Lesson 5: Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules (Lipids, Proteins, NA)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Lipids are not a true ____, they are repeating units of ___
polymer, monomer
Lipids are made up of what elements?
C, H, and O (no set ratio)
Lipids are hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic
What are fats?
combination of glycerol and fatty acids
What is glycerol
a 3 hydroxyl group alcohol
What are fatty acids?
hydrocarbon chains of 16-18 carbons, end has a carboxyl group
How do fatty acids link to glycerol?
Dehydration reaction occurs between hydroxyl and carboxyl group
Triglycerides are known as ___
dietary fats
Fatty acids can be ___ or ____
saturated, unsaturated
Saturated means they are saturated in___ and are __bonded
hydrogens, single
Saturated or unsaturated?
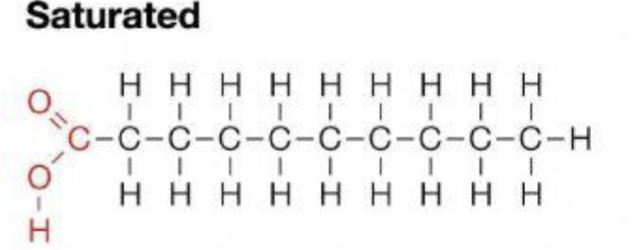
Unsaturated means they are ___ saturated with hydrogen and have ___ bonds
not, double
Saturated or unsaturated?
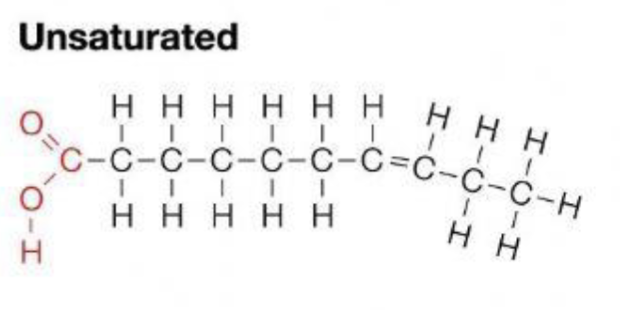
Saturated fats are straight so they ___ and ___. ____ at room temperature (ex. butter and animal fats on meat)
stack, clog, solid
Unsaturated fats are bent so they don’t ___ or ___. ___ at room temperature (ex. olive oil and avocado oil) They’re healthy for us
stack, clog, liquid
Cis or trans fats referes to what?
the placement of hydrogen atoms around the double bond
Trans fats are good or bad?
bad, they are lasting fats
What develops with a fatty diet in atherosclerosis?
plaque within the walls of your blood vessels
Phospholipids are essential for cells because they make up the ___
cell membrane
Phosopholipids are Amphipathic which means…?
they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
Bilayer
phospholipids self-organize into bilayers, hydrophobic tails together and hydrophilic heads face towards the water environment
Steroids are overall ____
hydrophobic
Majority of cell functions are carried out by ___ and we have ____
proteins, a lot
Proteins have a unique ___ shape
3D
Hormonal proteins
coordination of an organism’s activities (e.g. insulin)
Receptor proteins
response of cell to chemical stimuli
Contractile and motor proteins
movement (actin and myosin, muscle fibers)
Structural proteins
support (collagen, keratin for hair)
Enzymatic proteins
selective acceleration of chemical reactions
Defensive proteins
protection against disease
Storage proteins
storage of amino acids
Transport proteins
transport of substances
Enzymes
facilitate chemical reactions in living things, proteins that act as a catalyst
Catalyst
chemical agents that speed up chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Amino acids are the monomers of ___
proteins
Proteins are built from the same set of ___
20 amino acids
Amino acids are composed of what three groups?
amino, carboxyl, and r group (side chain)
9/20 amino acids are (mainly C-H) ___
hydrophobic
6/20 amino acids are (have O or OH/Polar) ___
hydrophillic
The backbone of a protein is the ___
linked chain of peptide bonds
First amino acid = amino end = ___
n-terminus (engine)
Last amino acid = carboxyl end = ____
c-terminus (caboose)
Four levels of protein structure (folding)
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
Primary phase
amino acid sequence in polypeptide chains
Secondary phase
alpha-helices and beta-sheets
Tertiary phase
gives it its 3D shape, side chains interact
Quaternary phase
several tertiary to make one protein with one specific function (not all have to go to this stage)
Sickle Cell Disease
primary phase mishap where there is a substitution in one amino acid for hemoglobin giving it a different shape
How often does protein folding happen?
spontaneously
What are chaperons?
proteins(help shy proteins in folding)
What are some ways proteins can be denatured?
pH imbalance, temperature change, and salinity change
Can proteins refold once being denatured?
yes
Nucleic Acid Monomer
nucleotide
Nucleic Acid Polymers
DNA & RNA
What does DNA do?
holds the codes for your protein to code you
What does RNA do?
Assist in protein production