Nasal Cavity Terms and Definitions | Biology Study Set
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
the nasal cavities communicate with the outside environment via what?
external nares
the external nose is predominantly what?
cartilaginous
what are the cartilaginous portions of the nose?
- lateral nasal cartilages
- major alar cartilages
- minior alar cartilages
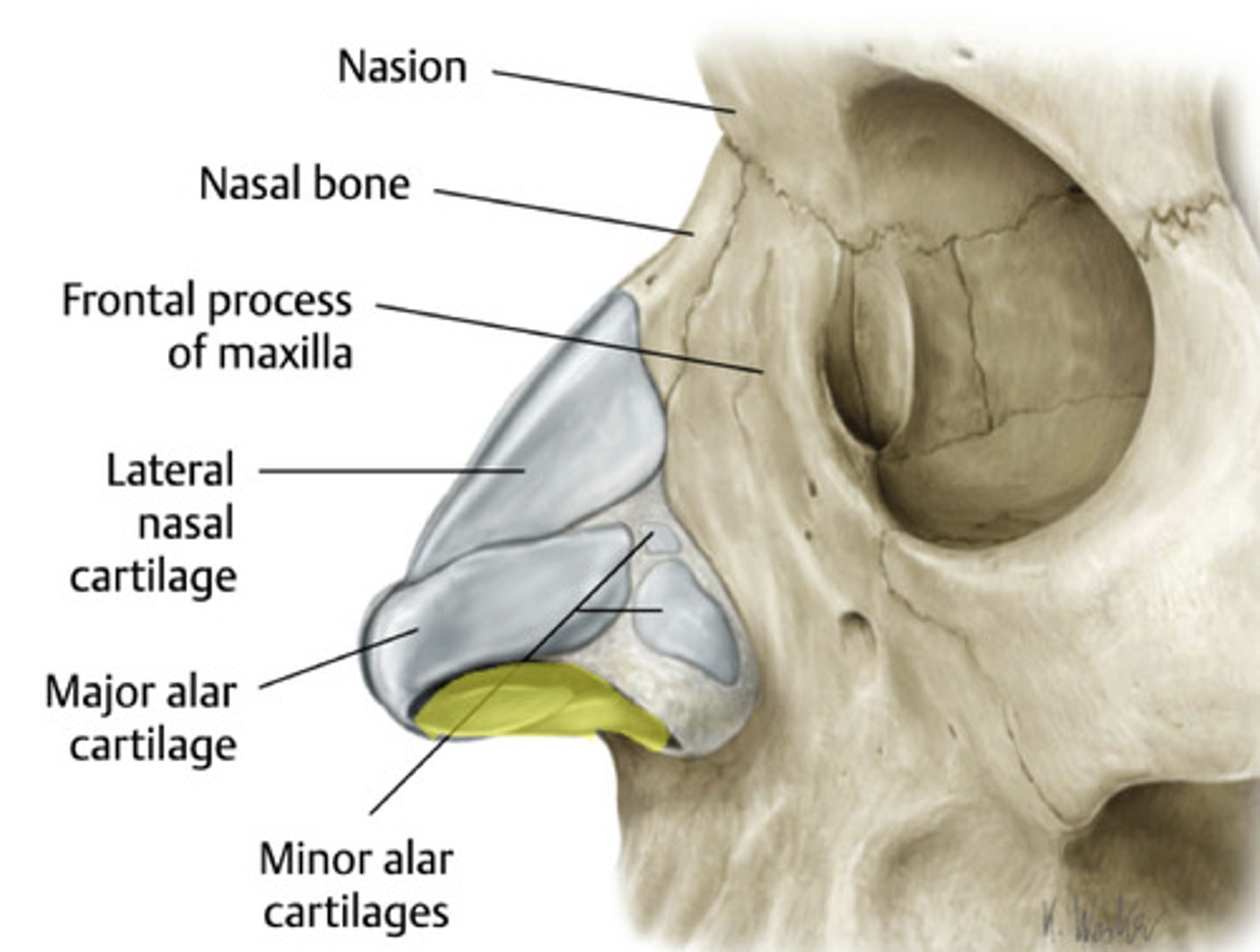
the bridge of the nose is made from what?
nasal bones
we get processes of the nose from what?
- frontal bone (nasion)
- maxillae
the nasal cavity is divided into a right and left cavity by what?
the nasal septum
the internal nares (choanae) are located where?
just before the pharynx
what is a clinical correlate of the nasal cavity?
NG tube placement for eating
deep to the nasal septum would be what?
the nasal cavity
what bones make up the nasal septum?
- perpendicular plate of ethmoid
- vomer
- septal cartilage (cannot see in a coronal view)
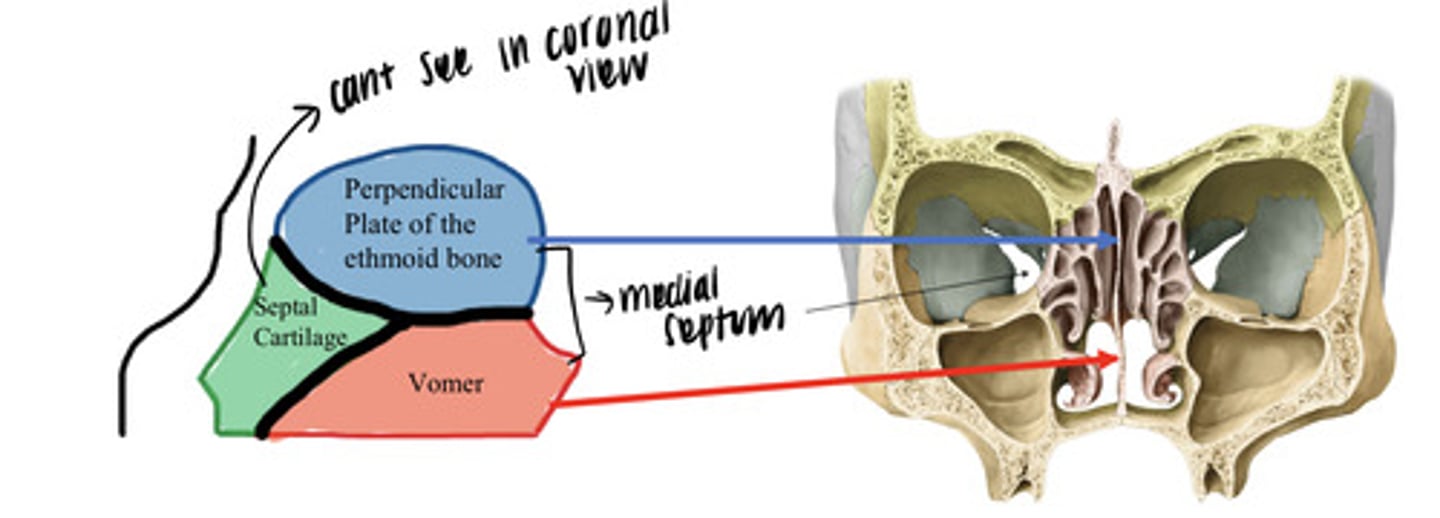
what is a clinical correlate of the nasal septum?
it can be deviated!
what is the roof of the nasal cavity?
- nasal bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, sphenoid bone
what do each of these bones have in common?
Nasal bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, sphenoid bone
they all have a sinus that drains into the nasal cavity
what is the floor of the nasal cavity?
the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of the palatine bone
what conchae are parts of the ethmoid bone?
superior and middle conchae
what conchae is its own bone?
inferior conchae
how does the appearance of the conchae bones contribute to their function?
they cause the air we breathe in to spiral and warm up (turbinate)
what is a natural body passage or canal?
a meatus
what are the 3 meatuses of the nasal cavity?
- superior meatus
- middle meatus
- inferior meatus
each meatus receives secretions from where?
paranasal sinuses
what happens once fluid is drained to the nasal cavity?
it is swallowed and travels to the stomach
the majority of the nasal cavity is covered by what?
respiratory epithelium
the upper 1/3 of the nasal cavity is composed of what epithelium?
olfactory
explain the olfactory bulb orientation
so we have an olfactory bulb with an olfactory tract connected to it...
filia olfactoria is found coming out of the olfactory bulb that travels through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid
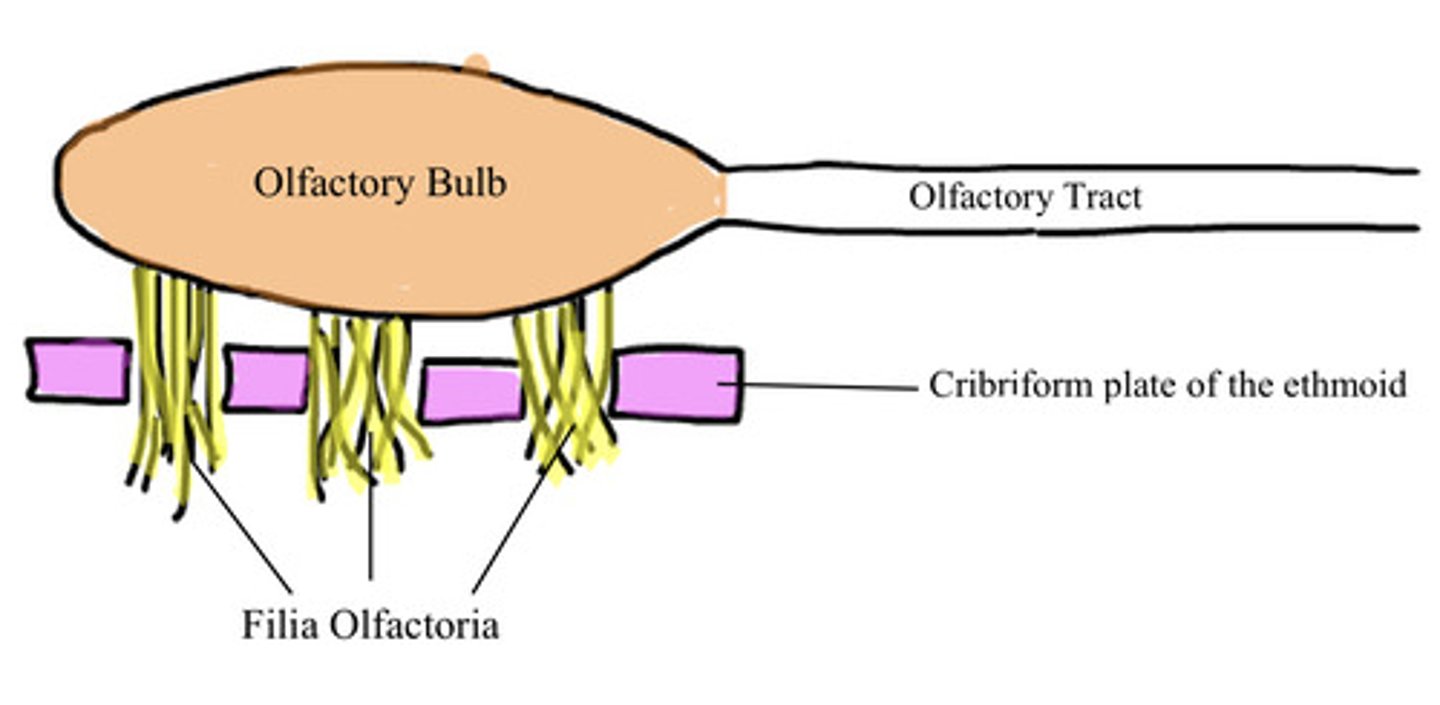
what is the clinical implication of the filia olfactoria coming off the olfactory bulb?
they can shear off easily like a cheese grater during trauma
they can become inflamed leading to a loss of sense of smell
what are our paranasal sinuses?
- frontal sinus
- ethmoid sinus
- sinus
- sphenoid sinus
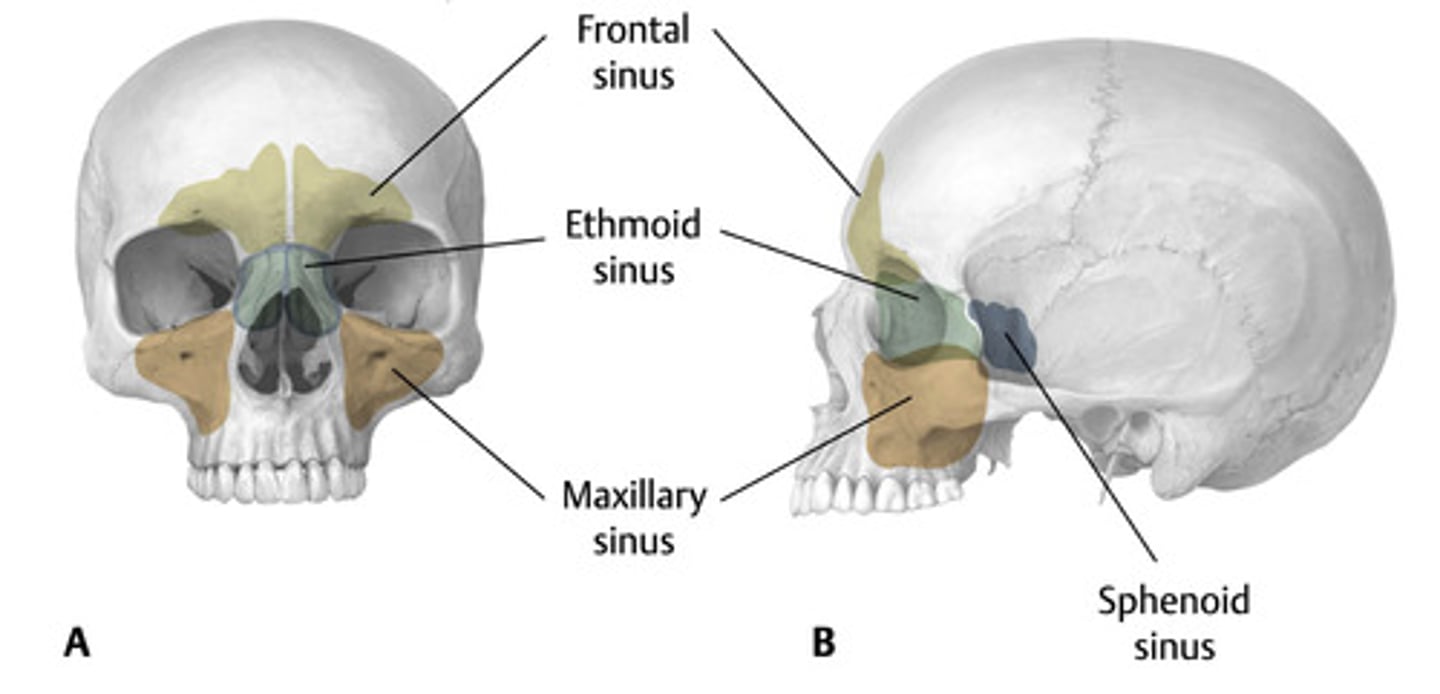
what is a function of the paranasal sinuses?
- lighten our skull
- resonate voices
where does the sphenoid sinus drain?
to the sphenoethmoid recess
where do the posterior ethmoid air cells drain?
the superior meatus
what drains into the middle meatus?
- anterior ethmoid air cells
- maxillary sinus
- frontal sinus
- middle ethmoid air cells
how do the anterior ethmoid air cells, maxillary sinus, and frontal sinus drain into the middle meatus?
via the hiatus semilunaris
how do the middle ethmoidal air cells drain into the middle meatus?
via bulla ethmoidials
where does the nasolacrimal duct drain?
inferior meatus
T/F: the nasolacrimal duct is a sinus
FALSE its just a duct
what is the nasolacrimal duct?
the tear duct!
what is a clinical correlate of the nasolacrimal duct?
puncta occlusion
what innervates the nasal cavity?
anterior: V1 via idk yet
posterior: V2 via nasopalatine
where do we have most of our blood supply in our noses? why does this matter?
anteriorly, it matters because it can cause nose bleeds with trauma