Chemical/functional groups & isomers
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
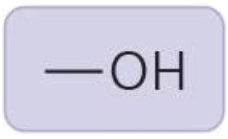
Hydroxyl group
polar, forms hydrogen bonds; "alcohol"
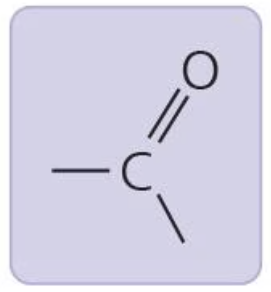
Carbonyl group
w/ ketone = ketoses
w/o ketone = aldoses
when within carbon skeleton, ketone
when at end of carbon skeleton, aldehyde
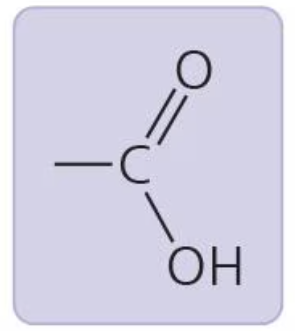
Carboxyl group
acts as acid, can donate H+; carboxylic acid or organic acid
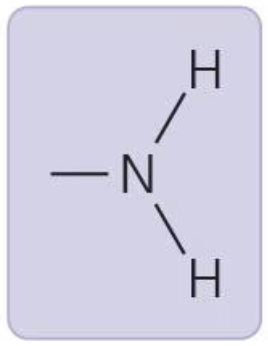
Amino group
acts as base, can accept H+; amine
Sulfhydryl group
2 of them can react forming a stabilizing structure

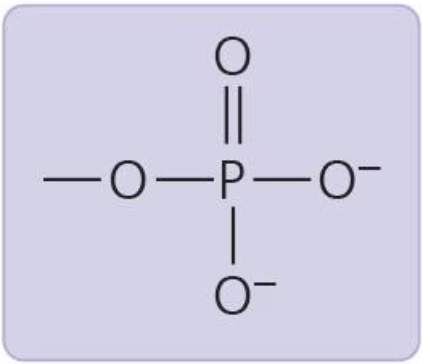
Phosphate group
contributes negative charge (1- when inside chain, 2- when on end); organic phosphate
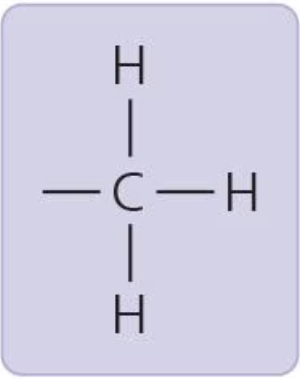
Methyl group
affects the expression of genes when bonded to DNA or proteins that bind to DNA; affects the shape and function of sex hormones
structural isomers
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
cis-trans isomers or geometric isomers
carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but differ in their spatial arrangement due to the inflexibility of double bonds
enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other and that differ in shape due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon, one that is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms (left-handed vs right-handed isomers)