COLOUR BY DESIGN
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
What is the MOLECULAR formula of benzene? :3
C6H6
What is the empirical formula of benzene?
CH
Why may the formulae of benzene ‘C6H6’ confused scientist who discovered it?
v.little H compared to C
If Kekule’s benzene structure was correct, what observation would happen when bromine water was added to a sample of benzene?
Turn orange to colourless
What actually happens when bromine water is added to benzene? (observation wise)
Remains orange
Why would kekule’s benzene structure be an irregular hexagon rather than a regular one?
Because double bonds are shorter than single bonds
If kekule’s benzene structure was correct, what would the shape be?
An irregular benzene
What is the shape of actual benzene?
A regular hexagon
What is the bond angle within benzene?
120
If kekule’s benzene structure were to go through electrophilic addition reaction with a halogen, how many isomers would there be?
2
What are pi bonds? (long ass answer)
Sideways overlap of 2 parallel p orbitals above and below the internuclear axis
Describe the formation of the ring within a benzene. (long ass answer/ exam answer)
There are 6 delocalised e-, one from each C, in an extended pi system above and below the ring of C’s
What is aromatic?
With benzene ring
What is aliphatic?
Without benzene ring
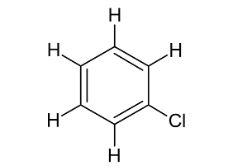
Name this compound.
Chlorobenzene
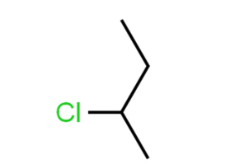
Name this compound.
2-chlorobutane
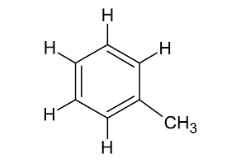
Name this compound.
Methylbenzene
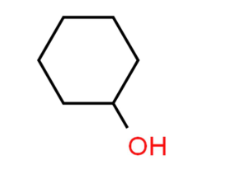
Name this compound.
Cyclohexanol
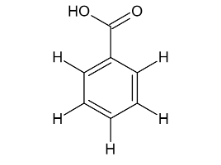
Name this compound.
Benzoic acid
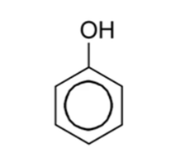
Name this compound
Phenol
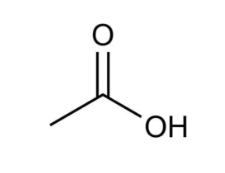
Name this compound.
Ethanoic acid
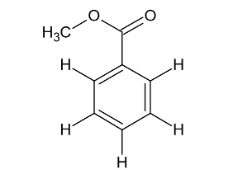
Name this compound.
Methylbenzoate
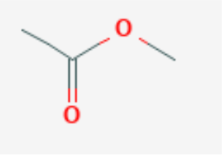
Name this compound.
Methylethanoate
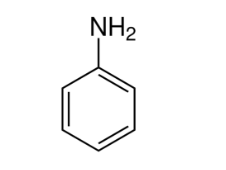
Name this compound.
Phenylamine
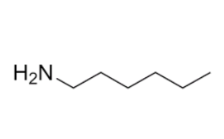
Name ts compound
1-aminohexane
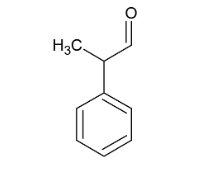
Name ts compound.
2-phenylpropanal
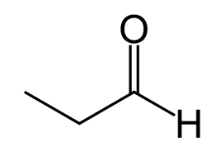
Name ts compound.
Propanal
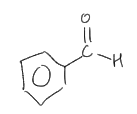
Name ts compound.
Benzaldehyde
When drawing fused benzene rings, do you draw with rings or c=c?
c=c
What reaction can benzene do?
Electrophilic substitution
What would happen if benzene ‘theoretically’ went though an addition reaction?
Delocalised pi system is lost, stability decreases
Why do benzene not go do addition reactions? (as in what would happen if benzene were to go through an addition reaction)
Delocalised pi system is lost, stability decreases
Why are substitution reactions good for benzene?
Delocalised pi system is retained, maintaining its stability
What are the reagents / catalysts / conditions in bromination?
Br2 / FeBr3
What are the reagents / catalysts / conditions in chlorination?
Cl2 / AlCl3 / anhydrous
What are the reagents / catalysts / conditions in sulphonation?
c.H2SO4 / reflux
What are the reagents / catalysts / conditions in nitration?
c.HNO3 / c.H2SO4 / <55 degrees
What are the reagents / catalysts / conditions in Friedel Crafts reactions?
R+ / AlCl3 / anhydrous / reflux
What are the products in bromination?
Bromobenzene AND hydrogen bromide (HBr)
What are the products in chlorination?
Chlorobenzene AND hydrogen chloride (HCl)
What are the products in sulphonation?
Benzene sulphonic acid / H2O
What are the products in nitration?
Nitrobenzene / H2O
What would happen if temperature exceeds 55 degrees in nitration?
If the reaction gets above 55, di or tri substitution can occur, which makes v.reactive / explosive products
What is the electrophile in bromination?
Br +
What is the electrophile in chlorination?
Cl +
What is the electrophile in sulphonation?
SO3
What is benzene sulphonic acid often reacted with? and why?
NaOH, to make a salt and can form ion-dipole forces with H2O / now soluble
What is the name of the salt produced by benzene sulphonic acid + NaOH?
Sodium benzene sulphonate
Where does the electrophile: SO3 come from in sulphonation?
H2SO4
What is the electrophile in nitration?
NO2+
What is the balanced equation that makes the electrophile in nitration?
HNO3 + 2H2SO4 → NO2+ + 2HSO4- + H3O+
What is the balanced equation that makes NO2+ in nitration?
HNO3 + 2H2SO4 → NO2+ + 2HSO4- + H3O+
What is the balanced equation that makes NO2+?
HNO3 + 2H2SO4 → NO2+ + 2HSO4- + H3O+
What does the R+ mean in Friedel Crafts reaction?
A Carbon / carbon compound
What are the 2 variations of Friedel Crafts reactions?
Alkylation / Acylation
What is Friedel Crafts alkylation?
Adding an alkyl group
What is Friedel Crafts acylation?
Adding an acyl group
What compound do you use to make the electrophile (R+) for Friedel Crafts alkylation?
A haloalkane
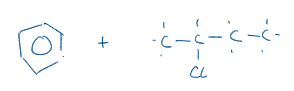
What are the reagents / catalysis / conditions for this reaction?
AlCl3 / anhydrous / reflux
What compound do you use to make the electrophile (R+) for Friedel Crafts acylation?
Acyl chloride OR acid anhydride
What is the NAME of an acyl chloride with 4 carbons?
Butanoyl chloride
What is the written structure of butanoyl chloride?
CH3CH2CH2COCl
What is the written structure of propanoic anhydride??
(CH3CH2CO)2O
What are all (4.5) reactions of alcohol (as a side chain of benzene but dont worry about this detail 🙂)?
Oxidation / esterification / dehydration & elimination / nucleophilic substitution
(QQS) What is a diazonium ion? (long ass answer ._.)
An aromatic compound with a N(triple bond)N attached where the N with 4 bonds is positive
(QQS) What is the first stage of forming azo compounds?
Diazotisation
(QQS) What is the mechanism of the coupling reaction?
Electrophilic substitution
(QQS) How do u find what reactants were used to make an azo dye?
Split up the azo dye on one side of the N=N
(QQS) What are the conditions for diazotisation? and why?
<5C, to prevent decomposition as N+(triple bond)N is very unstable
What are the conditions for diazotisation?
<5C
Why does the conditions for diazotisation need to be <5C?
Prevent decomposition as N+(triple bond)N is very unstable
What is the reaction that needs to be under 5C?
Diazotisation
What is the reaction that needs to be <5C
Diazotisation
(QQS) What is a typical coupling reagent?
An aromatic compound with a phenol or an amine group
(QQS) What are the 2 reactants required to form nitrous acid?
Sodium nitrite and an acid (HCl)
(QQS) What 3 reactants are needed to form a diazonium ion?
Phenylamine / nitrous acid / an acid (HCl)
(QQS) What conditions are needed for the coupling reaction?
Alkaline
(QQS) What is the chromophore?
The part of the molecule which gives it its colour
(QQS) What is an azo group?
N=N
(QQS) What is the second stage of making an azo dye?
The coupling reaction
Where would as azo group need to be, in order to be stable?
In between 2 benzene rings
In terms of pi bonds, what happens to the azo group when it is in between benzene rings?
The azo group becomes part of the delocalised pi system which increases stability
Why are azo groups (N=N) between 2 benzene rings?
To be stable
Each dye is made from a ____________ and a _____________. (fill in blanks)
Diazonium ion / coupling reagent
WHEN must the diazotisation reaction need to take place?
Just before the coupling reaction
What is the name of NaNO2?
Sodium nitrite
What is the systematic name of NaNO2?
Sodium nitrate (III)
Write the balanced equation to make HNO2
NaNO2 + HCl → HNO2 + NaCl
Write the balanced equation to make nitrous acid
NaNO2 + HCl → HNO2 + NaCl
What is the name of HNO2?
Nitrous acid
What does the diazonium ion act as in an electrophilic substitution reaction with a coupling reagent?
An electrophile
What is the name of the TYPE of reaction that occurs between a diazonium ion and a coupling reagent?
Electrophilic substitution
During an electrophilic substitution reaction between a diazonium ion and a coupling reagent, which atom/molecule is replaced? and from which reactant?
H on coupling reagent is replaced by the diazonium ion
If phenol or phenylamine is the coupling reagent, at what (carbon) position does the substitution take place at?
4th carbon
What is the electrophile in a coupling reaction?
The diazonium ion
What are the conditions for the coupling reaction?
Alkaline
WHAT IS THE EQUATION TO CALCULATE FREQUENCY? ∆
∆E=hv