anatomy final high yield review of exams 1-3
1/444
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
445 Terms
fundamental relationship between joint stability and movement
inverse relationship: high stability means less movement, and vice-versa.
fundamental rule about how muscles generate movement
muscles ONLY pull; they cannot push
difference between a muscle's origin and insertion
the origin is the stable attachment point, while the insertion moves towards the origin during contraction.
basic components involved in a reflex arc
Sensory input (afferent nerve), interneuron (in spinal cord), and motor output (efferent nerve).
conscious action vs reflex?
conscious actions involve brain analysis and planning; reflexes are predetermined responses at the spinal cord level without brain analysis.
isotonic vs isometric muscle contractions
Isotonic involves a change in muscle length; isometric produces force without changing muscle length (no movement).
two types of isotonic contractions
- Concentric (muscle shortens as it produces force)
- Eccentric (muscle lengthens while producing force).
'all or none' principle as it applies to a motor unit.
If the nerve innervating a motor unit fires, all of the muscle fibers connected to that nerve will contract, or none will.
how does the body increase the force produced by a muscle?
by recruiting more motor units (activating more muscle fibers).
What is the function of afferent nerves?
They carry sensory information TO the CNS.
What is the function of efferent nerves?
They carry motor commands FROM the CNS to muscles or glands.
general effects of the sympathetic nervous system and where are its ganglia located?
It mediates the 'fight or flight' response; its ganglia are close to the CNS (sympathetic trunk)
general effects of the parasympathetic nervous system and where are its ganglia located?
It mediates the 'rest and digest' response; its ganglia are near the target organs.
primary functions of fascia?
It protects and separates tissues, acting as 'wrapping paper' and forming compartments.
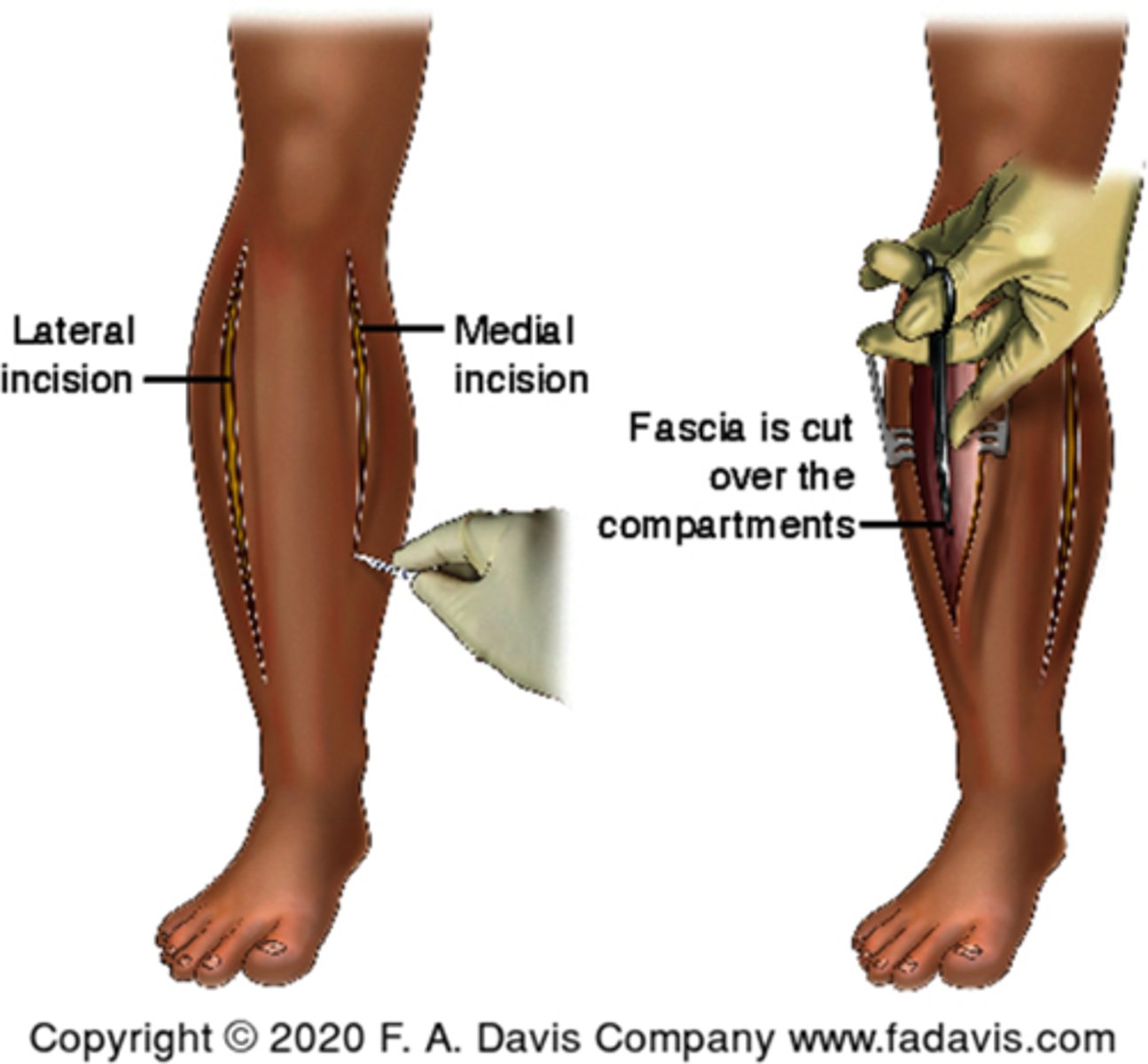
why is compartment syndrome a significant clinical concern related to fascia?
Fascial compartments can prevent swelling from spreading, but also trap pressure, compressing blood vessels and nerves.
primary role of synovial fluid in a joint?
To lubricate the joint, reducing friction
why is joint movement crucial for the health of articular cartilage?
Articular cartilage is avascular and relies on joint movement to circulate synovial fluid for nutrient delivery.
What is a bursa and its main purpose?
A fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between structures that move repetitively past each other.
What are the two main causes of bursitis?
direct contact trauma or repetitive friction/motion.
key characteristics of arteries.
Have a pulse, contain smooth muscle (for vasoconstriction/dilation), and carry blood away from the heart.
tonic contraction
A muscle maintains some level of tone/excitation even when relaxed.
what is the force differential during an eccentric contraction?
the resistance to movement is greater than the force the muscle is producing.
primary role of Schwann cells
To produce myelin, which insulates axons for efficient nerve conduction.
what are retinacula made of and what is their function?
they are thickened forms of fascia that hold tendons in place.
what defines a sesamoid bone, and what is the body's largest example?
a bone embedded in a tendon; the patella is the largest.
functional difference between a tubercle and a tuberosity
A tuberosity is large, a tubercle is small.
foramen vs meatus vs sinus.
Foramen: hole for passage
Meatus: empty/hollow hole
Sinus: empty cavity inside a bone
What is the primary function of the epiphyseal line (growth plate)?
the site where most bone lengthening occurs.
what is the periosteum and its function?
A fibrous connective tissue covering the bone, containing blood vessels.
how much movement is allowed in a syndesmosis, such as between the ulna and radius?
a little bit of shifting, but much less than a synovial joint.
what specific movements define a saddle joint?
flexion, extension, and rocking back and forth in abduction and adduction.
what specific movements define a modified hinge joint?
one segment pivoting on the other in a flexion-extension manner
what unique histological features characterize cardiac muscle?
Y-shaped fibers connected by intercalated discs.
functional advantage of pennate muscle architecture
allows for more stability and structural strength.
functional advantage of longitudinal muscle architecture
allows for very quick movement.
What structure allows arteries to control blood flow via vasoconstriction/vasodilation?
the smooth muscle in their walls.
mechanism of the musculovenous pump.
rhythmic muscle contractions compress veins, moving blood past one-way valves.
how does the lymphatic system move lymph, given it has no inherent pump?
relies on one-way valves and muscle contractions of adjacent muscles.
what type of information primarily enters the spinal cord through the dorsal horn?
afferent (sensory) information from the periphery.
what type of information primarily exits the spinal cord through the ventral horn?
efferent (motor) information going out to muscles.
what is unique about the pia mater layer of the meninges?
It's the deepest layer that adheres directly to the nervous tissue.
'rule of thumb' regarding anatomical variations?
Veins vary the most; nerves vary the least.
clinical difference in healing outcomes for incisions made parallel vs. perpendicular to tension lines.
Parallel: better healing, less scarring; Perpendicular: more gaping, higher scar risk.
purpose of the Allen's test
to check for preserved patency of radial and ulnar arteries.
how is spongy bone described under a microscope?
more open/porous compared to dense compact bone.
primary functions of the lower limb
support body weight, enable locomotion, and maintain balance.
when does the lower limb typically develop in gestation compared to the upper limb?
about a week later, around the 5th embryonic week.
Barlow test
If the hips will dislocate easily.
longest and heaviest bone in the human
femur
largest bone that makes up the hip
ilium
primary function of the membrane that closes the obturator foramen
minimize bone weight
main clinical advantage of an interosseous (IO) infusion
It provides super fast vascular access.
perfect location for an IO infusion in the lower limb
The proximal tibia, due to minimal tissue and large landmarks.
how does the deep fascia contribute to venous circulation?
It enables muscles to more effectively compress veins.
two structures that primarily form the iliotibial (IT) band
the aponeurosis of the tensor fascia latae and gluteus maximus.
common cause of compartment syndrome
trauma leading to hemorrhage, edema, and inflammation.
main clinical intervention for compartment syndrome
fasciotomy
superficial veins run ______ of arteries compared to deep veins
independent of arteries.
what type of veins have more valves, superficial or deep?
deep veins.
most significant clinical use for the great saphenous vein
It is commonly used for coronary artery bypass grafts (CABG).
only superficial spot on the femoral artery where a pulse can be reliably palpated
In the femoral triangle.
what is a syndesmotic fracture?
A tear of the strong interosseous membrane between the tibia and fibula.
cartilaginous structure that separates the ilium, ischium, and pubis before fusion
triradiate cartilage.
general innervation for the anterior thigh muscles?
femoral nerve
general innervation for the medial thigh muscles?
obturator nerve
pectineus innervation
1/2 obturator 1/2 femoral
general innervation for the posterior thigh muscles
tibial division of the sciatic nerve
what is uniquely described as the 'chief hip flexor' and a powerful muscle?
iliopsoas.
the largest and most powerful muscle in the body, stronger than the hamstrings.
quads
unique innervation pattern for the hamstring portion of the adductor magnus
It is supplied by the sciatic nerve, unlike most adductors.
three neurovascular structures that pass through the adductor canal
femoral artery, femoral vein, and saphenous nerve.
the three borders of the femoral triangle?
The inguinal ligament (superior), the lateral border of adductor longus (medial), and the sartorius (lateral).
largest branch of the femoral artery
profunda femoris artery
which artery uniquely supplies the head and neck of the femur?
medial circumflex femoral artery
what is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus?
the femoral nerve.
clinical significance of the femoral artery in the femoral triangle?
Its pulsations are palpable, making it a key site for pulse assessment and cannulation.
why is the femoral ring considered a weak area
It is a common site for femoral hernias
In which gender are femoral hernias more common?
females, due to a wider pelvis.
anatomical relationship of the piriformis muscle to the sciatic nerve
sciatic nerve typically exits from underneath the piriformis.
piriformis syndrome
pain in the buttocks and posterior thigh caused by the piriformis muscle compressing the sciatic nerve.
what is the safe area for intragluteal injections to avoid the sciatic nerve?
The superolateral quadrant, superior to the line connecting the psis to the greater trochanter.
most common origin point for the hamstring group
the ischial tuberosity (with the exception of the biceps femoris short head).
what two nerves does the sciatic nerve bifurcate into at the superior angle of the popliteal fossa?
The tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve.
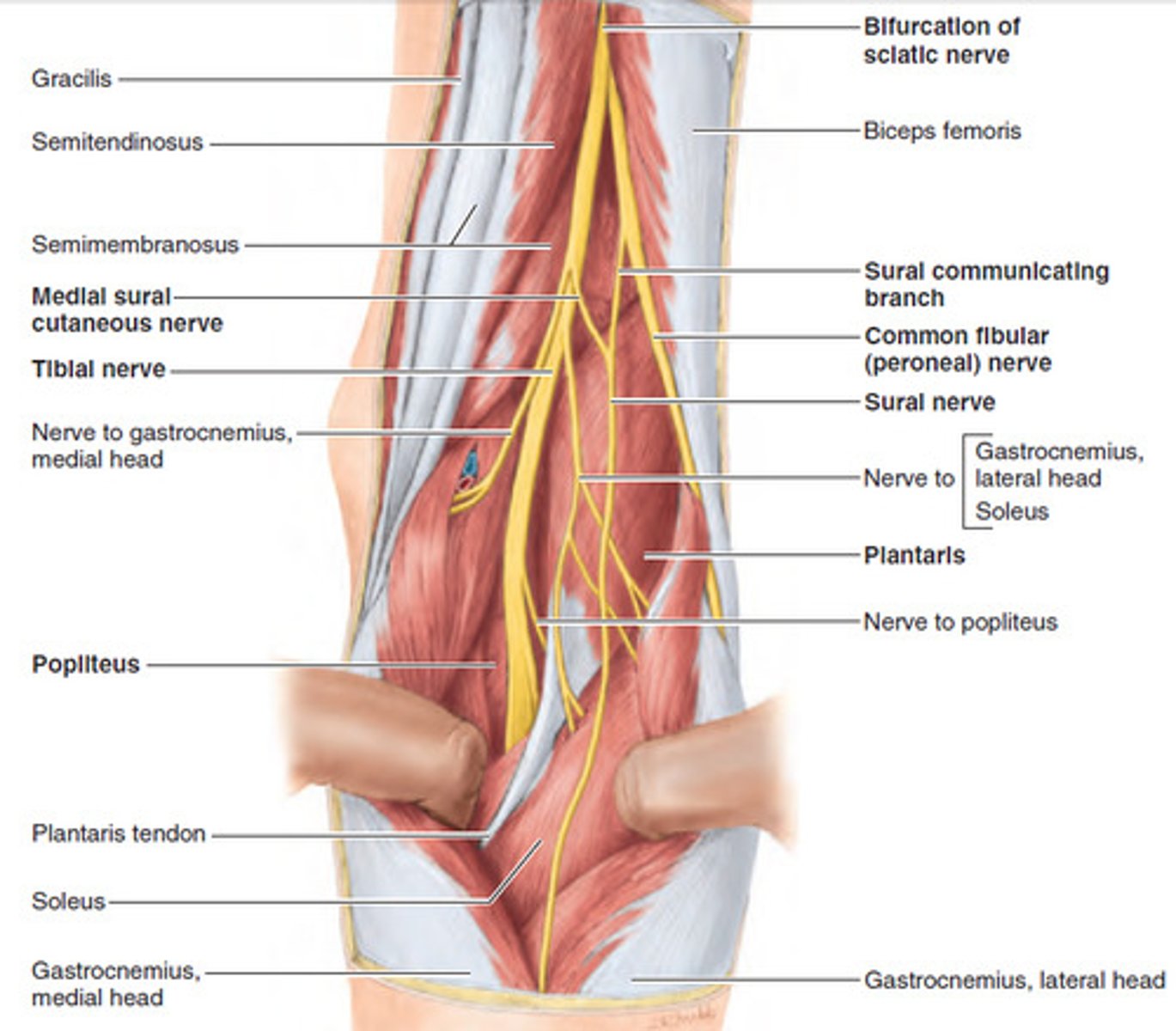
four neurovascular structures found within the popliteal fossa from medial to lateral
popliteal artery
popliteal vein
tibial nerve
common fibular nerve
*in that order, common fib is most lateral
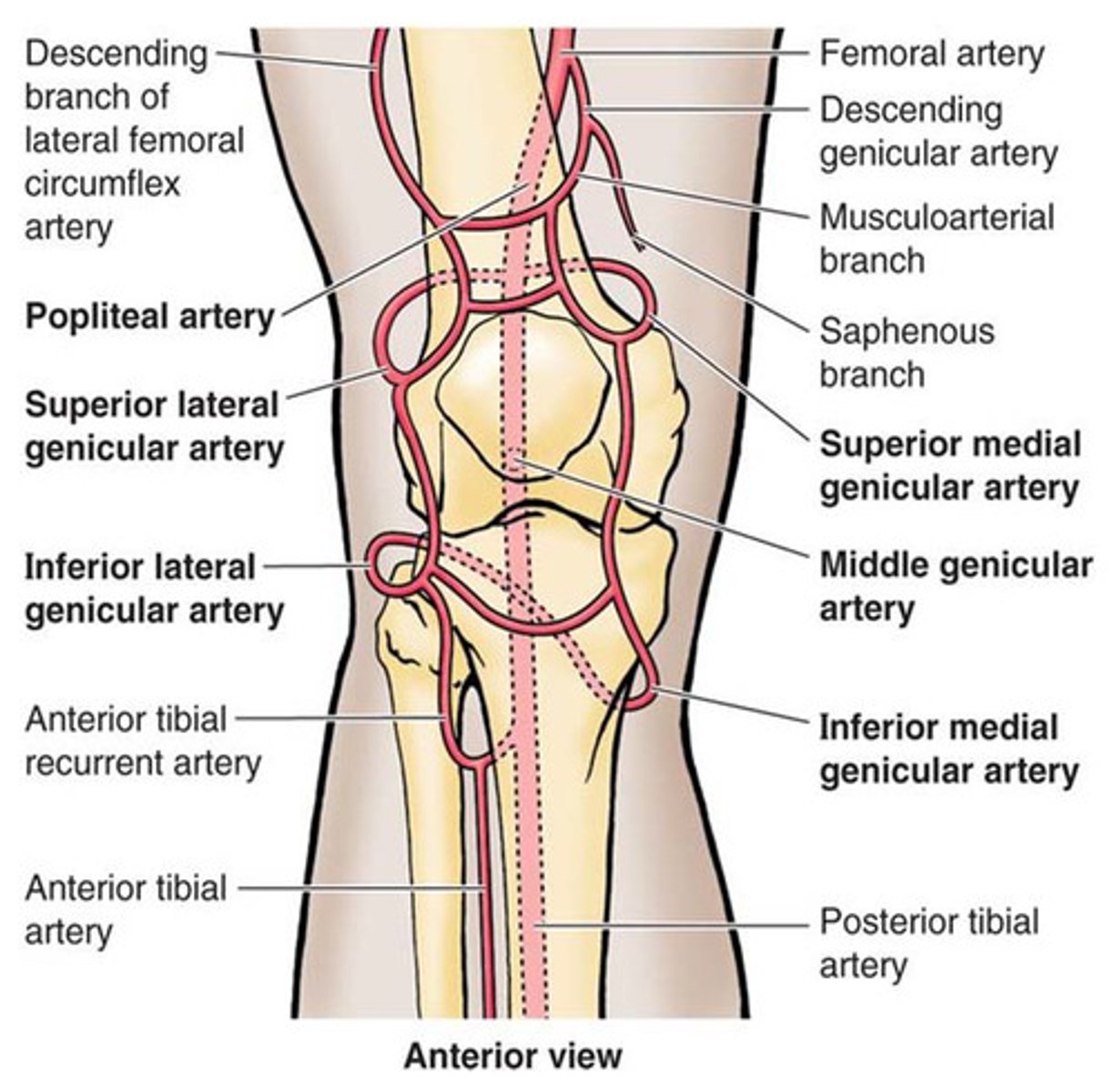
genicular arteries ensures arterial flow around the knee even during _____
flexion
*bc they form an anastomosis
primary nerve for the anterior compartment of the leg
deep fibular nerve.
major artery supplying the anterior compartment of the leg
anterior tibial artery
'triceps surae'
gastrocnemius and the soleus muscle
soleus vs gastrocnemius muscle fibers?
Soleus has more type I (slow-twitch) fibers for endurance
gastrocnemius has more type II (fast-twitch) fibers for explosive power.
unique characteristic of the plantaris muscle regarding its presence in the population?
It is missing in 5-10% of the population.
primary function of the popliteus muscle at the knee?
It 'unlocks the knee' by internally rotating the tibia from terminal extension.
deepest muscle in the deep posterior compartment of the leg, known for fixing the medial longitudinal arch?
the tibialis posterior.
the mnemonic 'tom dick an' harry' is used to remember what structures
structures passing behind the medial malleolus: tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, posterior tibial artery, tibial nerve, flexor hallucis longus.
major artery supplying the posterior compartment of the leg
posterior tibial artery
common term for a tibialis anterior strain
shin splints.
most common causes of 'shin splints'?
Overuse or insufficient recovery, leading to inflammation of connective tissue or stress fractures.
unique audible clinical sign of a ruptured calcaneal (achilles) tendon?
an audible snap, often described as a gunshot.
where can the posterior tibial pulse be palpated?
Between the posterior surface of the medial malleolus and the medial border of the calcaneal tendon.
classic symptom of plantar fasciitis?
Pain when getting out of bed that subsides with activity, and worsens with passive extension of the great toe.
What bony abnormality may develop in cases of plantar fasciitis?
Heel spurs.