knowledge test
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Kinetic energy
the energy stored by particles or objects which are moving
Potential energy
the energy stored when particles or objects are interacting
Internal energy
the total amount of energy stored inside a system by the particles (kinetic energy + potential energy)
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles
Specific heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C
Specific latent heat
the amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance with no change in temperature
where does kinetic energy occur in the substance
in the atoms
where does potential difference occur in the substance
in the bonds
potential difference
how much energy is transferred to or from the charges as they pass through a component
SHC unit
J/kgK
SLH unit
J/kg
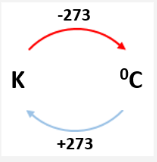
what is Kelvin
a temperature scale where zero reflects the complete absence of thermal energy
Determining the s.l.h of fusion
Place 2 beaker on separate balances then zero the scale.
Clamp a funnel above each beaker.
Connect immersion heater to power source.
Add ammeter in series and voltmeter in parallel.
Place immersion heater in one of the funnels.
Add 70g of ice to each funnel.
Turn on immersion heater and start stopwatch.
Record the potential difference and current.
After suitable period of time remove funnels, stop the stop watch and turn off heater.
Record the mass of water in the beaker.
Determining the s.l.h of vapourisation
Place the immersion heater into the fluid contained in the conical flask
Connect the immersion heater to the power supply.
Add an ammeter in series and a voltmeter in parallel with the heater
Turn on the immersion heater and start the stopwatch
Record the potential difference and current at regular time intervals.
After a suitable period of time, turn off the immersion heater and stop the stopwatch
Record the mass of the fluid remaining in the conical flask.
Current
how much charge (electrons) flows each second
Energy
the ability to do work (transfer from one store to another)
Power
how much energy is transferred per second
Charge unit
Coulombs, C
Power unit
Watts, W
Energy transferred unit
Joules, J
Potential difference unit
Volts, V
Current unit
Amps, A
Resistance unit
Ohms, Ω
How do you calibrate a voltmeter?
Connect power pack to the mains.
Connect power pack to the voltmeter.
Connect voltmeter to the top of resistor.
Connect the bottoms of the resistor to the power pack.
Set up the multimeter with the cables in correct ports.
Connect the multimeter from the power pack to the top of the resistor.
Take note of the readings.
ohms law
Potential difference is directly proportional to current and resistance
Resistivity
A measure of how strongly a material resists electrical current
Random error
occur in every measurement and cant be removed
only way to deal with them is to take repeat measurements and calculate average.
Systematic error
occur because there is a problem with the equipment or method
Accuracy
how close the measured value is the true value
Precision
how reproducible the results are
what if the readings are not the same (calib)
note down the difference between the reading on the collaborated device and component. add or minus this value from any readings you make on ammeter or voltmeter
Thermistor function
changes resistance dependent on the temperature of its surroundings
LDR function
changes resistance dependent on the brightness of its surroundings.
Diode function
only allows current to flow in one direction
Photodiode
converts light to electrical current
If i place a diode in forward bias what happens
Low Resistance - High Current (steep gradient)
if i place a diode in reverse bias what happens
High Resistance - Almost no current (almost flat gradient)
what happens to resistance when there’s a present thermistor
Resistance decreases if the temperature increases.
what happens to resistance when there’s a present LDR
Resistance decreases if the light intensity increases.
Example of thermistor
fire alarm
Example of LDR
street lights
filament lamp example
vintage lighting
led example
traffic lights, screens
diode example
Converting AC to DC
photodiode example
remote controls, solar panels