10. Aqueous Humor
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
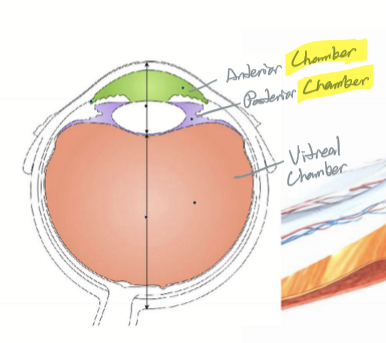
What delineates the anterior chamber?
Cornea to iris
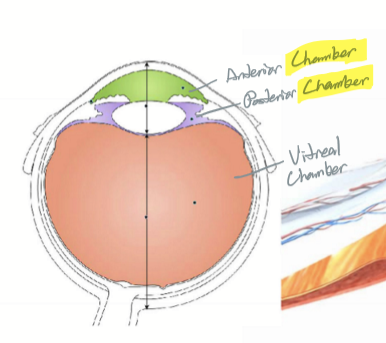
What delineates the posterior chamber?
Back of iris to vitreal surface
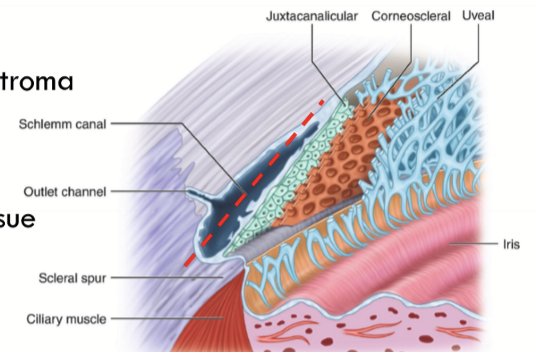
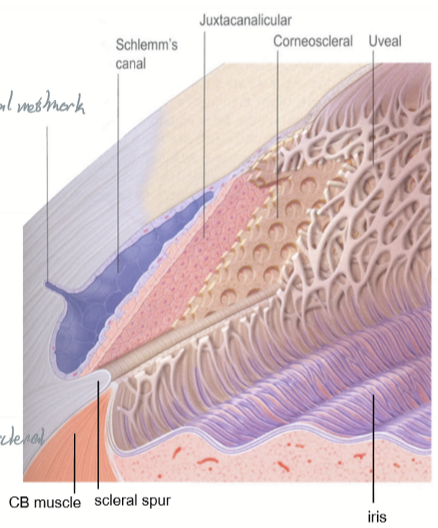
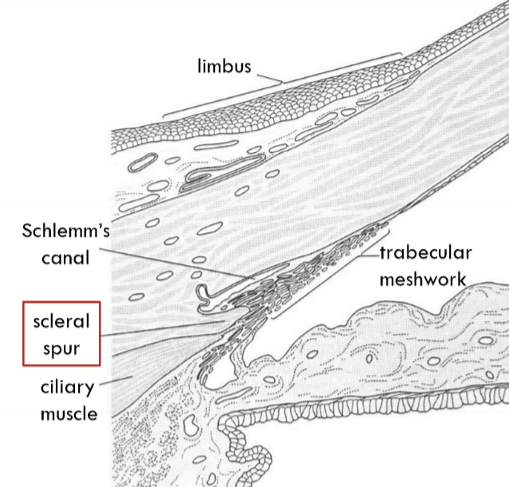
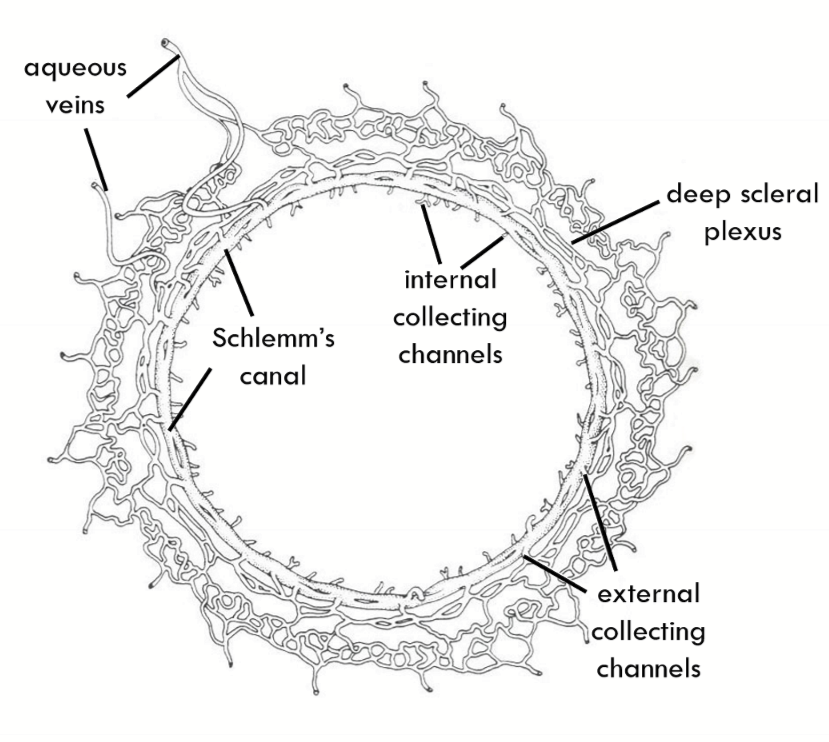
Schlemm’s Canal
Also called sinus venosus sclerae
Located anterior to scleral spur
Provides an exit for AH and nourishment for adjacent tissues
Lined by endothelial cells with incomplete basement membrane
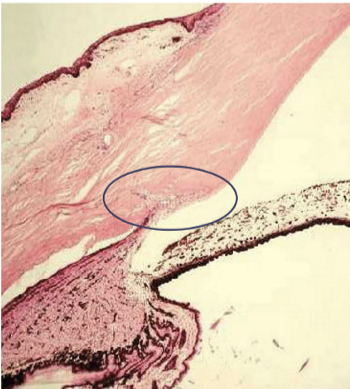
Schlemm’s canal external wall
Next to limbal stroma
Schlemm’s canal internal wall
Adjacent to the juxtacanalicular tissue (JCT)
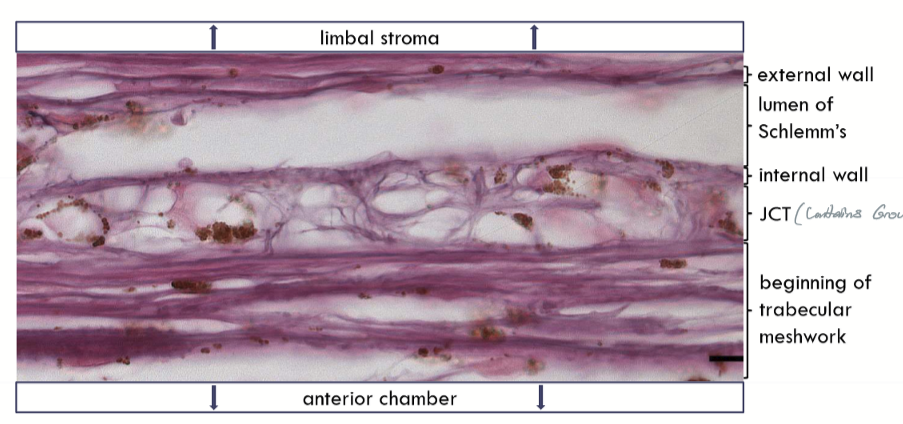
Juxtacanalicular Tissue (JCT)
region between Schlemm’s canal and the trabecular meshwork
Composed of loose connective tissue matrix; Collagen types I, IV, V, and VI; elastin, laminin, fibronectin, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid …
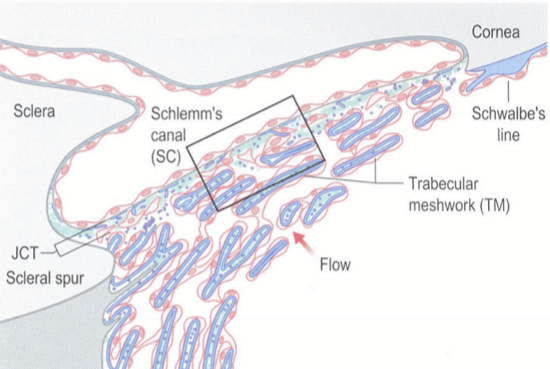
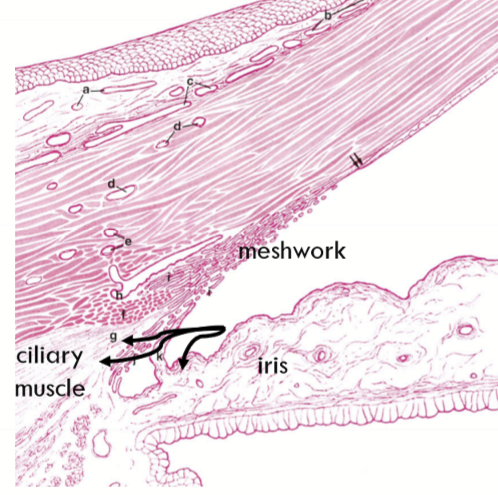
Trabecular Meshwork Location
Apex lies at Schwalbe’s line, base lies at scleral spur.
Inner side lines the anterior chamber
Outer side lies against the JCT and close to Schlemm’s canal
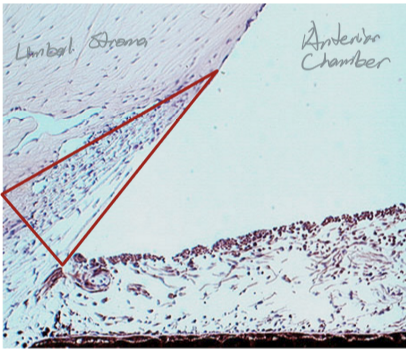
Trabecular Meshwork appearance
Has a triangular shape
Has flattened perforated sheets that branch
Lattice work of branching and interconnected meshwork
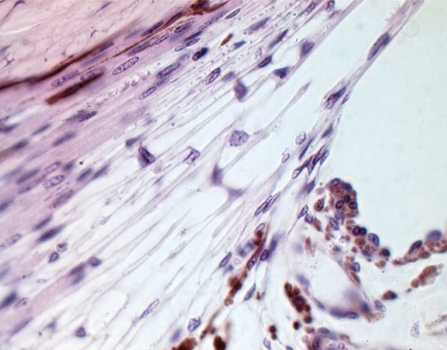
Anatomical Divisions of the trabecular meshwork
Corneoscleral meshwork
external
attaches to scleral spur
starts at Schwallbe’s Line at edge of cornea
spaces are smaller compared to uveal meshwork
Uveal meshwork
internal (closer to anterior chamber)
attaches to the ciliary stroma and muscle
Holes are 2x larger than corneoscleral meshwork
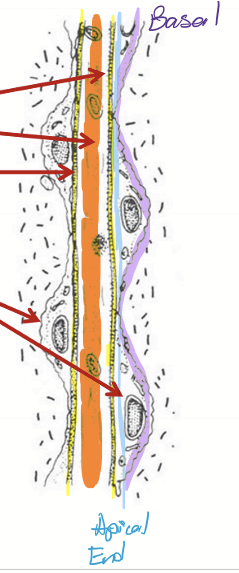
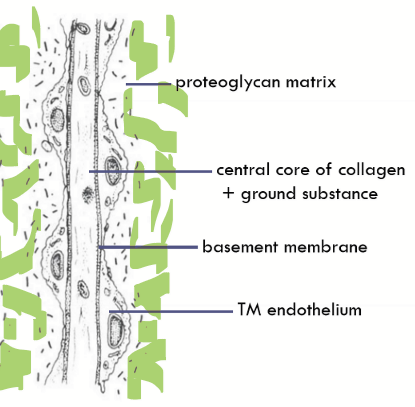
Composition of trabecular meshwork
Inner cores of extracellular matrix (collagen, aggregates of elastic tissue, ground substance)
Thin basement membrane
Covered by TM endotheilum (continuous with corena endothelium)
gap junctions and some tight junctions
What occupies the spaces in the meshwork?
Proteoglycans
Scleral Spur
Made of dense collagen fibers
an annular ridge
an attachment site
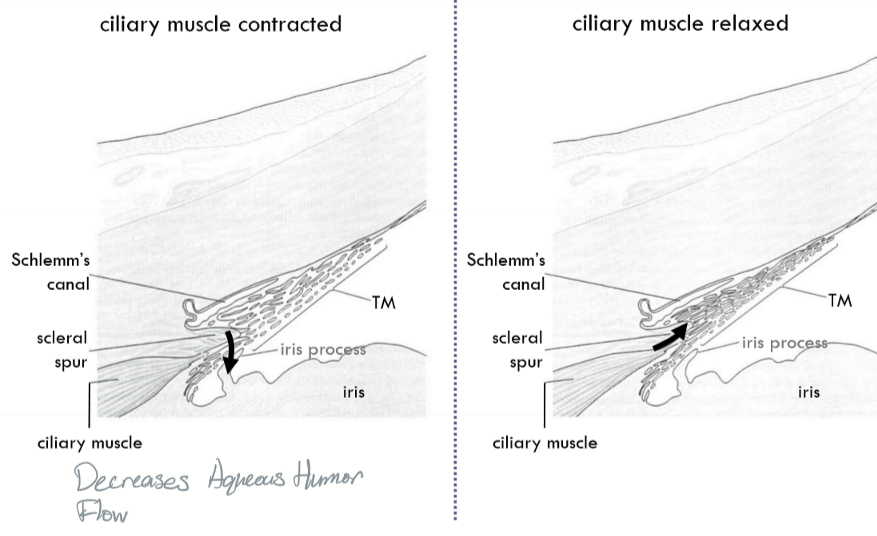
What happens to AH flow when the ciliary muscle contracts?
Decrease in AH flow
Pathways for AH production:
One delivers plasma-derived proteins directly to the posterior chamber
One delivers plasma-derived proteins directly to the anterior chamber
Aqueous production occurs via:
Diffusion = movement of molecules along a gradient from higher to lower concentration
Facilitates movement of small, uncharged moleculesUltrafiltration = movement of fluid along a hydrostatic pressure gradient from higher to lower pressure
Active transport = movement of ions and molecules across cell membranes against opposing concentration or electrical gradients. Water moves via osmosis.
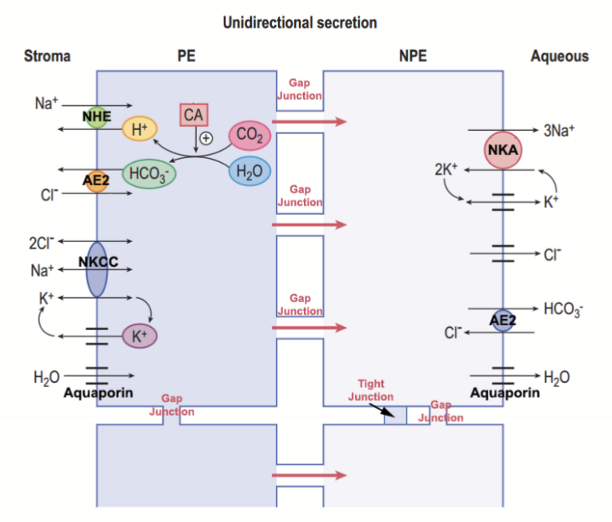
What is AH secreted by?
The epithelium of the ciliary process. The molecules pass from the vasculature through the pigmented and nonpigmented epithelium
Role of Iris epithelium in AH flow
Forces the AH to go around the lens and exit through the pupil
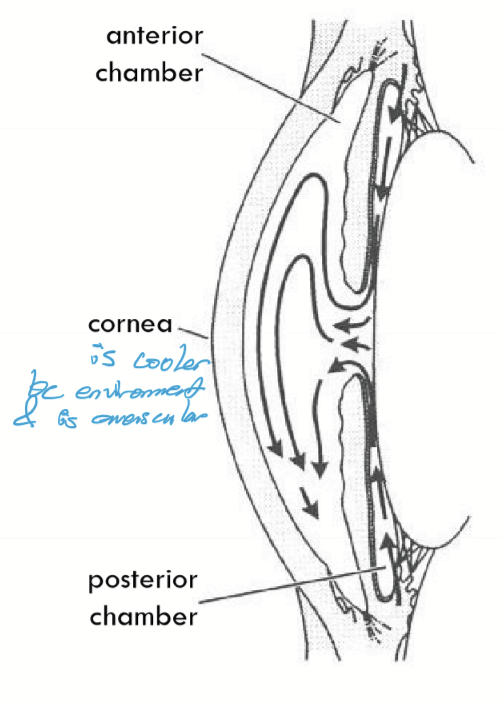
Classic Theory Aqueous flow
Secreted into the posterior chamber and goes through the pupil into the anterior chamber. Convention currents moves ``AH to exit via aqueous outflow structures.
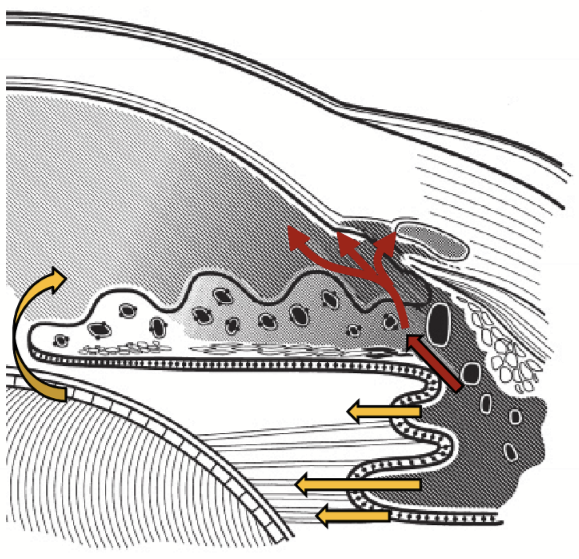
Secondary Path Aqueous Flow
Nutrients enter the AH by secretion from the ciliary body stroma vasculature → iris stroma → anterior chamber
(red arrows)
AH exit from anterior chamber
Uveoscleral Outflow- unconventional outflow (20%)
Trabecular Outflow - conventional outflow (80%); “passive” passage through the meshwork
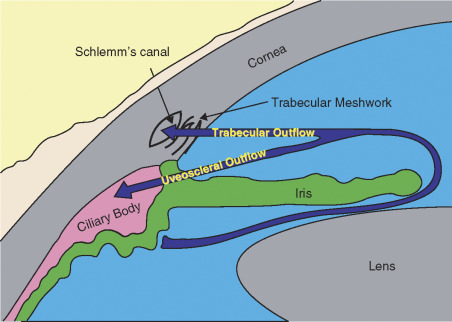
Uveoscleral Outflow Pathway
Absorbed across the uveal meshwork → absorbed into the face of the ciliary body and iris root → absorbed into the ciliary muscle veins
Trabecular Outflow Pathway
Uveal meshwork → corneoscleral meshwork → JCT → Giant Vacuole → Schlemm’s canal
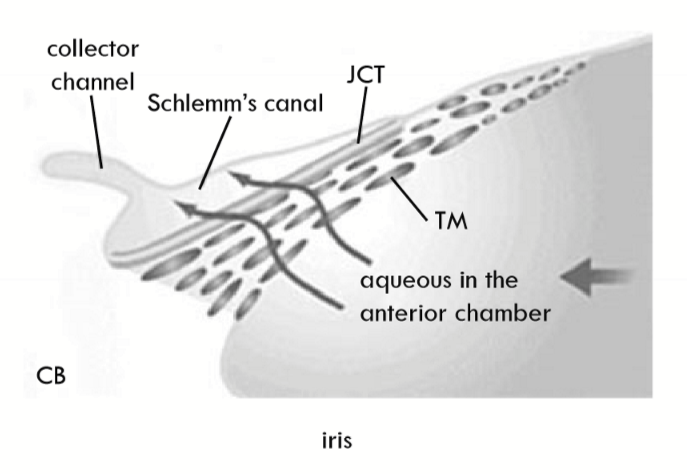
What forms in Schlemm’s canal to move AH across the inner wall?
Giant vacuoles
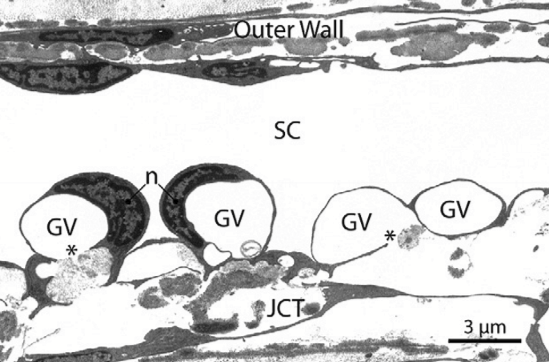
External collector channels move AH from __1.__ to __2.__
Schlemm’s canal
Deep Scleral plexus
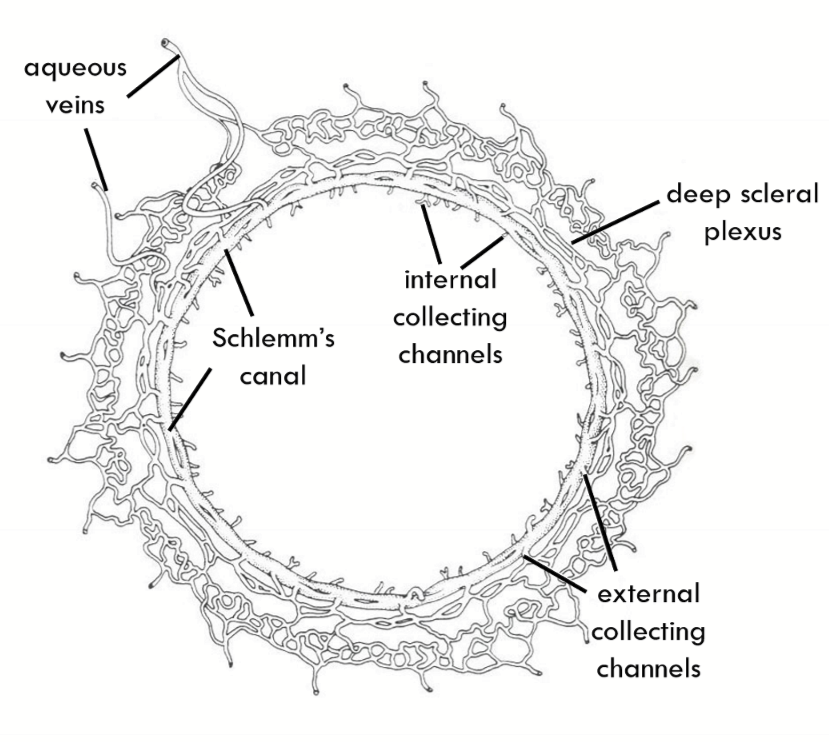
Internal collector channels are:
evaginations of Schlemm’s canal and are long and branching
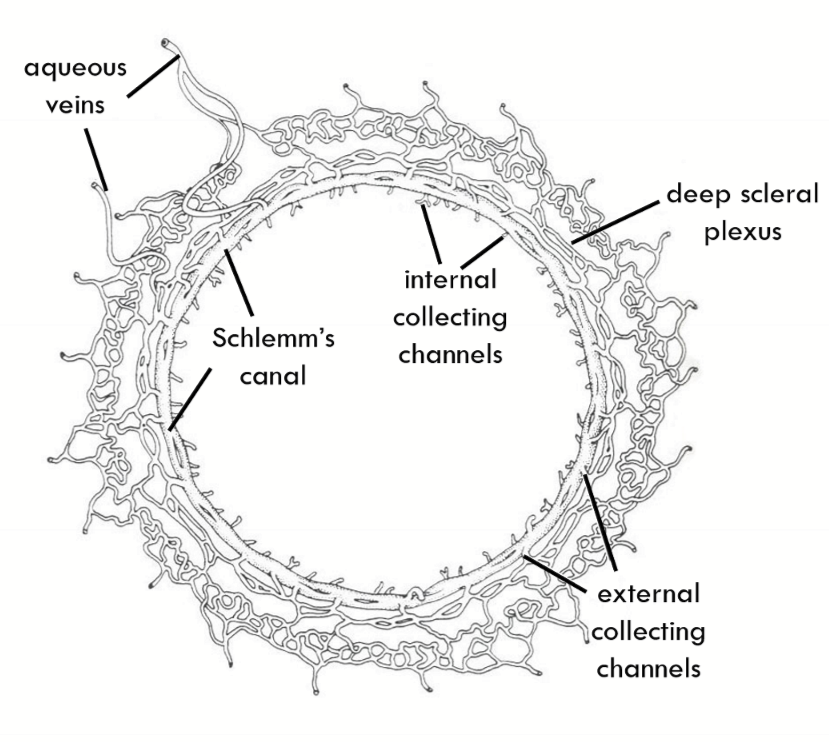
Deep Scleral plexus
Encircles the limbus
Fed into by External collector channels and empties into interascleral plexus
Intrascleral plexus move AH from __1.__ to __2.__
deep scleral plexus
episcleral plexus
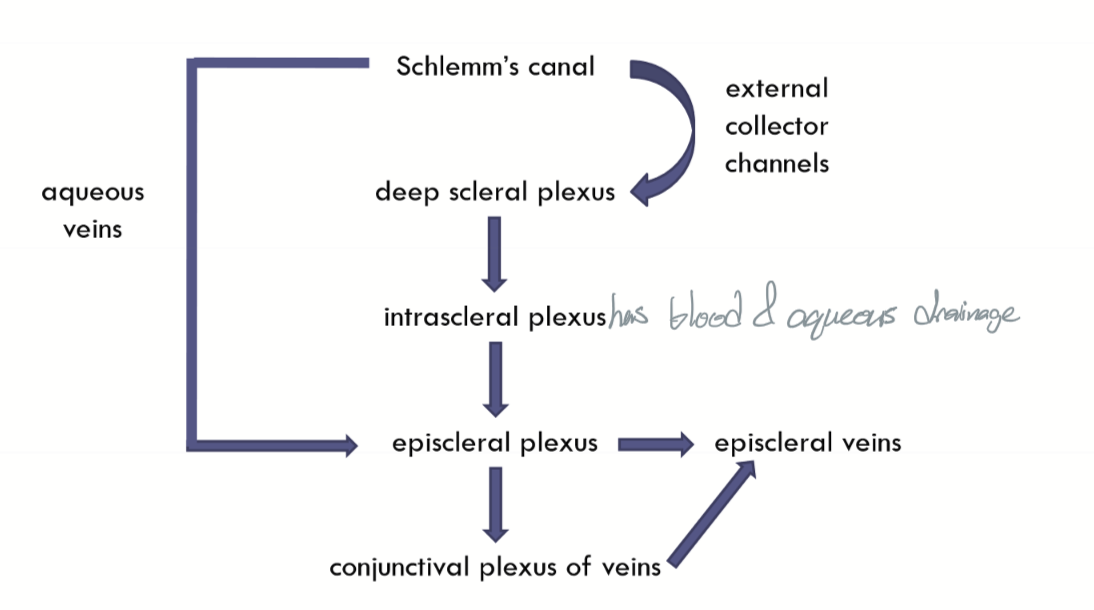
Episcleral plexus move AH from __1.__ to __2.__
intrascleral plexus
episcleral veins AND conjunctival plexus of veins
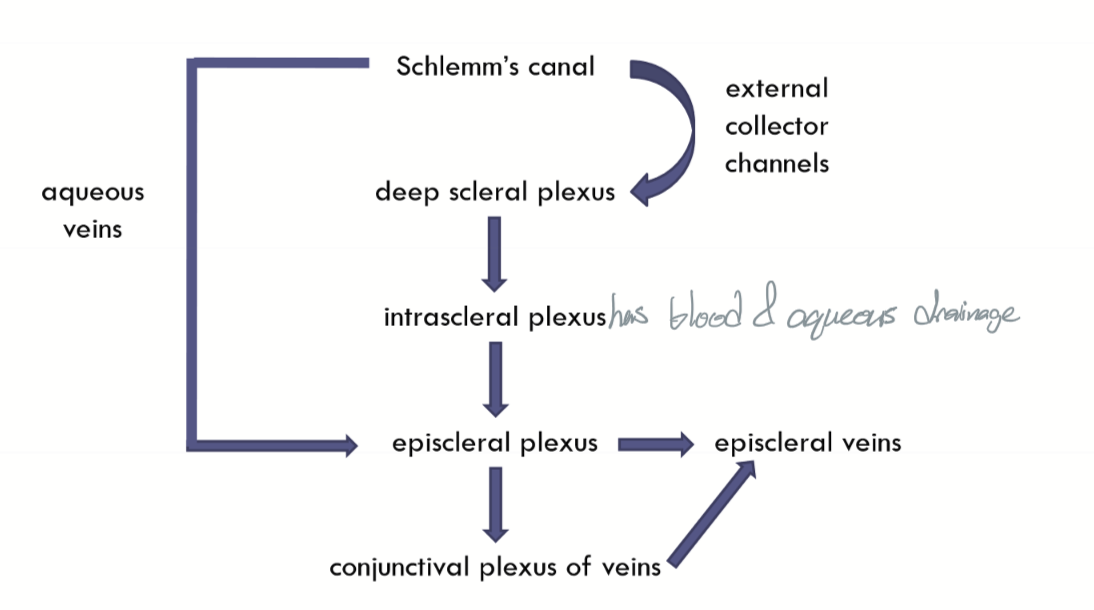
What parts of the Aqueous outflow carries blood?
intrascleral plexus
episcleral plexus
episcleral veins
Aqueous veins (of Ascher) move AH from __1.__ to __2.__
Schlemm’scanal
Episcleral plexus
Functions of AH
Nutrition
waste removal
maintenance of IOP
optical
protection
Blood:aqueous barrier
enables the AH to have a lower protein concentration relative to the blood
exists mainly because of the cellular junctions between the ciliary epithelial cells and the non-fenestrated blood vessels in of the iris
Glaucoma
Optic neuropathy that is typically characterized by optic nerve damage
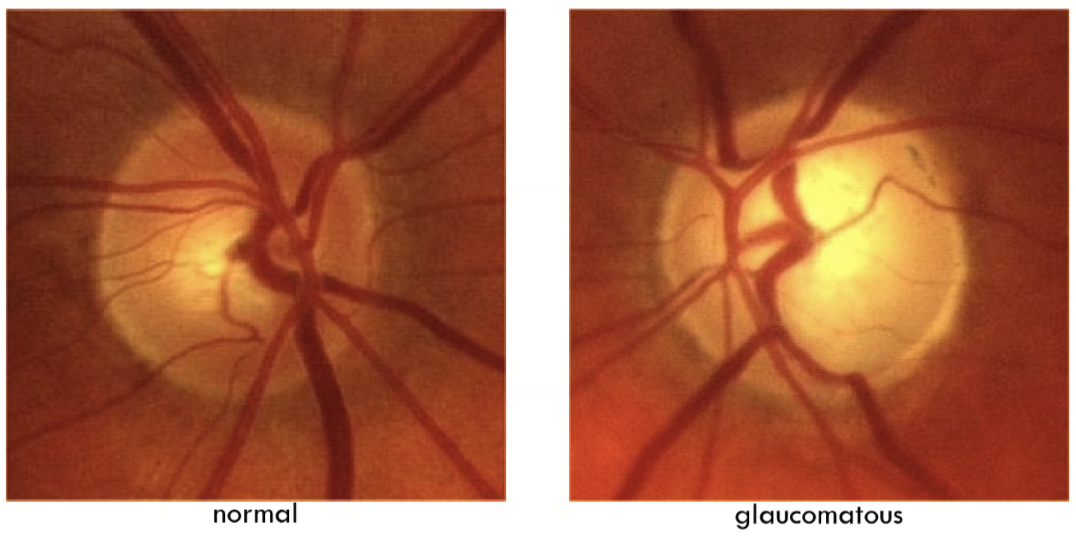
Classifications of glaucoma
open vs closed angle glaucoma
normotensive glaucoma
primary vs secondary glaucoma