Module 2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Financial accounting
Managerial accounting
is concerned with reporting financial information to external parties, such as stockholders, creditors, and regulators.
is concerned with providing information to employees within an organization so that they can formulate plans, control operations, and make decisions.
direct costs and indirect costs
2 types of cost objects
1.Assigning costs to cost objects
2.Accounting for costs in manufacturing companies
3.Preparing financial statements
4.Predicting cost behavior in response to changes in activity
5.Making decisions
Purposes of Cost Classification
Direct
Indirect
_ costs
•Costs that can be
easily and conveniently traced to a unit of product or other cost object.
•Examples: direct material and direct labor
_ costs
•Costs that cannot be easily and conveniently traced to a unit of product or other cost object.
•Example: manufacturing overhead
direct materials
direct labor
manufacturing overhead
classifications of manufacturing costs
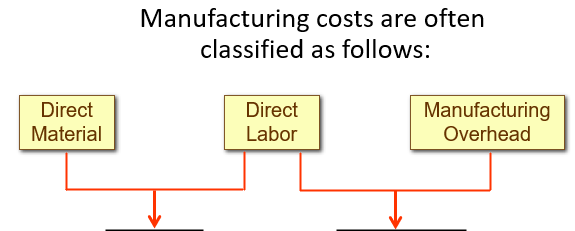
Direct materials
Direct labor costs
Manufacturing overhead
are raw materials that become an integral part of the product and that can be conveniently traced directly to it.
ex. the car seat of an aircraft
are those labor costs that can be easily traced to individual units of product.
ex. wages paid to automobile assembly workers
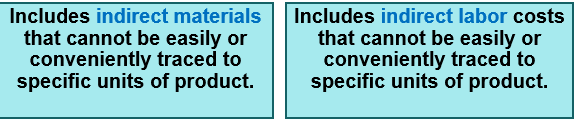
includes all manufacturing costs except direct material and direct labor. These costs cannot be readily traced to finished products.
yes
does the manufacturing overhead include indirect materials and indirect labor costs?
•Depreciation of manufacturing equipment
•Utility costs
•Property taxes
•Insurance premiums incurred to operate a manufacturing facility
operating the factory
give examples of manufacturing overhead
Only those indirect costs associated with _ are included in manufacturing overhead.
prime cost
conversion cost
where do they point to
selling costs
administrative costs
Costs necessary to secure the order and deliver the product. can be either direct or indirect costs
All executive, organizational, and clerical costs. can be either direct or indirect costs.
Product
_ costs “attach” to a unit of product as it is purchased or manufactured and they remain attached to each unit of product as long as it remains in inventory awaiting sale.
raw materials
work in process
finished goods
for manufacturing companies, product costs include
Raw materials
Work in process
Finished goods
: include any materials that go into the final product.
: consists of units of product that are only partially complete and will require further work before they are ready for sale to the customer.
: consist of completed units of product that have not yet been sold to customers.
Raw Materials
Work in Process
Finished Goods
Cost of Goods Sold
TRANSFER OF PRODUCT COSTS
•When direct materials are used in production, their costs are transferred from _ to Work in Process.
•Direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs are added to _ to convert direct materials into finished goods.
•Once units of product are completed, their costs are transferred from Work in Process to _.
•When a manufacturer sells its finished goods to customers, the costs are transferred from Finished Goods to _.
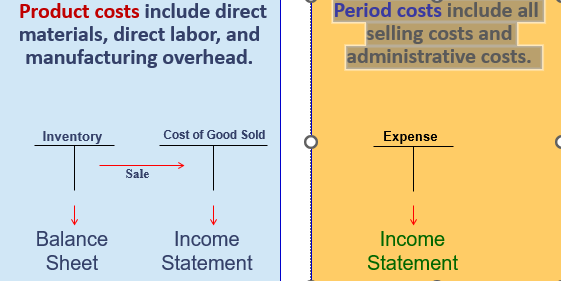
Product costs
Period costs
_ include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
_ include all selling costs and administrative costs.
Cost behavior
variable, fixed, and mixed costs
_ refers to how a cost will react to changes in the level of activity.
The most common classifications are:
variable
constant
A cost that varies, in total, in direct proportion to changes in the level of activity.
A variable cost per unit is _.
units produced, units sold, machine hours, labor hours
a measure of what causes the incurrence of a variable cost
fixed cost
inversely
a cost that remains constant, in total, regardless of changes in the level of activity
if expressed on a per unit basis, the average fixed cost per unit varies _ with changes in activity
committed
discretionary
types of fixed cost
Long-term, cannot be significantly reduced in the short term
May be altered in the short term by current managerial decisions
The Linearity Assumption and the Relevant Range
A straight line closely approximates a curvilinear variable cost line within the relevant range.
(read more of this in book)
$30,000
1,000 square feet
The relevant range of activity pertains to fixed cost as well as variable costs. For example, assume office space is available at a rental rate of $30,000 per year in increments of 1,000 square feet. This means that fixed costs would increase in a step fashion at a rate of $________ for each additional _____________
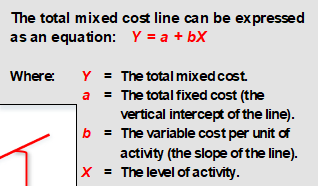
Y = a + bX
express the total mixed cost line as an equation
Differential costs (or incremental costs)
differential revenue.
Differential costs
_ are the difference in cost between any two alternatives.
A difference in revenue between two alternatives is called _
Both are always relevant to decisions.
_ can be either fixed or variable.
opportunity cost
The potential benefit that is given up when one alternative is selected over another.
sunk costs
have already been incurred and cannot be changed now or in the future
contribution income statement
The _ format is used as an internal planning and decision-making tool.
traditional format
contribution format
used primarily for external reporting
used primarily by management