Cybersecurity Incident Reponse ( Chapter 4)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
a plan for responding to a cybersecurity incident methodically. If an incident is “nefarious”, steps are taken to quickly contain, minimize, and learn from the damage (AT&T).
Incident response

a division under Cybersecurity Bureau of Department of Information and Communication Technology (DICT).
responsible in receiving, reviewing, and responding to computer incident reports and activities.
This division will ensure that a systematic information gathering/ dissemination, coordination and collaboration among stakeholders, especially computer emergency response teams.
National Computer Emergency Response Team (NCERT)
NIST Cyber Security Framework
Identify – focus on the identifying and knowing what should be protected.
Protect – implementation of necessary level of protection for the identified assets.
Detect – capability to recognize if there is any cyber security incident impacting the protected assets.
Respond – capability to handle the detected cyber security incidents.
Recover – restore business operation.

Incident Response Lifecycle
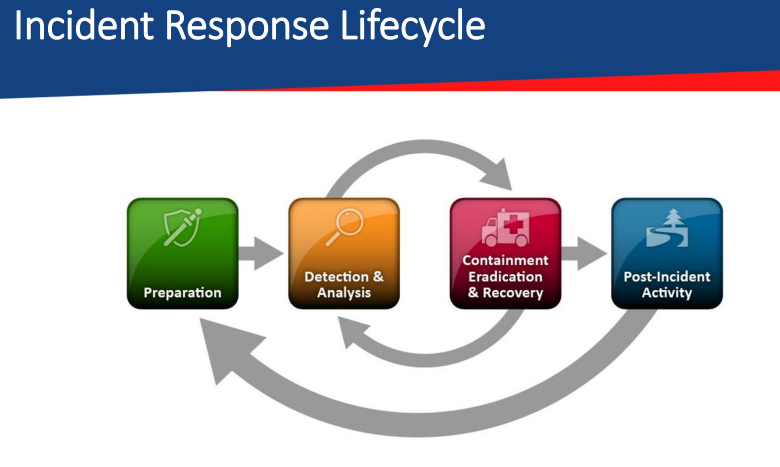
Preparation

Focus on: Unusual Activities and Events
• Alerts and reports about potential malicious activity or vulnerabilities. This can include alerts from your technology or network provider. • Loss or breach of a device, including personal mobiles that staff use to access work emails. • General day-to-day indicators, such as unusual email activity, incident reports, or being informed by staff or customers that breach has already occurred.
. Detection and Analysis
Focus on: Applying different strategies
Removing the system from the network by disconnecting it
Isolating the systems by way of network segmentation
Utilize virtual local area network (VLAN)
Utilize firewall sets
Careful gathering of information and evidence for legal proceedings
Redirecting traffic
Whitelisting of IP’s to boot out attackers
Containment
5 THINGS NOT TO DO DURING AN INCIDENT

4 THINGS TO DO DURING AN INCIDENT

Wipe out content and re-image of affected system hard drives to ensure any malicious content is removed
Preventing the root cause- understanding what caused the incident •
Preventing future compromise, for example by patching a vulnerability exploited by attacker
Applying basic security best practices- example upgrading old software versions and disabling unused services.
Scan for malware
Eradication
Involves cautiously bringing back all systems affected to full operation after verifying systems are clean, and the threats removed.
Recovery Phase
Lessons learned meeting
When was the problem first detected and by whom • The scope of the incident
How it was contained and eradicated
Worked performed during recovery
Areas where the CERT team were effective
Areas that need improvement
Post Incident Activity
It derived from military kill chain
Describe the structure of an attack
7 stages of targeted attack
Trademark of Lockheed Martin
What is the Cyber Kill Chain?
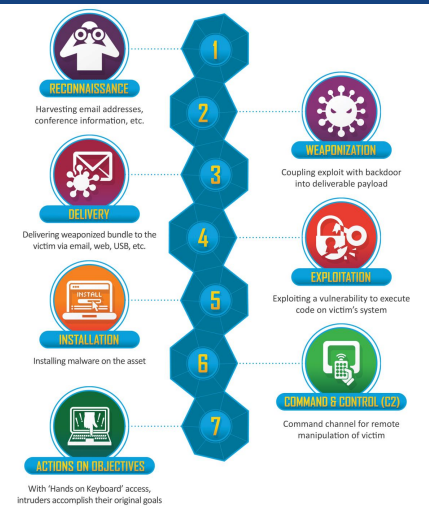

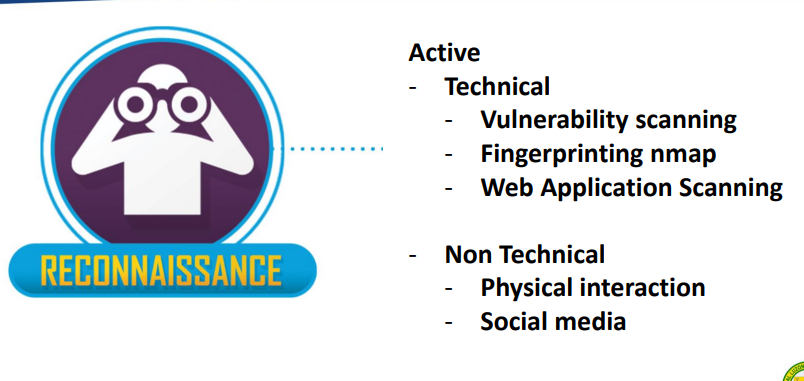
Preparing the malwares & hacking tools for the attack
Malicious payload is created
Example: Known malware, Customized Malware, 0 day, Metasploit
Weaponization
The attacker sends the malicious payload to the victim
Example:
File attachment on email
•External devices
Malicious Website
SET
Delivery
Exploiting a vulnerability to execute code on victim’s system
Example:
Exploiting Legacy system
Exploiting old versions of software
Exploitation
Installing malware on the asse
Installation
Command channel for remote manipulation
Command and Control (C2)
With ‘Hands on keyboard’ access, intruders accomplish their original goals
Actions On Objectives
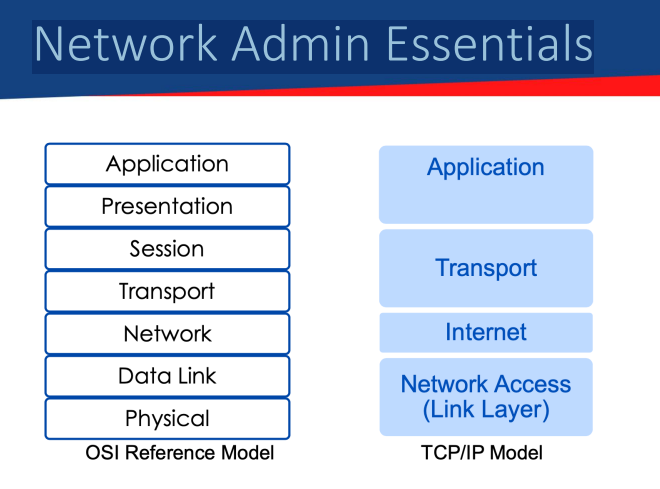
Network Admin Essentials
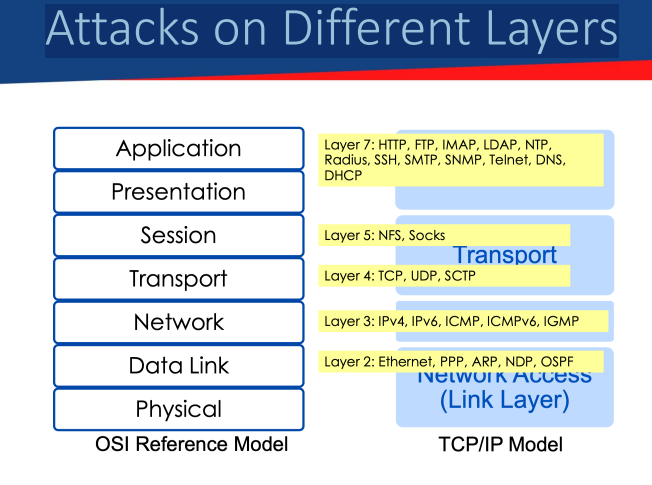
Attacks on Different LayersA
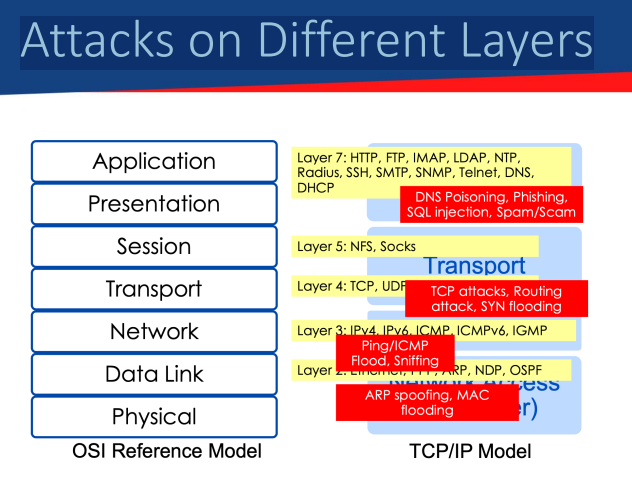
Attacks on Different LayersA
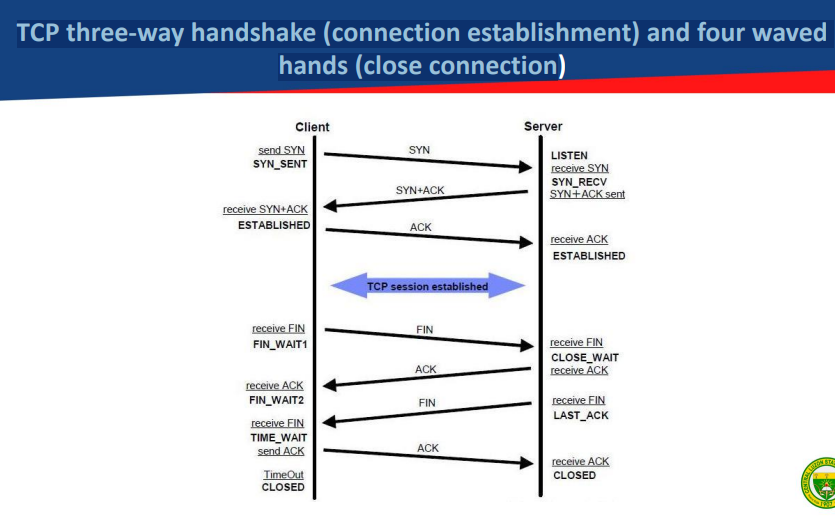
TCP three-way handshake (connection establishment) and four waved hands (close connection