PPHC: L6 Observational Studies I
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are the 2 types of observational studies?
Descriptive and analytic
What are 3 examples of descriptive studies?
Case report, case series, and cross-sectional
What are 3 examples of analytic studies?
Cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional
Observational studies
Individuals are followed ('“observed”) in … settings
No … assignment by researcher
real-world, intervention/exposure
Descriptive observational studies
Describes … of an … (i.e. disease)
Goal: examine … (of exposure or outcome)
… evaluate an intervention
Start: … hypothesis
End: … hypothesis
occurrence, outcome, patterns, do not, no, possible
Analytic observational studies
Goal: evaluate … (between exposure and outcome)
… evaluate an intervention (not assigned by researcher)
Start: … hypothesis
End: … hypothesis
relationship, do, defined, confirm or reject
Case …
Detailed presentation of 1 case (‘n of 1’)
What they do
Report a new or … condition
Describe previously … disease
Show unexpected new … effect
Report … events
What they don’t do
Measure disease … (describe prevalent disease)
Identify … factors
Identify … of disease
reports, unique, undescribed, therapeutic, adverse, incidence, risk, cause
Case …
Detailed presentation of 2 or more cases
What they do
Report a new or unique condition
Describe previously undescribed disease
Show unexpected new therapeutic effect
Report adverse events
What they don’t do
Measure disease incidence (describe prevalent disease)
Identify risk factors
Identify cause of disease
series
… study is an observational design that surveys exposures and/or outcomes at a … (‘snapshot’)
Can be analytic (i.e. measure association between exposure and disease)
Temporal sequence of exposure and outcome … to determine (don’t know which occurred first) → main limitation (compared to cohort and case-control studies)
Can be descriptive (i.e. focus on exposure or disease)
Measures prevalence not incidence
Cross-sectional, single point in time, impossible
… observational studies describe relationship between exposure and outcome
Disease can be the exposure OR outcome
Can evaluate intervention, though not assigned by researcher
Analytic
Analyzing analytic cross-sectional study … measure … of an outcome because we don’t know when outcome occurs
In analytical cross-sectional study, exposure and outcome are assessed at the same time
So relevant concept is …
cannot, risk, odds
The … of an event can be defined as the ratio of the number of ways the event can occur to the number of ways the event cannot occur
odds
What is the formula for odds?
odds = event/(1-event)
We are betting on a horse named Epi who has a 60% probability of winning the race. What are the odds that Epi will win the race?
1.5
What are the 2 measures of association?
Odds ratio (OR) and relative risk/risk ratio (RR)
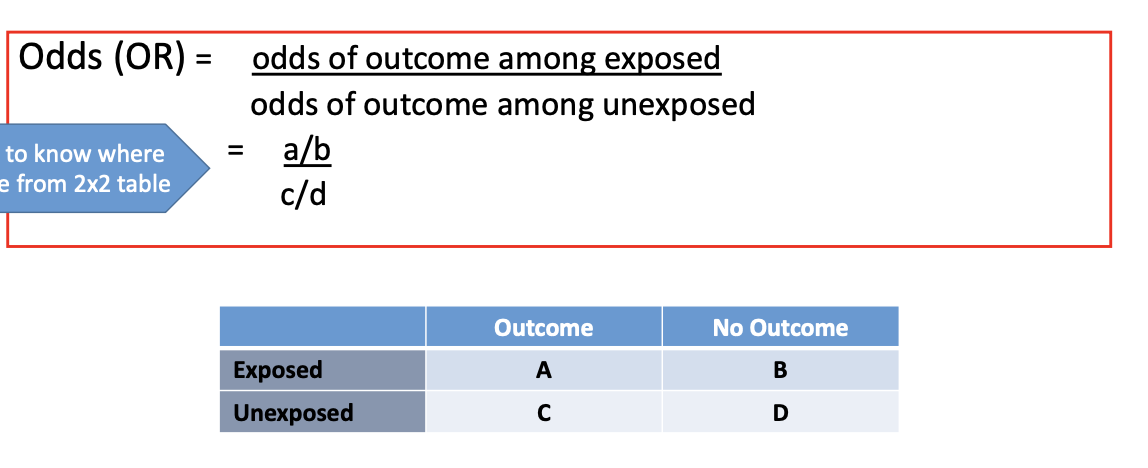
What is the formula for odds ratio for analytic cross-sectional study?
Odds = odds of outcome among exposed/odds of outcome among unexposed = (a/b)/(c/d) = ad/bc
OR … 1 = association (exposed group have higher odds of outcome compared to unexposed group)
Or … 1 = no association
Or … 1 = inverse association (exposed group have lower odds of outcome compared to unexposed group
>, =, <
OR > 1
% … = (OR - 1) x 100
If OR = 1.58 then % … = (1.58 - 1) x 100 = 58% higher odds
OR < 1
% … = (1 - OR) x 100
If OR = 0.25 then % … = (1 -0.25) x 100 = 75% lower odds
increase, increase, decrease, decrease
“Big Picture” for analytic epidemiology: is there a relationship (…)
association