Week 3 - Embryonic Development Gastrulation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How is the bilaminar embryo formed? When does it form?
Due to proliferation and morphometric movement of the inner cell mass (ICM) cells
Develops when elongation occurs in pigs/ruminants in 2nd week of pregnancy
What are the two layers of the embryonic disc?
Top layer: epiblast
Bottom layer: hypoblast - continues to form a sheet lining the interior of the blastocyst
What does the yolk sac do?
Called “the first placenta” - absorbs nutrients for growing embryo
How is the trilaminar embryo formed?
Due to proliferation and morphometric movement of epiblast cells - forms the third germ layer, the mesoderm
Also when the primitive streak forms on dorsal surface of embryonic disc (responsible for formation of mesoderm)
What are the two areas mesoderm cells will not populate?
The future mouth and anus
What is Hensen’s node?
At cranial end of primitive streak, responsible for formation of the notochord
What is the notochord?
A solid rod of mesoderm cells expanding cranially from the primitive node and will form the mesoderm of the head
What are the 3 germ layers that will become the organ systems in the body?
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
What will the ectoderm form in the adult?
Single cell outer layer - will become epithelial surface (skin) and neural tissue (neuroderm)
What will the mesoderm form in the adult?
Multiple, loosely arranged cell layers in the middle - will become muscle, bone, blood, connective tissue, gonads, & kidneys
What will the endoderm form in the adult?
Single cell inner layer - will become gut lining, associated structures (ex: liver), trachea, & lungs
What are the 3 different derivatives of intra-embryonic mesoderm?
Paraxial (next to notochord) mesoderm
Intermediate mesoderm
Lateral mesoderm
What will the paraxial mesoderm form?
Becomes somites which will differentiate into dermatome (subcutis), myotome (muscles, ligaments), and sclerotome (vertebra, ribs)
What will the intermediate mesoderm form?
Forms lateral to somites - will become the urogenitial system (embryonic & adult kidneys, urinary duct system, gonads & repro duct system)
What will the lateral mesoderm form?
Splits into somatic (top) layer and splanchnic (bottom) layer - fluid accumulates between two layers and forms the intra- and extra- embryonic coelom with transient portals
Which parts will form the placenta?
Chorionic villi combined with the endometrium form the placenta
somatic layer forms the chorion of placenta
allantois expands into extra-embryonic coelom and makes contact w/ chorion for final placenta
What is the septum transversum?
Divides pleural and peritoneal cavities, will become the diaphragm - essential for continued development
How is the outer tube formed?
The somatopleure (ectoderm + somatic lateral mesoderm) closes over the body cavities forming the body wall
the disc-shaped trilaminar embryo undergoes tubulation
What is the inner tube?
The embryonic gut (intestinal) system - digestive tube
also forms when disc-shaped trilaminar embryo undergoes tubulation
midgut is still continuous with yolk sac via umbilical stalk
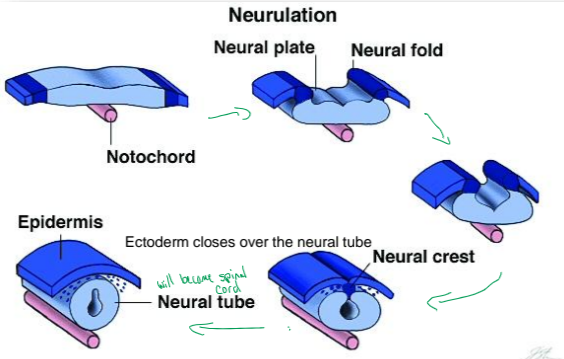
How is the neural tube formed? What will it become?
The primary neural plate folds inwards and the neural fold edges fuse
will become the spinal cord
What happens when the embryo undergoes flexion?
The embryo takes on it’s typical body form of a C-shape
the cranial cardiogenic area folds down and under itself, bringing the heart beneath the head area
a head and tail is now easily recognizable as are the limb buds