Acid base balance (incomplete)
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
H+
vital to life
expressed as pH
circulate in 2 forms
volatile hydrogen of carbonic acid
nonvolatile form of hydrogen and organic acid
What are produced as end products of metabolism?
acids
Acids contain
hydrogen ions
Acids
hydrogen ion donors- they give up H+ to neutralize or decrease the strength of an acid or to form a weaker base
Lungs excrete 13,000-30,000 mEq of volatile hydrogen per day in the form of carbonic acid (H2CO3) as CO2
The kidneys excrete 50 mEq of nonvolatile acids per day
More H+ correlate with lower pH
strength of an acid is determined by
the number of hydrogen ions it contains
number of hydrogen ions in body fluid determines ts
acidity, alkalinity, or neutrality
Bases
contain no hydrogen ions (H+)
hydrogen ion (H+) acceptors
accept hydrogen ions (H+) from acids to neutralize or decrease the strength of a base or to form a weaker acid
pH 6.9 suggest
individual is close to death
slide 6-7
Buffer
weak acid/base that can combine with strong acids/bases to minimize changes in pH
Major buffer systems: intracellular
potassium-hydrogen ion exchange
increase H+ → H+ moves into cells & K+ moves out
decrease H+ → H+ moves out of cells & K+ moves in
Major buffer systems: extracellular
Protein buffers:
Hgb (80%)
Albumin & plasma globulins (20%)
Bicarbonate buffer: carbonic acid + bicarbonate
Phosphate buffer: HPO4-2 + H+ H2PO4-
Bone buffer: 2H+ + CO32- CO2 + H2O
Buffers as regulatory systems for H+ concentration in blood
fastest acting regulatory system
immediate protection against changes in H+ concentration in ECF
function to keep pH within narrow limits of stability when too much acid/base is released
react immediately with acids or bases to minimize changes in pH
absorb or release H+ as needed
serve as a transport mechanism that carries excess hydrogen ions (H+) to the lungs
once primary buffer systems react, they are consumed, leaving the body less able to withstand further stress until they are replaced
What role does K+ play in major intracellular buffer?
K+ plays an exchange role in acid-base balance
K+ level changes to compensate for hydrogen ion level changes
In acidosis:
Body protects itself from acid state by moving hydrogen ions (H+) into the cell potassium (K) moves out to make room for hydrogen ions (H+) & the potassium (K) level goes up
In alkalosis:
Cells release hydrogen ions (H+) into the blood in an attempt to increase the acidity of the blood and combat alkalinity potassium (K) moves into the cells and the potassium (K) level goes down
In DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis), you need to keep an eye on their potassium because
the blood test may show normal/high potassium levels despite potassium being low
insulin is the primary treatment for DKA but it causes both glucose and potassium to leave blood and enter cells→ rapid drop in potassium levels when it is already low can cause the heart to stop
Major buffer systems in extracellular fluid
if we have an acidic pH, what happens to serum chloride?
serum chloride decreases
serum bicarb decreases less base= acidic
pH decreases
HCO3 out; CI in
if we have an alkaloid pH, what happens to serum chloride?
serum chloride increases
serum bicarb increases more base= alkalotic
pH increases
HCO3 in; CI out
HCO3= bicarbonate
14-17
Second defense that interacts with the buffer system to maintain acid-base balance
lungs
In acidosis
pH goes down & respiratory rate/depth go up in an attempt to blow off acids
carbonic acid (created by neutralizing action of bicarbonate) can be carried to the lungs where it is reduced to carbon dioxide (CO2) + water and exhaled, thus hydrogen ions (H+) are inactivated & excreted
In alkalosis
pH goes up & respiratory rate and depth go down
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is retained & carbonic acid builds to neutralize and decrease the strength of excess bicarbonate
how long does it take to correct deficit/excess H+ in lungs
in ½ minute you can correct a deficit or excess
lungs is faster than kidneys at correcting acid base
Lungs
action of lungs is reversible in controlling an excess or deficit
can hold H+ until deficit is corrected or can inactivate hydrogen ions, changing them to water molecules to be exhaled as carbon dioxide (CO2), thus correcting excess
Lungs are only capable of inactivating H+ carried by
carbonic acid
Kidneys excrete other excess hydrogen ions
Anion Gap is equal to
[Na+] - ([HCO3-]+[Cl-])
concentration of unmeasured anions (other than Bicarb & CI)
phosphates, sulfates, ketone bodies, lactic acid & proteins
everything before slide 33
What happens in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Insulin is given to speed up movement of serum glucose into cell→ decreasing concurrent ketosis
When glucose is being properly metabolized, body stop converting fats to glucose
What do you need to monitor for in DKA
monitor for circulatory collapse due to polyuria which may result from hyperglycemic state, as polyuria or diuresis may lead to extraceullar volume deficit
What happens in renal failure?
dialysis may be used to remove protein & waste products, thereby lessening the acidosis state
diet low in protein & high in calories will lessen the amount of protein waste products due to protein catabolism; this in turn, will lessen the acidosis
Metabolic acidosis treatment
Definition of Metabolic acidosis
Cause of metabolic acidosis
How does body compensate for metabolic acidosis?
What will the pH look like if metabolic acidosis is compensated?
pH will be low normal; less than
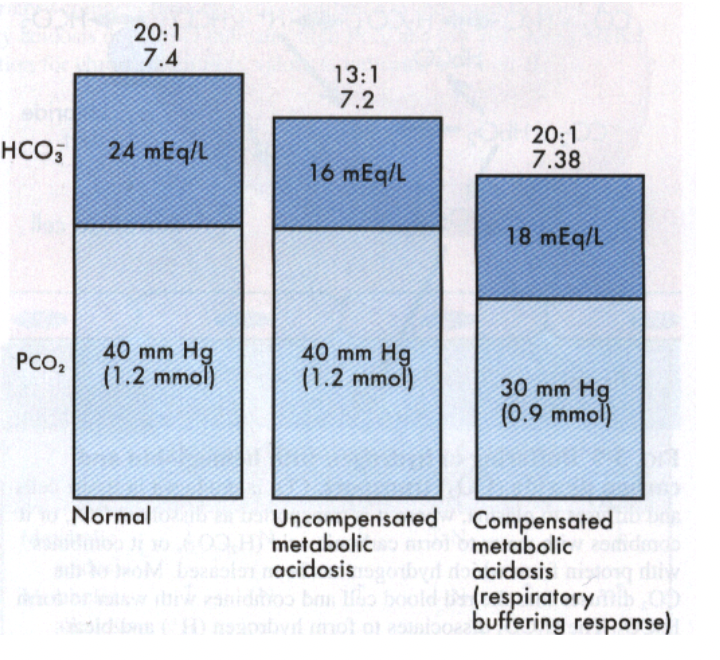
why does the graph show that the metabolic acidosis has been compensated?
the ratio has been restored to 20:1
which part of the body compensate when there’s an issue with the metabolic system?
respiratory system compensate for problem in metabolic system
Metabolic alkalosis
deficit of carbonic acid (H2CO3) & decrease in hydrogen ion concentration
Results from the accumulation of base or from a loss of acid without a comparable loss of base in body fluids
we either took on too much base or lost too much acid
Metabolic alkalosis causes
malfunction of metabolism leading to an increased amount of basic solution in the blood and a decrease in available acids in the blood
ingestion of excess sodium bicarbonate (causes an increase in the amount of base in the blood)
excessive vomiting (leads to excessive loss of acids)
GI suctioning
Diuretics
hyperaldosteronism
massive transfusion of whole blood
How does GI functioning contribute to metabolic alkalosis?
it leads to an excessive loss of acids from the suctioning
How does diuretics contribute to metabolic alkalosis?
loss of hydrogen ions and potassium causes a compensatory increase in the bicarbonate in the blood
How does hyperaldosteronism contribute to metabolic alkalosis?
increased renal tubular reabsorption of sodium occurs with the resultant loss of hydrogen ions
How does massive transfusion of whole blood contribute to metabolic alkalosis?
citrate anticoagulant used for storage of blood in metabolized to bicarbonate
could cause hypocalcemia so blood centers would also give calcium
Metabolic alkalosis etiologies
excess gain of bicarbonate
increased bicarb retention
loss of chloride
excessive loss of H+
volume contraction
loss of body fluids
diuretic therapy
abrupt correction of respiratory acidosis by mechanical ventilation
excessive loss of H+ occur through
NG suctioning (most common reason)
vomiting
bulimia
potassium deficit
prolonged diuretic therapy (lassie & thiazides)
hyperaldosteronism
excess gain of bicarbonate can occur through
administration or ingestion of HCO3
administration of solutions containing lactate
administration of citrate containing blood transfusions
NaHCO3 during CPR
Metabolic alkalosis assessment
respiratory rate & depth go down to conserve carbon dioxide (CO2)
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
numbness & tingling in the extremities
restlessness and twitching in the extremities
hypokalemia
hypocalcemia
sinus tachycardia
dysrhythmias
Metabolic alkalosis neural manifestations
confusion
hyperactive DTRs
tetany
convulsions
paresthesias in fingers & toes
circumoral paresthesias
carpopedal spasm
Metabolic alkalosis cardiovascular manifestations
hypotension
dysrhythmias
Metabolic alkalosis GI manifestations
nausea and vomiting
How do you compensate for metabolic alkalosis?
decrease in RR & depth
increase in urine pH
slide 44-45
Metabolic alkalosis definition
fixed acid deficit
cause of Metabolic Alkalosis
base accumulation
loss of acid
Metabolic Alkalosis compensation
respiratory retention of H2CO3 (CO2 + H2O)
47 chart
Respiratory acidosis
total concentration of buffer base is lower than normal with a relative increasing hydrogen ion (H+) concentration
more hydrogen ions circulating in the blood than can be absorbed by the buffer system
Causes of respiratory acidosis
due to primary defects in the function of the lungs or by changes in normal respiratory patterns due to secondary problems
remember that any condition that causes an obstruction of the airway or depresses respiratory status can cause respiratory acidosis
hypoventilation
infection
medication
pneumonia
Atelectasis
brain trauma
emphysema
asthma
bronchitis
pulmonary edema
bronchiectasis
Respiratory acidosis causes: hypoventilation
carbon dioxide is retained and hydrogen ions increase leading to the acid state; carbonic acid is refined and the pH goes down
Respiratory acidosis causes: infection
caused by inflammation and bacterial agents aeration decreases due to the obstruction of airways
Respiratory acidosis causes: medications
sedatives, narcotics, and anesthetics depress the respiratory center leading to hypoventilation; an increase in hydrogen ions occurs leading to carbon dioxide narcosis
Respiratory acidosis causes: pneumonia
caused by infection, irritants, and immobility; obstruction of airway passages leads to inadequate oxygenation due to fluid accumulation
Respiratory acidosis causes: Atelectasis
excessive mucus collection with the collapse of alveolar sacs caused by mucus plugs, infectious drainage, or anesthetic medications, results in decreased respiration
Respiratory acidosis causes: brain trauma
excessive pressure on the respiratory center or medulla oblongata depresses respiration
Respiratory acidosis causes: emphysema
loss of elasticity of alveoli sacs restrict air flow in and out, primarily out, leading to an increased carbon dioxide (co2) level
Respiratory acidosis causes: asthma
spasms due to allergens, irritants, or emotions cause the smooth muscles of the bronchioles to constrict
Respiratory acidosis causes: bronchitis
inflammation causes airway obstruction
Respiratory acidosis causes: pulmonary edema
extracellular accumulation of fluid in acute congestive heart failure (CHF) causes disturbances in alveolar diffusion and perfusion
Bronchiectasis
bronchi become dilated due to inflammation; destructive changes and weakness in the walls of the bronchi occur
Respiratory acidosis etiologies
Acute***
lung disease
acute pulmonary edema
aspiration
atelectasis
pneumothorax
severe pneumonia
depression of respiratory center
sedative or narcotic overdose
head injury
Chronic Lung disease
chronic bronchitis
asthma
cystic fibrosis
emphysema
COPD
Chest wall & respiratory muscles
obesity
post op pain
high abdominal or thoracic incisions
abdominal distention from ascites or bowel obstruction
Respiratory acidosis assessment
respiratory rate & depth will increase
headache, mental status changes, confusion
drowsiness, restlessness
visual disturbances
diaphoresis
cyanosis as the hypoxia becomes more acute
hyperkalemia
rapid and irregular pulse leading to dysrhythmias and vernacular fibrillation
Respiratory acidosis manifestations
Neural
dilation of cereal vessels & depression of neural function
feeling of fullness in head
headache, weakness
behavior changes- confusion, depression, paranoia, hallucinations
tremors, paralysis, depressed DTRs
stupor & coma
Skin
warm & flushed
Cardiac
tachycardia
Respiratory
dyspnea and cyanosis
Compensation
acid urine
Interventions for respiratory acidosis
maintain patent airway
improve ventilation and aeration based on the clinical manifestations
monitor for signs of respiratory distress
administer oxygen as prescribed
place client in semi-fowler’s position unless contraindicated
encourage & assist client to turn, cough & deep breathe
prepare to administer chest physiotherapy & postural drainage as prescribed
encourage hydration to thin secretions unless excess fluid intake is contraindicated
suction client as necessary
Respiratory acidosis interventions 4 parts
reduce
reduce restlessness by improving ventilation other than by the administration of sedatives and narcotics
monitor
monitor electrolyte values
avoid
avoid use of tranquilizers, narcotics & hypnotics because they further depress respiration
administer
administer antibiotics for infection as prescribed
Respiratory acidosis treatment
encourage TCDB every 2 hrs
chest PT
suctioning
semi-fowler’s or orthopedic position
encourage fluids
supplemental O2 to treat hypoxemia (use with caution in COPD d/t loss of hypoxemic stimulus)
monitor VS, ABGs, serum K+ levels
bronchodilators
antibiotics for pneumonia
administer sedatives with caution
be prepared for intubation & mechanical ventilation
Respiratory acidosis definition
carbonic acid excess
cause of Respiratory acidosis
altered alveolar ventilation leading to retention of carbon dioxide
Respiratory acidosis compensation
renal retention of HCO3-
acidic urine excreted
slide 59 chart
Respiratory alkalosis
deficit of carbonic acid (H2CO3) & decease in hydrogen ion concentration
Results from accumulation of base or from loss of acid without a comparable loss of base in the body fluids
causes for respiratory alkalosis
due to conditions that cause over-stimulation of respiratory system
hyperventilation
rapid respiration causes blowing off of carbon dioxide→ leads to decrease in carbonic acid
hysteria
often neurogenic in nature and related to psychoneurosis; however, this condition leads to vigorous breathing & excessive exhaling of carbon dioxide
over-ventilation by mechanical ventilators
administration of oxygen and the depletion of carbon dioxide can occur from mechanical ventilation; client may be hyperventilated by mechanical ventilation
conditions that increase metabolism such as fever
pain/brain trauma
causes overstimulation of the respiratory center in the brain stem with resultant carbonic acid deficit
salicylates
hypoxia
Respiratory alkalosis causes: hypoxia
causes respiratory stimulation with resultant carbonic acid deficit
Respiratory alkalosis causes: salicylates
stimulate the respiratory center causing hyperventilation
Respiratory alkalosis etiologies
excessive ventilation
extreme anxiety (most common)
hypoxemia
stimulation of respiratory center
high fever
early salicylate (aspirin) poisoning
encephalitis
CNS lesions affecting respiratory center
increase blood ammonia
excessive mechanical ventilation (may deliberate to decreased cerebral edema)
pregnancy (increase sensitivity to CO2)
hyperventilation during L & D
Taking a bottle of aspirin initially start off as respiratory acidosis but it eventually develops into
metabolic acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis assessment
initially hyperventilation & respiratory stimulation will cause rapid respiration (tachypnea); To compensate, RR & depth decreases
headache, mental status changes
vertigo= dizziness
lightheadedness
paresthesias as tingling of the fingers and toes
hypokalemia
hypocalcemia
tetany
convulsions
Respiratory alkalosis manifestations
cerebral vasoconstriction
lightheadedness, syncope
inability to concentrate
blurred vision, vertigo
loss of consciousness
neuromuscular irritability
paresthesias
tinnitus
carpopedal spasms (Trousseau’s sign)
spasms (Cvostek’s)
tetany, twitching
hyperactive DTRs
seizures, convulsions, coma
cardiovascular
cardiac dysrhythmias
hyperventilation
rapid deep respirations
dry mouth
GI function
N & V, epigastric pain
Respiratory alkalosis interventions
maintain patent airway
provide emotional support and reassurance to the client
encourage appropriate breathing patterns
assist with breathing techniques and apply breathing aids as prescribed
voluntary holding of breath
rebreathe exhaled carbon dioxide (co2)
rebreathing mask as prescribed
carbon dioxide breaths as prescribed
provide cautious care with ventilator clients so that the client is not forced to take breaths too deeply or rapidly
monitor electrolyte values
administer medications as ordered
prepare to administer calcium gluconate for tetany as prescribed
Respiratory alkalosis treatment
monitor VS
encourage breathing slowly and less deeply
breath into paper bag
use rebreather mask
administer sedatives
correct underlying cause
monitor ABGs
adjust mechanical ventilator settings
monitor K+ levels
provide emotional support
Respiratory alkalosis definition
carbonic acid (H2CO3) deficit
Respiratory alkalosis cause
hyperventilation leading to excessive elimination of carbon dioxide (CO2)
Respiratory alkalosis compensation
renal excretion of HCO3-
slide 69 chart
70
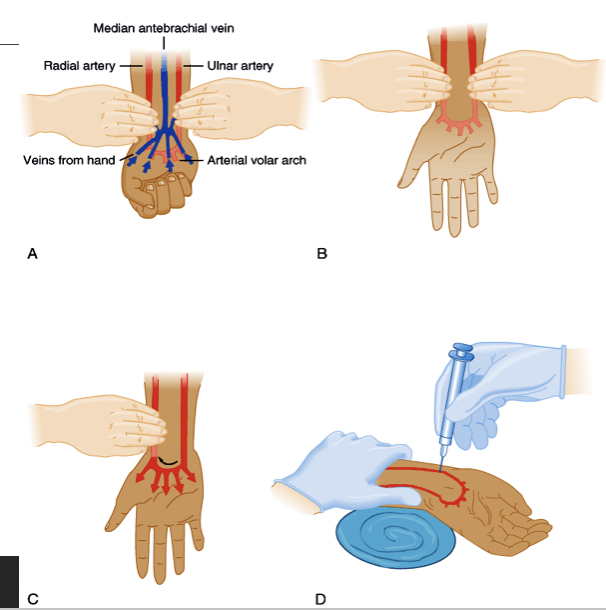
stick needle in compromised artery because
if you stick it in good artery, you may cause blood to spill out and possibly hinder normal flow
performing Allen’s test
ask client to make tight fist
apply direct pressure over client’s ulnar & radial arteries
while pressure is applied, ask client to open their hand
remove pressure from ulnar artery & assess color of extremity distal to pressure point
pH 7.0 and 6.9 indicate patient
is approaching death
72