geometric reasoning
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Linear Equation: Slope-Intercept Form
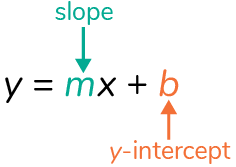
one way to write a linear equation (y = mx + b) where the product of the slope (m) and the variable (x) are added to the y-intercept (b)
Example.
y=2x+4y=2x+4
Perpendicular Lines
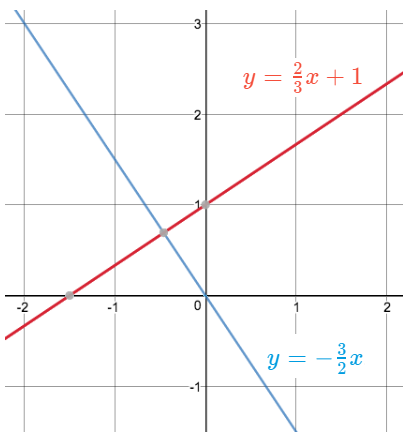
Lines that intersect at a right (90º) angle.
They have slopes that are opposite reciprocals, meaning their signs (positive or negative) are opposite and their fractions are flipped.
Example.
y=2/5x+3 and y= -5/x2 - 4 and y=−52x−4
Coplanar
lying on the same plane
Theorem
A statement that is accepted because it has been proven
Example.
if a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then alternate interior angles are congruent
Plane
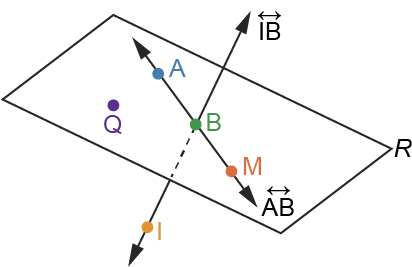
an infinite “surface” with no thickness that extends infinitely in all directions
Reflex angle
an angle measuring between 180° and 360°
Proof
A new true statement using multiple axioms and theorems.
Alternate exterior angles
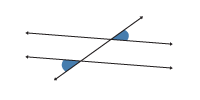
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate exterior angles are congruent.
Corresponding Angles
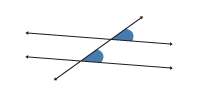
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, the pairs of corresponding angles are congruent.
Point

a location in space without any dimension
Parallel Lines
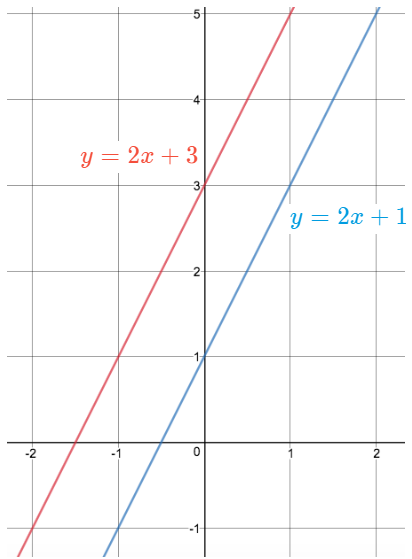
Lines that never intersect (coplanar).
They have slopes that are congruent.
Example.
y=2x+4 and y=2x−5
Acute Angle
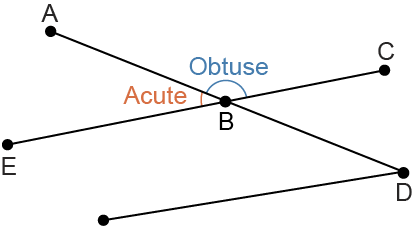
an angle measuring between 0° and 90°
Quadrant
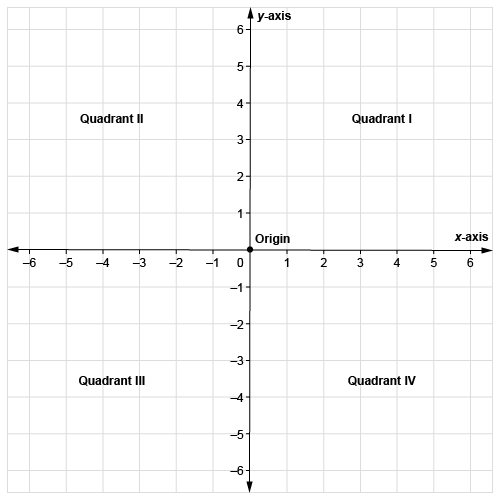
One of the 4 areas bounded by the x-axis and y-axis of a coordinate plane
Right Angle
Term definition.
An angle measuring exactly 90°, such as the corner of a piece of paper.
All right angles are congruent
Origin

The point of intersection of the x-axis and y-axis of a coordinate plane, often designated as (0,0)
Congruent Shapes
shapes in which corresponding angle measures and side lengths are congruent; denoted by ≅
Similar Shapes
shapes that have congruent angle measures and the same number of sides, but different overall size
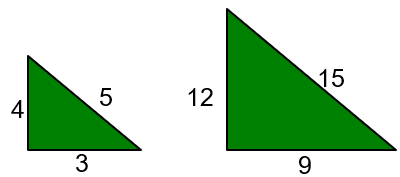
Vertex
a point where two rays, lines, or line segments meet, such as the point where two rays, lines, or line segments intersect to form an angle
Spatial Reasoning
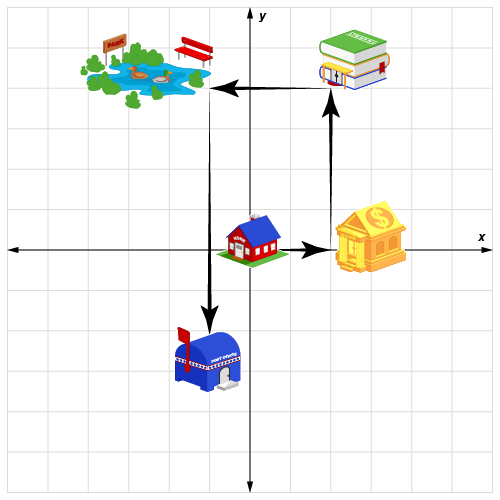
The ability to think about how things appear in real life, often by use of a drawing.
Example.
Vector Diagram
Straight angle
an angle measuring exactly 180°
Ordered Pairs
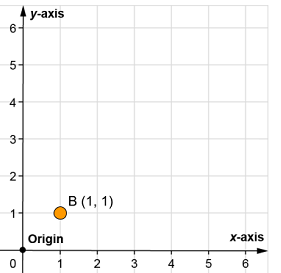
representations in the form (x, y) of points in the coordinate plane
Example.
A point of (4,3)(4,3) represents an x-value of 4 and a y-value of 3.
Axiom / Postulate
a truth that is accepted as being self-evident, without proof
Example.
Given any two distinct points, there is a line that contains them.
Complementary angles
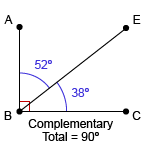
two angles that sum to 90°
Line

an infinite set of points arranged “straight” in opposing directions, with infinite length and no thickness
Supplementary Angles
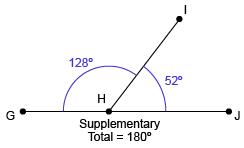
two angles that sum to 180°
Alternate interior angles
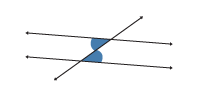
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate interior angles are congruent.
Obtuse Angle

an angle measuring between 90° and 180°
Collinear
lying on the same line
Coordinate Plane

A plane, often divided into a grid, with a horizontal x-axis and a vertical y-axis that intersect at the origin
Angle
the figure formed by the intersection of two rays, lines, or line segments, or else by two rays with a common endpoint
Vertical Angles
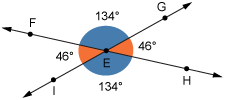
The pair of opposite angles created when two lines (or line segments) intersect.
The angles are congruent (equal).