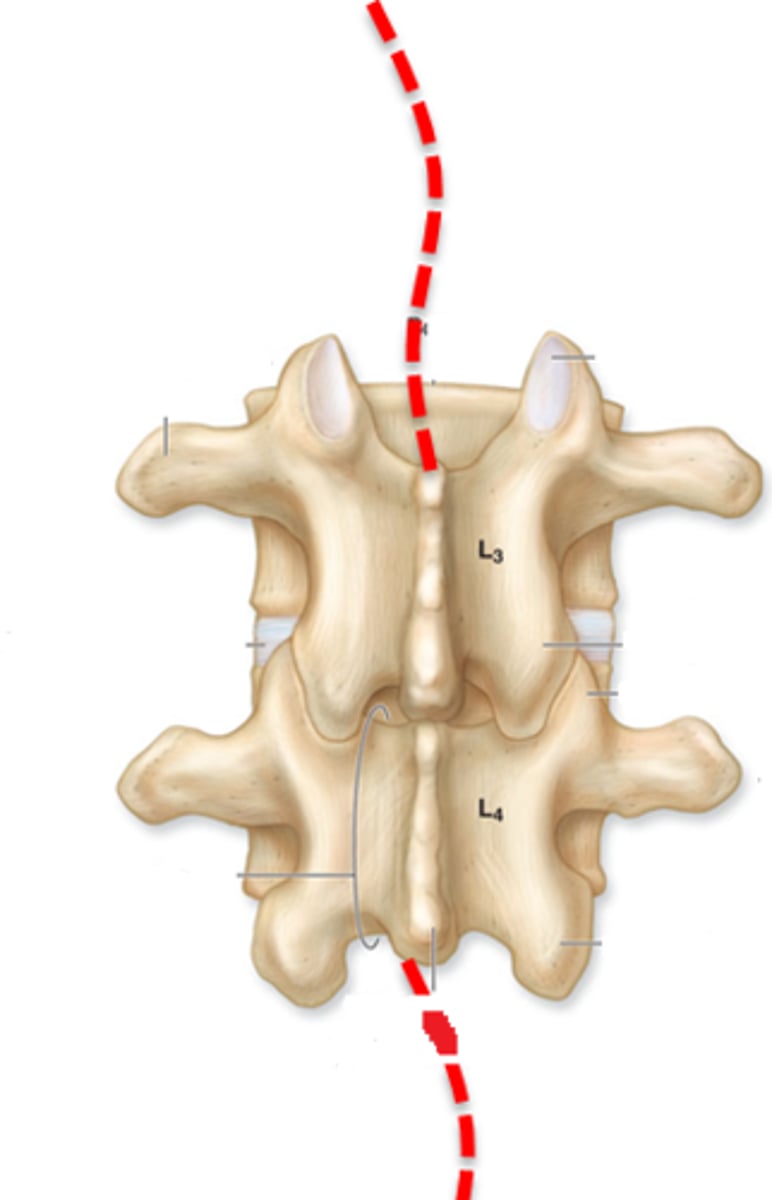
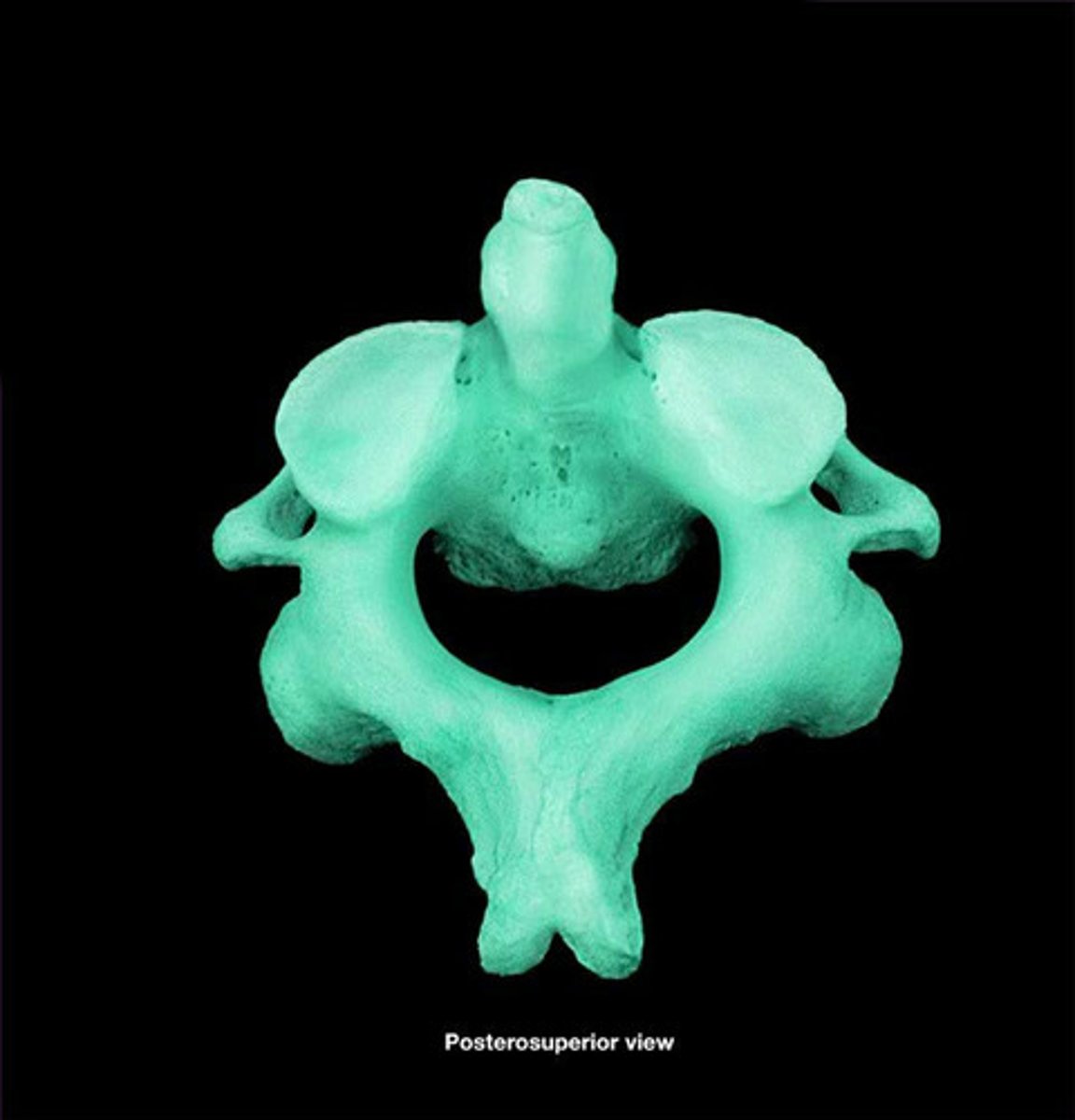
Lumbar Vertebrae
Bodies massive, spinous processes much heavier & broader, height of lamina is less than body, transverse processes are long & slander, L1-L5
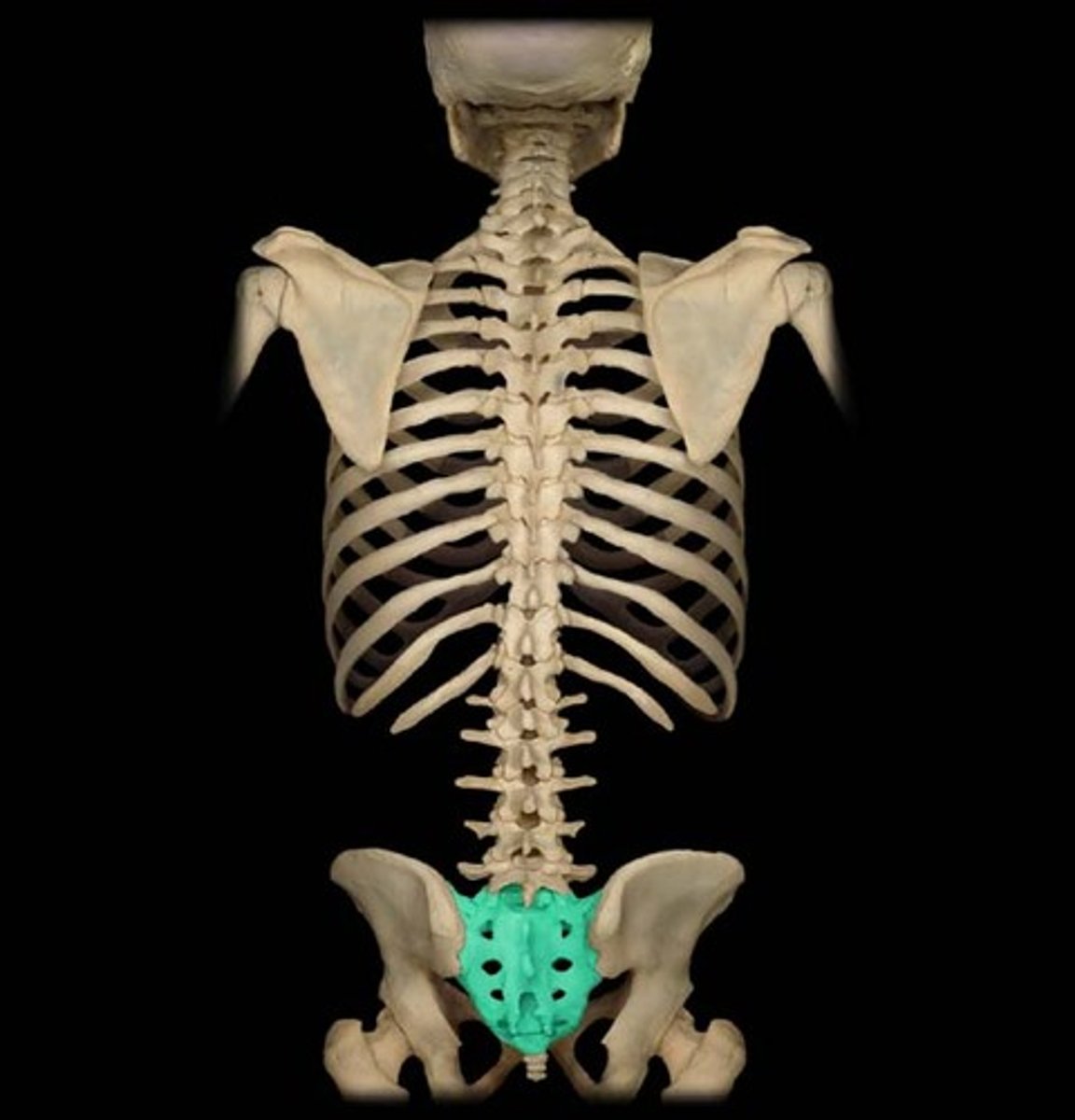
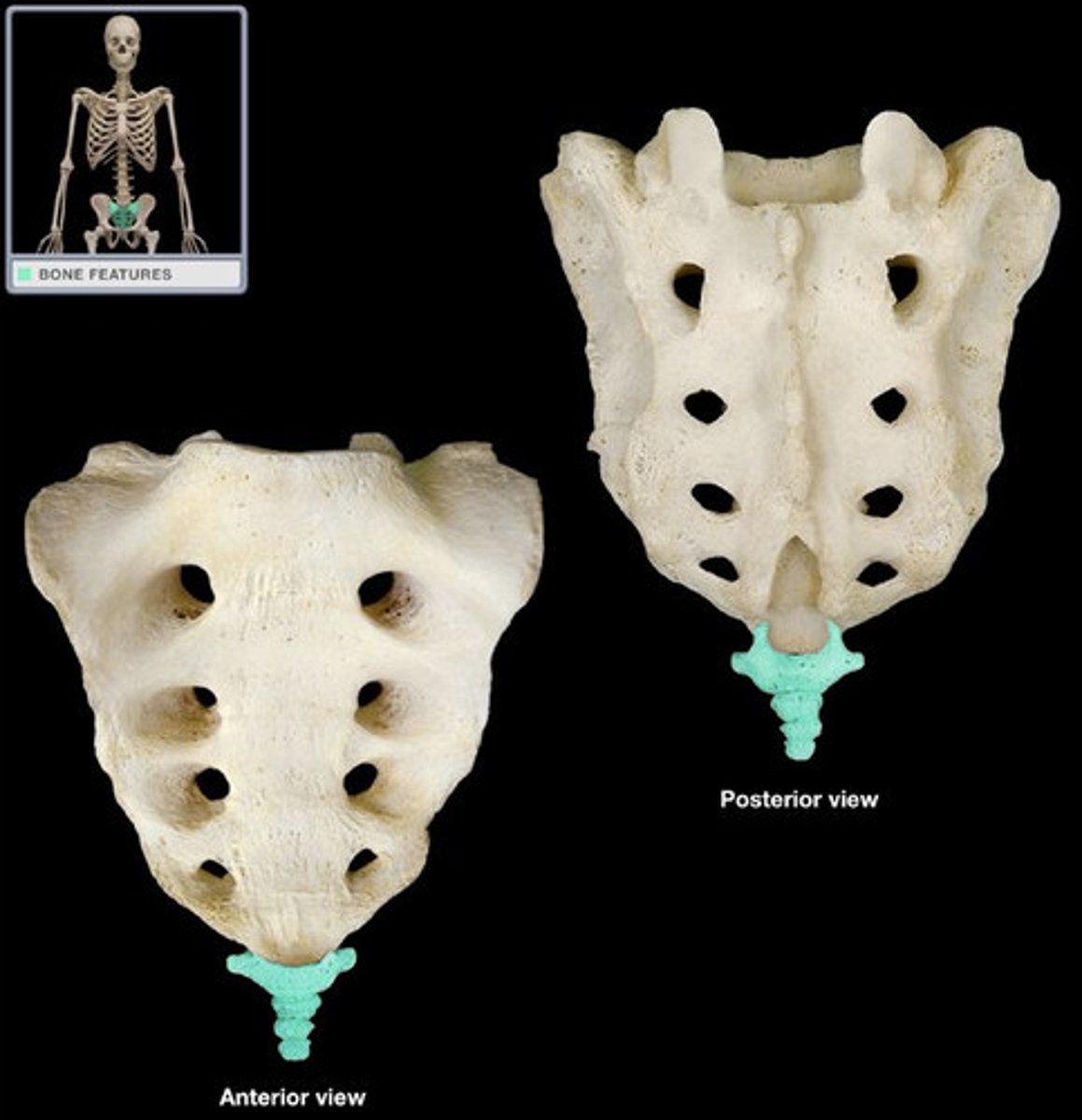
Sacrum
The large, triangle-shaped bone in the lower spine that forms part of the pelvis , made of 5 fused bones of the spine
Pelvis Sacral Foramina
Ventral rami of S1-S4 exit
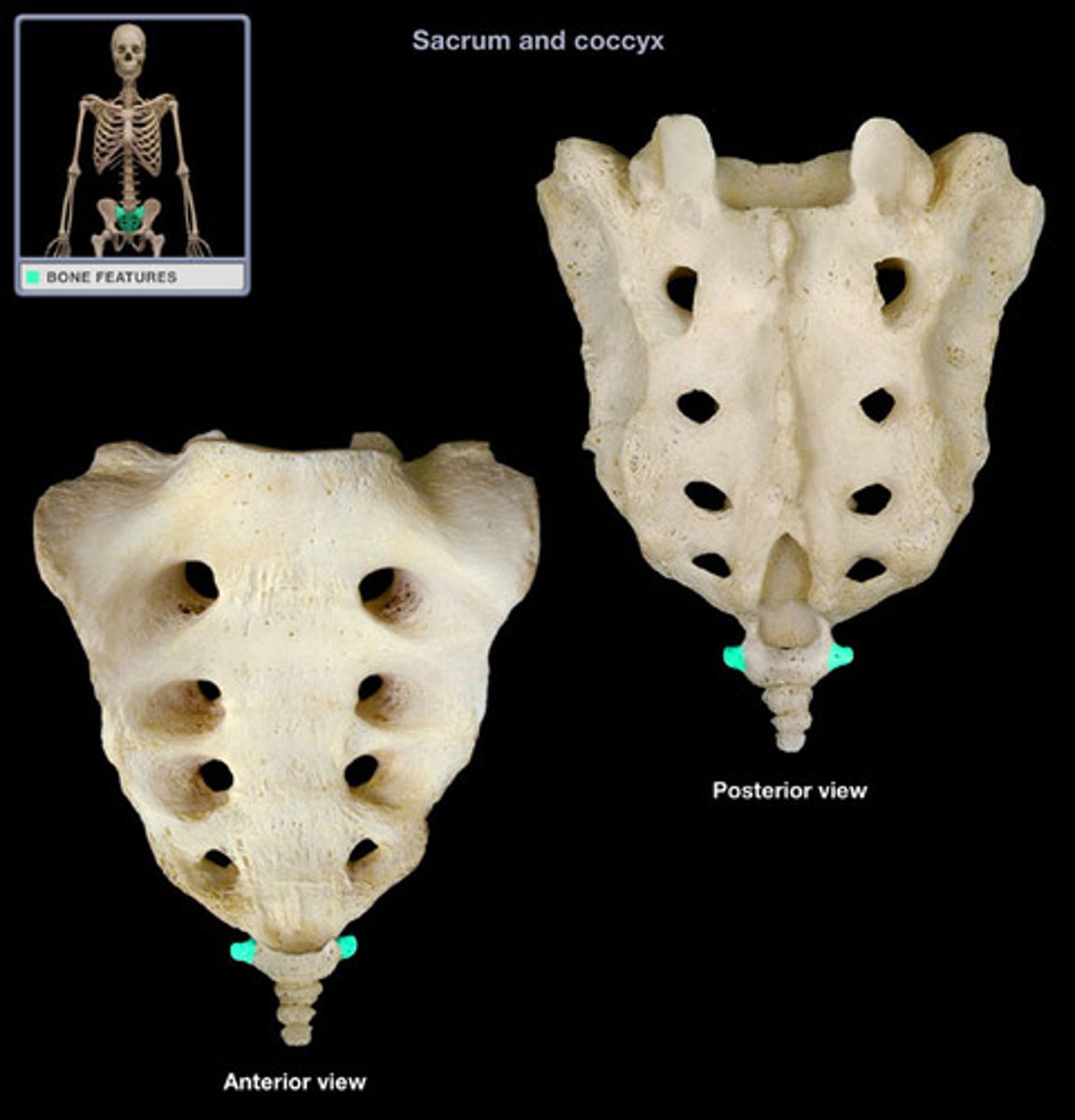
Transverse Process of Coccyx
Articulate with hip
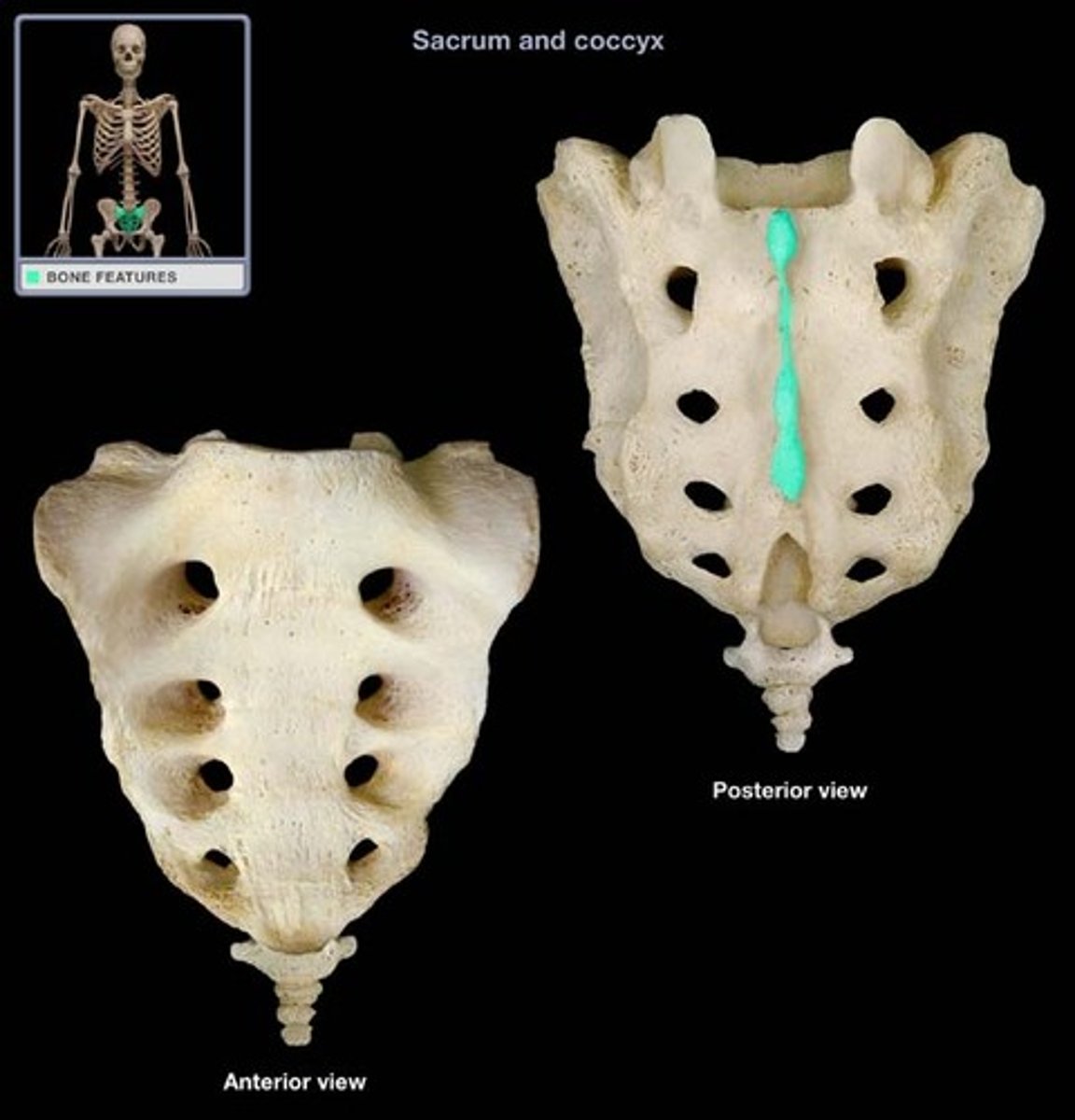
Median Crest of Sacrum
Rudimentary spinous processes
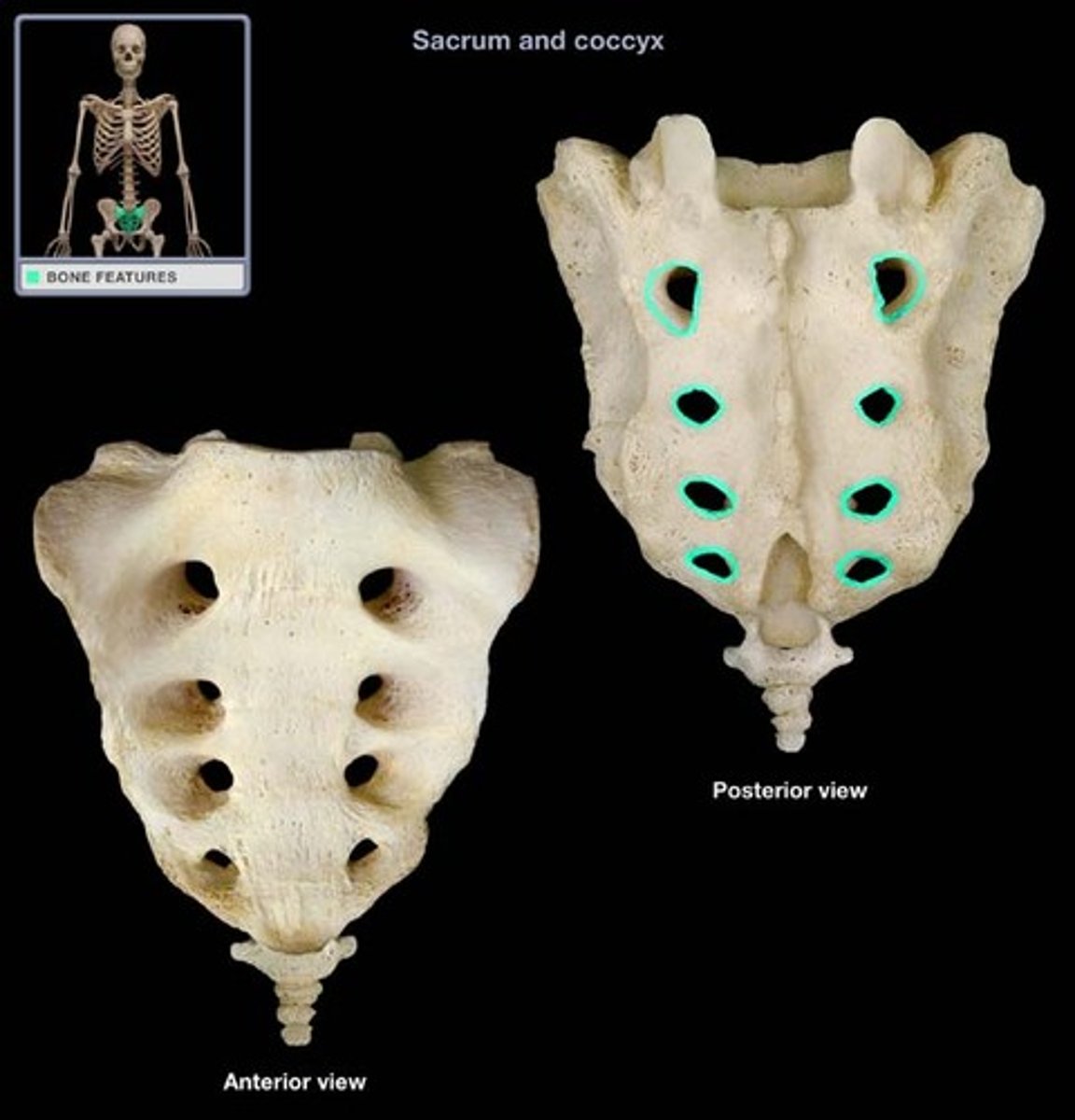
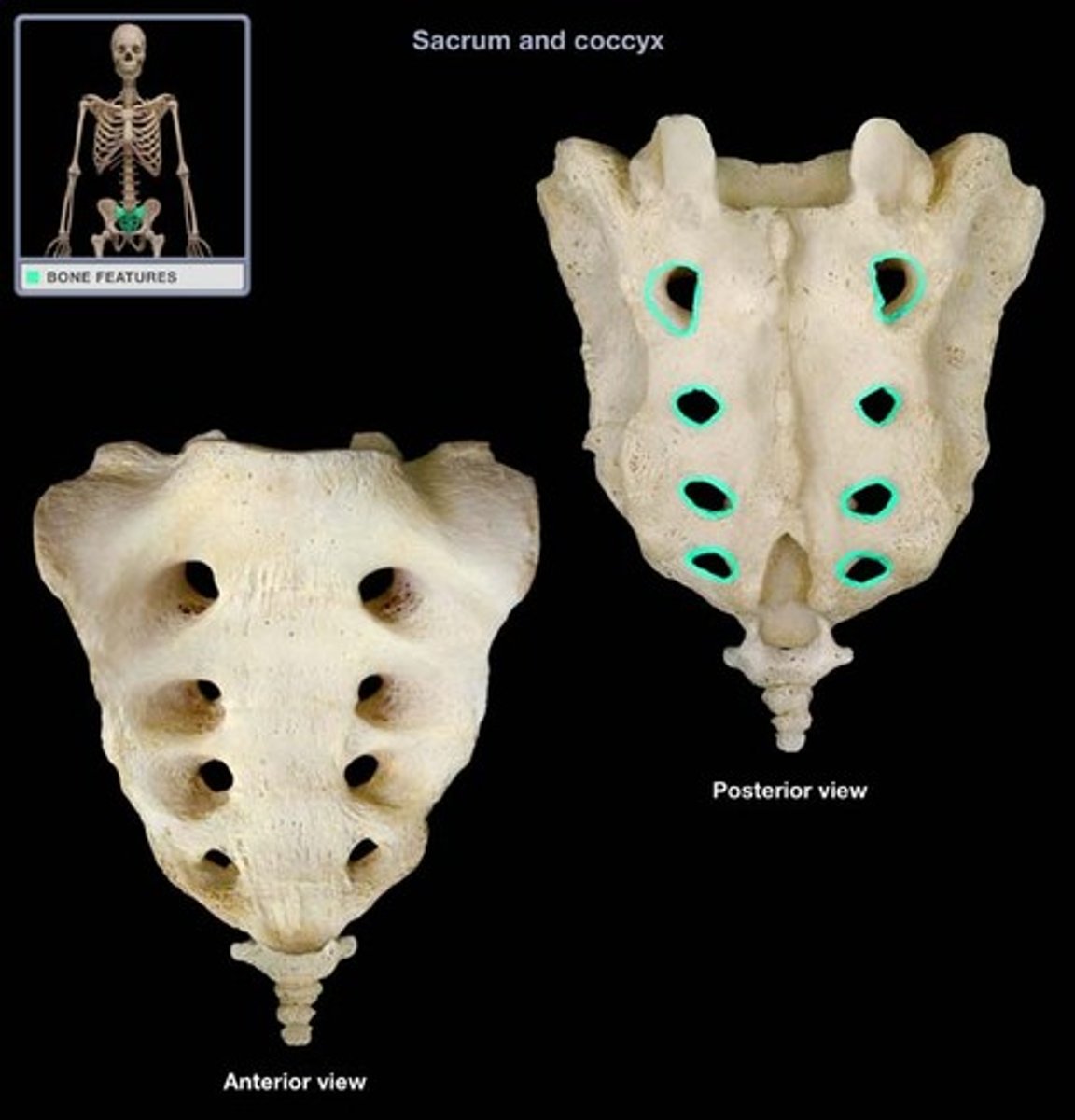
Dorsal Sacral Foramina
Dorsal rami of S1-S4
Coccyx
3 or 4, 1st is usually separate from rest, tailbone
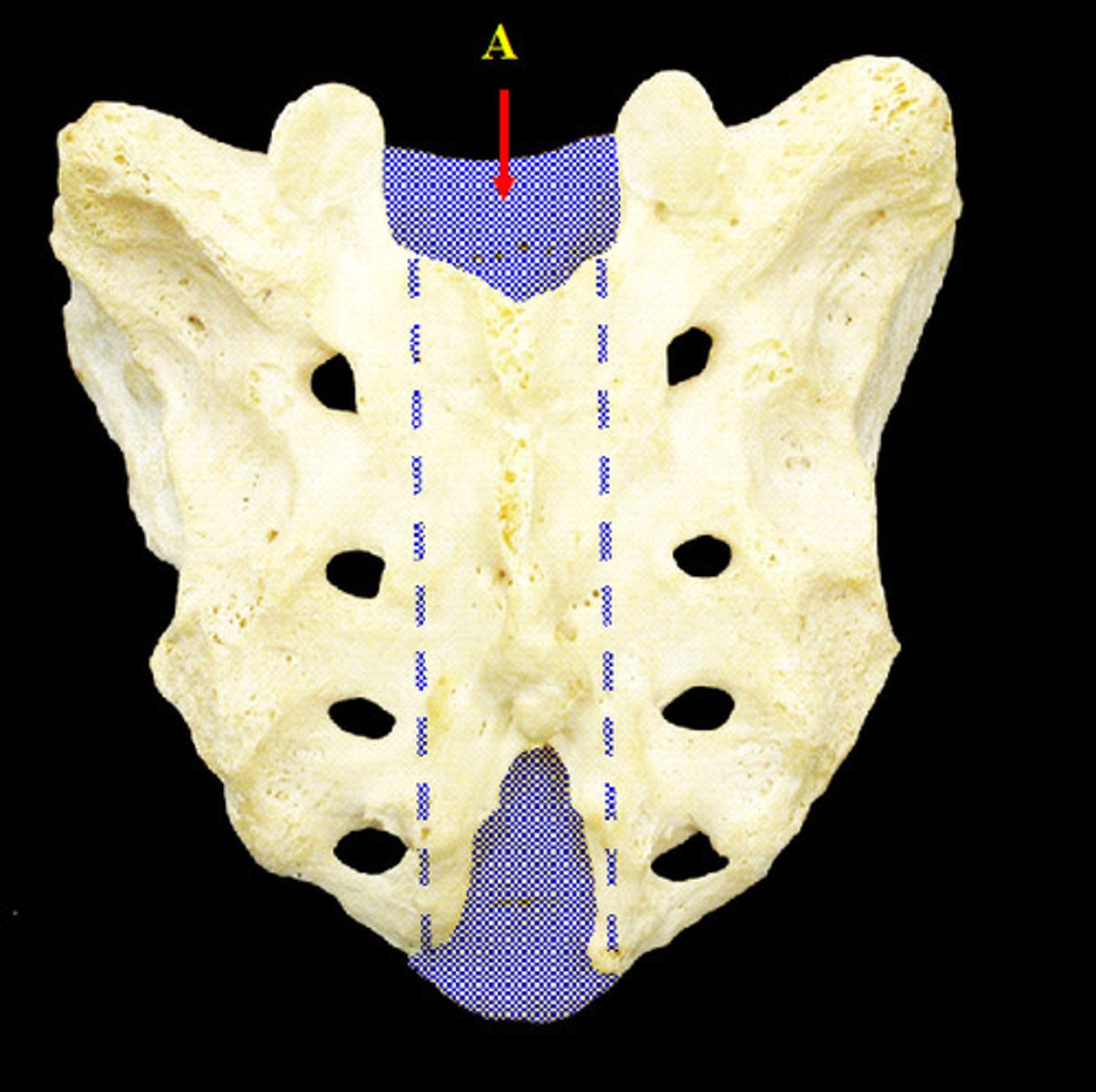
Sacral Canal
continuation of vertebral canal
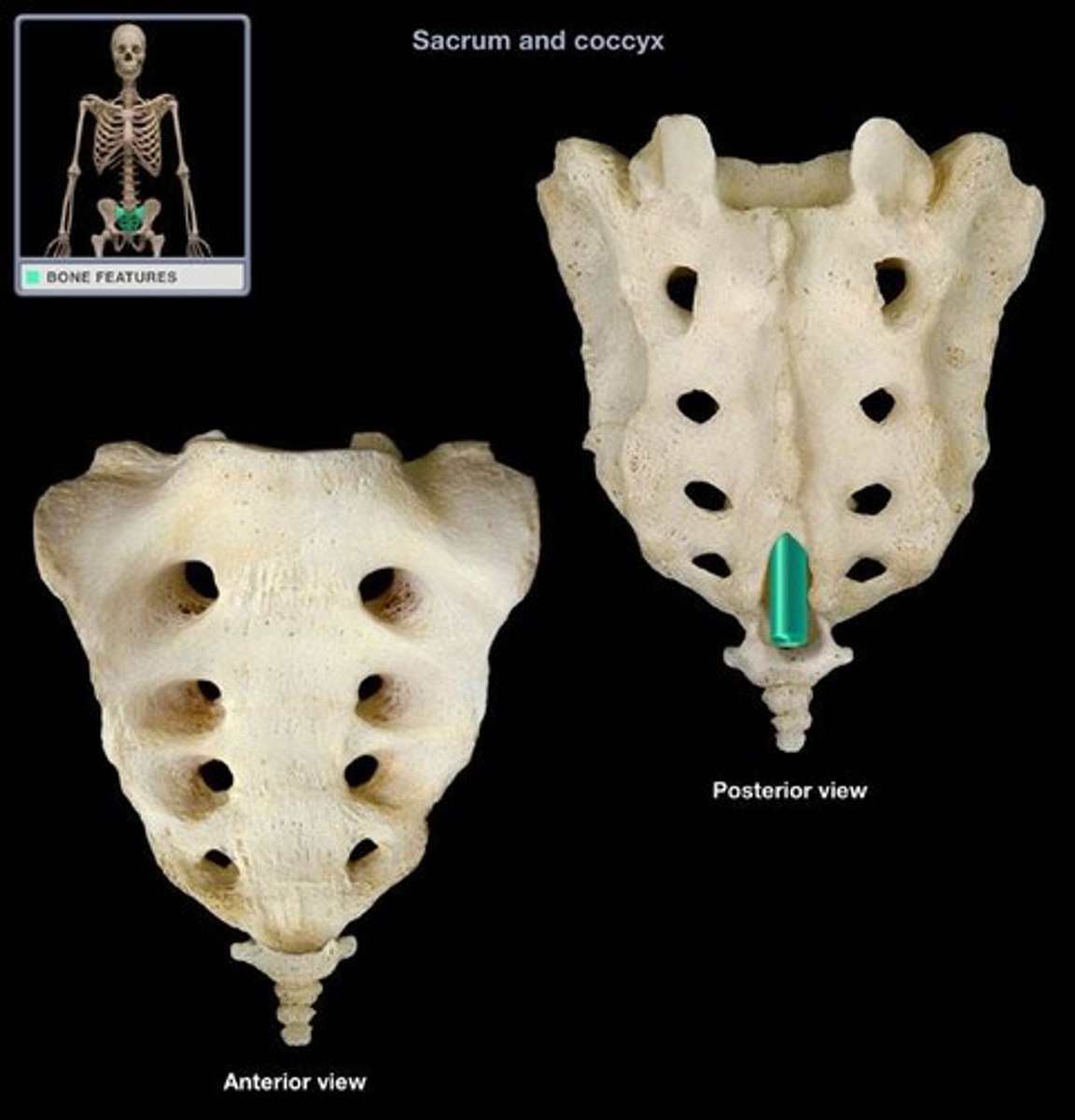
Sacral Hiatus
the opening into the spinal canal in the midline of the dorsal surface of the sacrum between the laminae of the fifth sacral vertebra
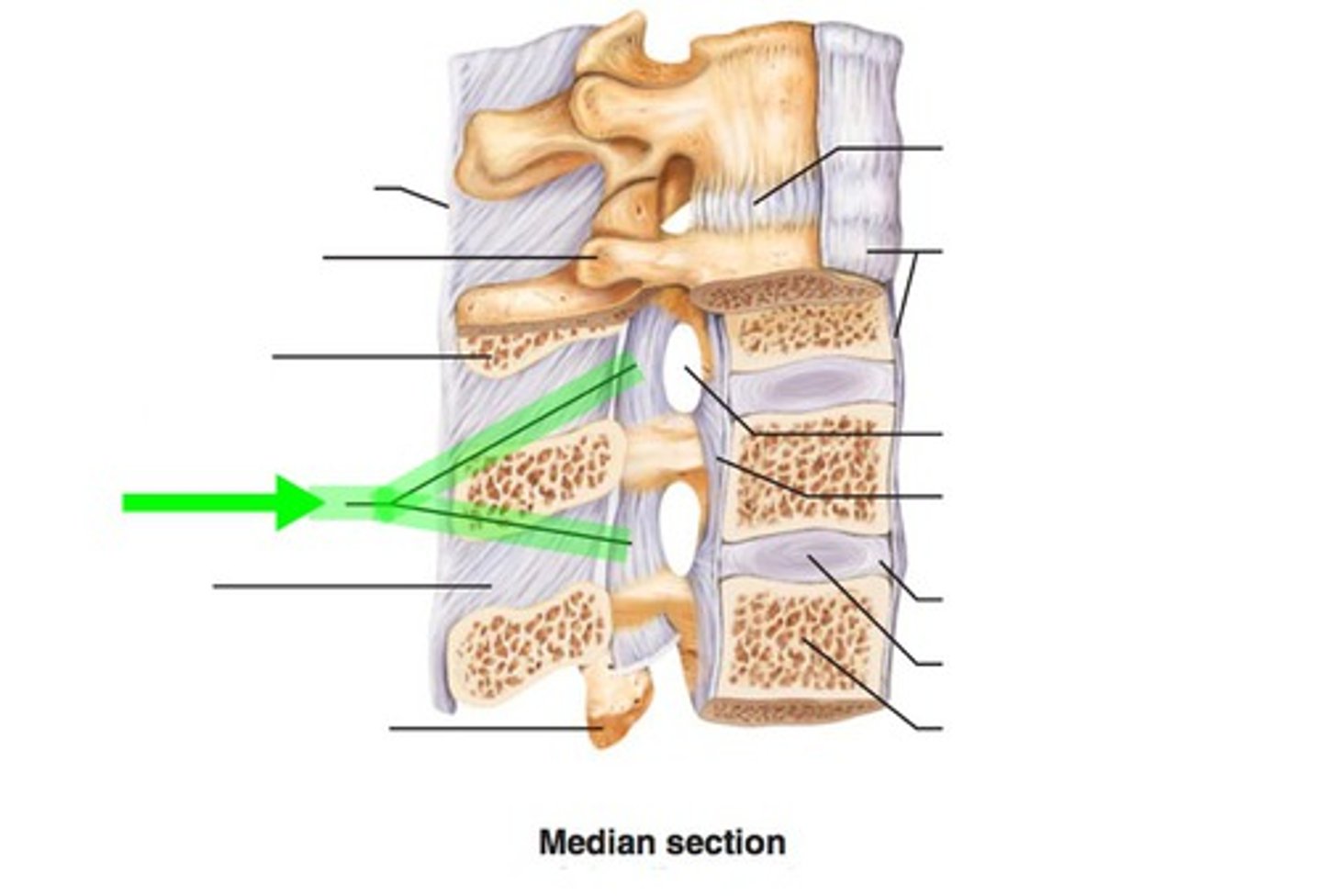
Intervertebral Discs
fibrocartilage pads that separate and cushion the vertebrae, most superior between C2 & C3, most inferior between L5 & S1, composed of annulus fibrosis and surround nucleus pulposis
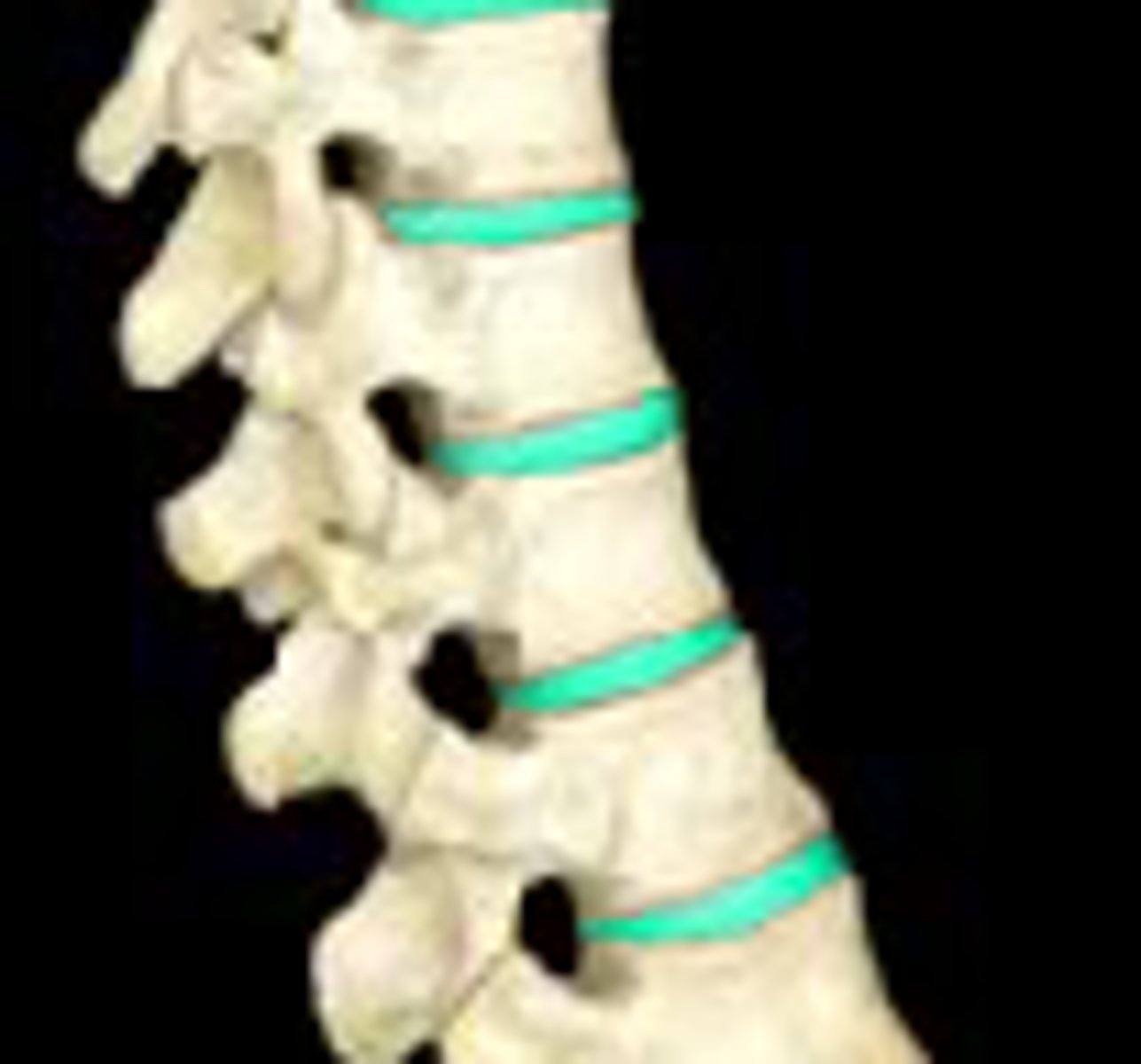
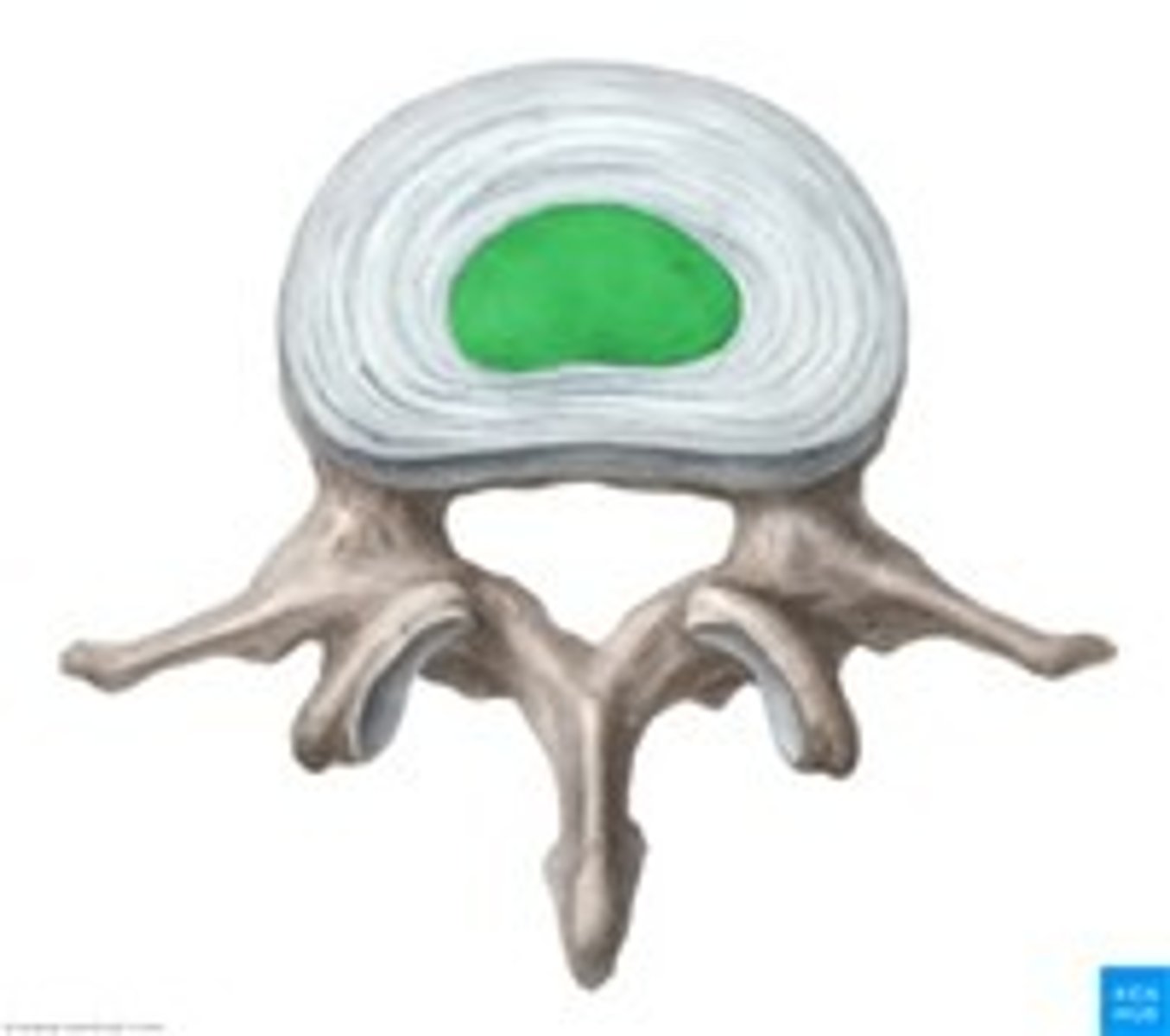
Annulus Fibrosis
outer layer of intervertebral disc, inserts into smooth, rounded rims on articular surface of vertebral bodies
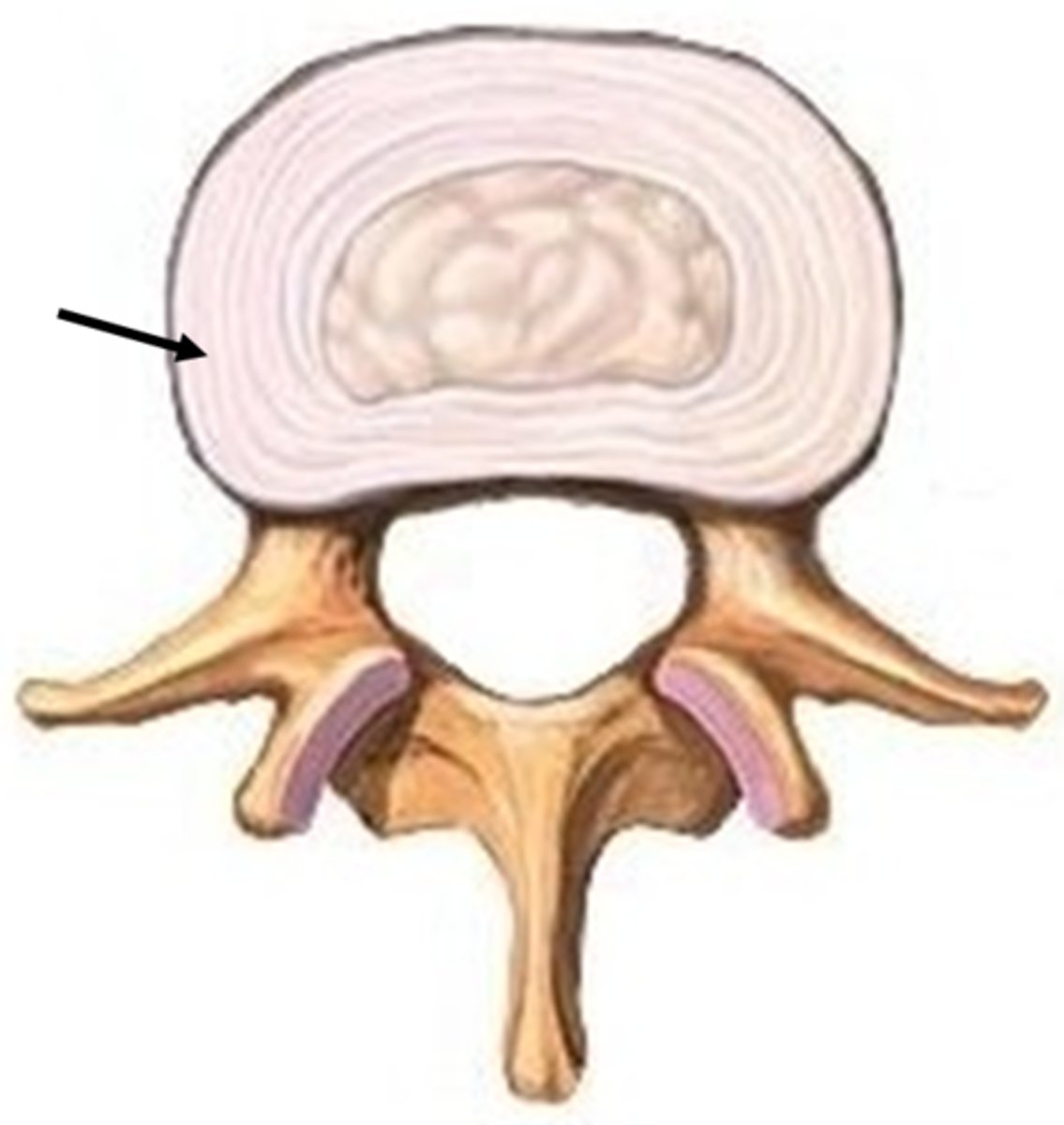
Nucleus Pulposus
inner gelatinous nucleus, gives disc its elasticity and compressibility
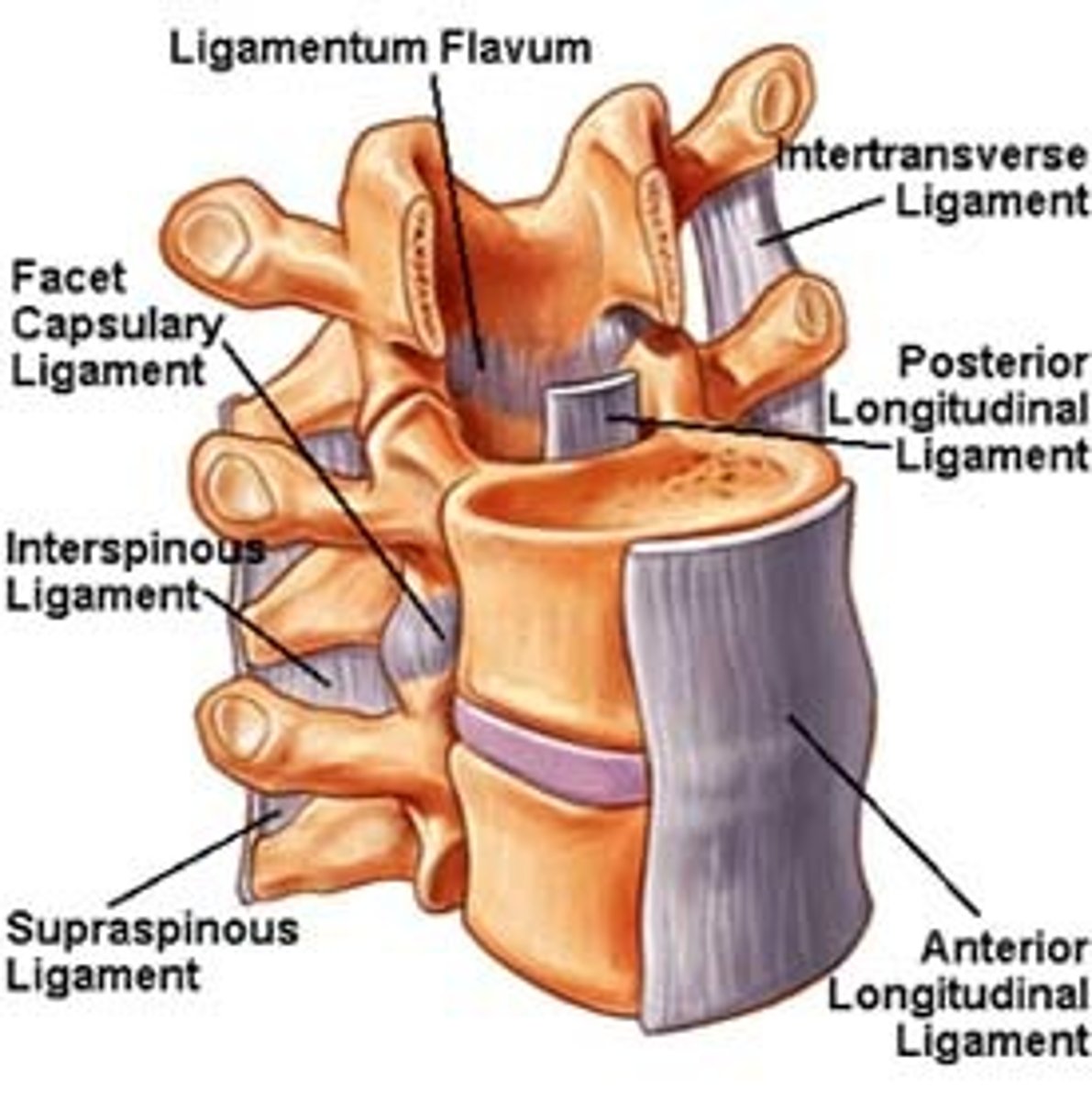
Anterior longtitudinal ligament(ALL)
strong fibrous band which covers & connects anterior aspects of vertebral bodies & intervertebral discs, stretches from sacrum to C1 & occipital bone
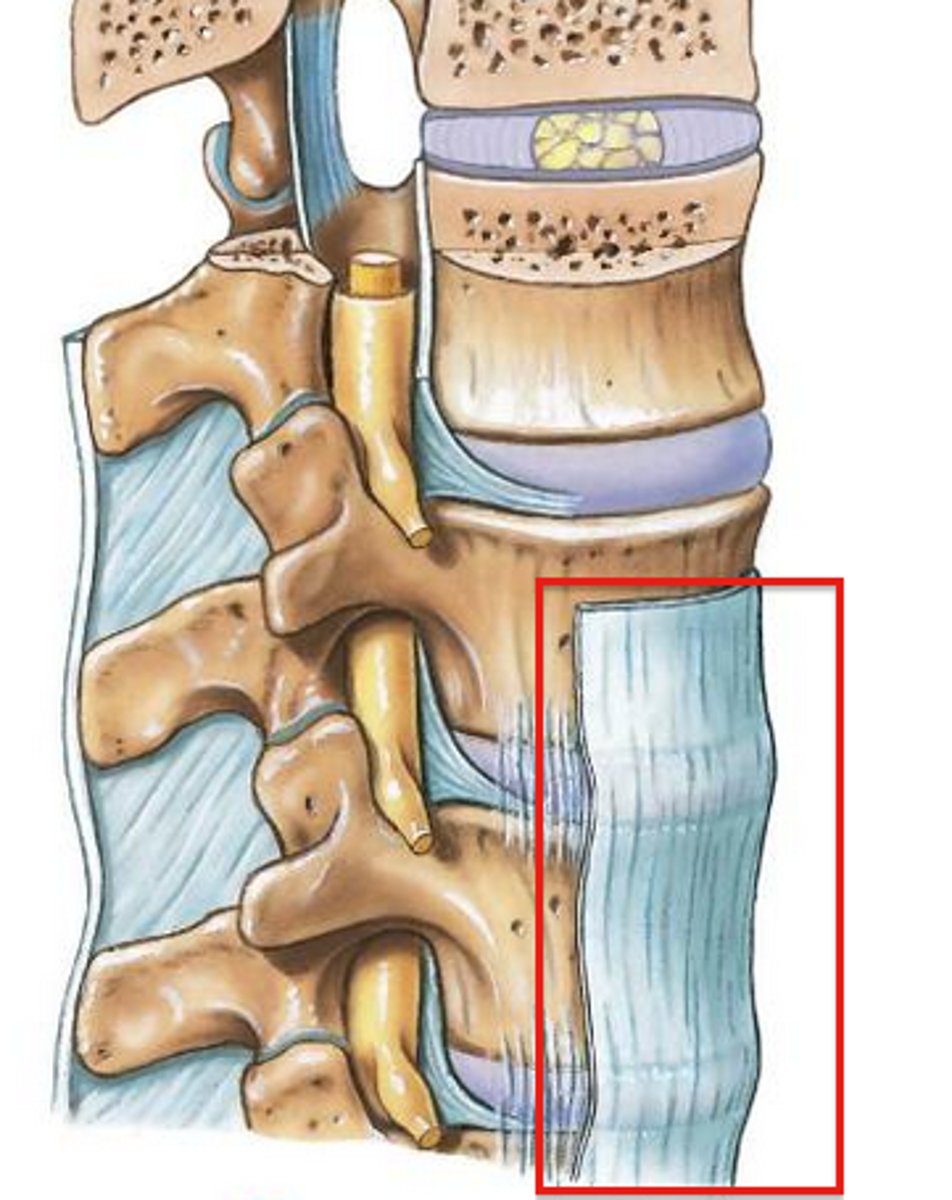
Function of ALL
maintains stability of joints between vertebral bodies & prevents hyperextension of spine
Posterior longitudinal ligament(PLL)
narrower & weaker than ALL, runs along posterior aspect of vertebral bodies within vertebral canal
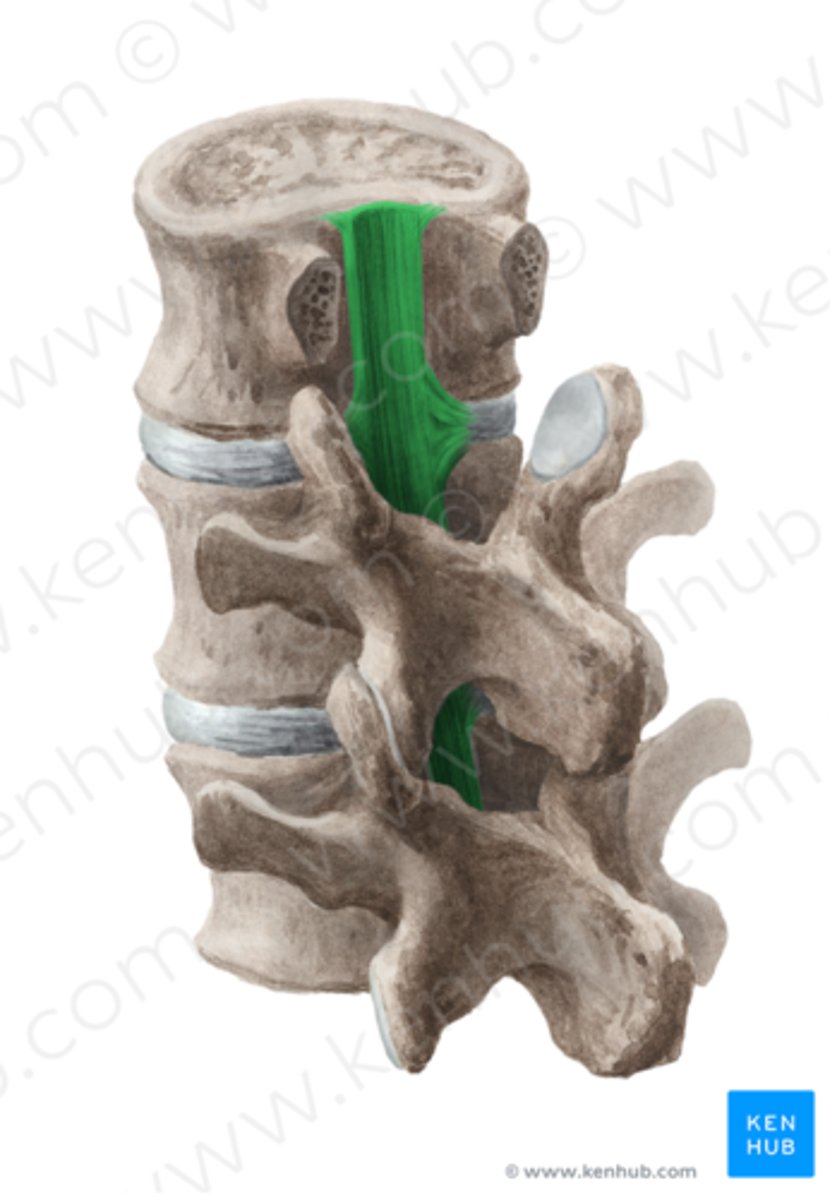
Function of PLL
prevents hyper flexion of spine & posterior protrusion of nucleus pulposus of disc
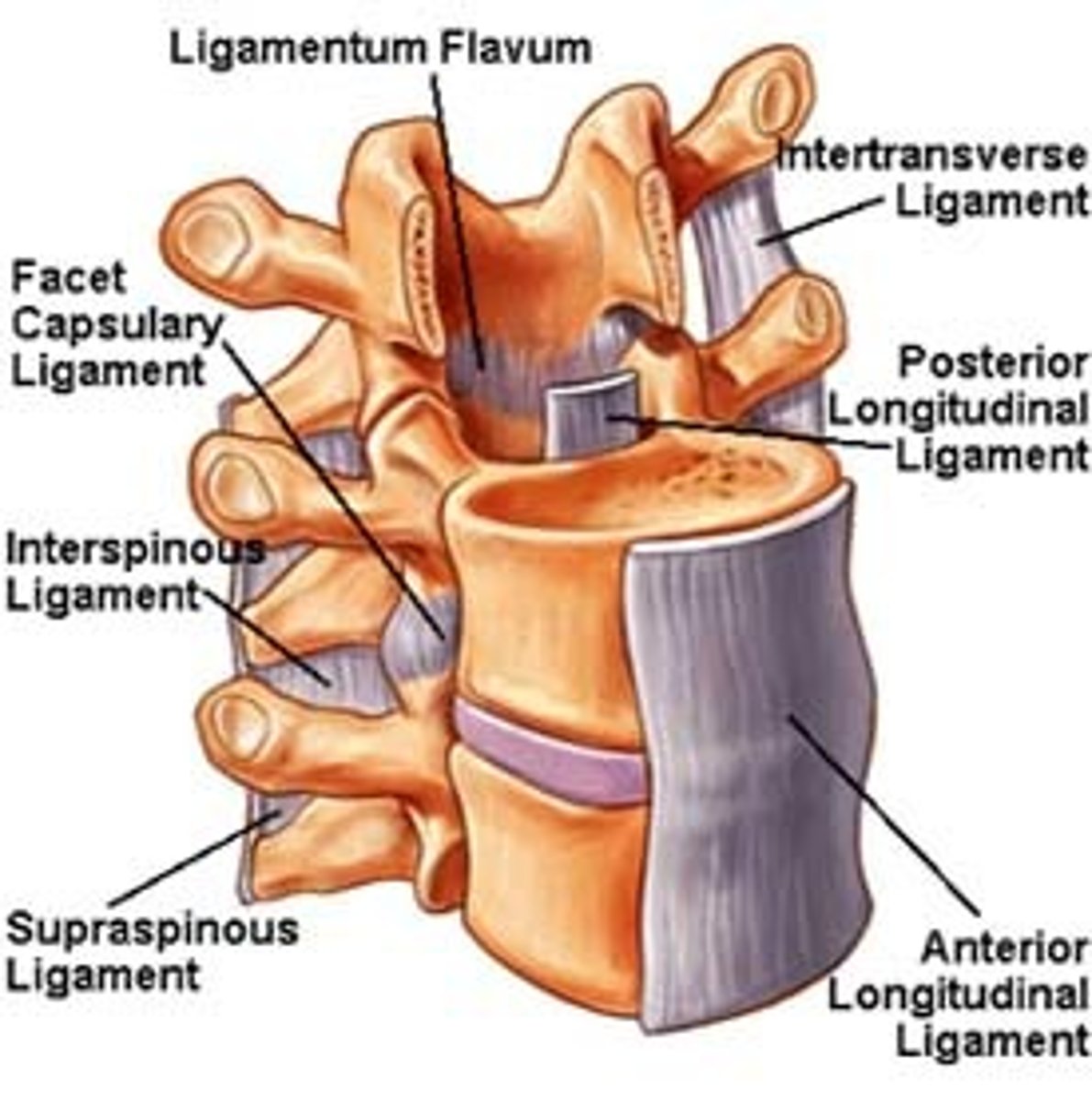
Ligamenta flava
connect laminae of adjacent vertebrae
Interspinous ligament
connects the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae(weak)
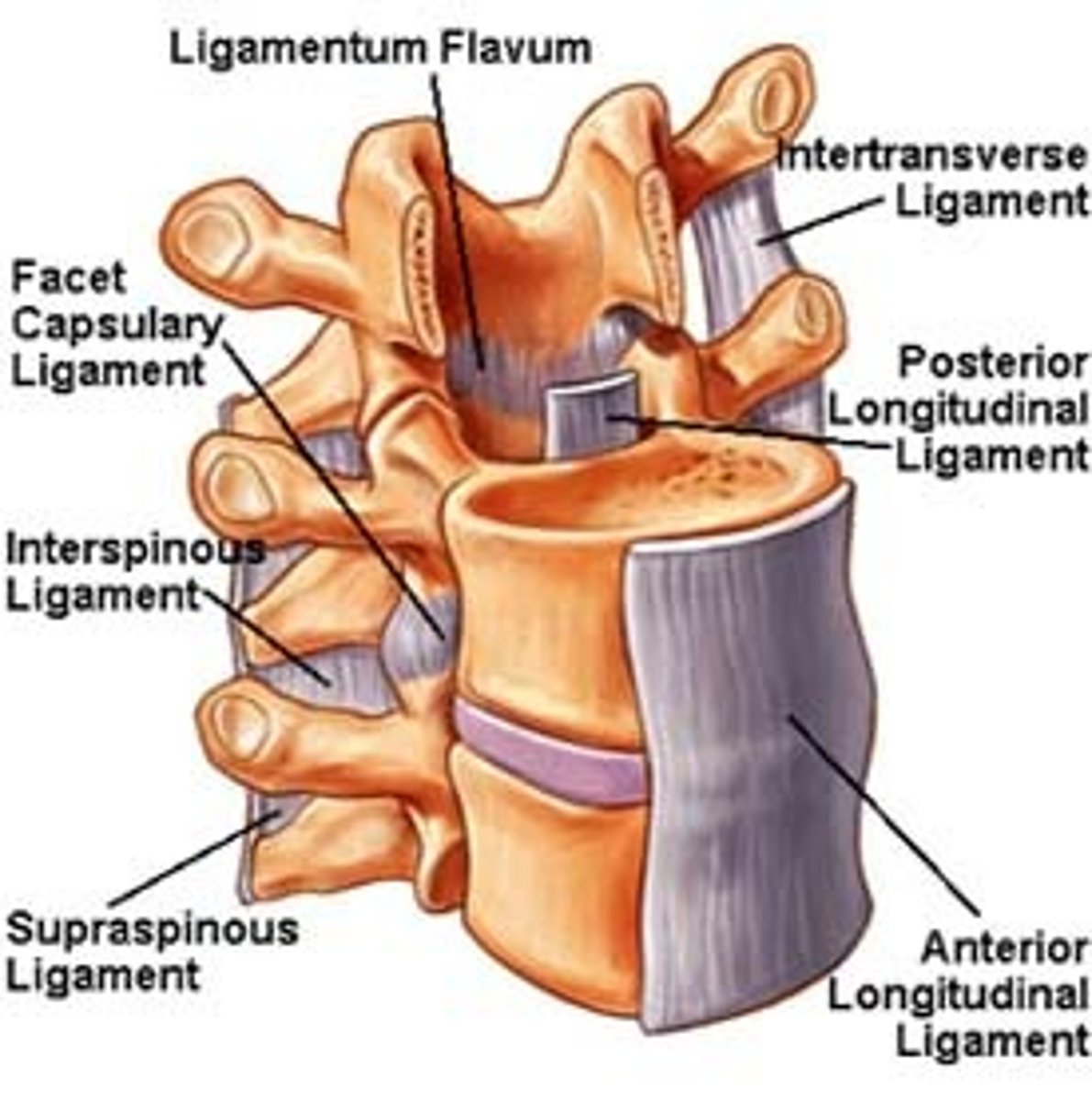
Supraspinous ligament
connects tips of spinous processes (C7 to sacrum)
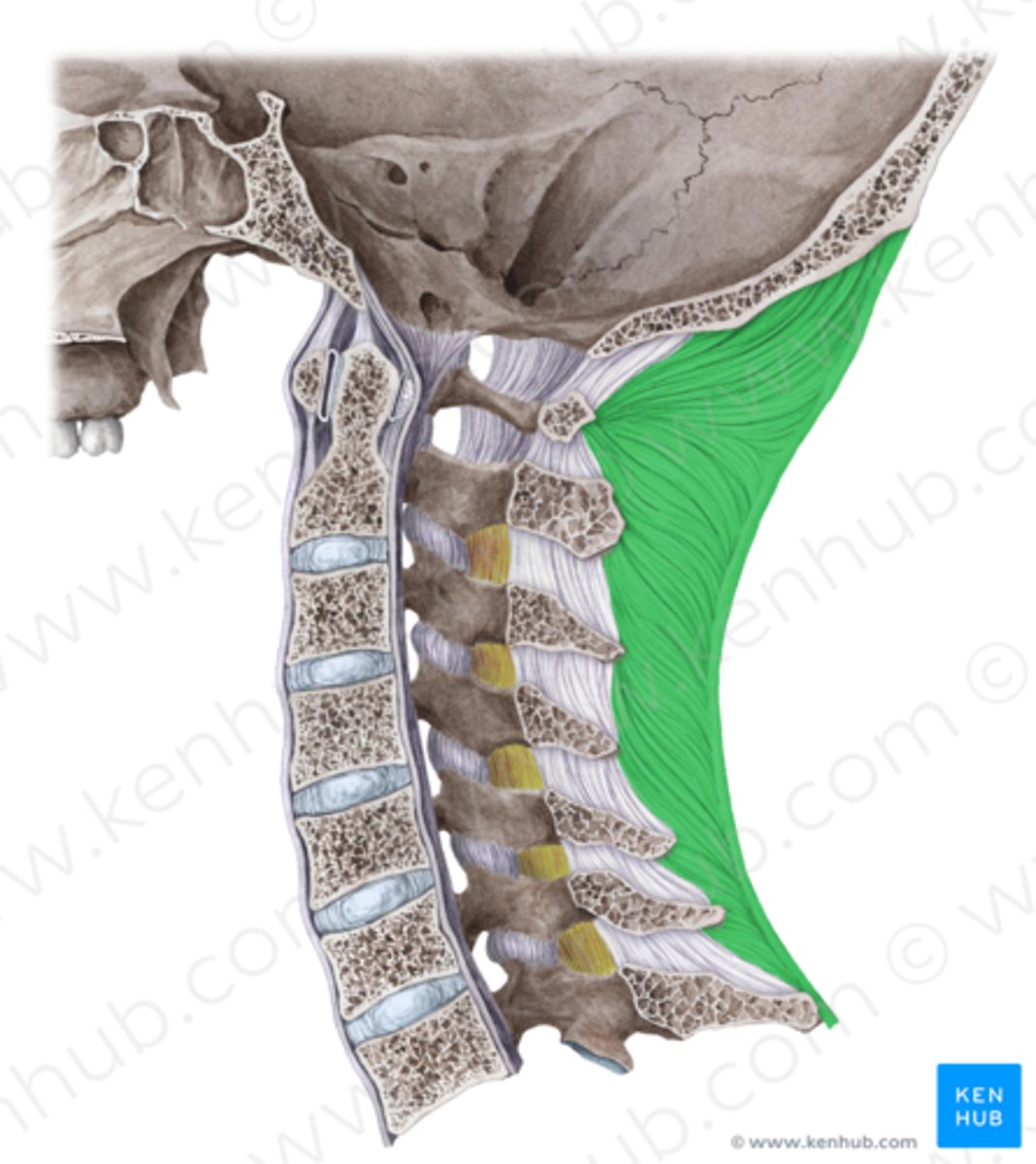
Ligamentum nuchae
superior aspect of ligaments, triangular median septum between muscles on each side of posterior aspect of neck
Intertransverse ligaments
connects adjacent transverse processes
Atlanto-occipital joint
permits nodding of head(between skull & C1)
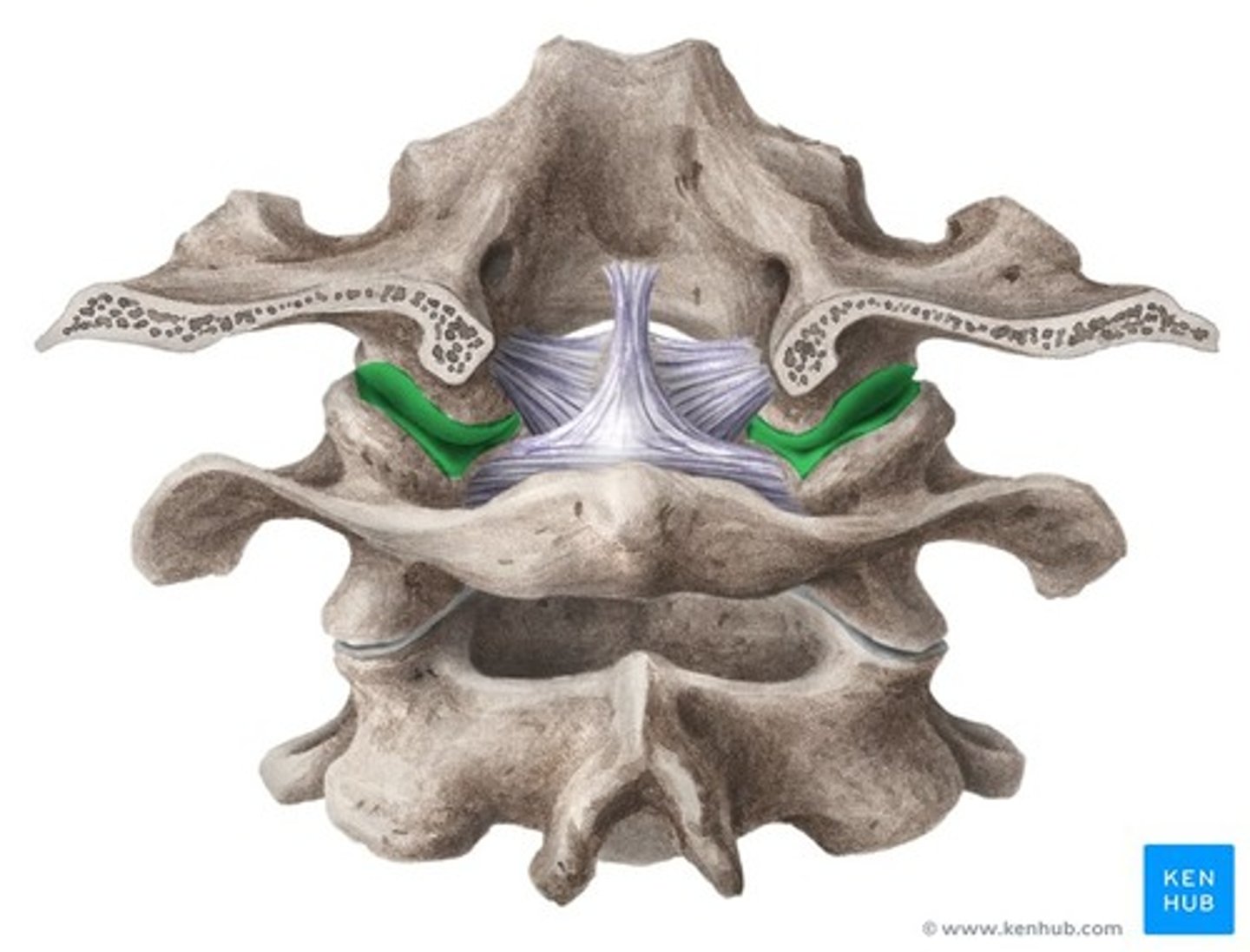
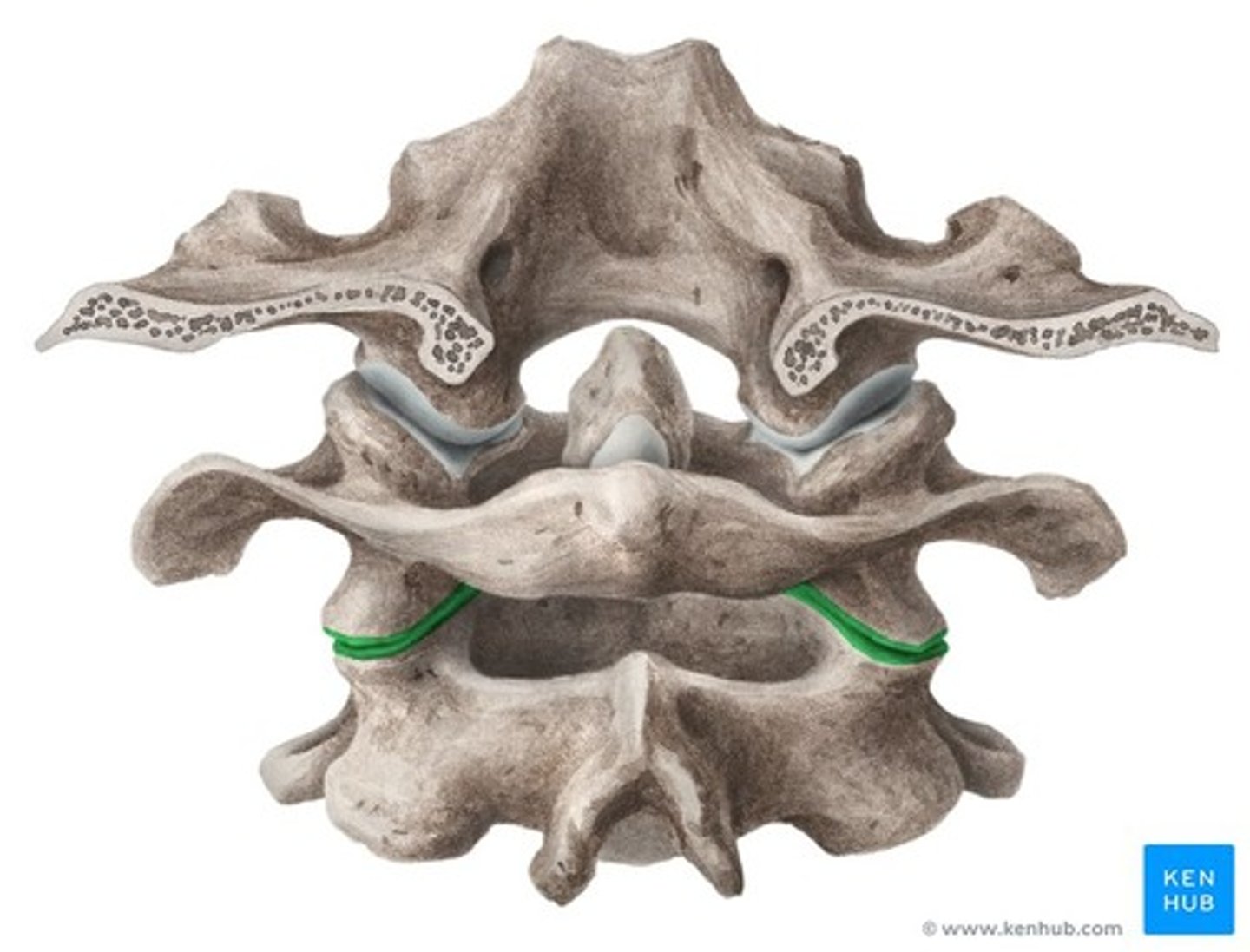
Atlanto-axial joint
permits rotation of head(skull & C1 rotate about C2)
Transverse ligaments of axis
holds dens against anterior arch of atlas
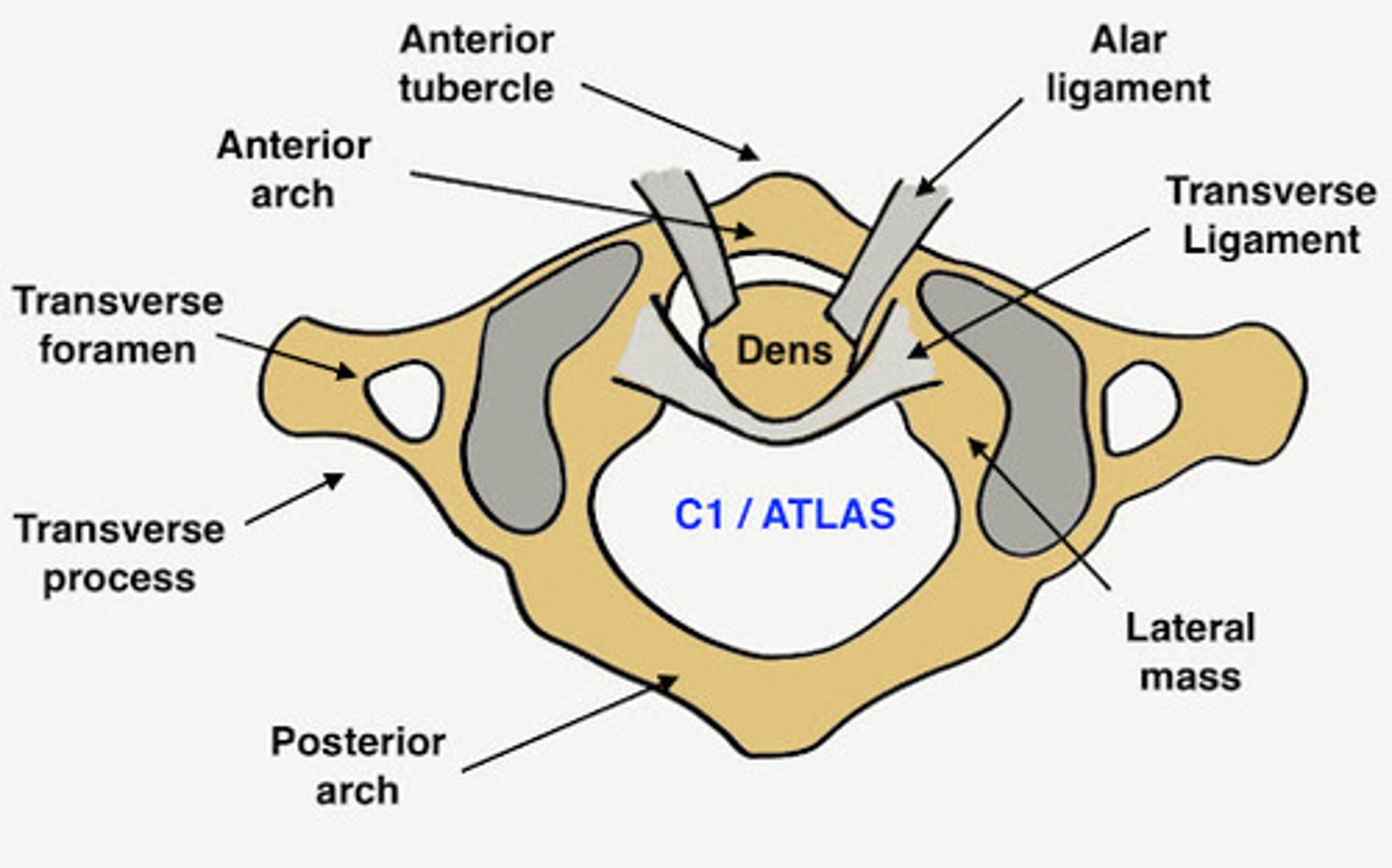
Cruciform ligament
transverse ligament of atlas and vertical ligament from skull; holds body of C2 and dens to the inside of the skull
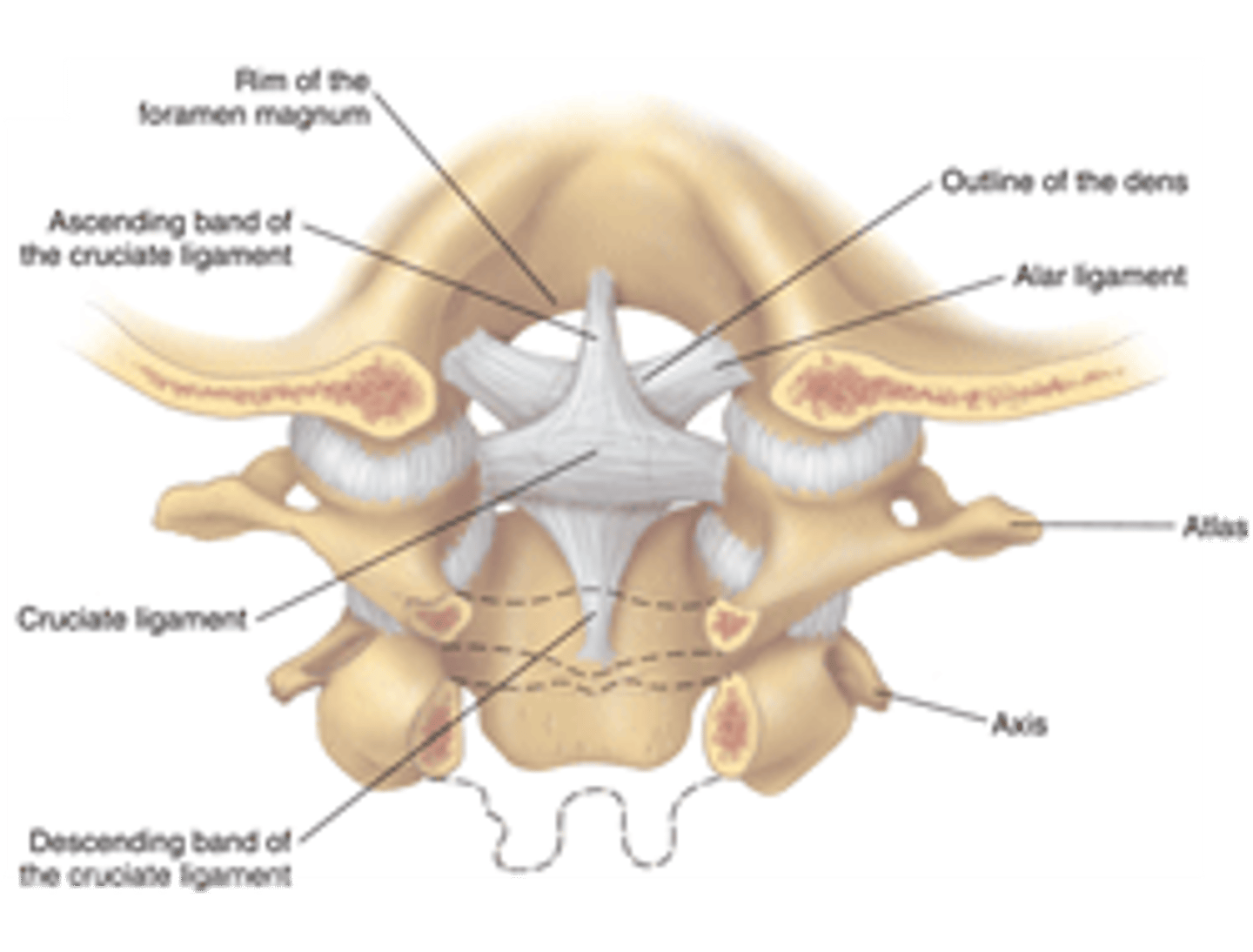
Altar ligament
extends from side dens to lateral margins of foramen magnum, rotation and side to side movements
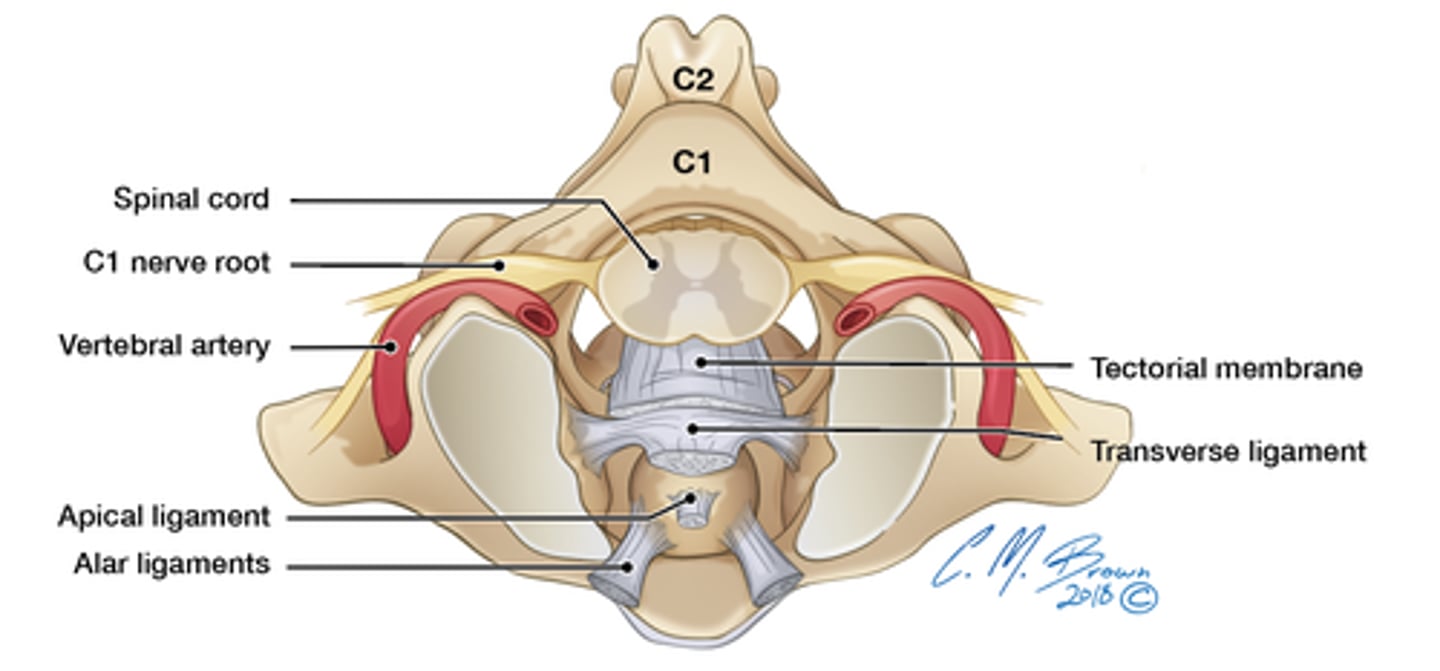
Tectorial membrane
superior continuation of posterior longitudinal ligament, extends from body of atlas to occipital bone
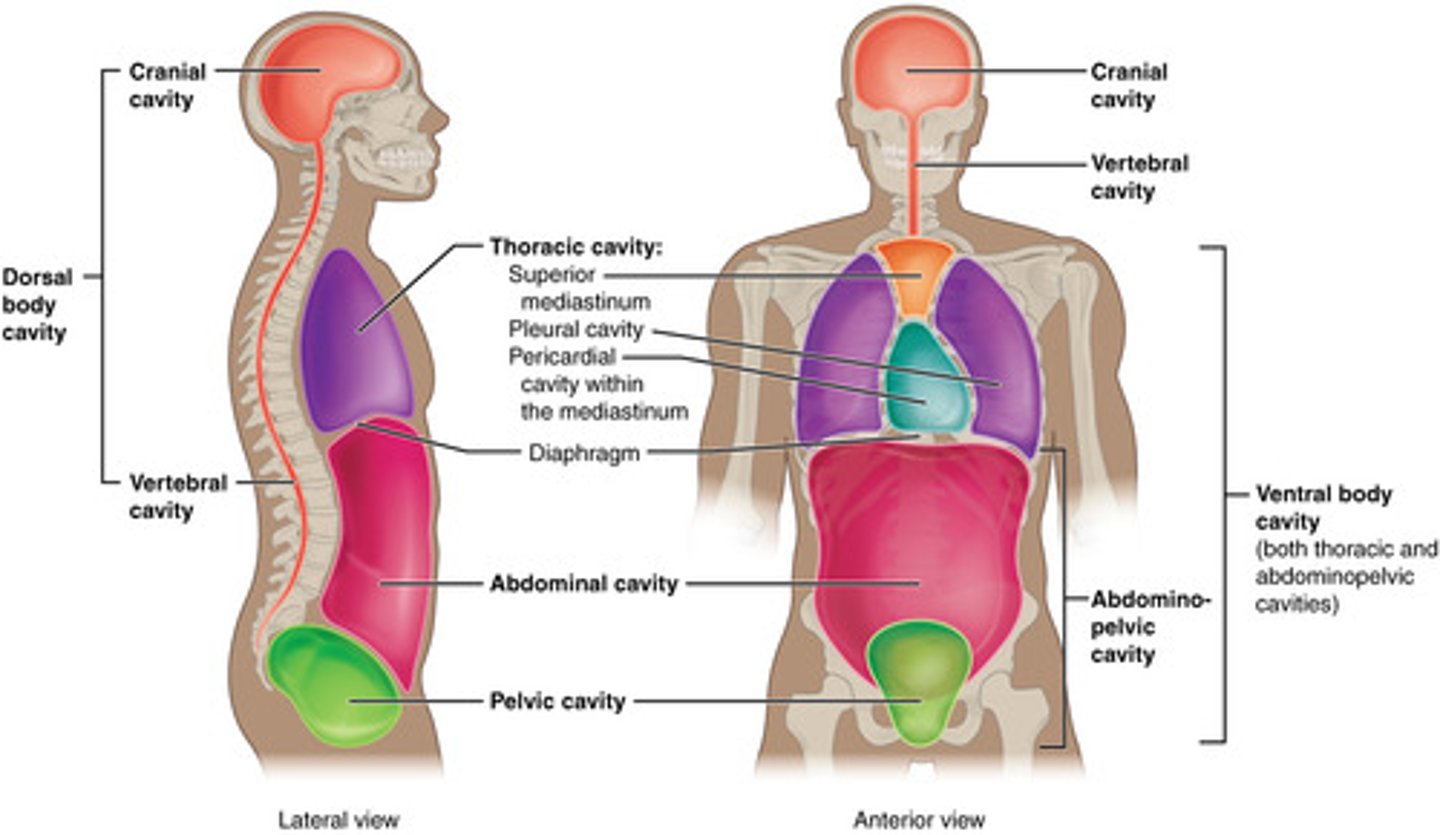
Thoracic & Abdominopelvic Cavities
ventral body cavity
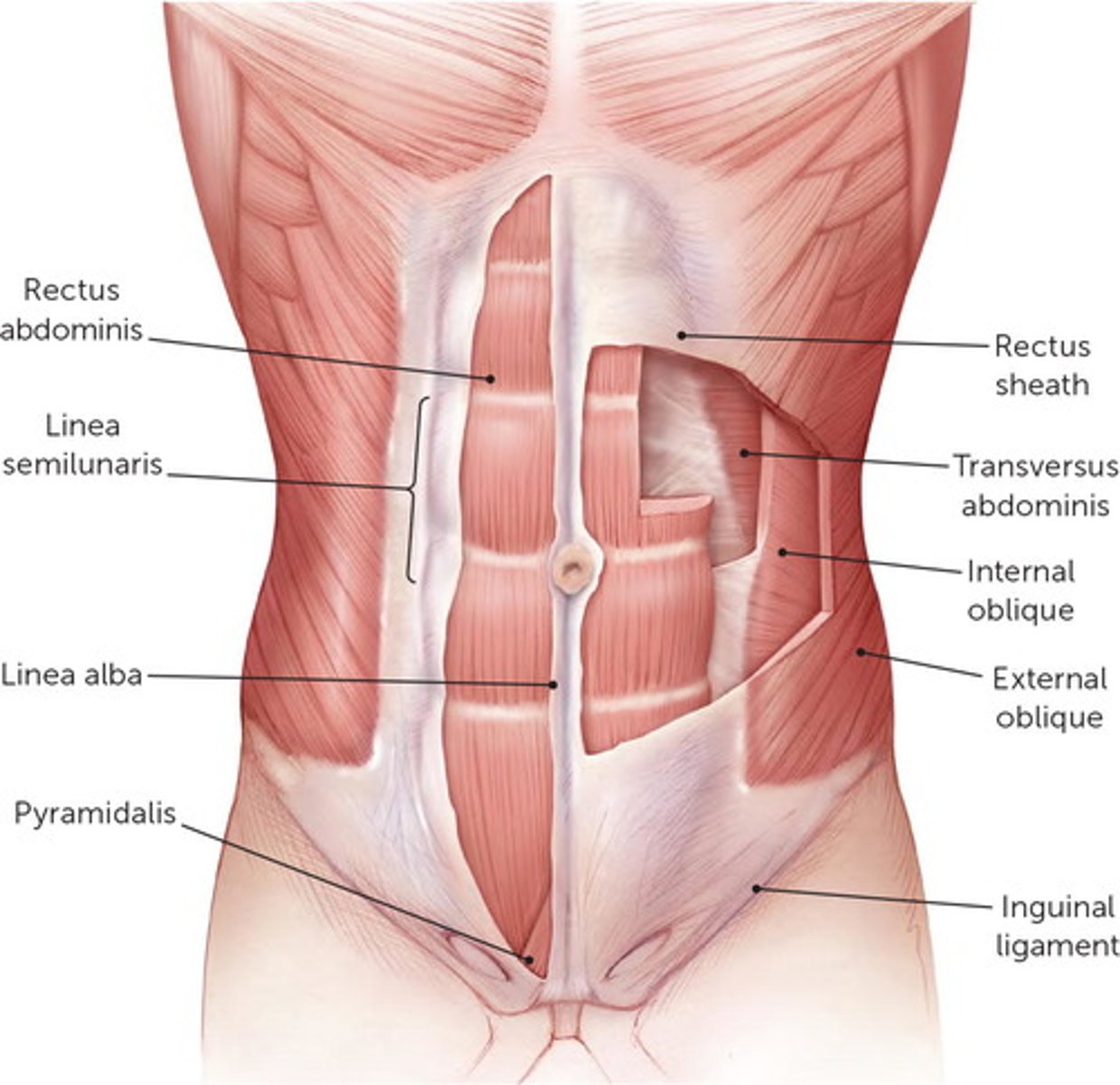
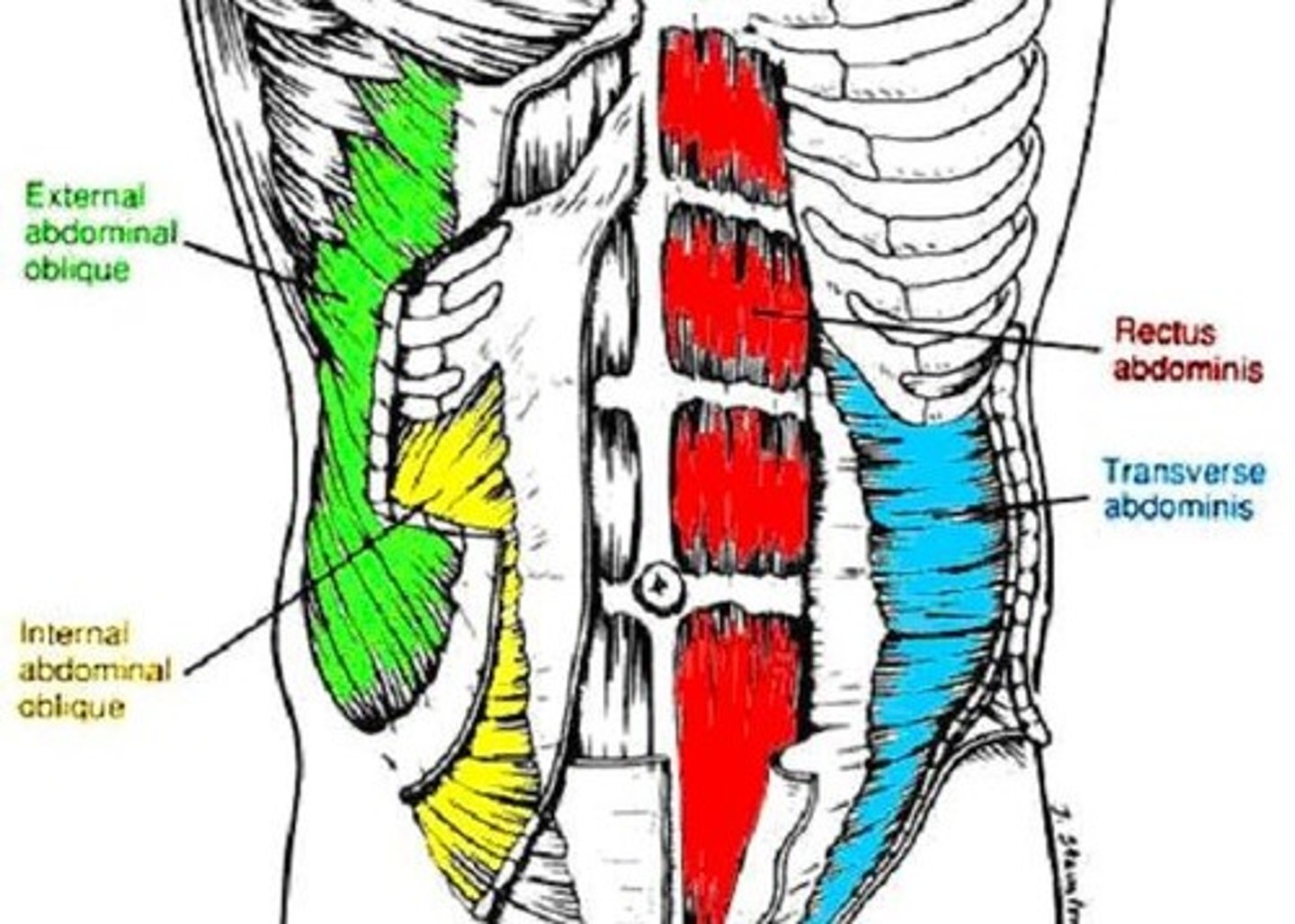
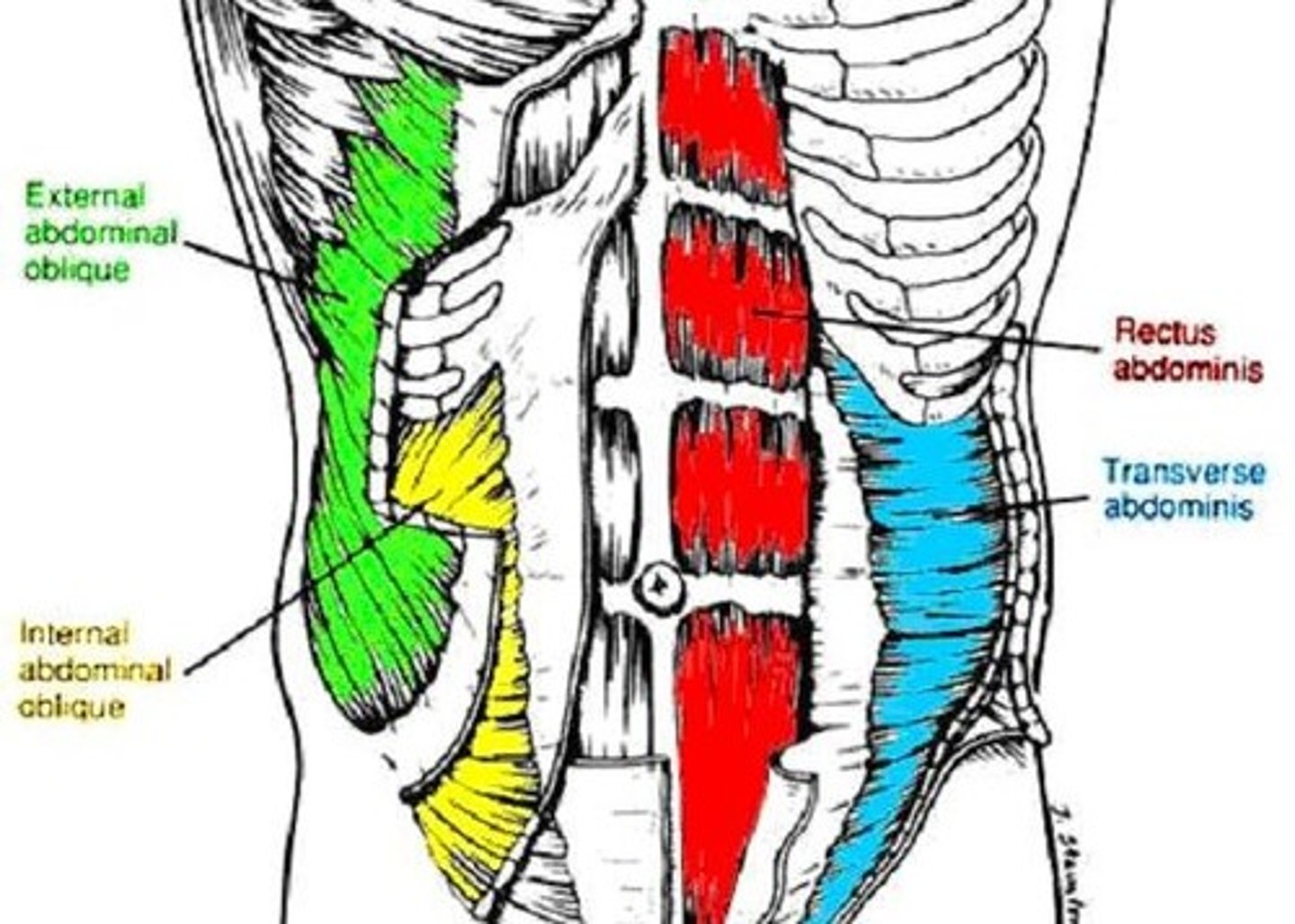
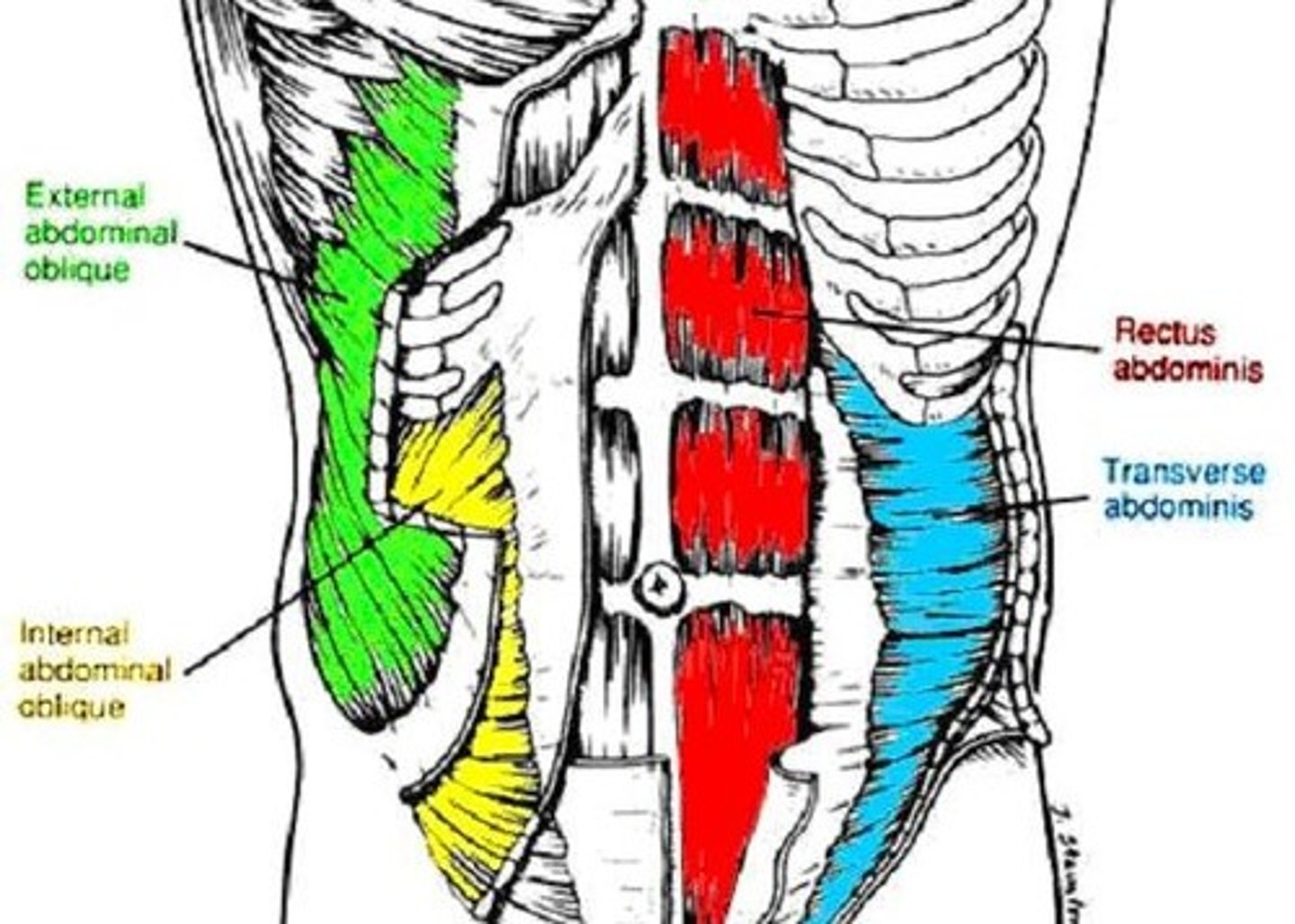
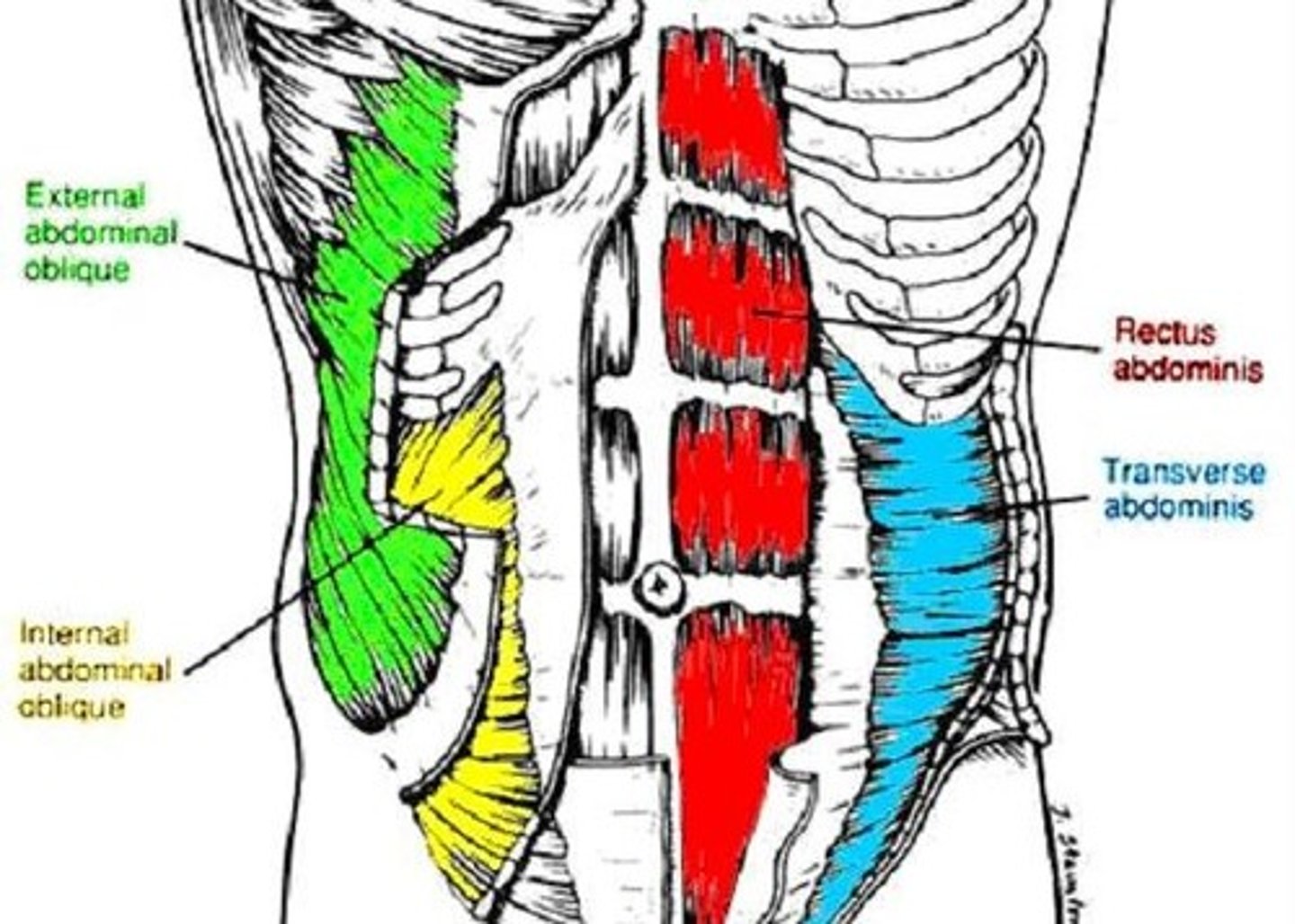
Muscles of Abdominal Wall
5 paired muscles in anteriolateral wall:
3 flat: form layers
-external oblique, internal oblique, transverse abdominis
2 vertical: contained within texture sheath
-rectus abdominis, pyramidalis
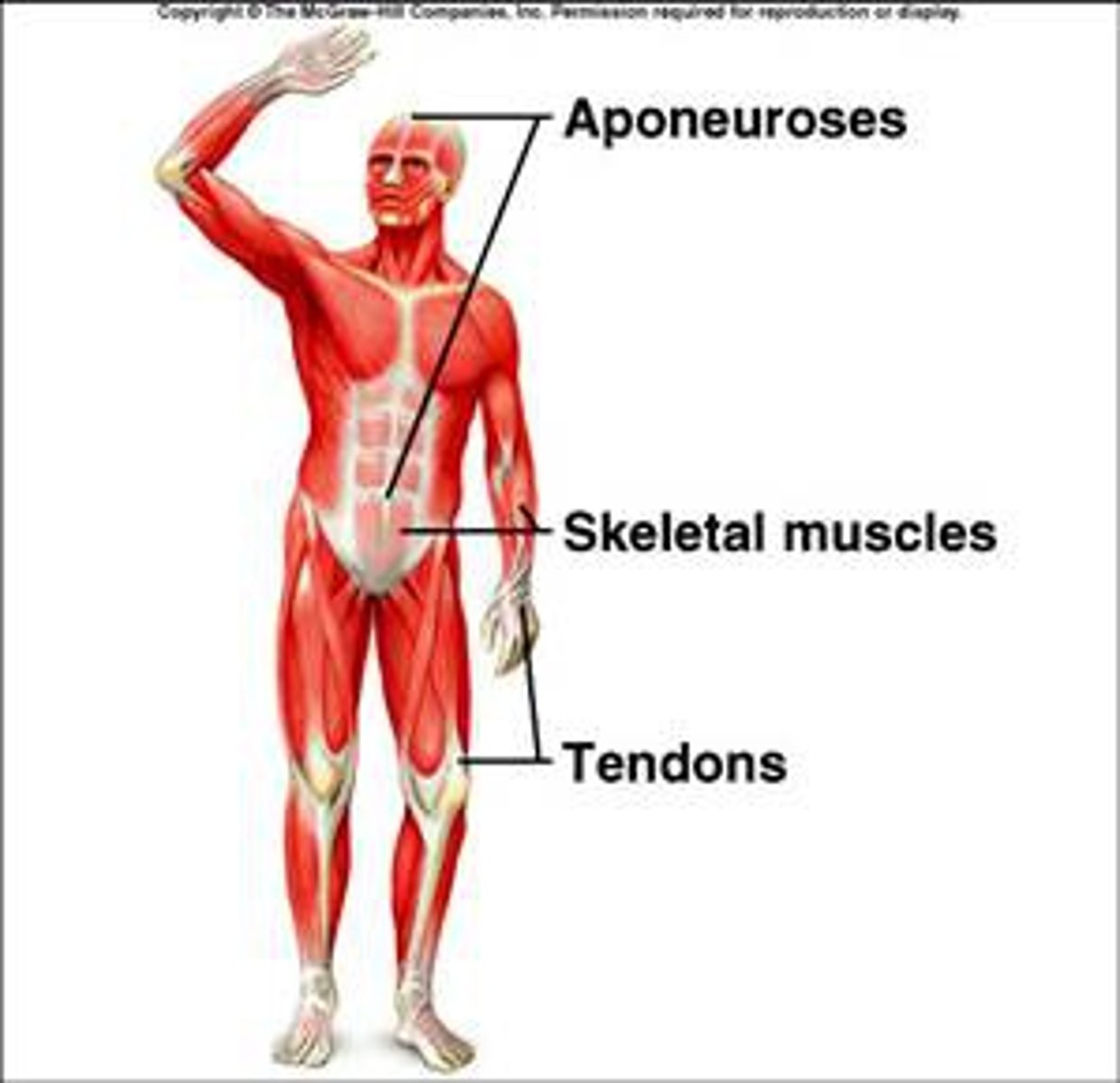
Aponeuroses
fibrous or membranous sheet connecting a muscle and the part it moves
External Oblique
largest and most superficial layer
Origin of external oblique
external surface of 5-12th ribs
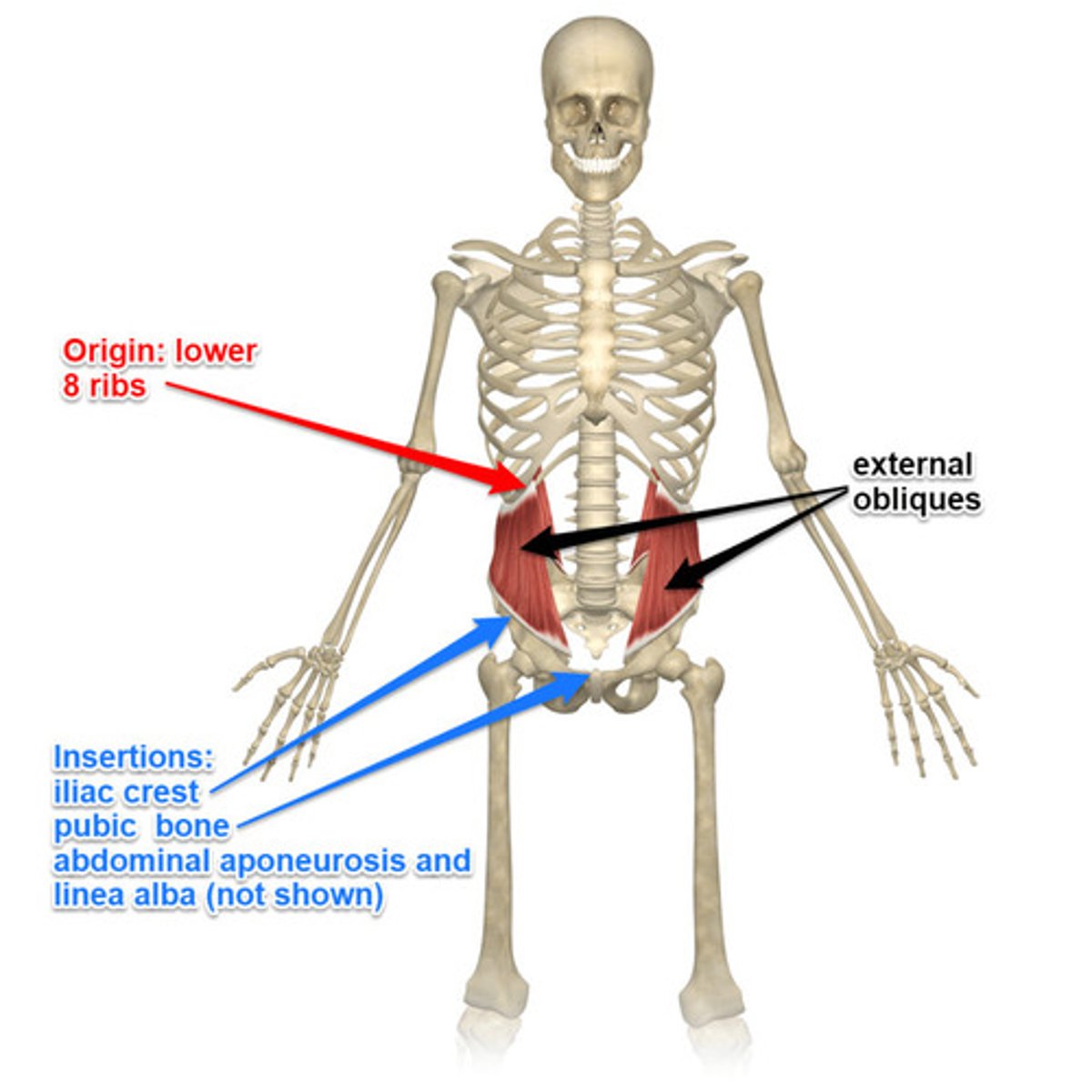
Insertion of external oblique
linea alba, pubic tubercle, iliac crest
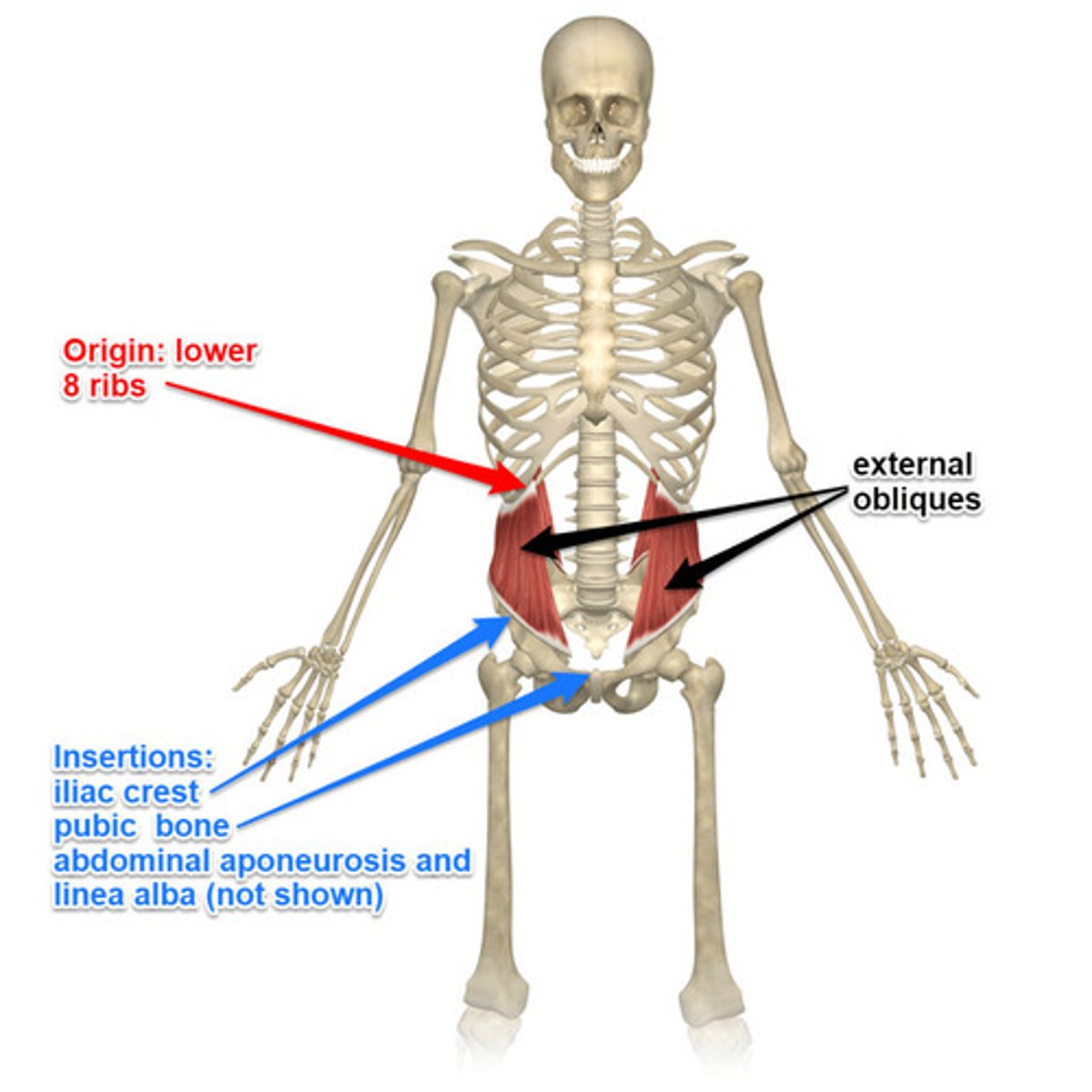
Action of external oblique
assists in torsional rotation of trunk
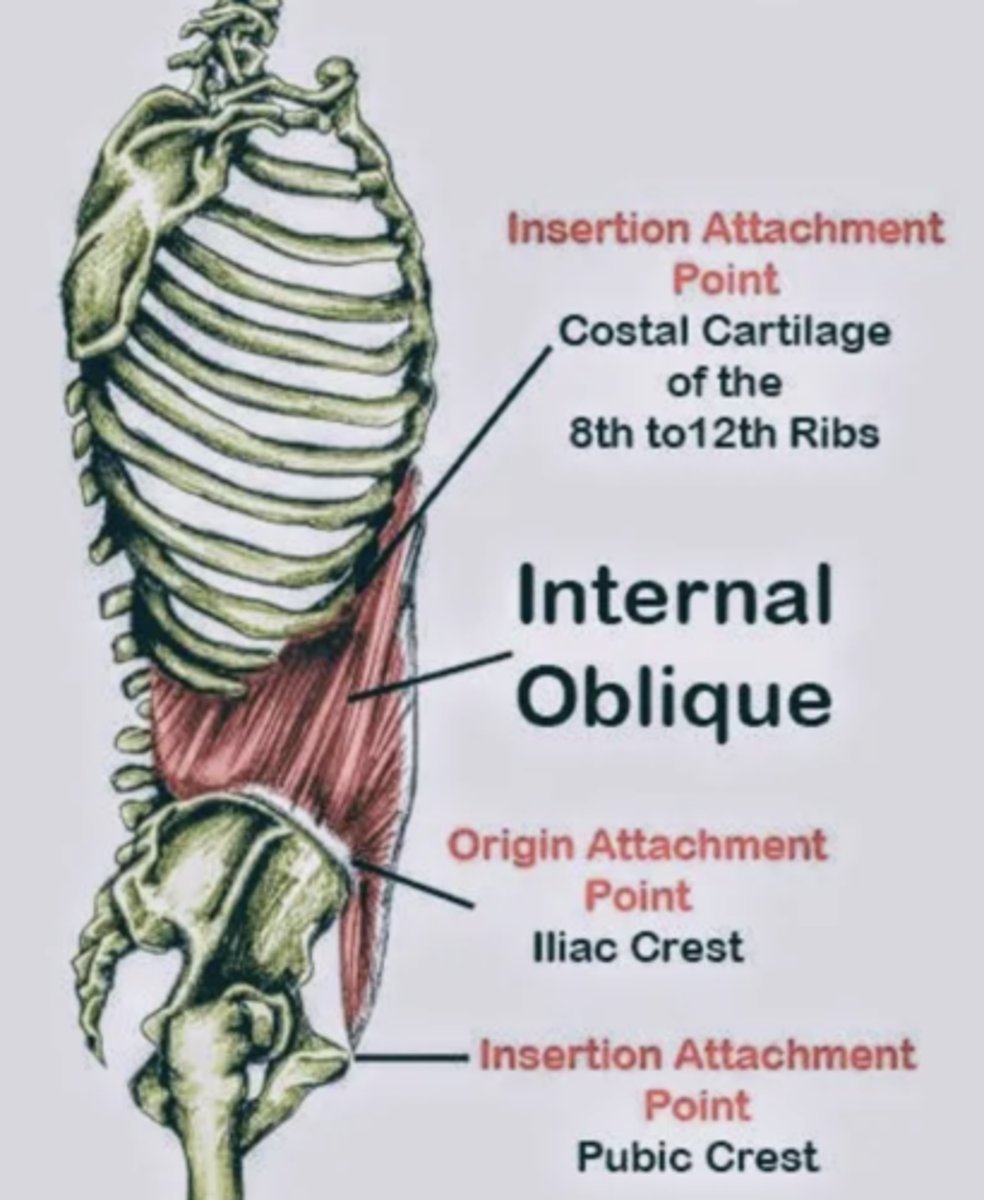
Internal Oblique
tenses abdominal wall and compresses abdominal contents
Origin of internal oblique
thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 2/3 of iliac crest, connective tissue lateral 2/3 of inguinal ligament
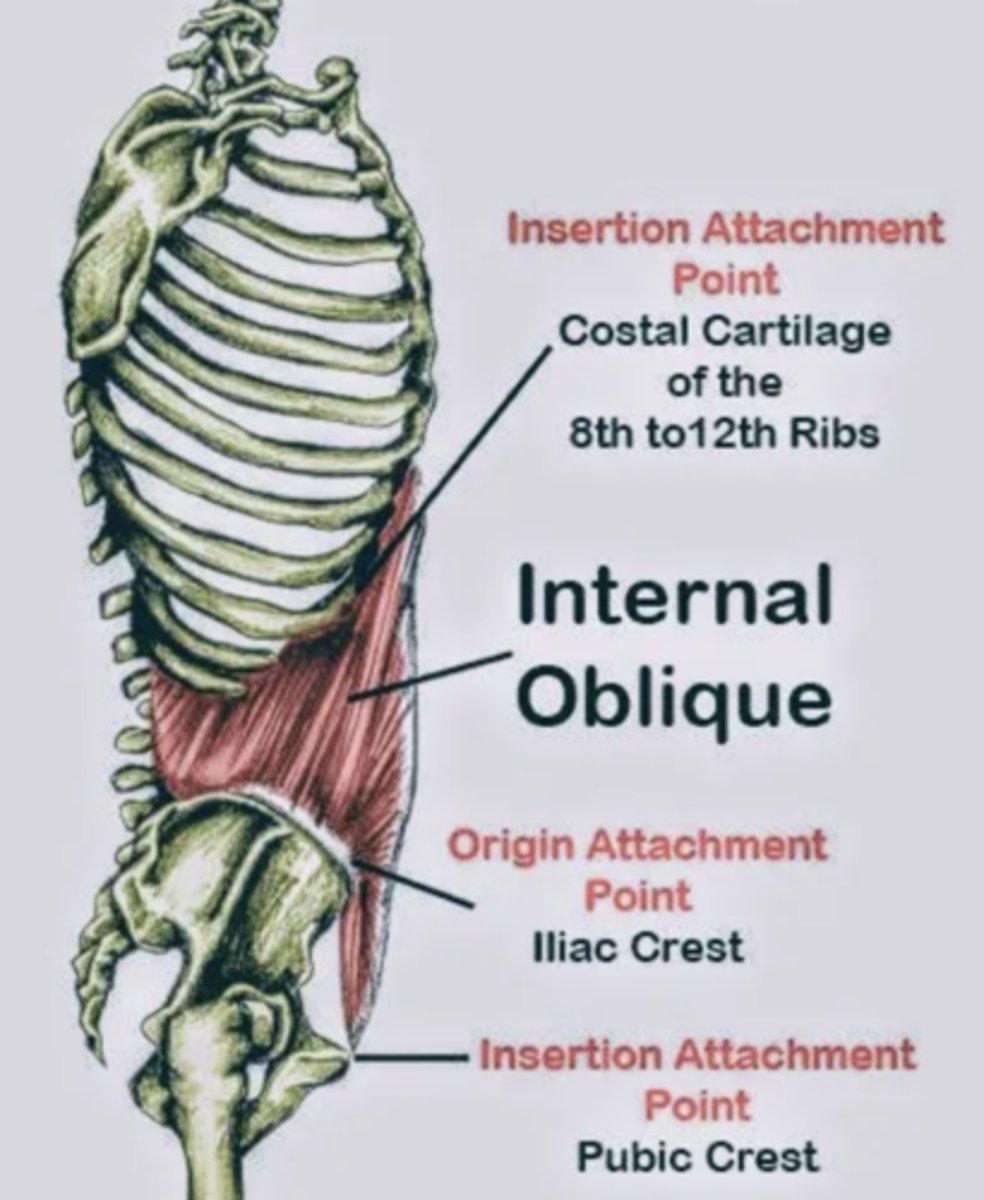
Insertion of internal oblique
inferior border of 10-22 ribs, linea alba, & pectin pubis
Action of internal oblique
compress and support abdominal viscera, flex and rotate trunk
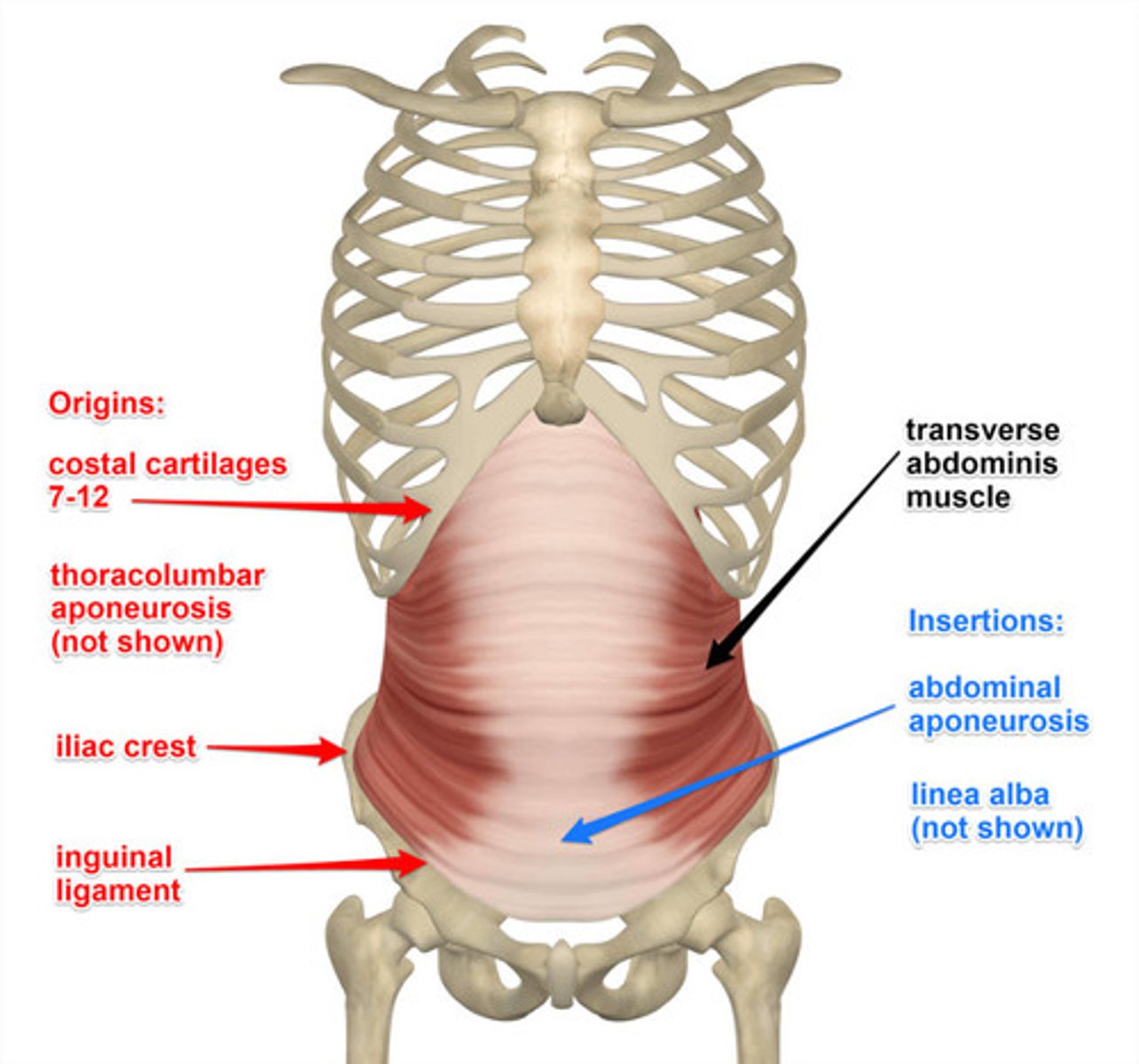
Transverse abdominis
compresses abdomen & increases intra-abdominal pressure
Origin of transverse abdominis
internal costal cartilage ribs 7-12, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, lateral 1/3 inguinal ligament deep connective tissues
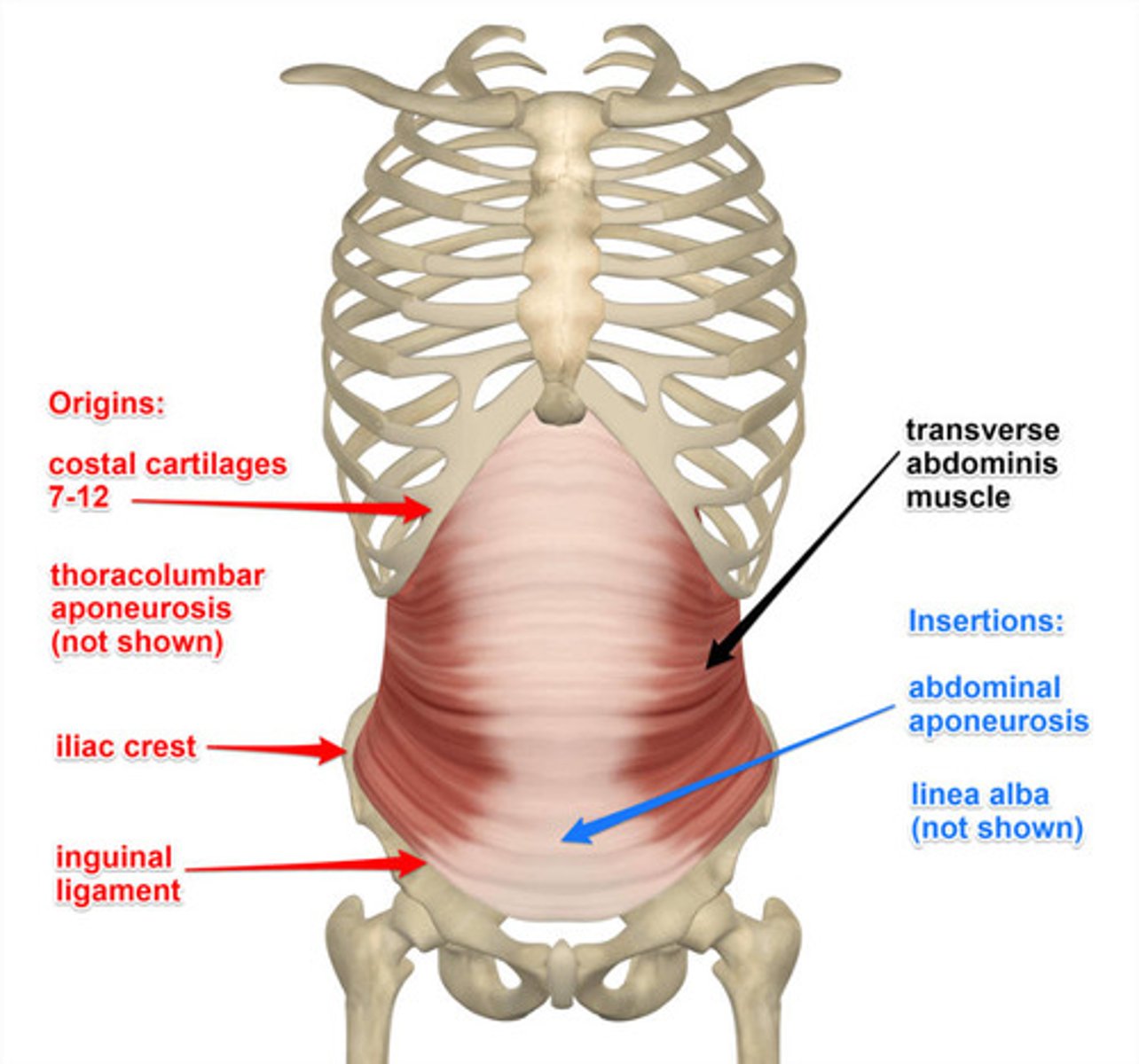
Insertion of transverse abdominis
linea alba & internal oblique aponeurosis, pubic crest & pectin pubis
Rectus abdominis
flexes and rotates vertebral column
Origin of rectus abdominis
pubic symphysis & pubic crest
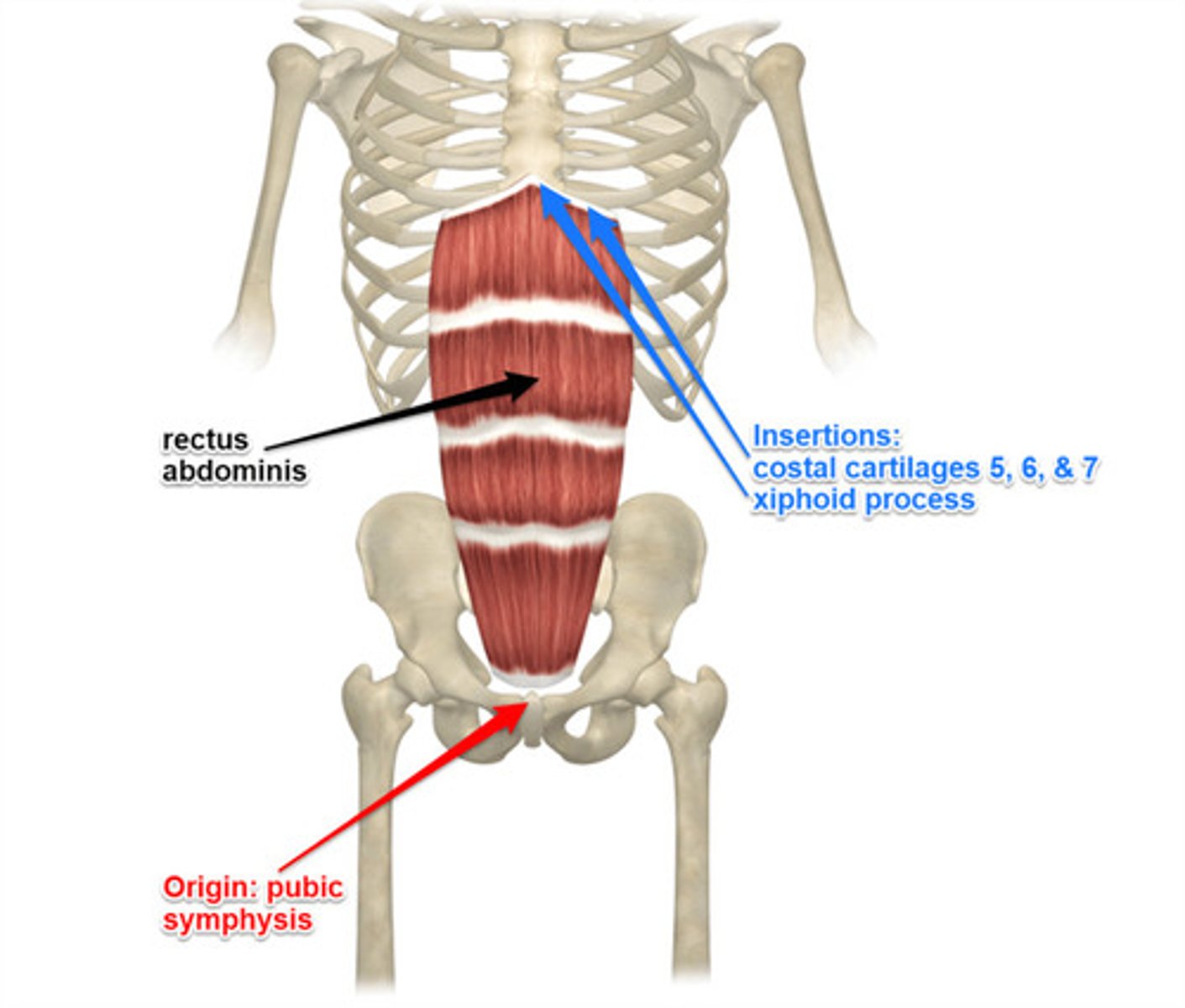
Insertion of rectus abdominis
xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs 5-7
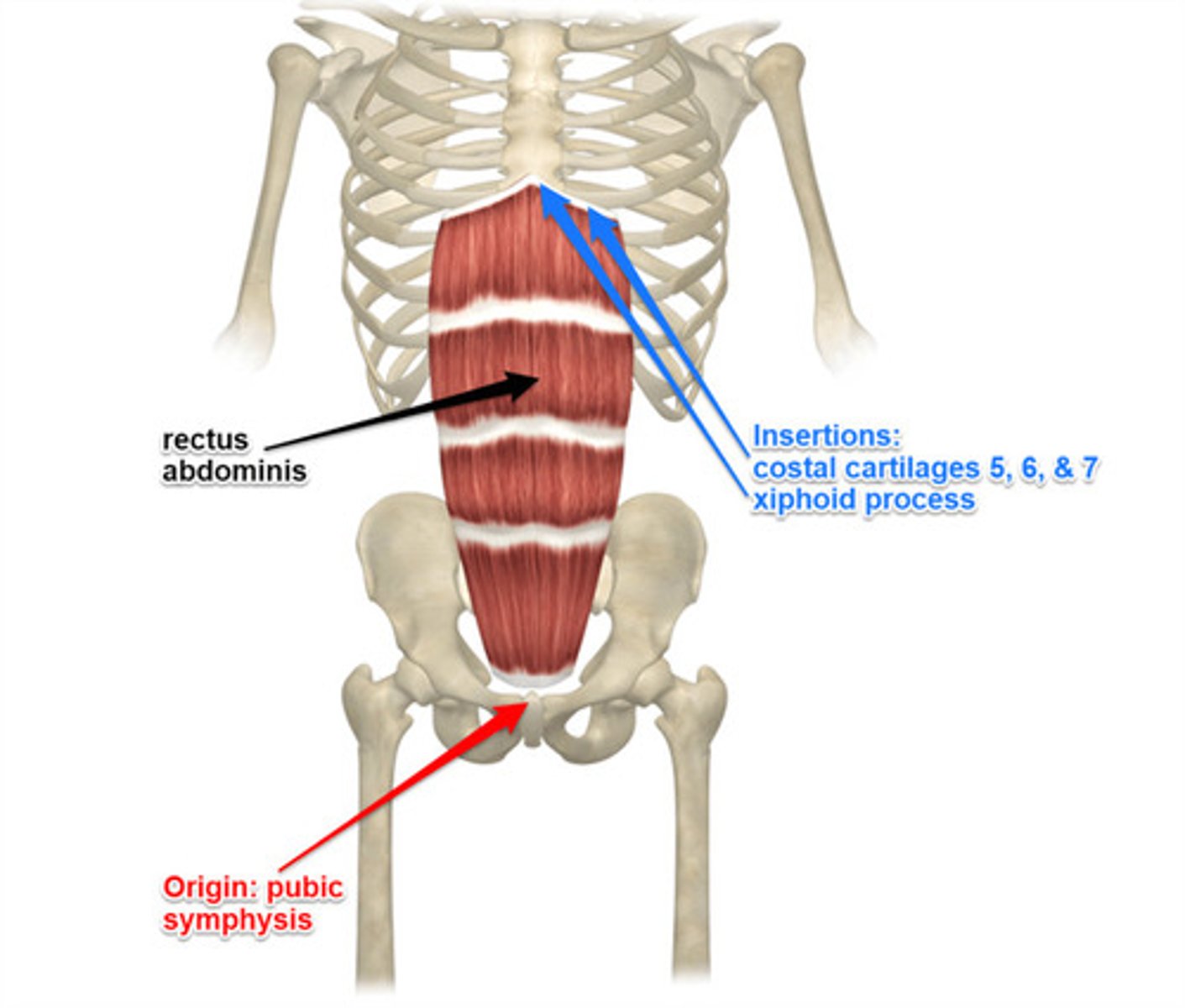
Action of rectus abdominis
flexes trunk(lumbar) & compress abdominal viscera; stabilizes & controls pelvic tilt
Pyramidalis
small triangular muscle of the lower front part of the abdomen that is situated in front of and in the same sheath with the rectus and functions to tense the linea alba
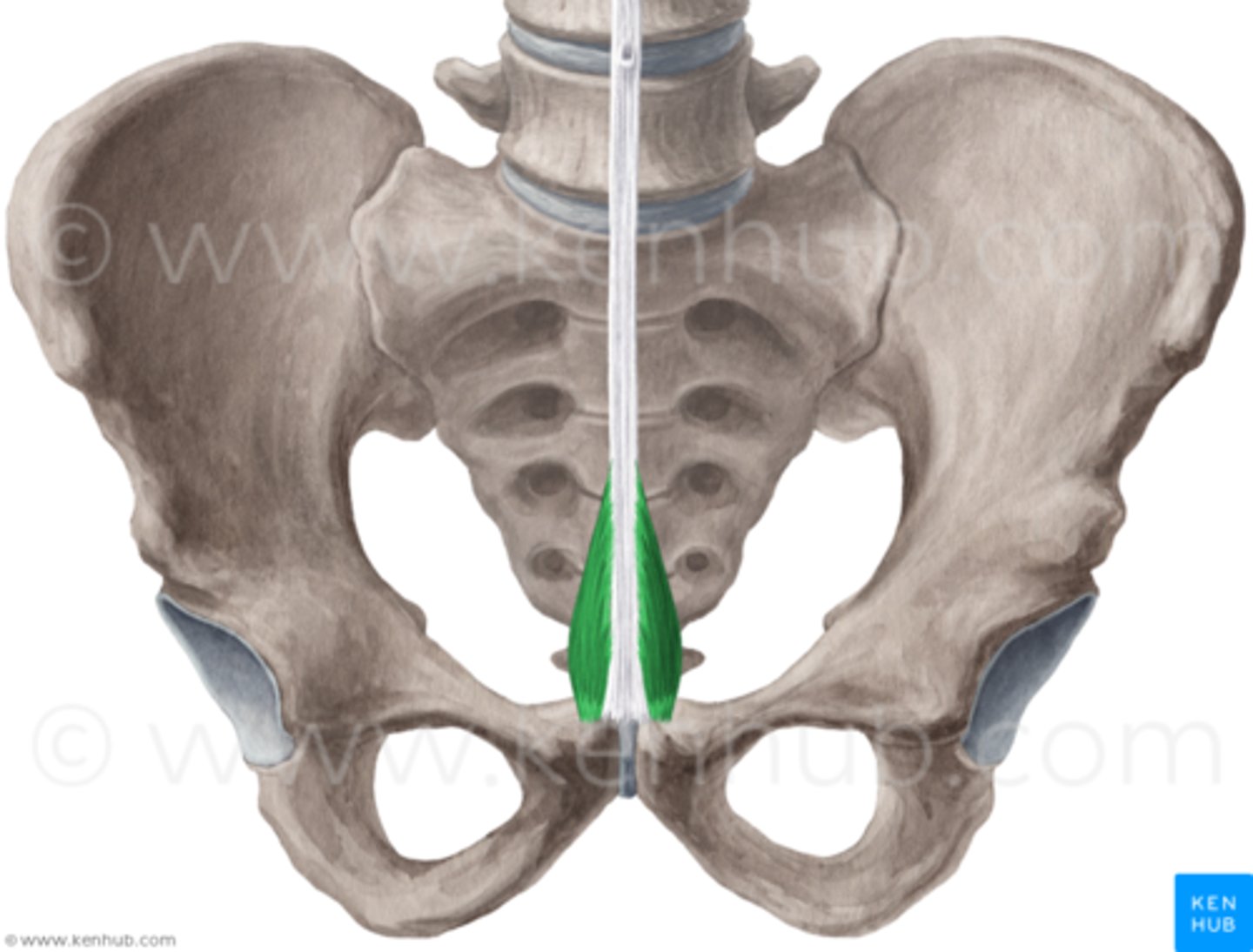
Origin of pyramidalis
anterior surface of pubis & anterior pubic ligament
Insertion of pyramidalis
linea alba
Action of pyramidalis
tenses linea alba
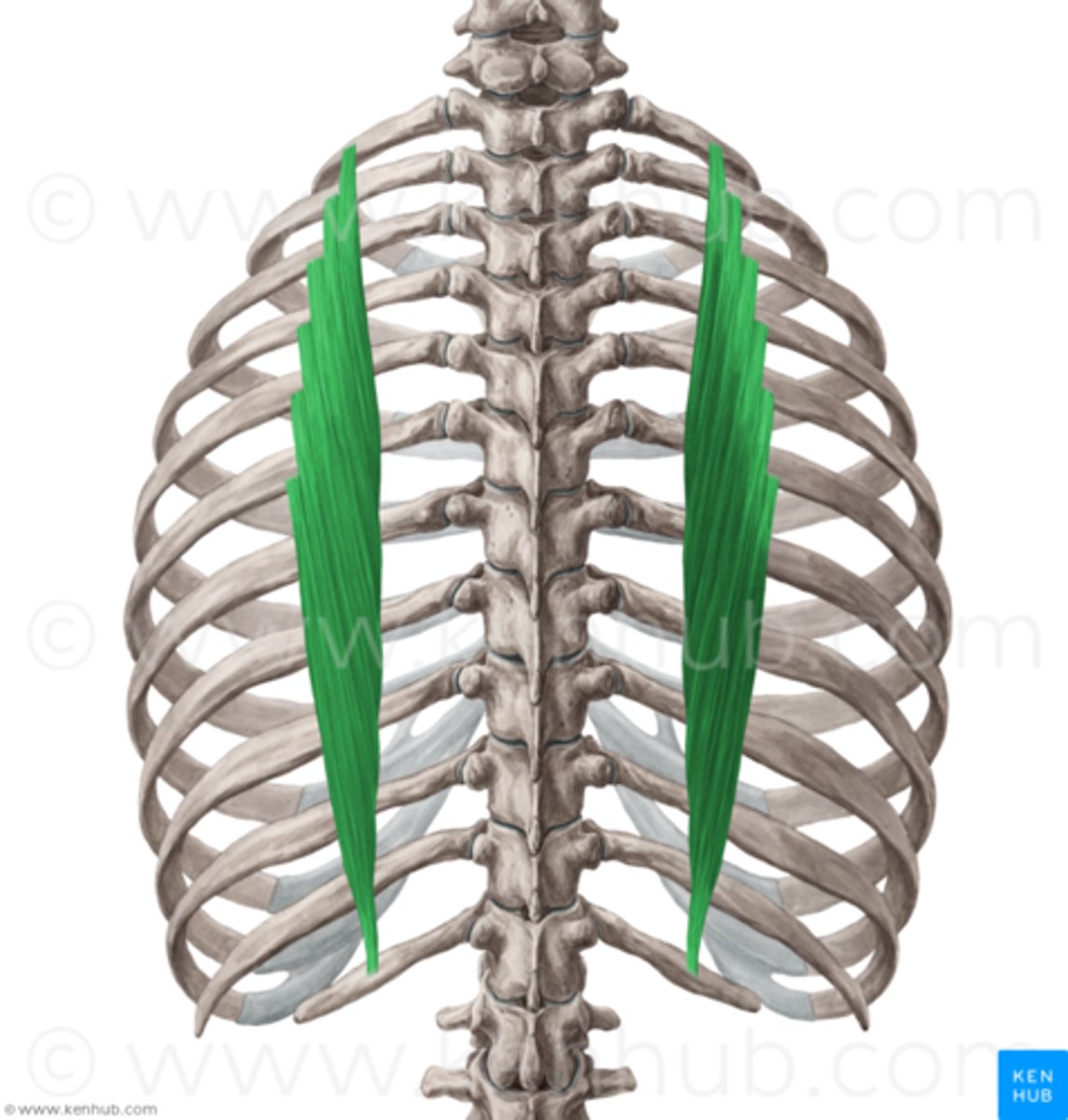
Serratus Posterior Superior
extend obliquely from the vertebral column to the rib cage
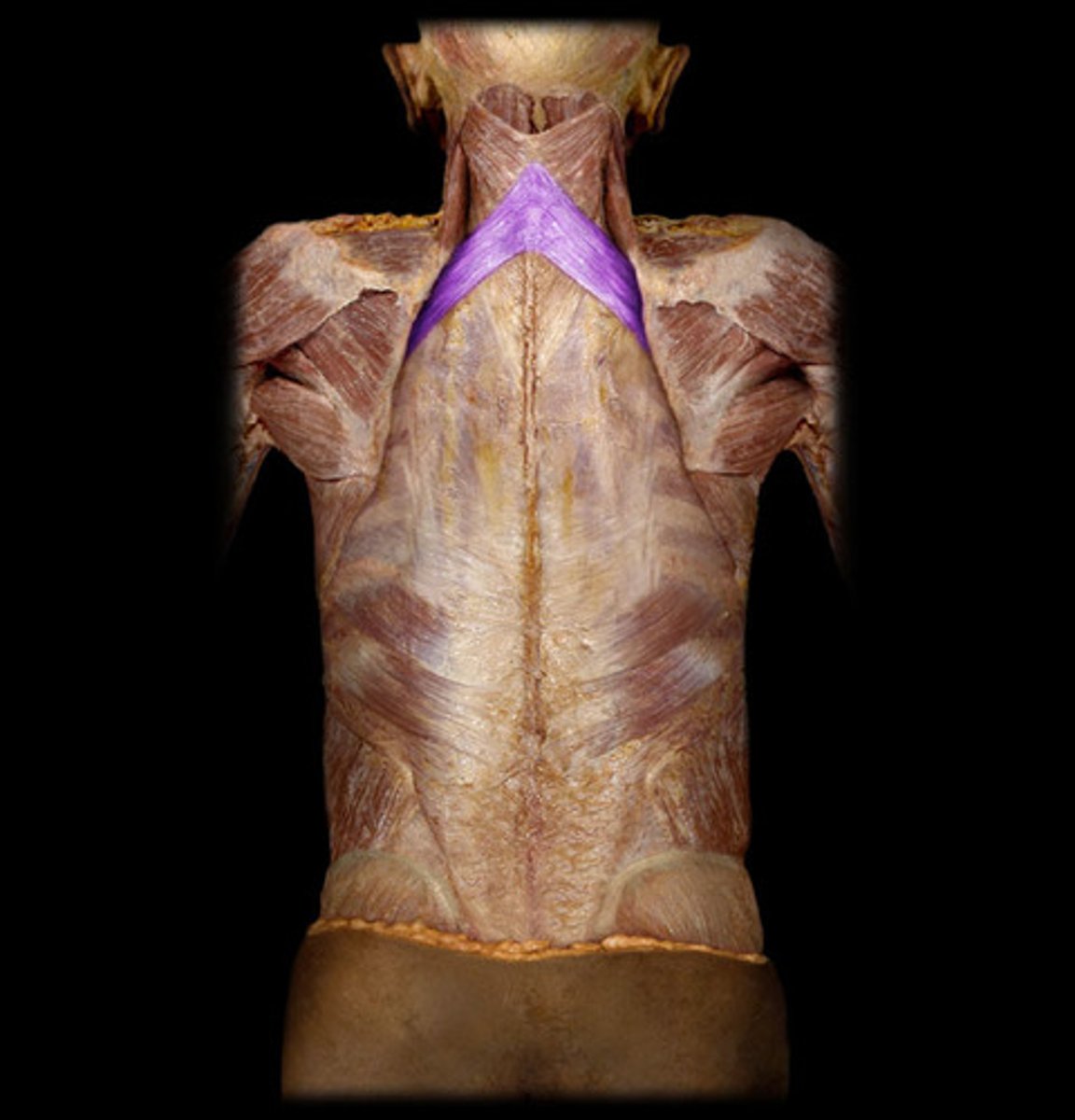
Origin of serratus posterior superior
lower part of ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of C7-T2/3
Insertion of serratus posterior superior
2nd-5th ribs
Nerve Innervation of serratus posterior superior
first 3 or 4 intercostal nerves(ventral ram of spinal nerves)
Action of serratus posterior superior
assists in elevating ribs
Serratus Posterior Inferior
an extrinsic muscle of the back and is found in the lower back region
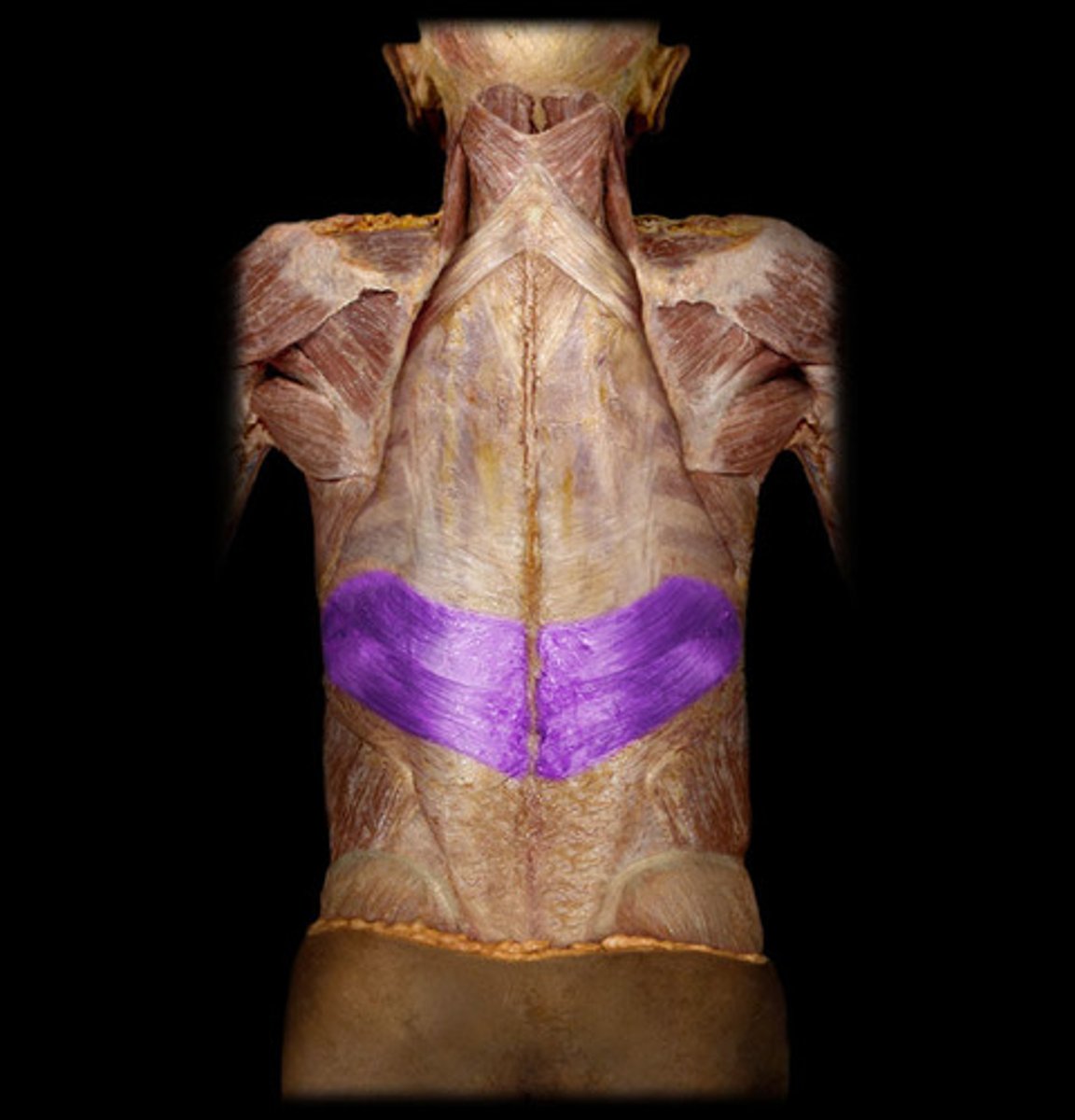
Origin of serratus posterior inferior
T1-L2 of spinous processes
Insertion of serratus posterior inferior
9th-12th ribs
Nerve innervation of serratus anterior inferior
9th-12th intercostal nerves
Action of serratus anterior inferior
draw lower ribs downward to enlarge thoracic cavity & stabilize ribs against pull of diaphragm
Splenius Capitis
rotates head, bends head to one side, or extends neck
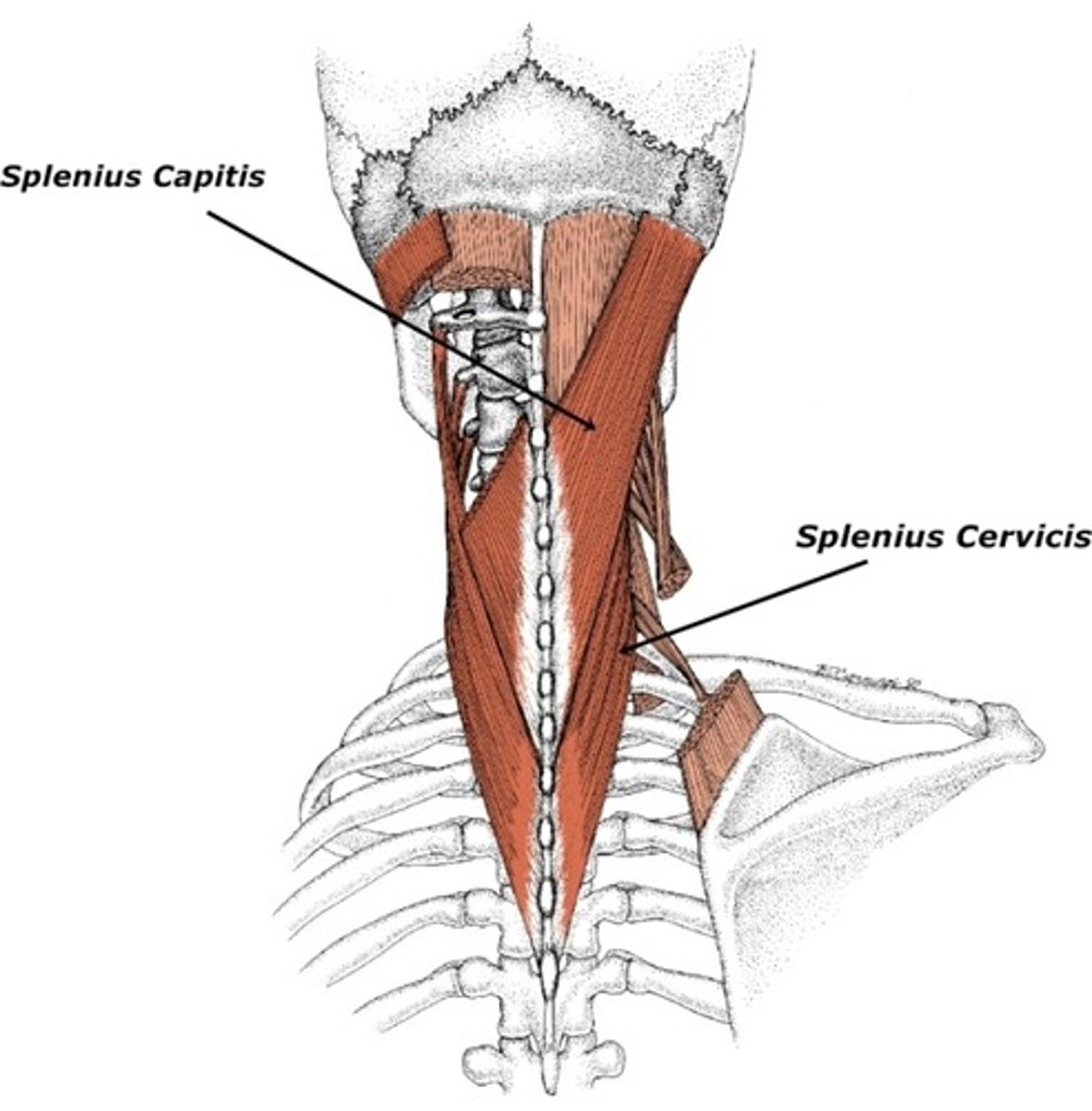
Origin of splenius capitis
lower half of ligamentum nuchae & spinous process of C7 & T1-T3/4
Insertion of splenius capitis
mastoid process & occipital bone
Splenius Cervicis
a paired back muscle found in the prevertebral space of the neck
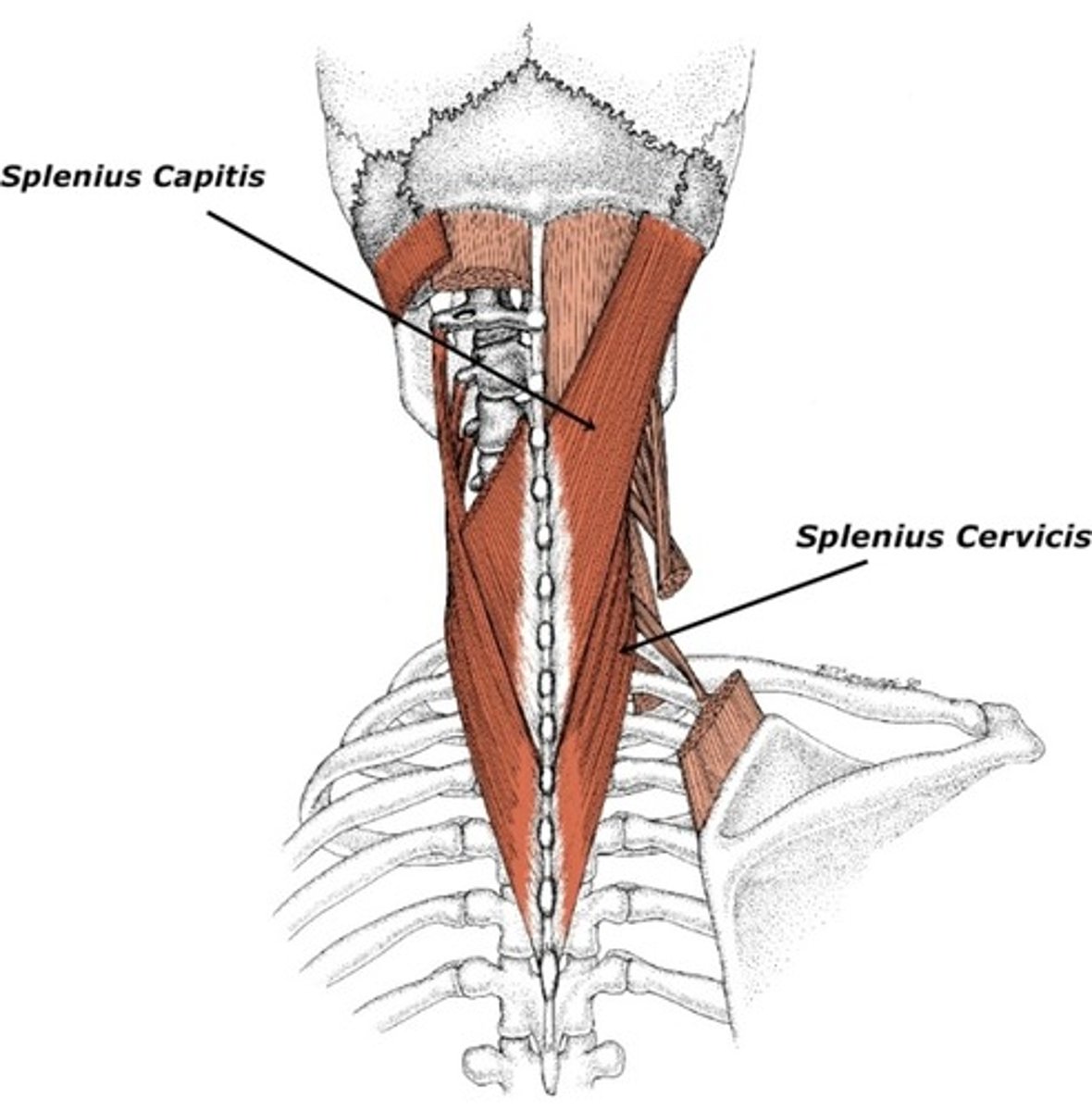
Origin of splenius cervicis
spinous process of T3-T6
Insertion of splenius cervicis
transverse processes of C1 & C2-C4
Nerve Innervation of splenius cervicis
both are innervated by dorsal rami of middle & inferior cervical spinal nerves
Action of splenius cervicis
unilateral: rotate head & cervical spine toward same side
bilateral: assist in extension of head & neck
Erector Spinae
large mass of muscle with origin over the upper sacral & lower lumbar vertebrae
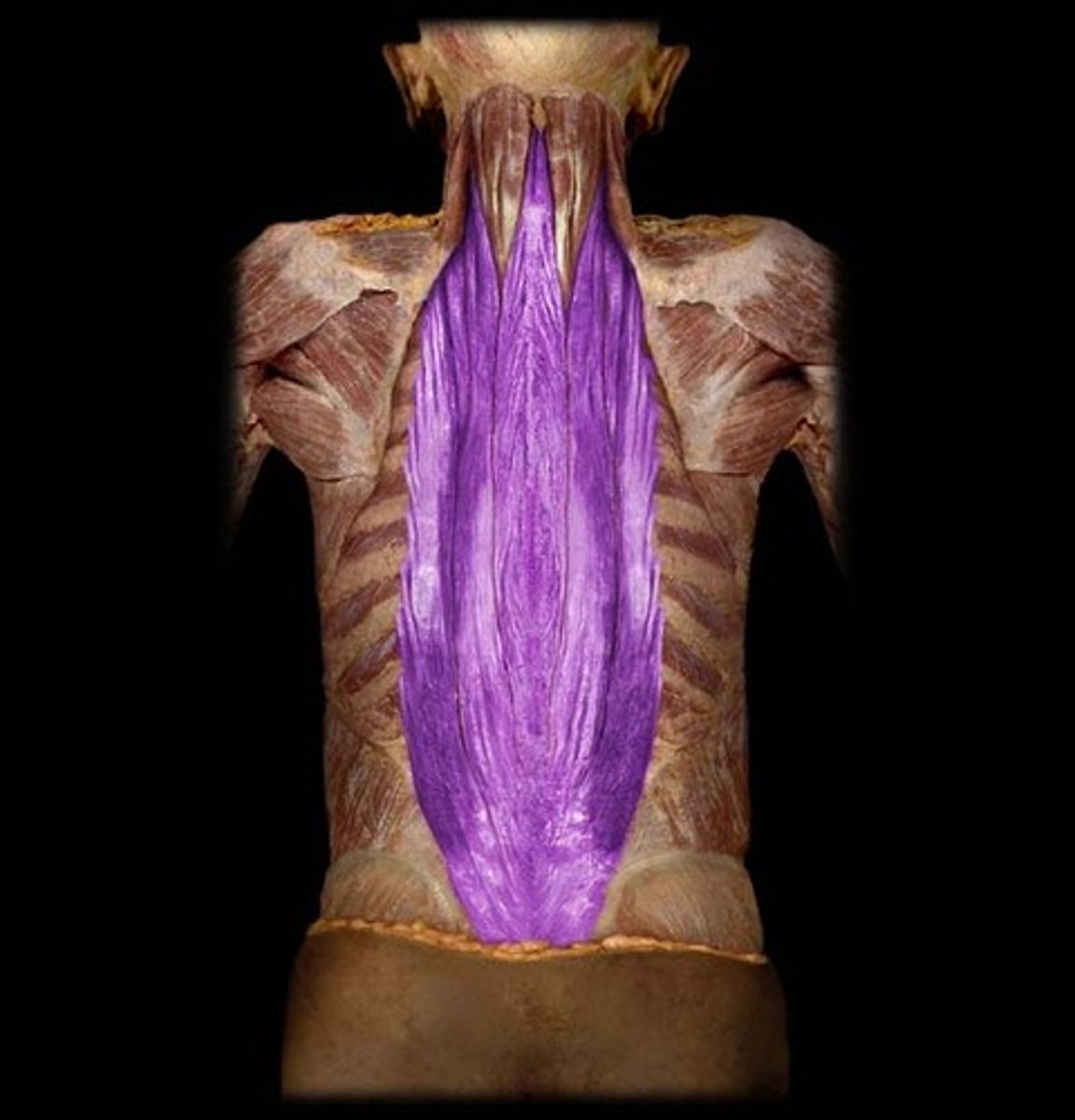
Insertion of erector spinae
medial crest of sacrum
Origin of erector spinae
posterior surface of sacrum, iliac crest & solid processes of T11-L5
Nerve innervation of erector spinae
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Action of erector spinae
extends thoracic vertebral column
Iliocostalis lumborum
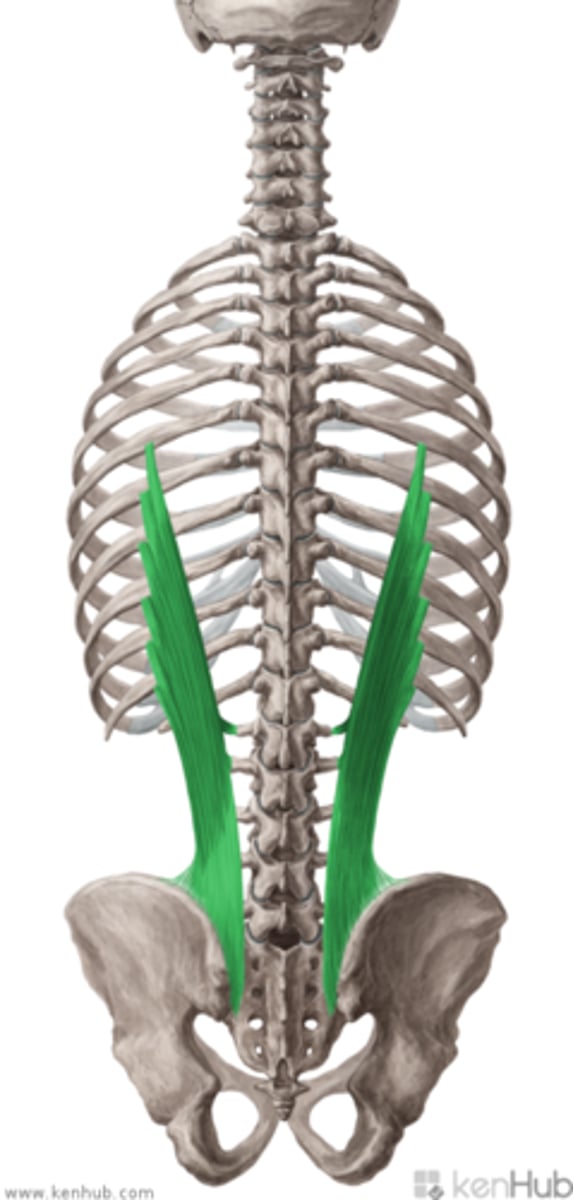
Origin of Iliocostalis lumborum
iliac crest & sacrum
Insertion of Iliocostalis lumborum
slips into lower 6/7 ribs
Iliocostalis cervicis
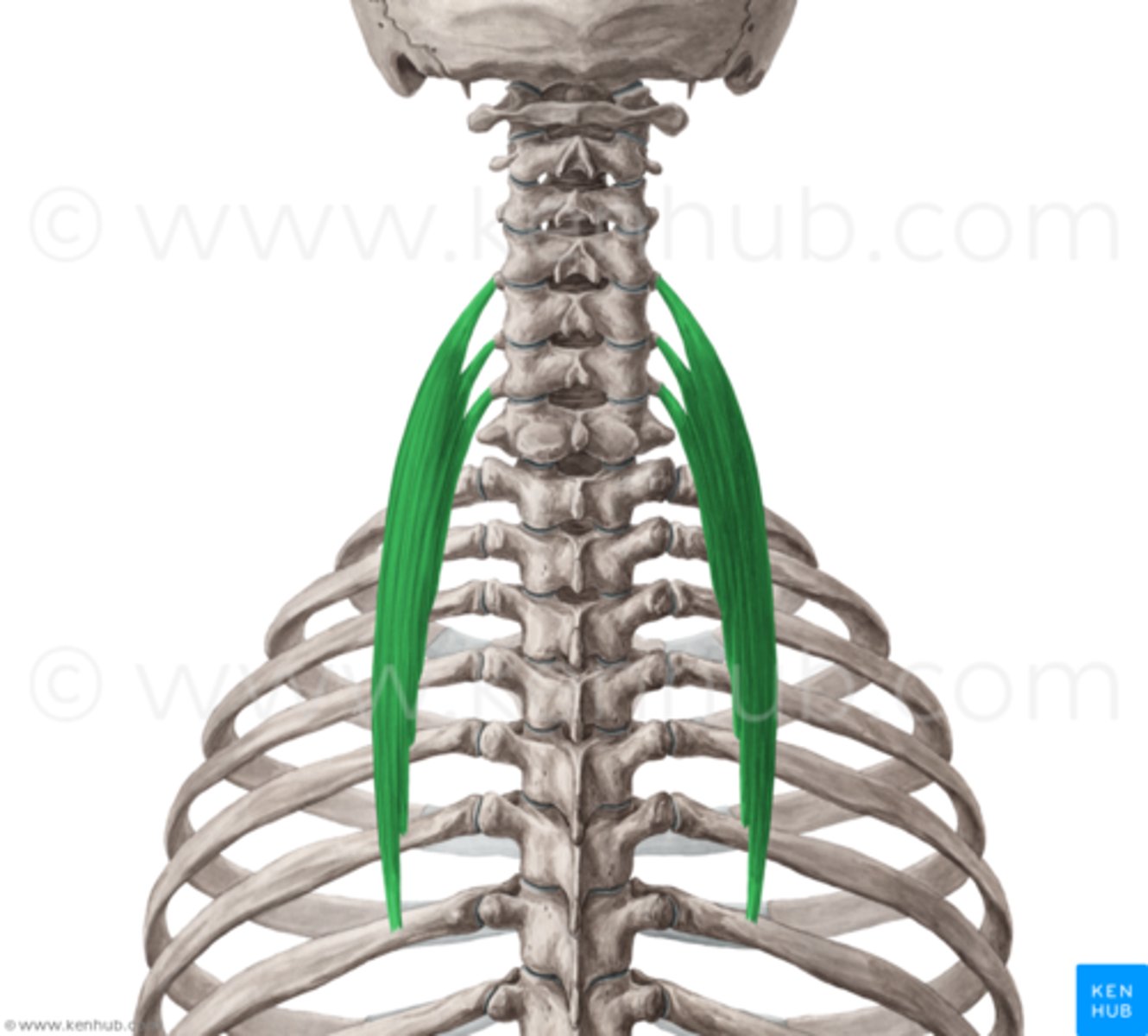
Origin of Iliocostalis cervicis
angles or upper 6 ribs(medial to iliocostalis thoracic insertion)
Insertion of Iliocostalis cervicis
transverse processes of C4-C6
Iliocostalis thoracis