ANAT242 - quizlet
1/312
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
313 Terms
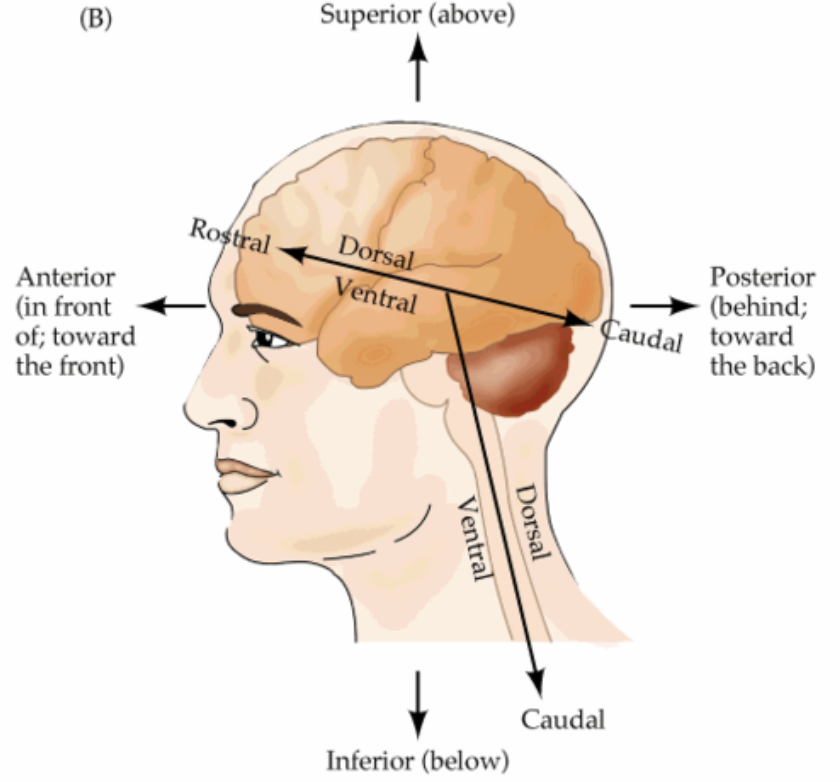
rostral/anterior
front
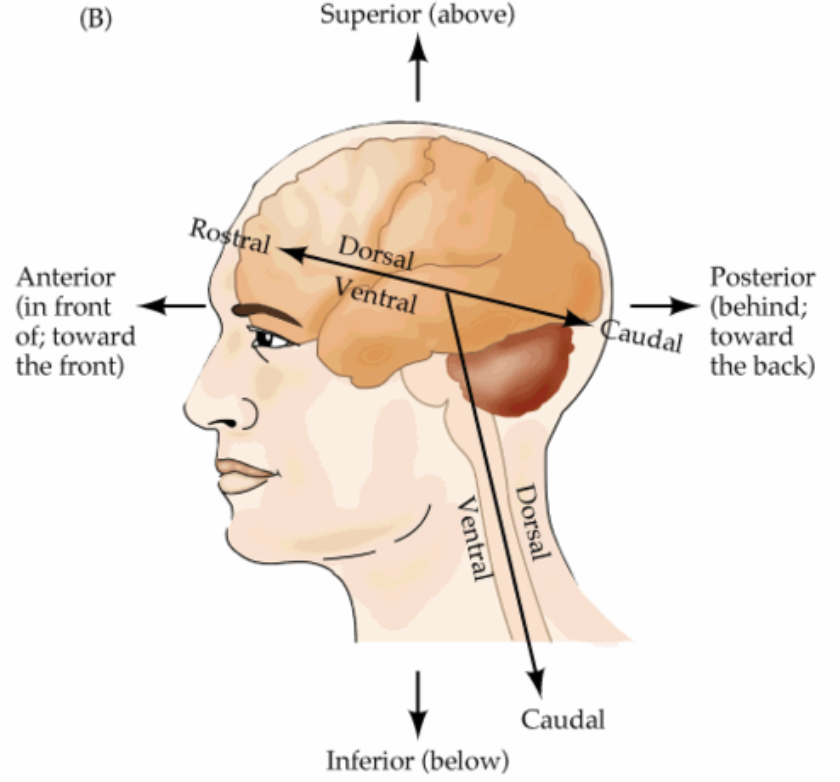
caudal/posterior
back
insula
cerebral lobe located deep within lateral sulcus
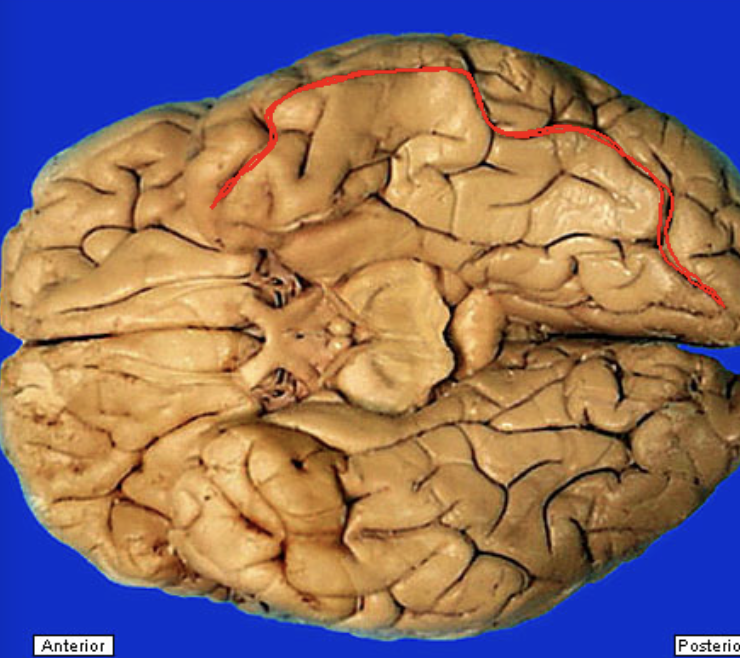
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
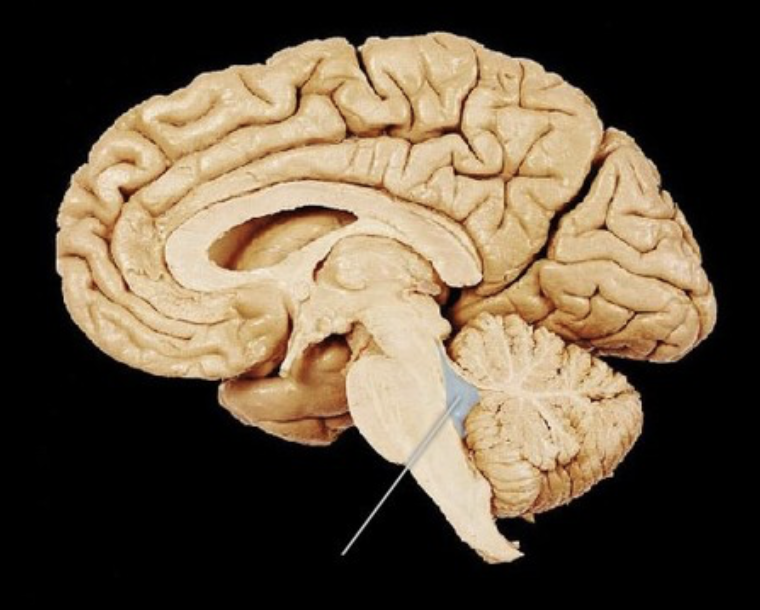
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
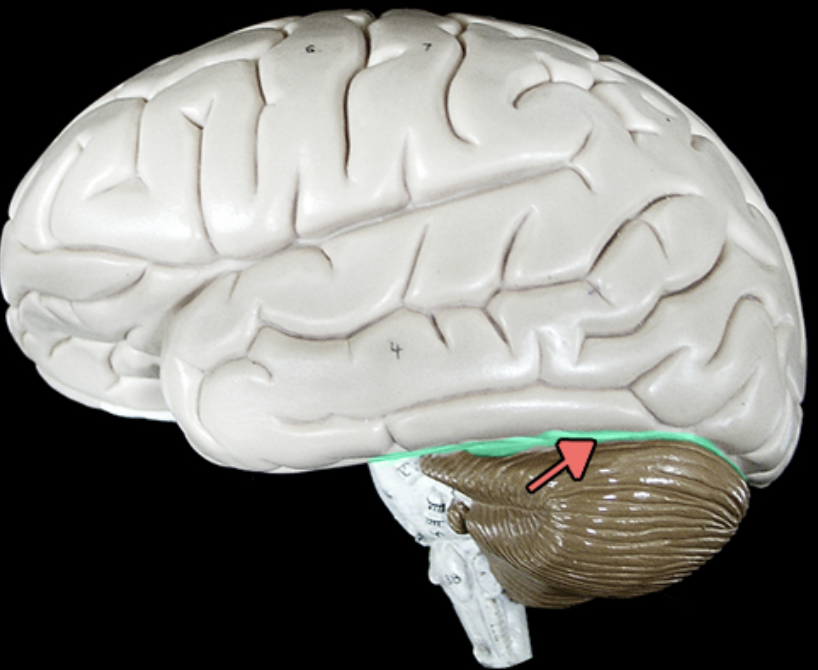
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
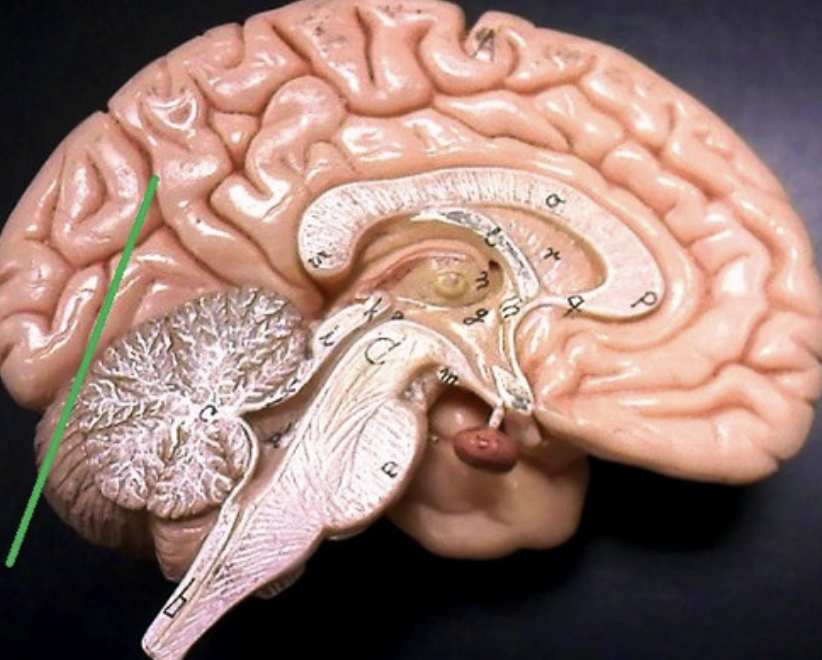
parieto-occipital sulcus
only seen on medial side
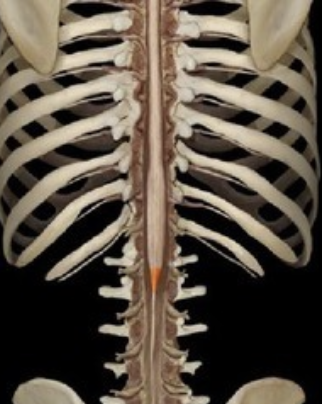
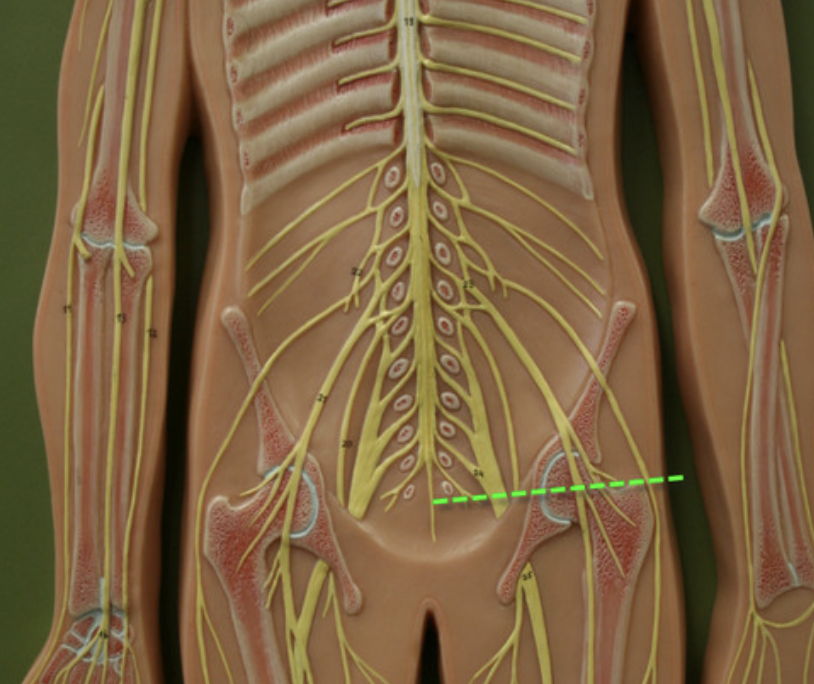
pairs of spinal nerves
8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral 1 coccygeal
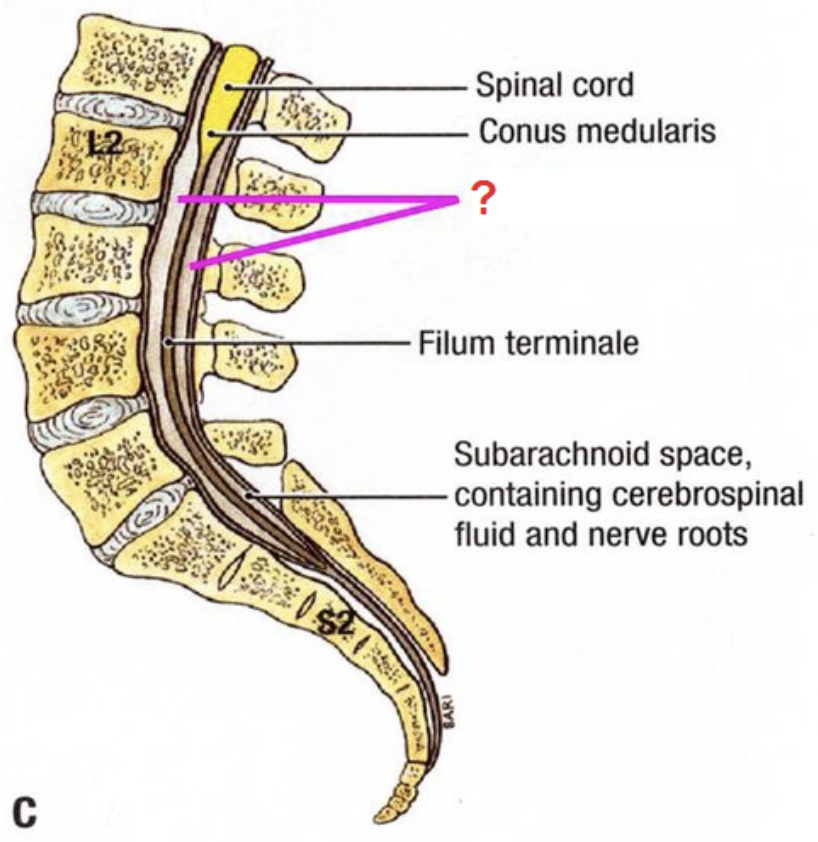
conus medullaris
tapered end of spinal cord
cauda equina
"horse's tail", a fan of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
filum terminale
fibrous extension of the pia mater; anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
paralysis
loss of motor function
paresthesias
sensory loss
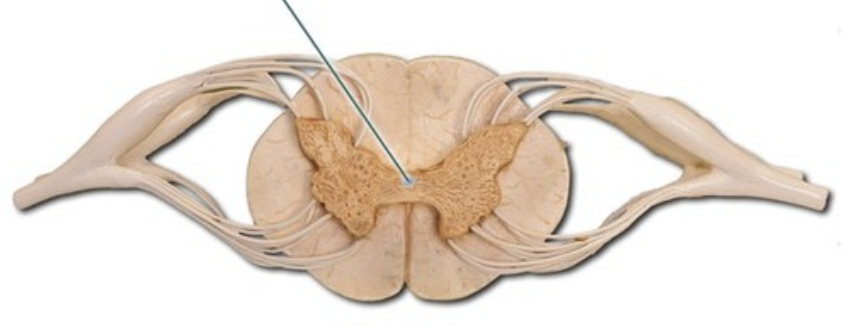
central canal
a fluid-filled channel in the center of the spinal cord
C1-C4 spinal injury
high tetraplegia
C5-C8 spinal injury
low tetraplegia (some upper limb movement)
thoracic/lumbar/sacral spinal injury
paraplegia
Ventral horn damage
motor loss
Dorsal horn damage
sensory loss
Dural layers
periosteal and meningeal
falx cerebri
separates cerebral hemispheres
falx cerebelli
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
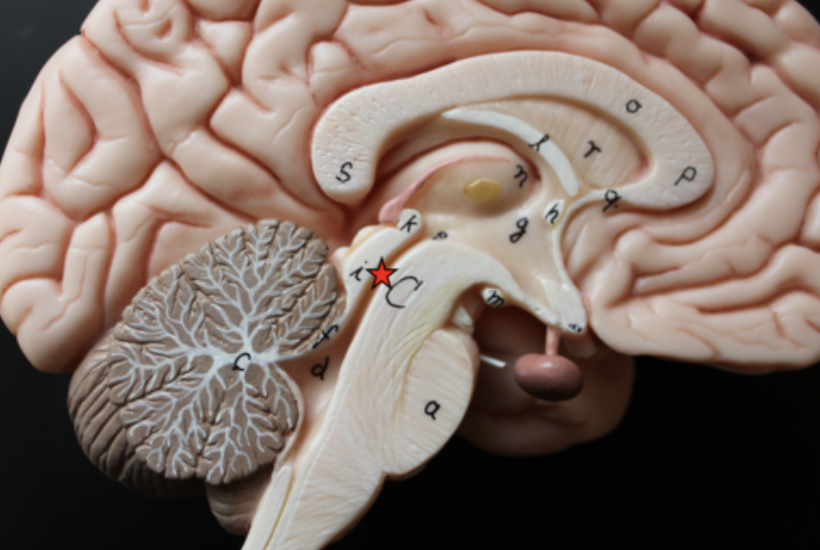
pontine cistern
lies over the pons
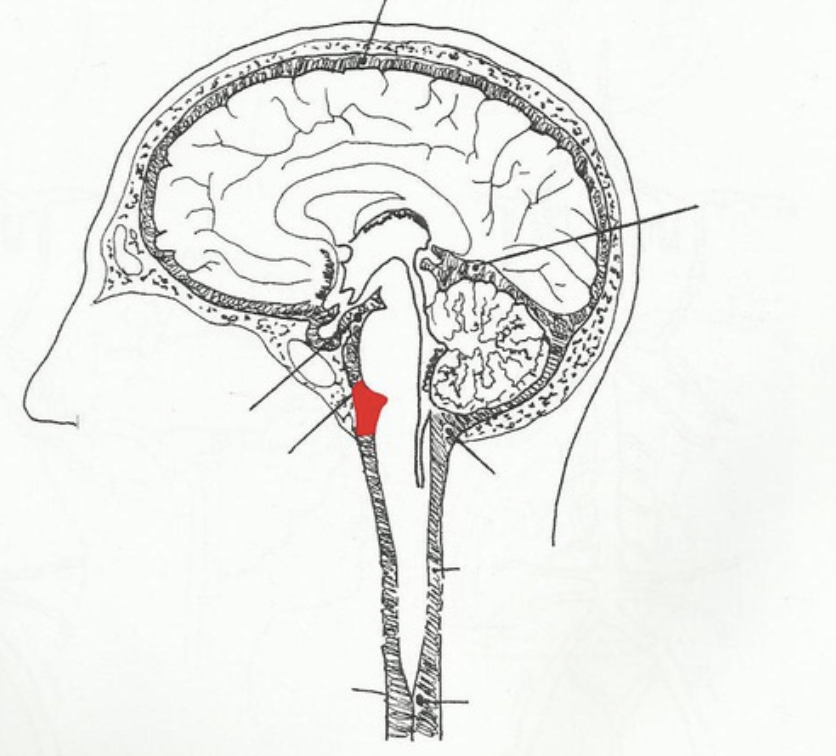
Interpeduncular cistern
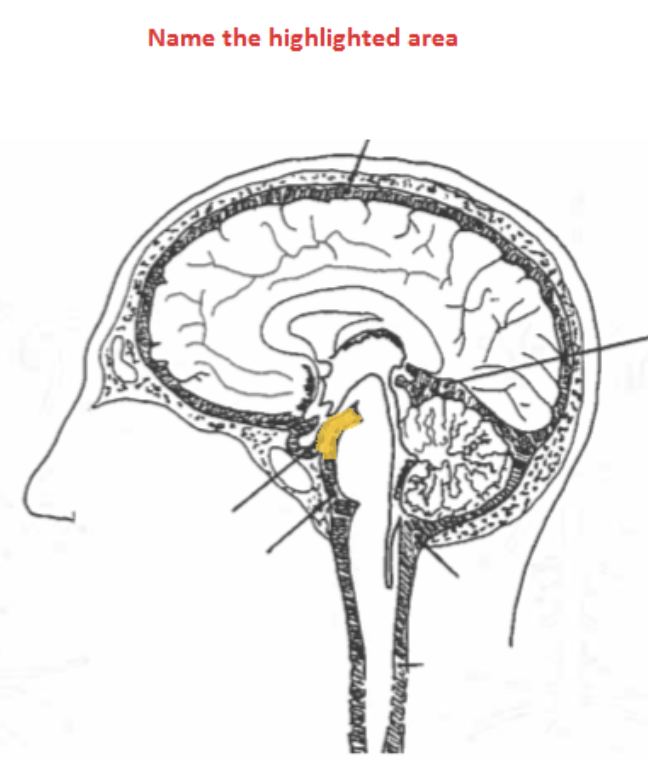
superior cistern
the cistern between the cerebellum and cerebrum
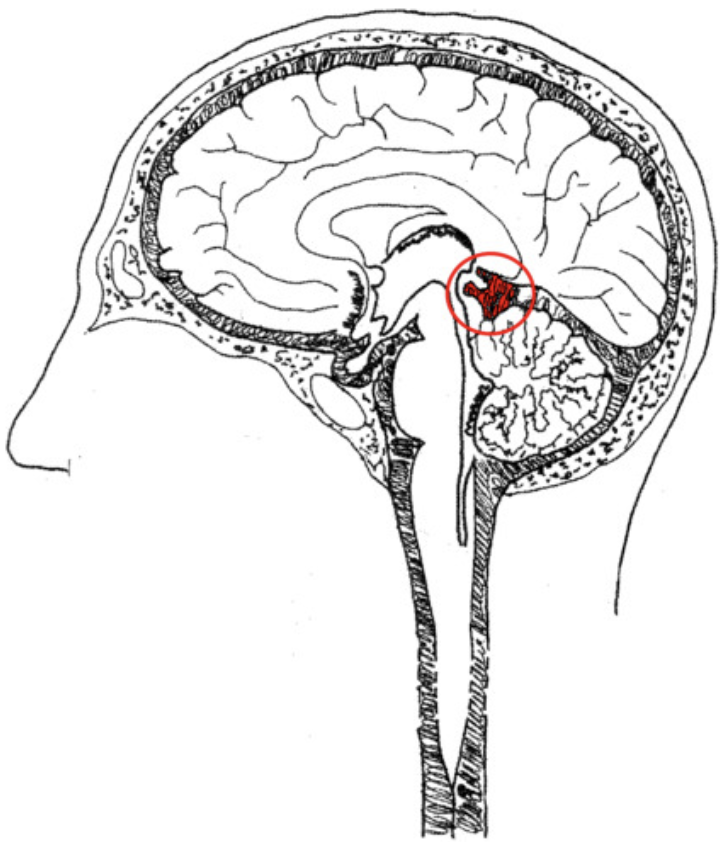
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
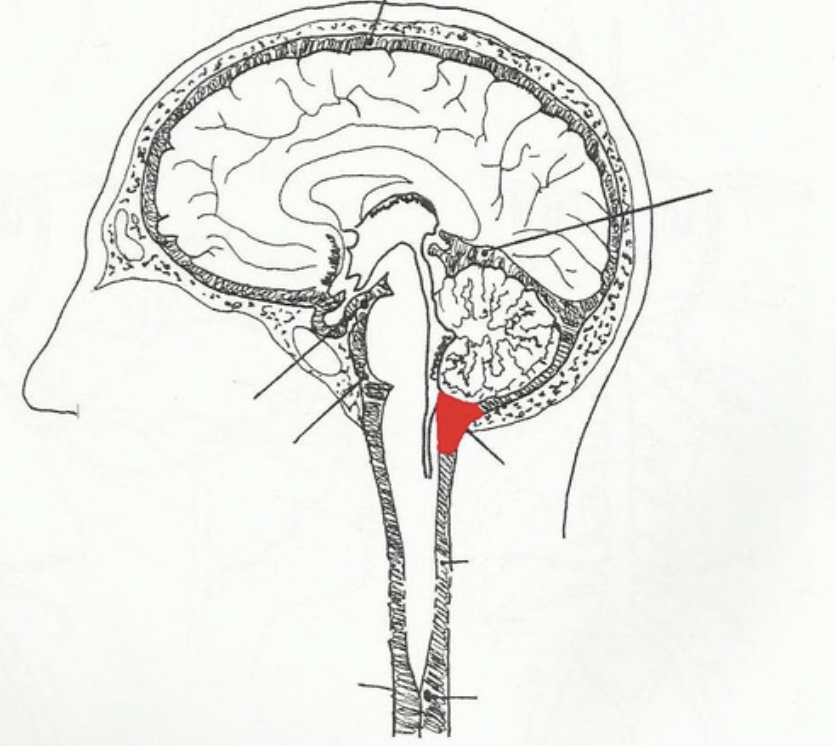
cerebellomedullary cistern (cisterna magna)
lentiform nucleus
putamen and globus pallidus
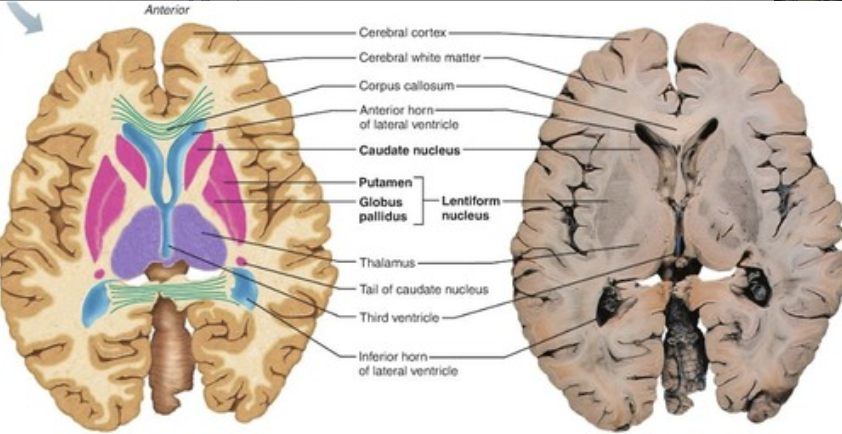
corpus striatum
caudate, putamen, globus pallidus
Striatum
caudate nucleus and putamen
basal ganglia
corpus striatum, subthalamic nuclei, substantia nigra
commisural tracts
connect left and right hemispheres e.g. corpus callosum
projection tracts
connect brain to spinal cord e.g. internal capsule
association fibres
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
vertebral arteries
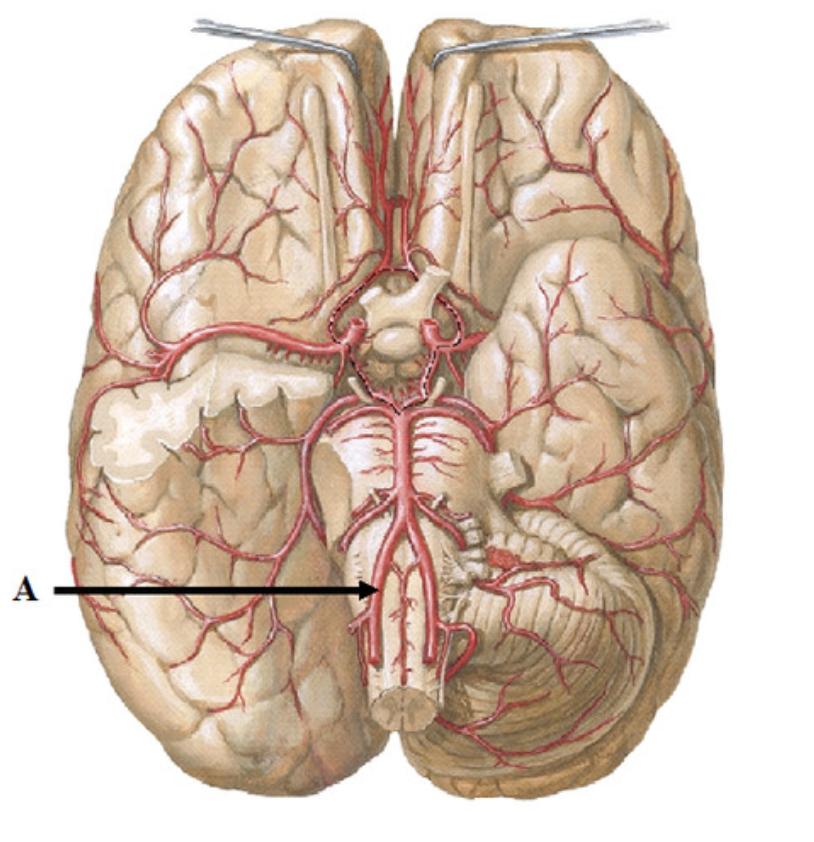
internal carotid artery
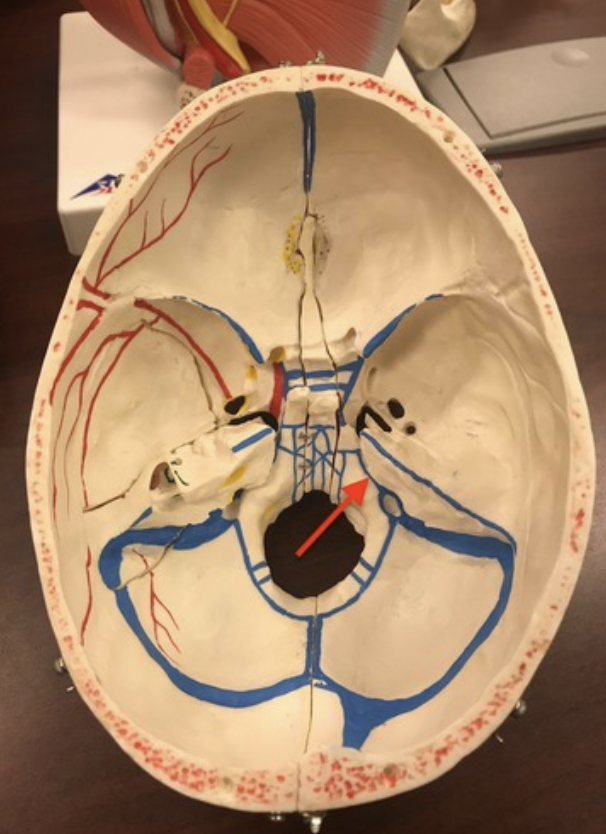
Number 4
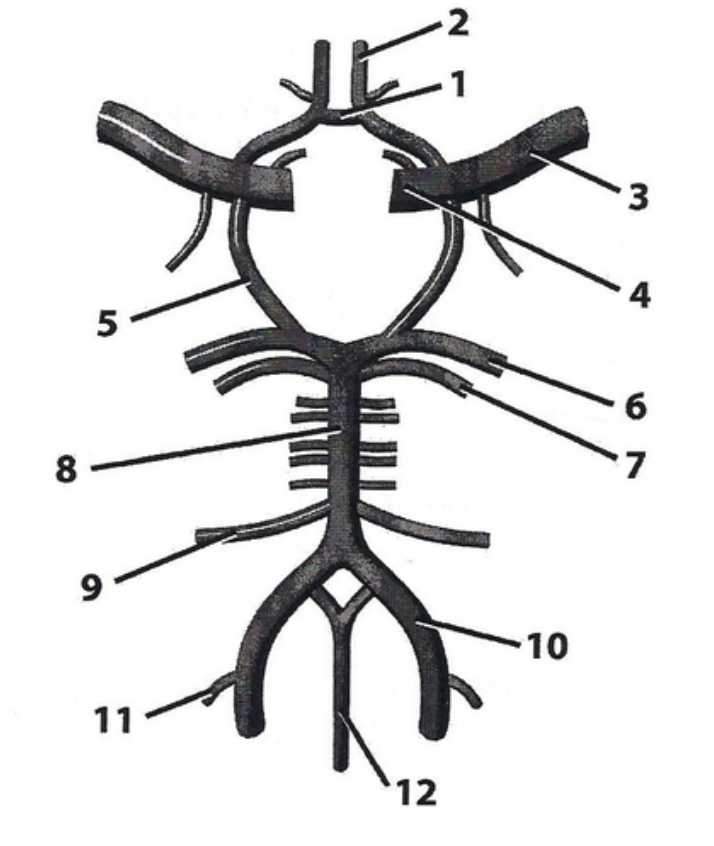
basilar artery
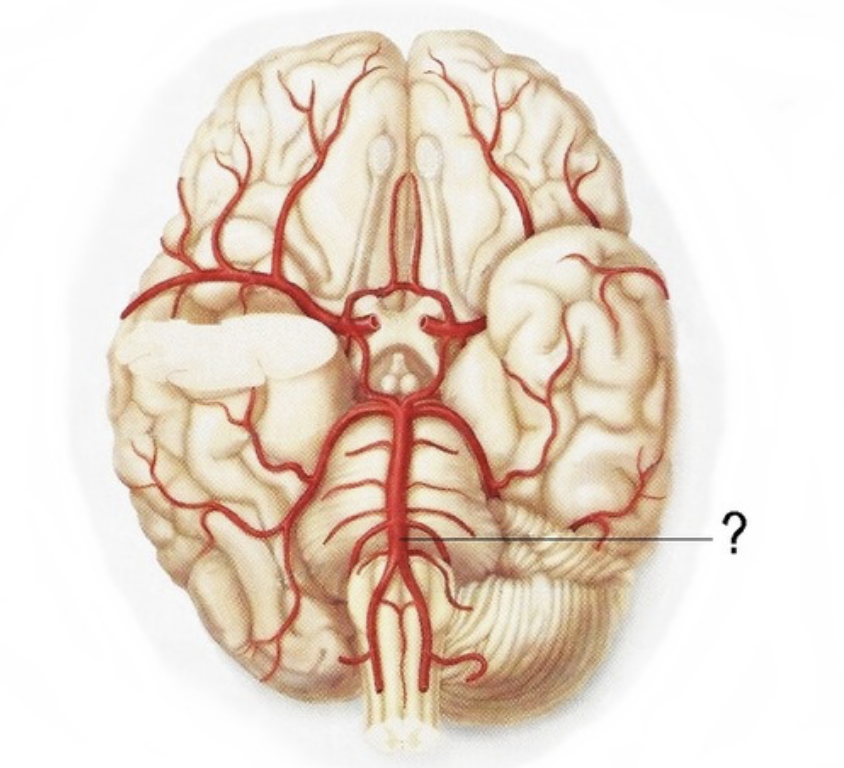
anterior inferior cerebellar artery
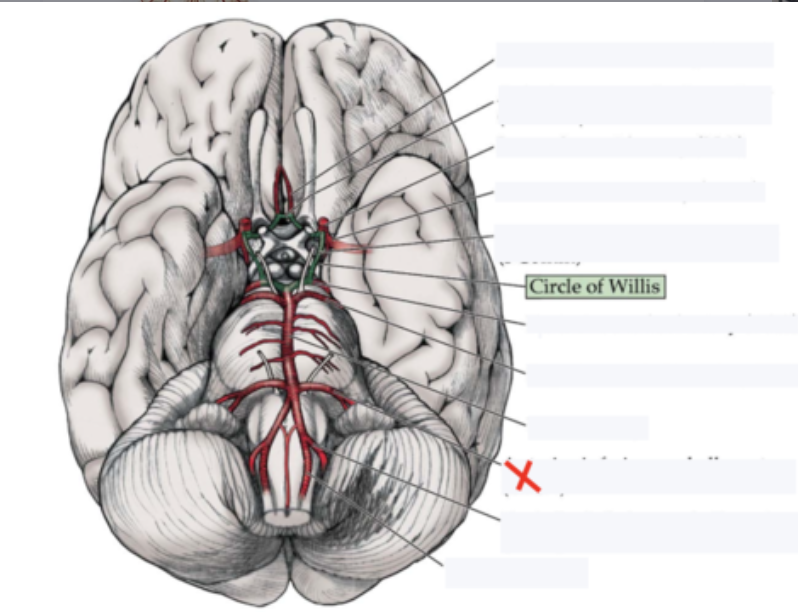
posterior inferior cerebellar artery
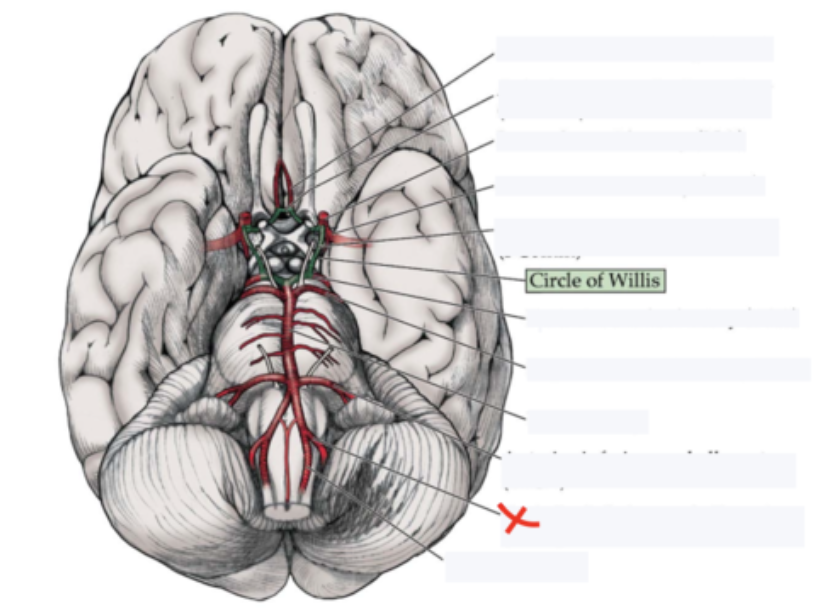
superior cerebellar artery
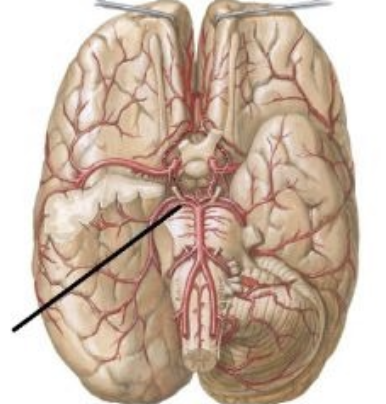
posterior cerebral artery
Supplies posterior 2/3 cerebrum on medial side - occipital lobe
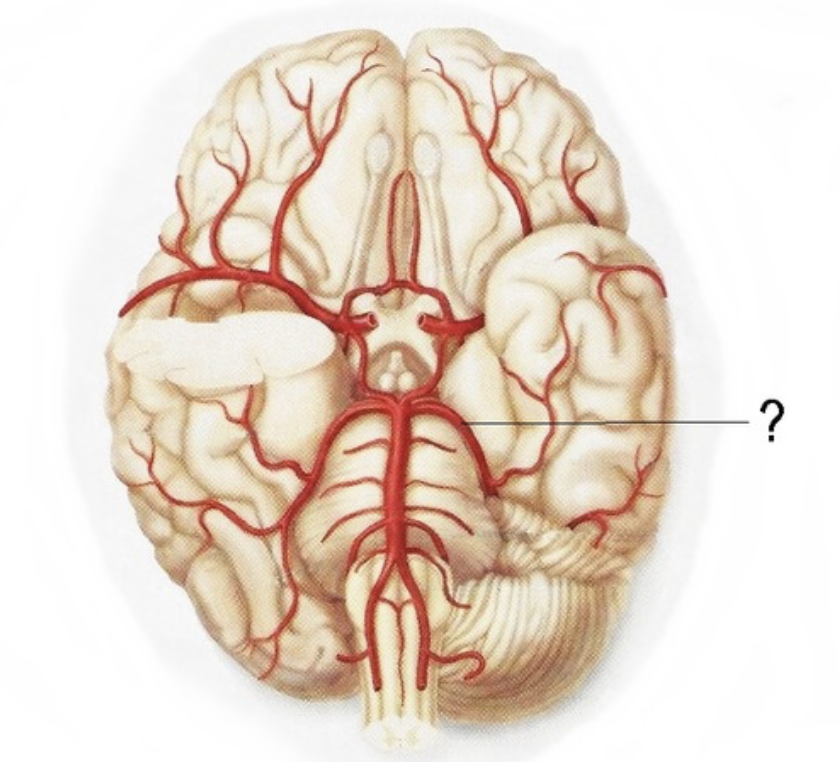
middle cerebral artery
Supplies the lateral part of the cerebral hemispheres
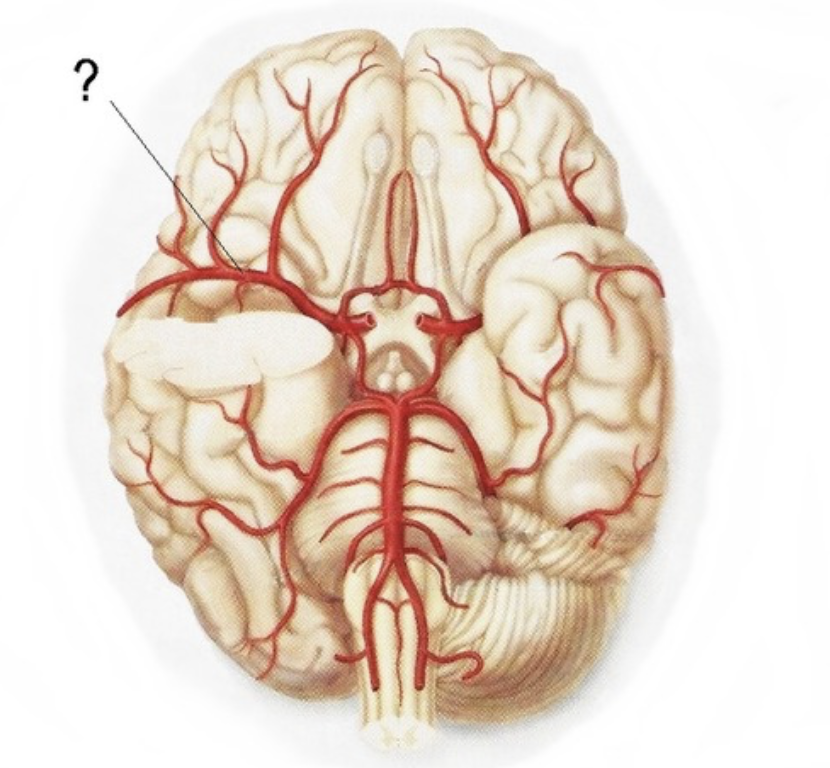
anterior cerebral artery
Supplies anterior 2/3 medial aspect of cerebrum and basal nuclei
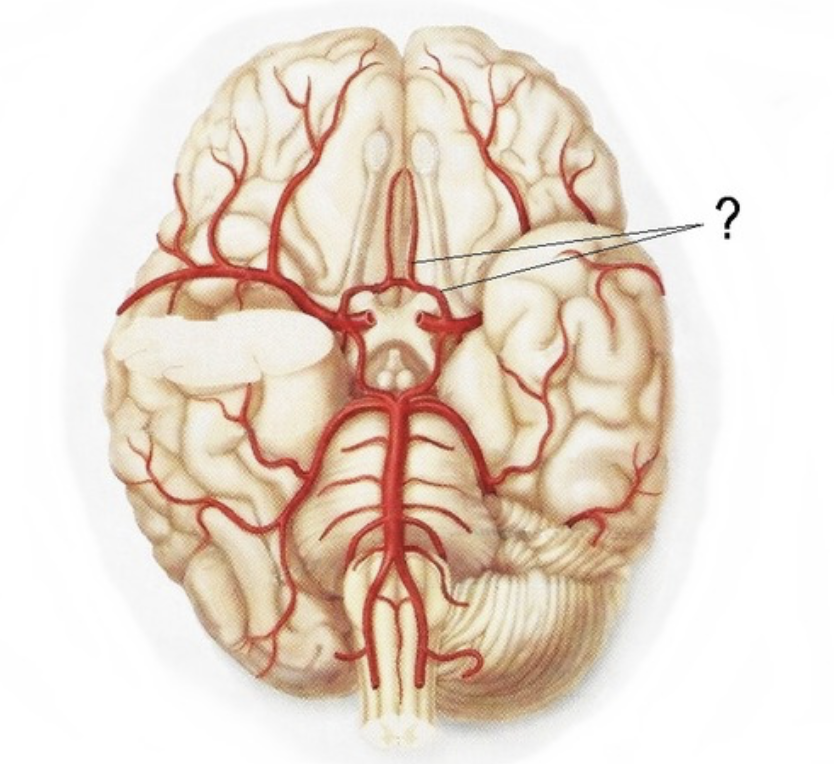
anterior communicating artery
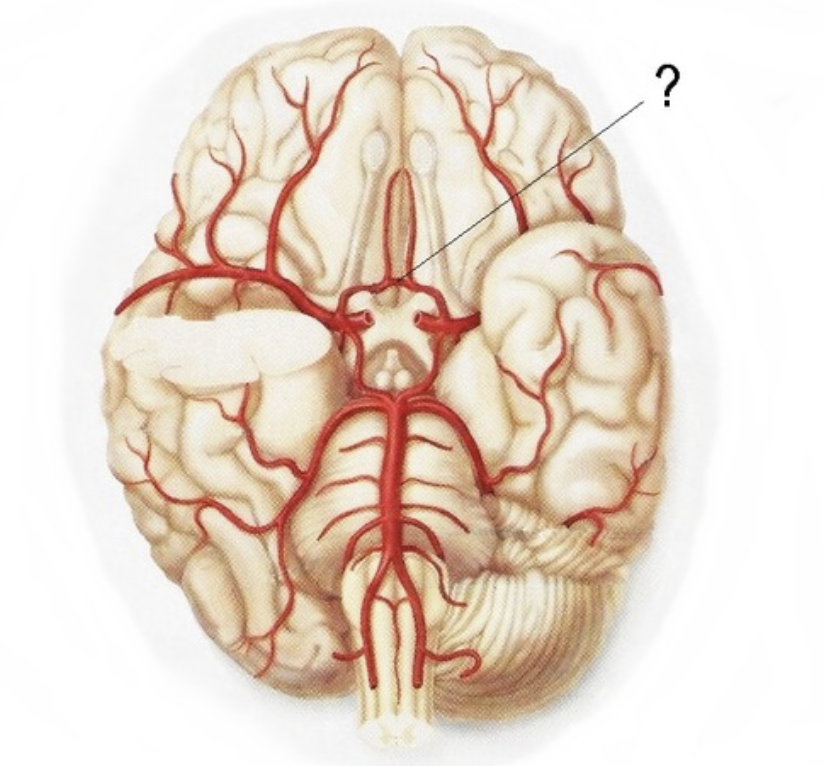
posterior communicating artery
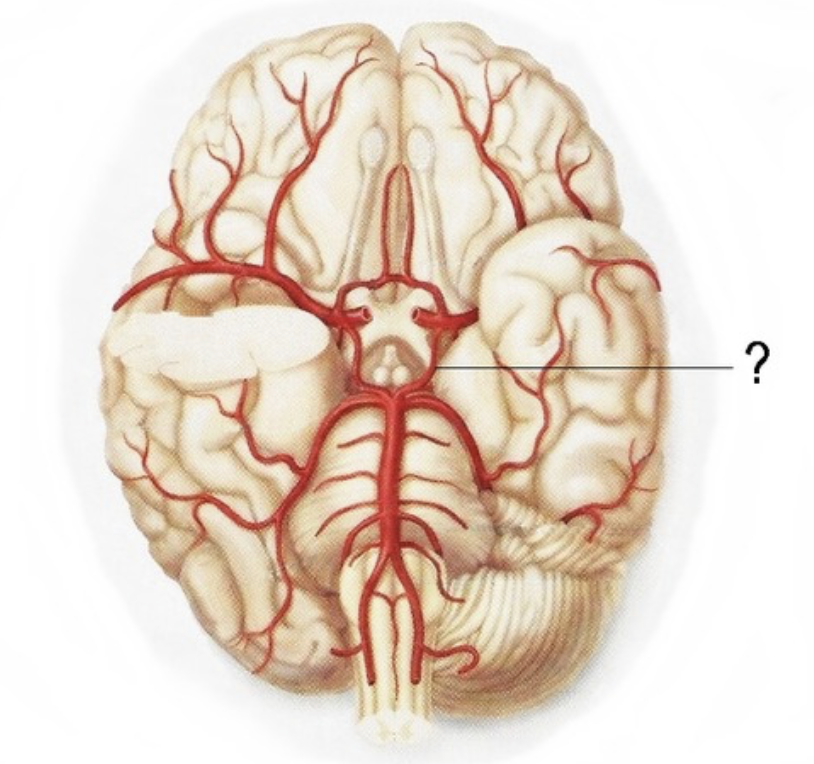
brain system
A collection of structures in the brain that work together to perform a common function
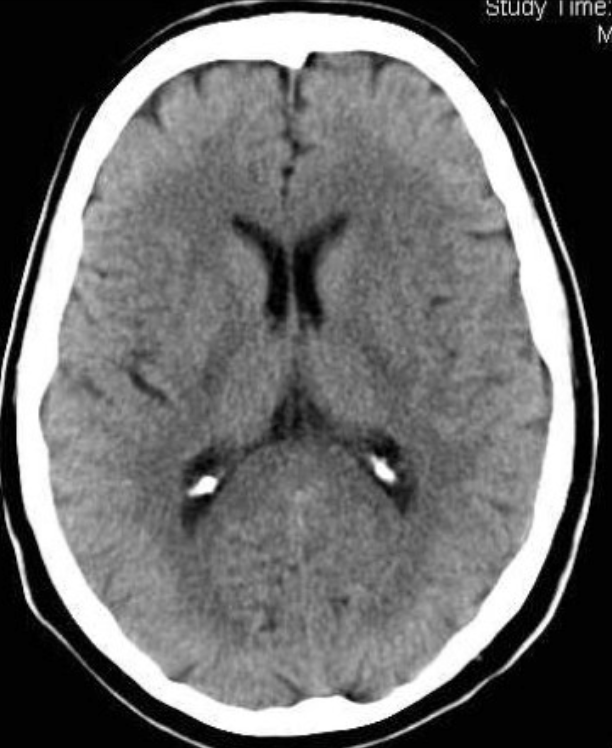
CT (computed tomography) scan
X-rays (brightest) bone - blood - grey matter - white matter - CSF - fat (darkest) Advantages: Acute bleeding, skull fracture, quick, cheap, less scary than MRI Disadvantages: low resolution, radiation, structure only (no function)
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
high powered magnet aligns H+ in the body
Radio frequency pulse moves atoms out of alignment
Measure time for atoms to recover alignment - different tissues take different times Advantages: high resolution Disadvantages: long, loud and scary, not good for seeing bone/bleeding
T1 weighted MRI
Time for axis realignment (brightest) fat - white matter - grey matter - CSF (darkest)
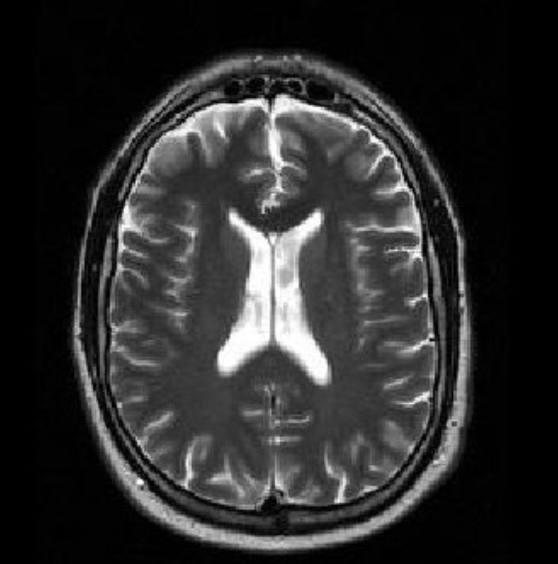
T2 weighted MRI brain
Axial spin recovery time (brightest) CSF/water - grey matter - white matter - fat
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
lumbar cistern
Used to sample CSF
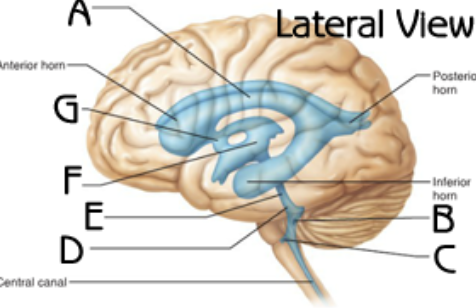
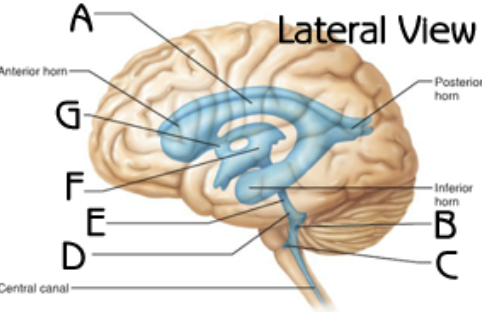
lateral ventricles
third ventricle
inter ventricular foramen
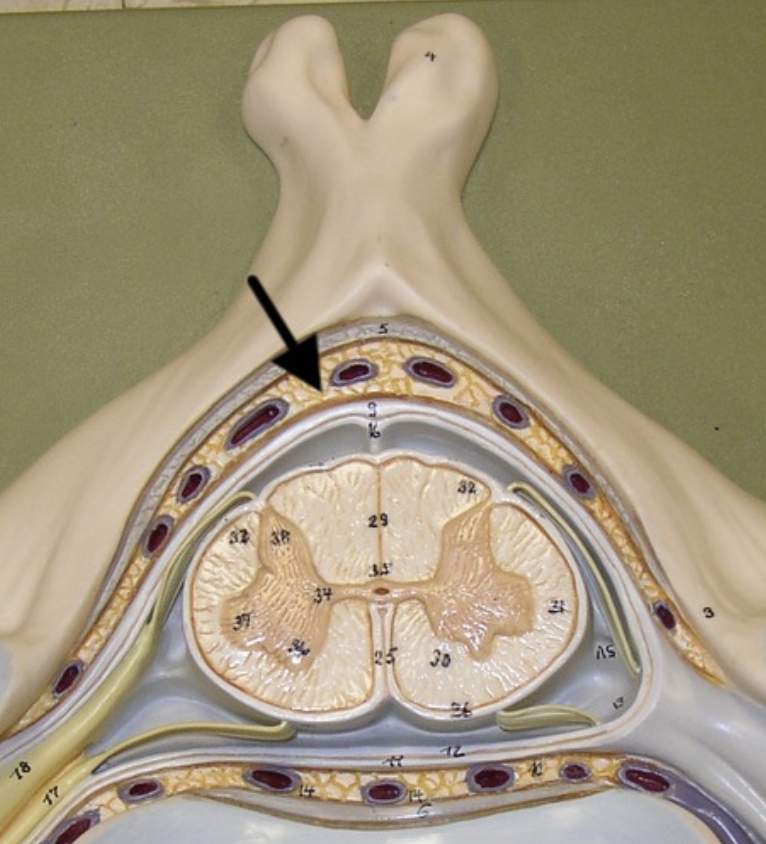
epidural space
Fat-filled space between the vertebrae and dura mater - largest at T2
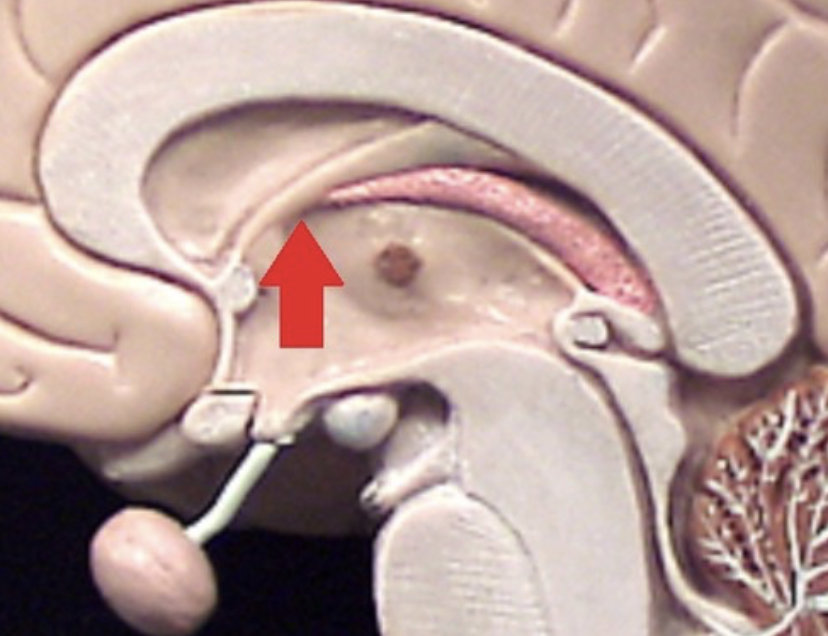
Choroid plexus in lateral ventricle
body and inferior horn
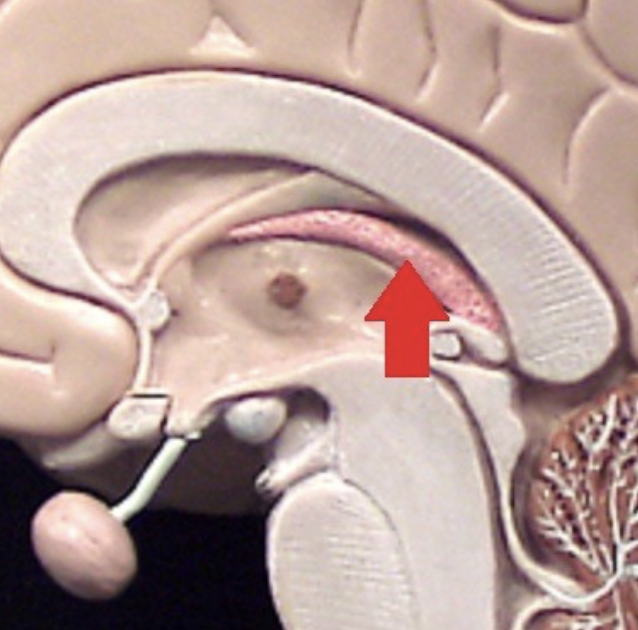
Choroid plexus in third ventricle
In roof
Fourth ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
superior and inferior medullary velum
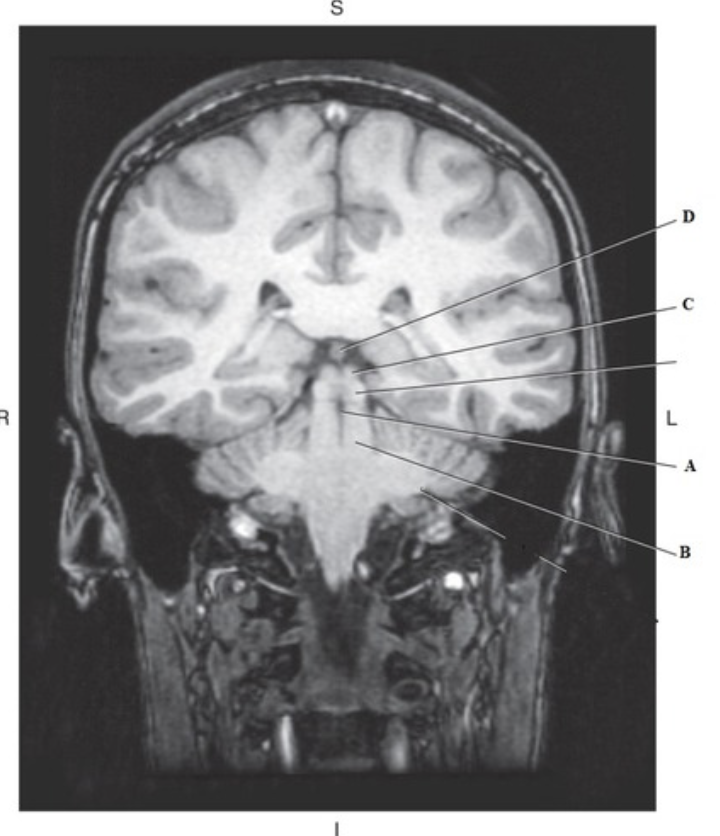
choroid plexus in forth ventricle (A and C)
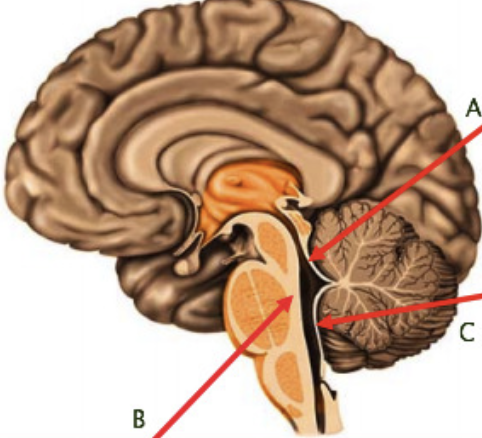
Formina of Luschka (lateral apertures)
pair of openings from the fourth ventricle to the subarachnoid space on either side and between the medulla and cerebellum - C
median aperture (foramen of Magendie)
B
Arterial supply to lateral surface of the brain
middle cerebral artery
Arterial supply to posterior 1/3 of cerebral hemispheres
posterior cerebral artery
Arterial supply of anterior 2/3 of hemispheres + basal nuclei
Anterior cerebral artery
superior saggital sinus
joins right transverse sinus
inferior sagittal sinus
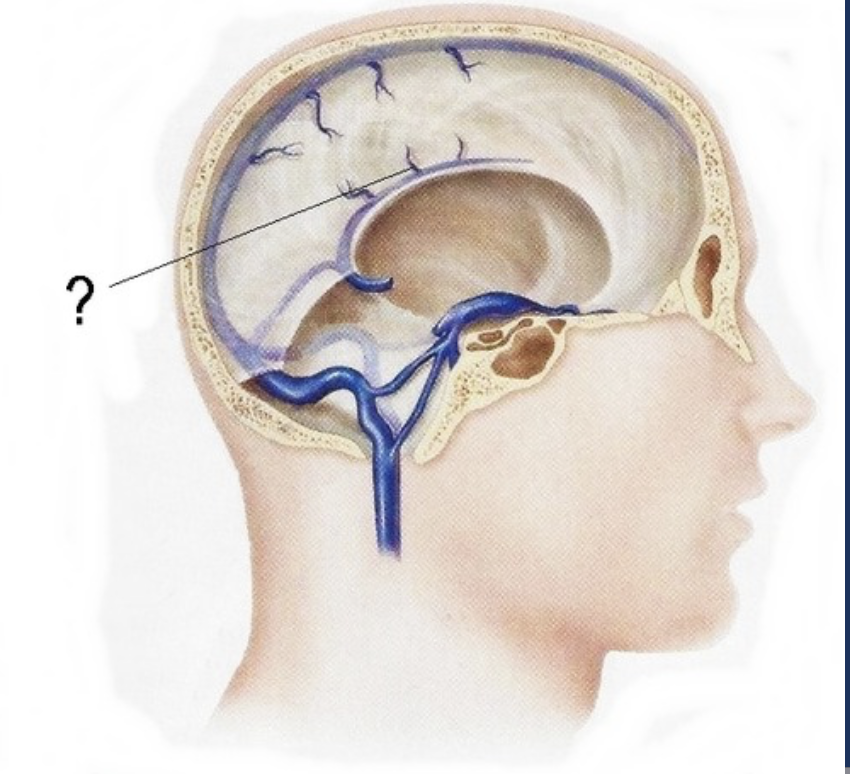
straight sinus
joins left transverse sinus
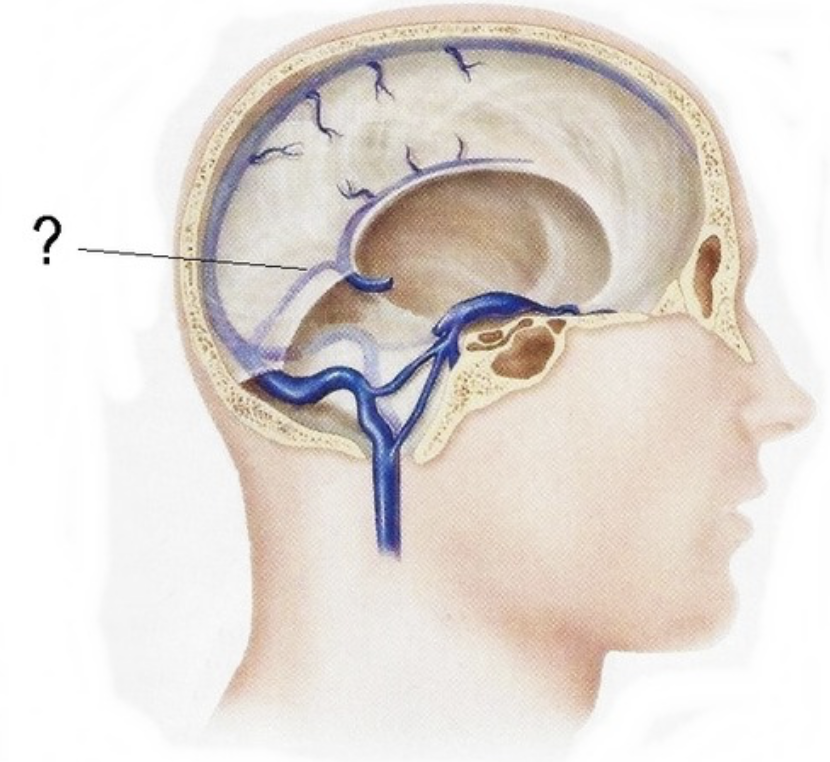
transverse sinus
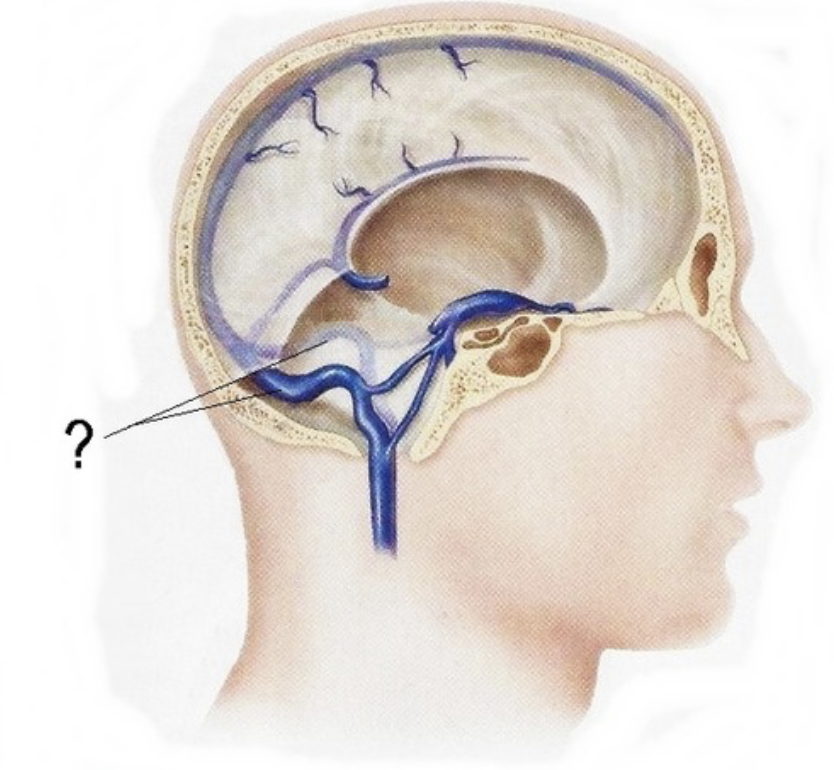
Confluens of sinuses
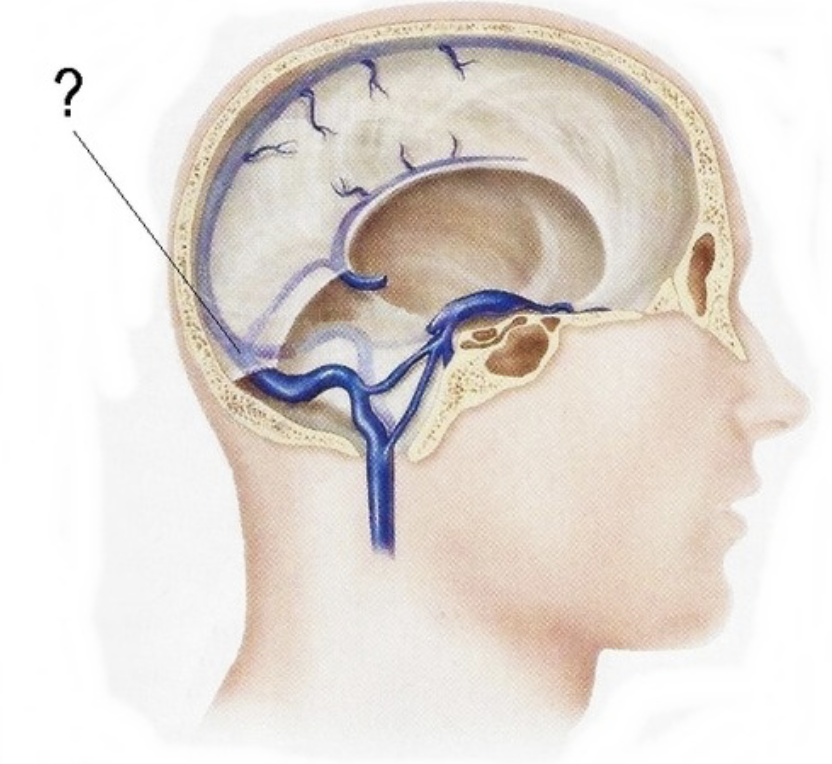
sigmoid sinus
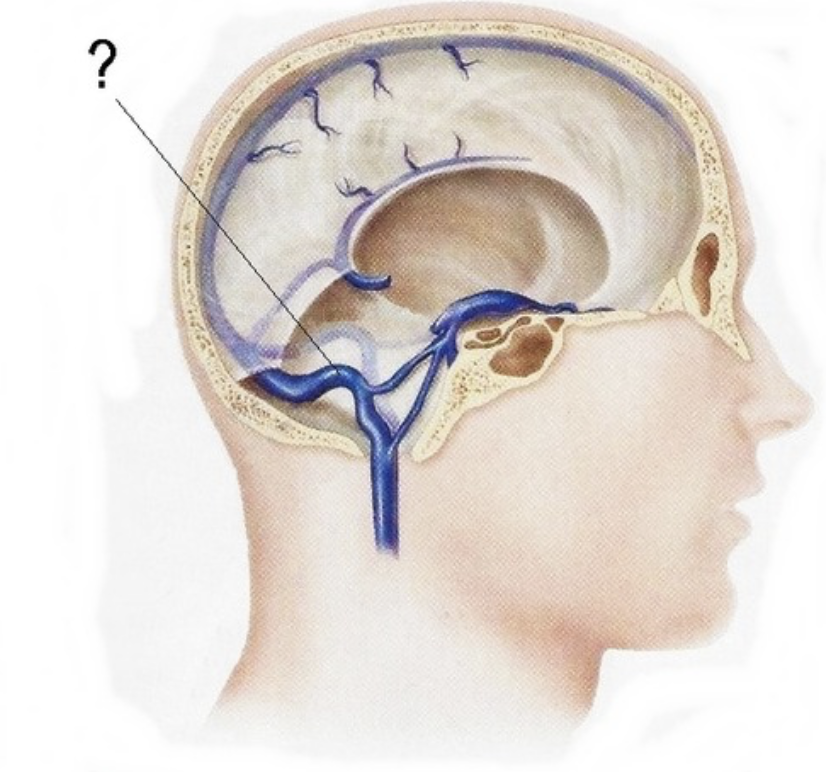
cavernous sinus
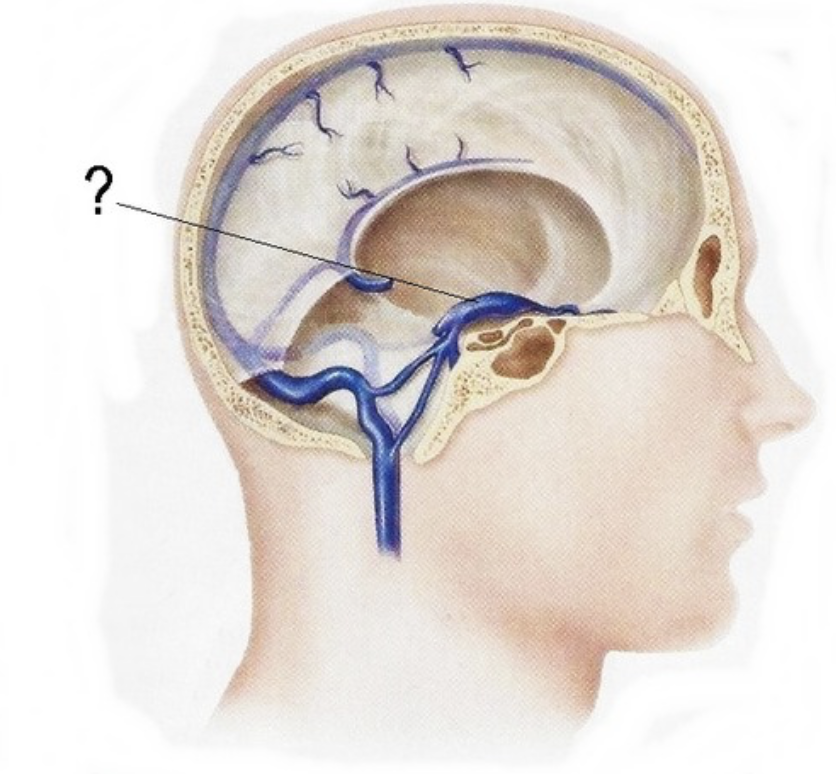
superior petrosal sinus
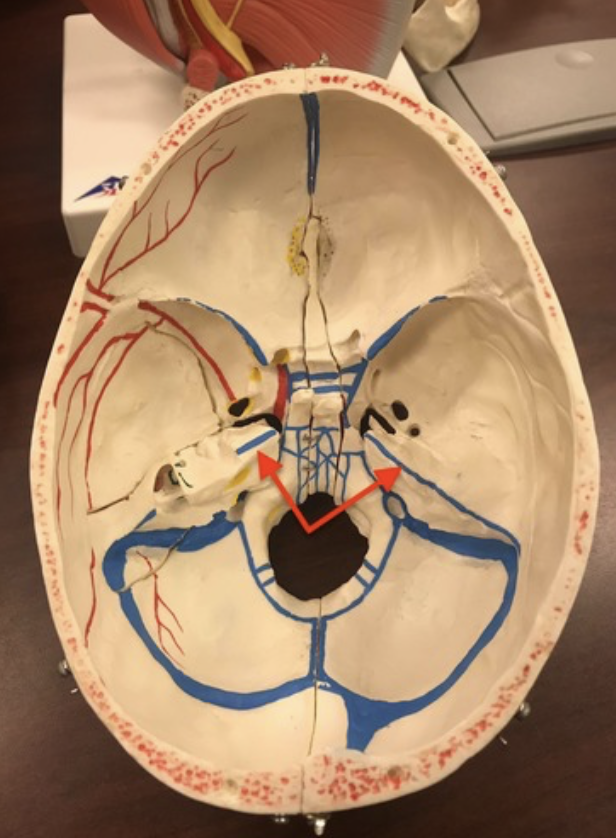
inferior petrosal sinus
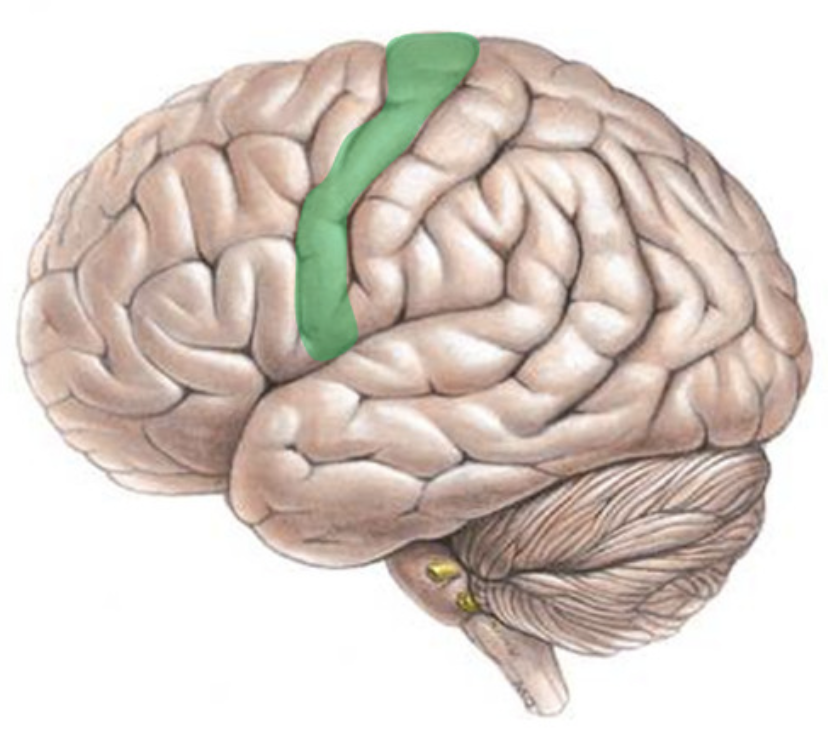
precentral gyrus
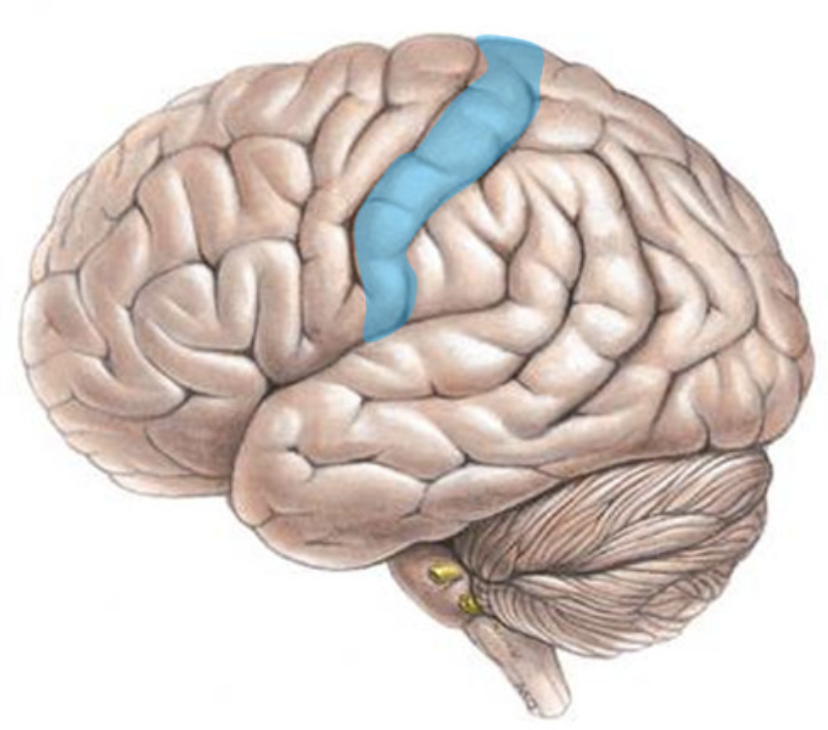
postcentral gyrus
superior frontal gyrus
middle frontal gyrus
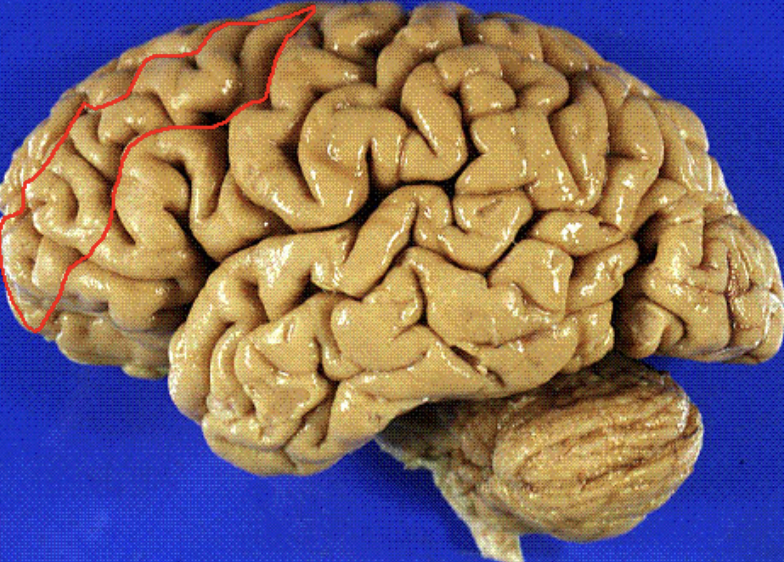
inferior frontal gyrus
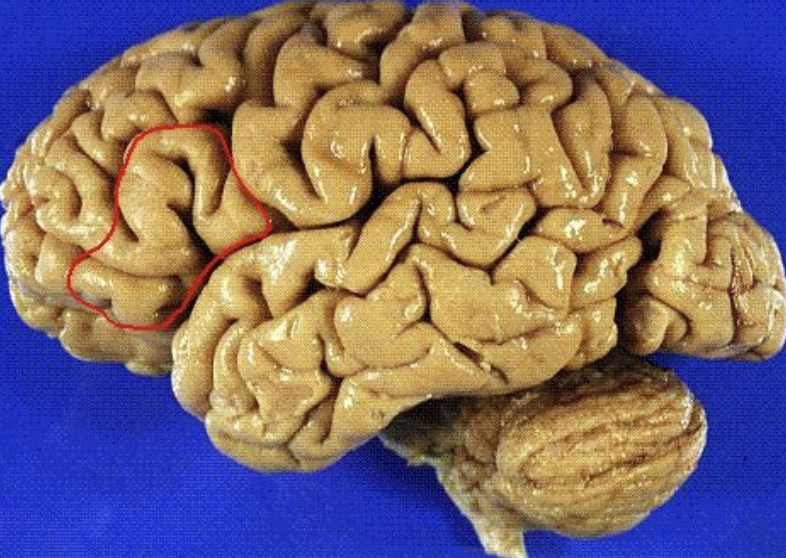
Broca's area
speech production
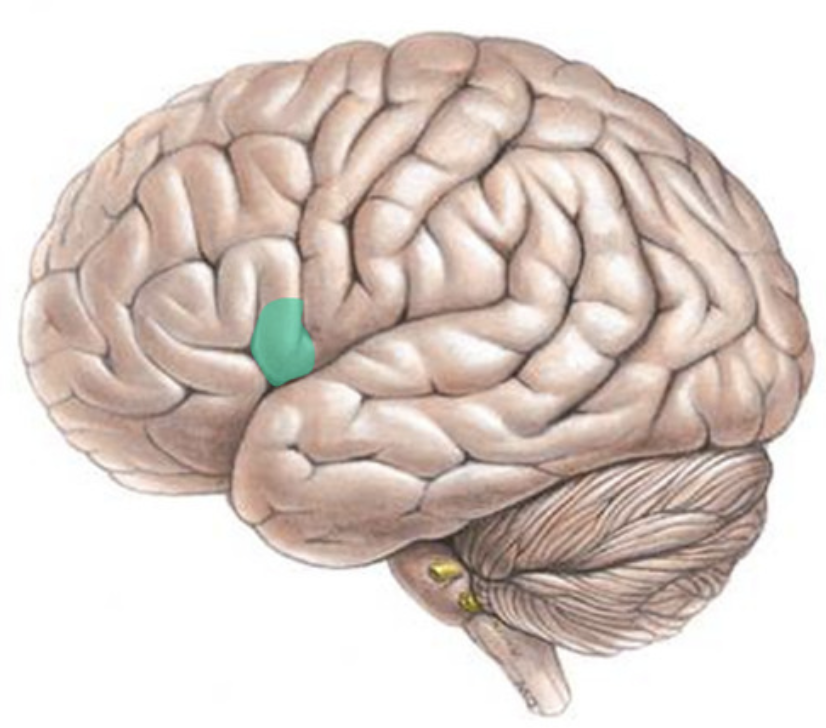
orbital inferior frontal gyrus
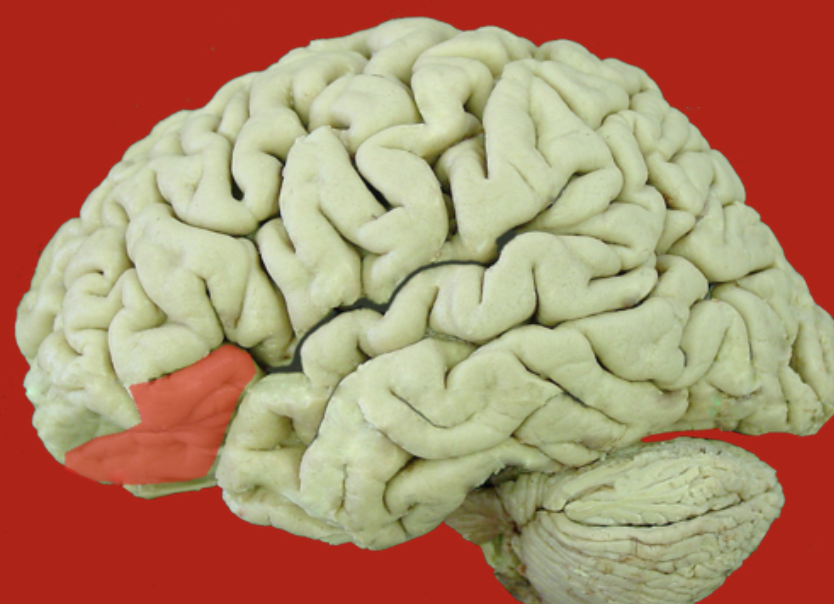
triangular inferior frontal gyrus
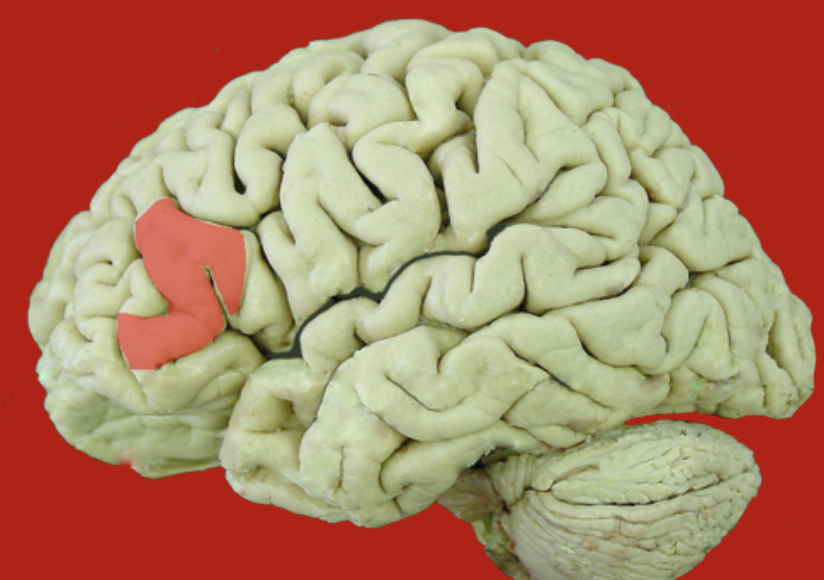
opercular inferior frontal gyrus
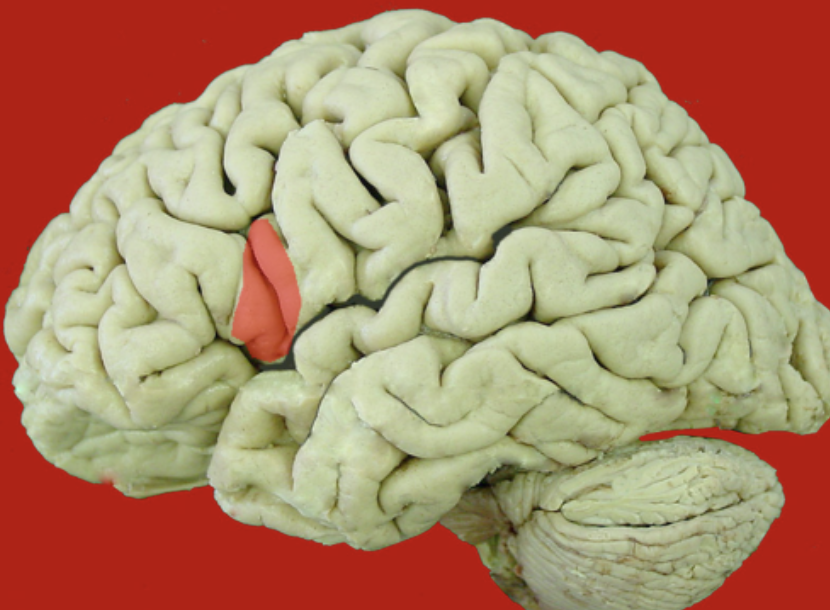
premotor cortex
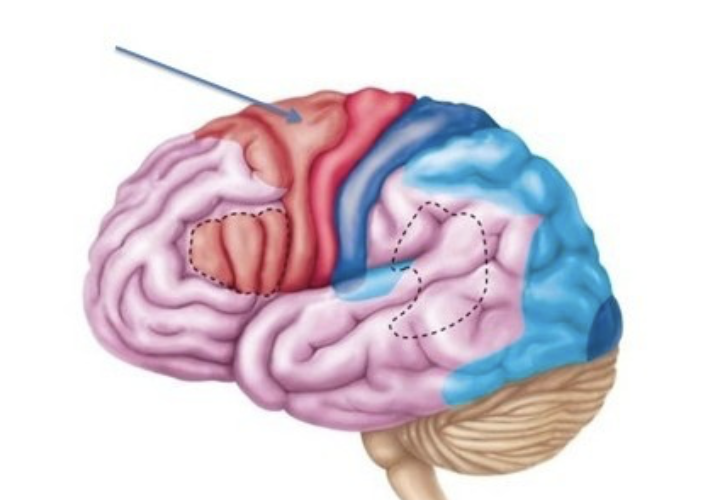
cingulate gyrus
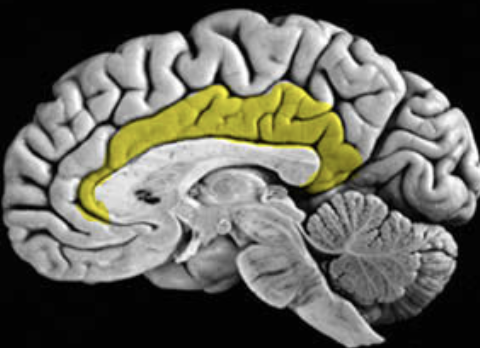
supplementary motor area
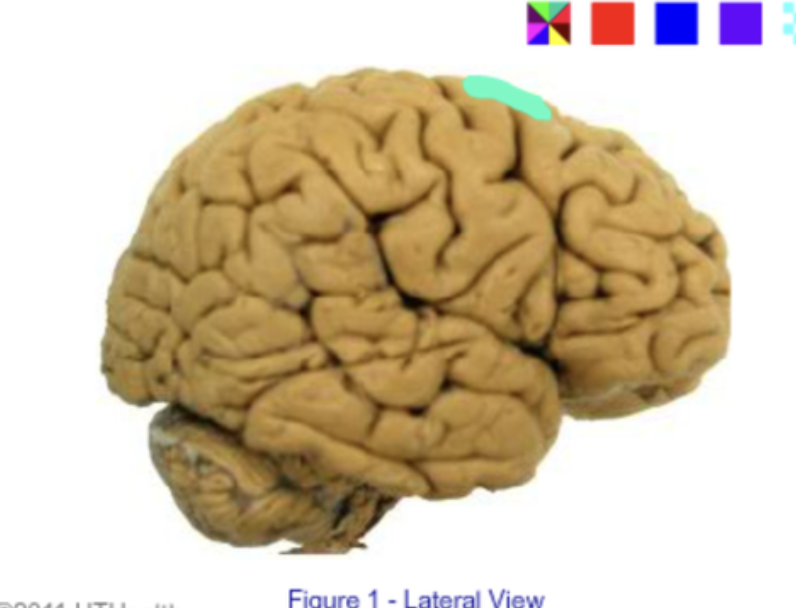
intraparietal sulcus
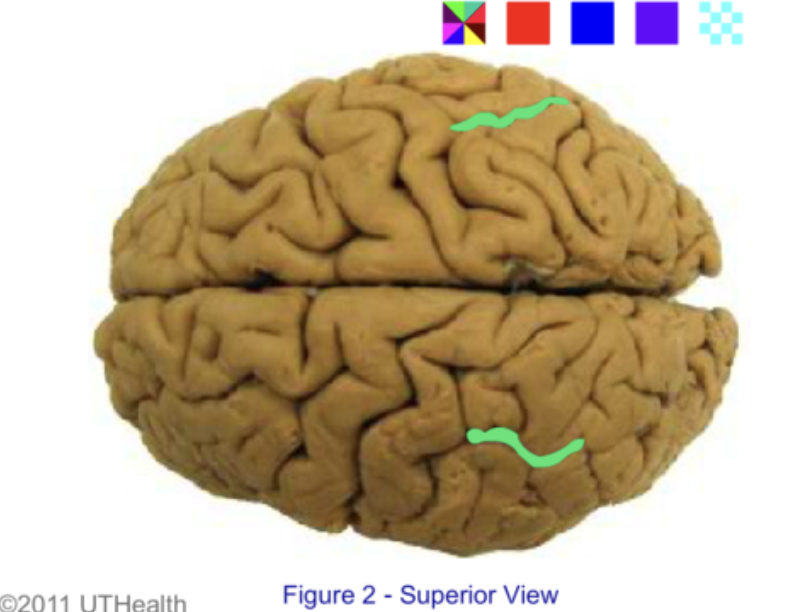
superior parietal lobule
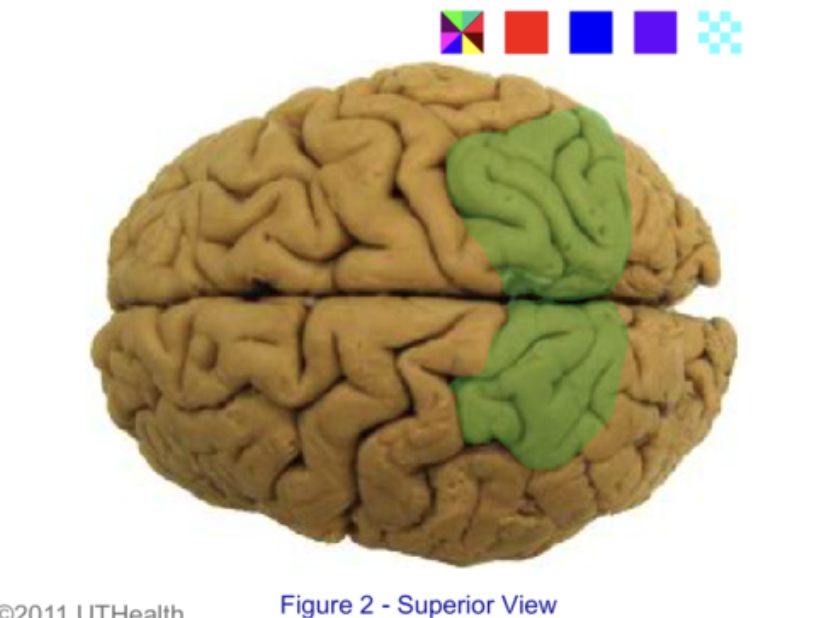
inferior parietal lobule
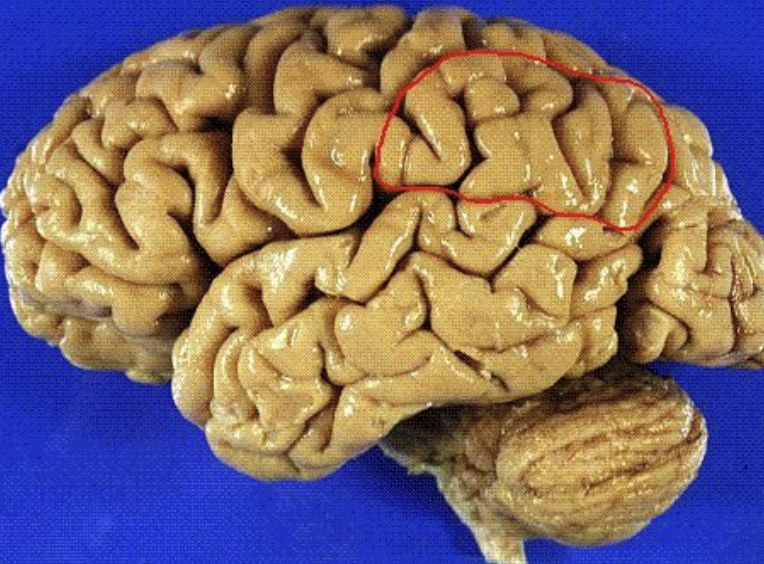
supramarginal gyrus
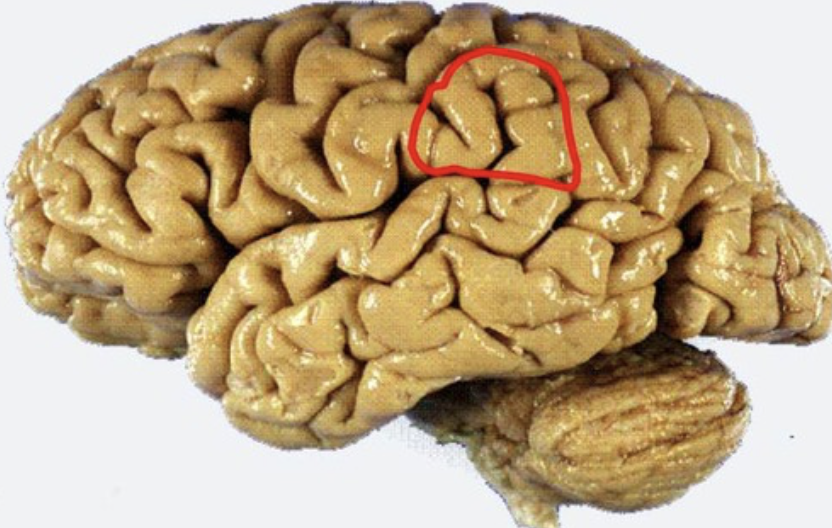
angular gyrus
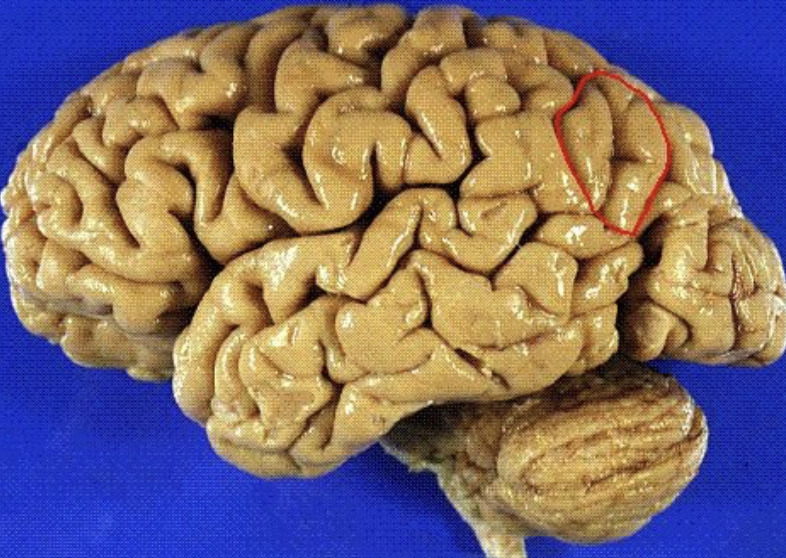
calcarine sulcus
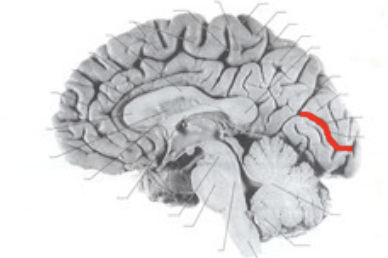
superior temporal gyrus
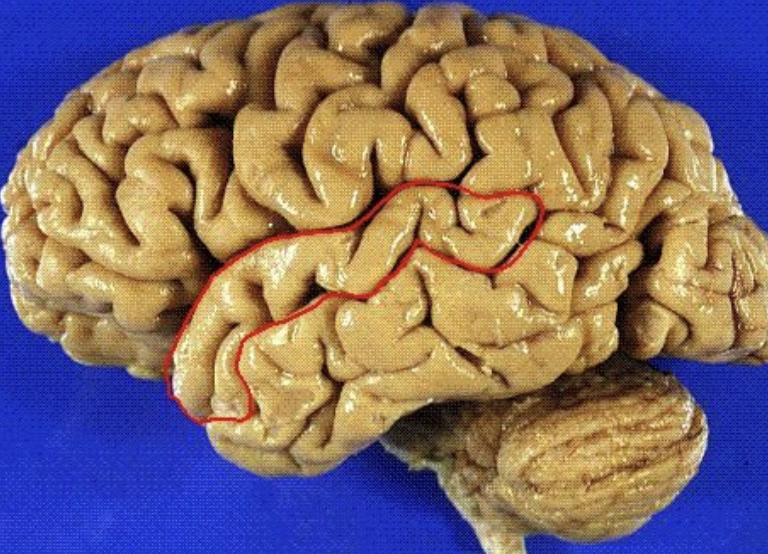
middle temporal gyrus
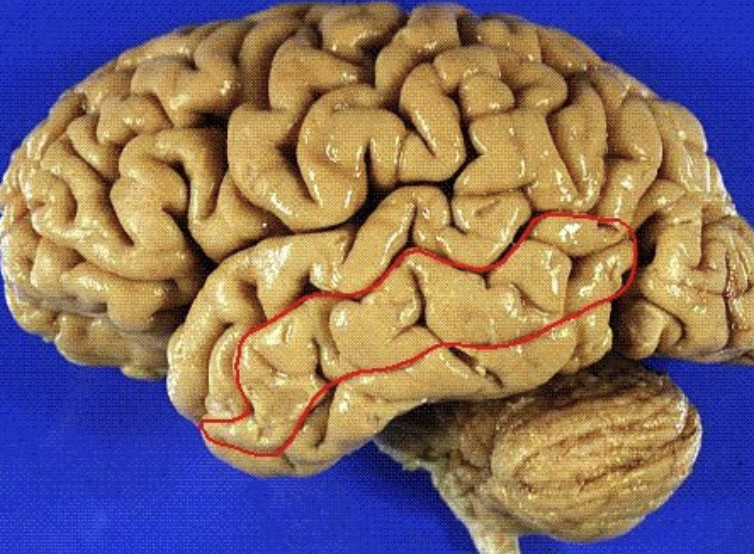
inferior temporal gyrus
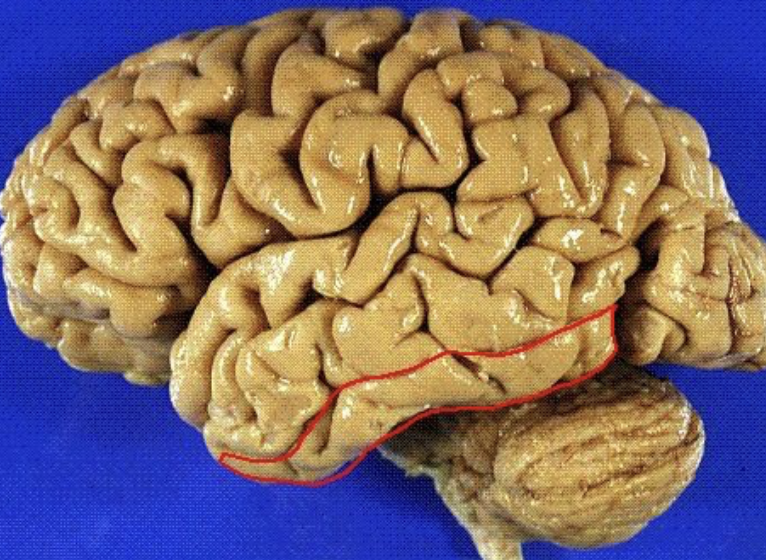
superior temporal sulcus
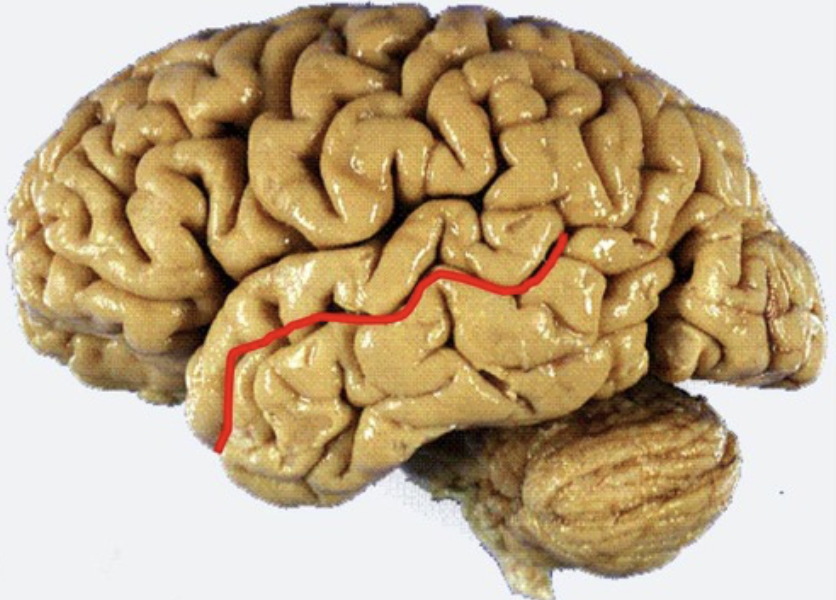
inferior temporal sulcus
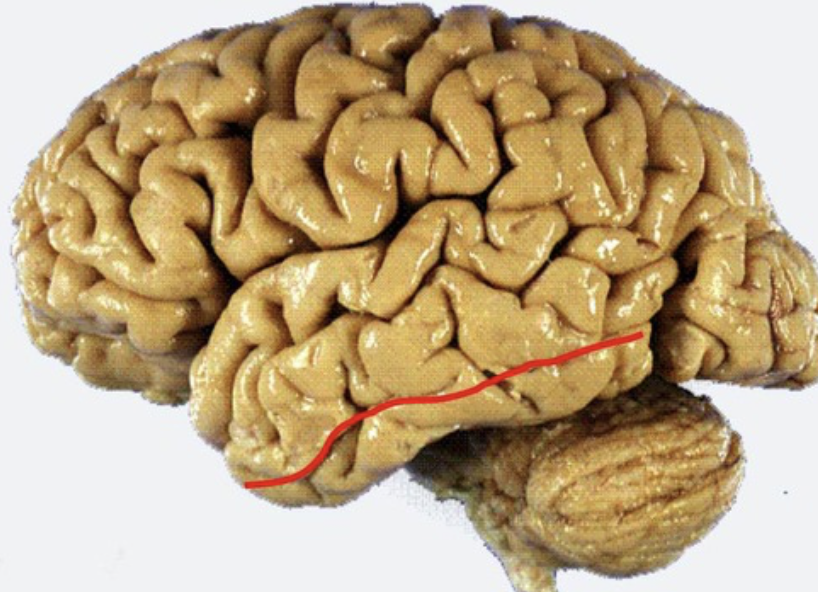
occipitotemporal sulcus