U4 APES Earth Systems
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Earths Core
innermost layer of the planet
(nickel & iron) inner core is solid.
The outer core is liquid. The interaction between
the two form magnetic field
Mantle
Above core. Contains magma where
convention currents occur.
The spongy Material movement, drive plate tectonics
Crust
outermost layers of the planet;
thinnest layer contains basement rock of
ocean & continents.
Lithosphere
The brittle outermost layer of the Earth
Asthenosphere
Outer part of the mantle (Semi-molten, Flexible rock)
Crust (continental)
Mostly granite, Si, O
Crust (Oceanic)
Mostly Basaltic, Fe & Mg
Convection
It involves hot rock rising and cooler rock sinking, creating convection currents.
Hot spots
Places where molten material from the mantle reach the lithosphere
Continental Drift
The theory that the Earth's continents were once connected as a single supercontinent called Pangaea, and over millions of years, they slowly moved apart to their current positions.
Theory of Plate tectonics
The theory of plate tectonics explains how the Earth’s outer shell (the lithosphere) is divided into large, rigid plates that move over the semi-fluid asthenosphere below. These movements are responsible for many geological phenomena like earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountain ranges.
Divergent Plate boundaries
When plates move apart from one another
Convergent Plate boundaries
When the plates move towards one another
Transform Fault Boundaries
Plates Move sideways past eachother
Volcano formation
As a plate moves over a hot spot, rising magma forms a volcano
Faults
A fault is a crack or fracture in the Earth’s lithosphere where two blocks of rock have moved relative to each other. Faults are created by stress and are often the cause of earthquakes.
Earthquakes
occurs when the rocks across of the lithosphere unexpedly rupture along a fault
Soil
Soil is the top layer of Earth’s surface where plants grow. It’s made up of a mixture of minerals, organic matter (like decayed plants and animals), air, and water.
Soil formation
Soil formation begins
when bedrock is broken
by physical, chemical, &
biological processes
called weathering
Soil components
Pore space 50% (air/water)
Soil Space 50% (Mineral matter & Organic Matter)
Soil Properties (Texture)
Clay, Sand, & Silt
(Ex. If a soil sample contains: (Silty Clay)
30% clay
10% sand
60% silt
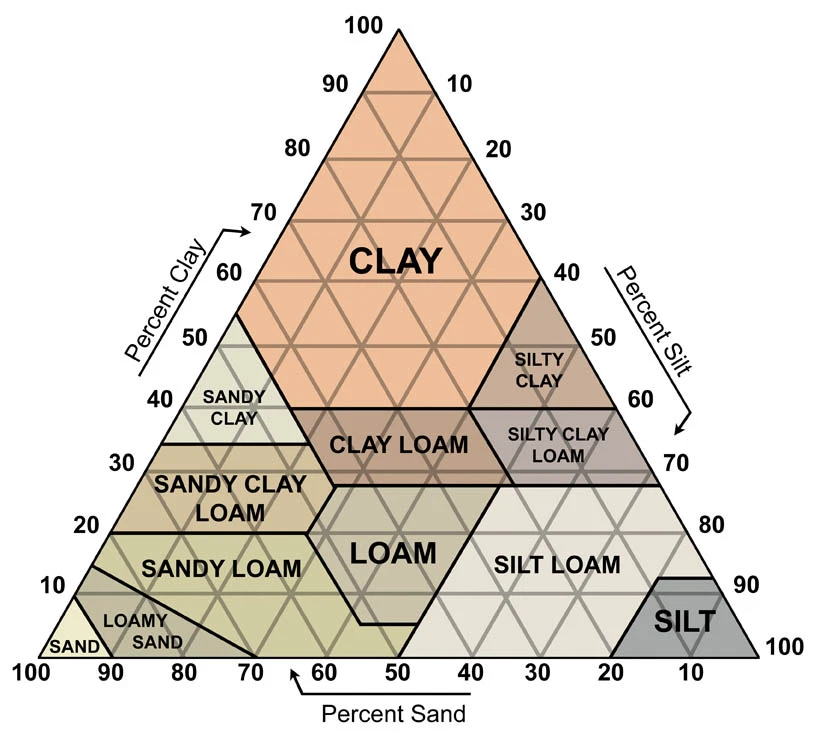
Soil Texture
Largest → Smallest
Sand → Silt → Clay
Sand = easily seen
silt = size of flour
clay = electronic microscope
O horizon
composed of organic detritus in various
stages of decomposition.
A horizon
topsoil, a zone of organic material &
minerals that have been mixed together.
E horizon
Zone of leaching, found in some acidic soils
under the O horizon or, less often, the A horizon.
B horizon
primarily of mineral material with very little
organic matter.
C horizon
least-weathered soil horizon, always
beneath the B horizon, & similar to the parent material.
Atmospheric composition
78% Nitrogen
21% Oxygen
1% Other gases
Layers of the Atmosphere
Troposphere (Closest to surface)
Stratosphere (Further out)
Atmospheric Composition
78% Nitrogen gas (N2)
21% Oxygen gas (O2)
1% Other Gases
Layers of the Atmosphere
Troposphere (Closest to ground level)
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Exosphere (Farthest from ground level)
Oceans + Atmosphere
The 2 main systems that distribute heat from equator to polar regions
Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis Effect is the way the rotation of the Earth causes moving air and water to curve instead of moving in a straight line.
Atmospheric Cells Part 1
Clouds from in areas where air is rising and theres typically a wet climate
Atmospheric Cells Part 2
Areas with no clouds, the air is sinking and typically has Dry climate
Effects of rising air
Where air is rising an area of low pressure is created, so theres an increase of rainfall
Effects of descending air
Where air is descending an area of high pressure forms giving large clear skies & little rain fall
Solar radiation
the energy emitted by the sun that reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves, primarily in the form of visible light and infrared radiation.
Reasons for seasons
The Earth is tilted on its axis 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the Sun.
This tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive different amounts of sunlight during the year.
The tilt stays constant as Earth orbits the Sun, so the orientation of each hemisphere changes with the seasons.
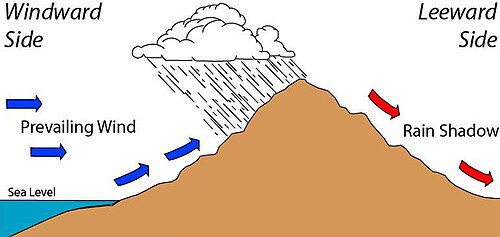
Rain shadow effect
a dry area on the leeward side of a mountain range that forms when moist air rises, cools, and loses its moisture on the windward side.
ENSO (El Niño–Southern Oscillation)
a natural cycle where the Pacific Ocean and atmosphere shift between three phases: El Niño, La Niña, and Neutral.
Upwelling
nutrient rich cold water rises to the surface
ENSO (El Nino conditions)
WEAK trade winds
warming of ocean
surfaceIndonesia: less rainfall
pacific ocean: more
rainfallsouth america: warmer
surface waterupwelling decreases -
fish move away or dieAustralia: drought
ENSO (La nina conditions)
STRONG trade winds
cooling of ocean surface
indonesia: rainfall
increasespacific ocean: rainfall
decreasesupwelling drastically
increases
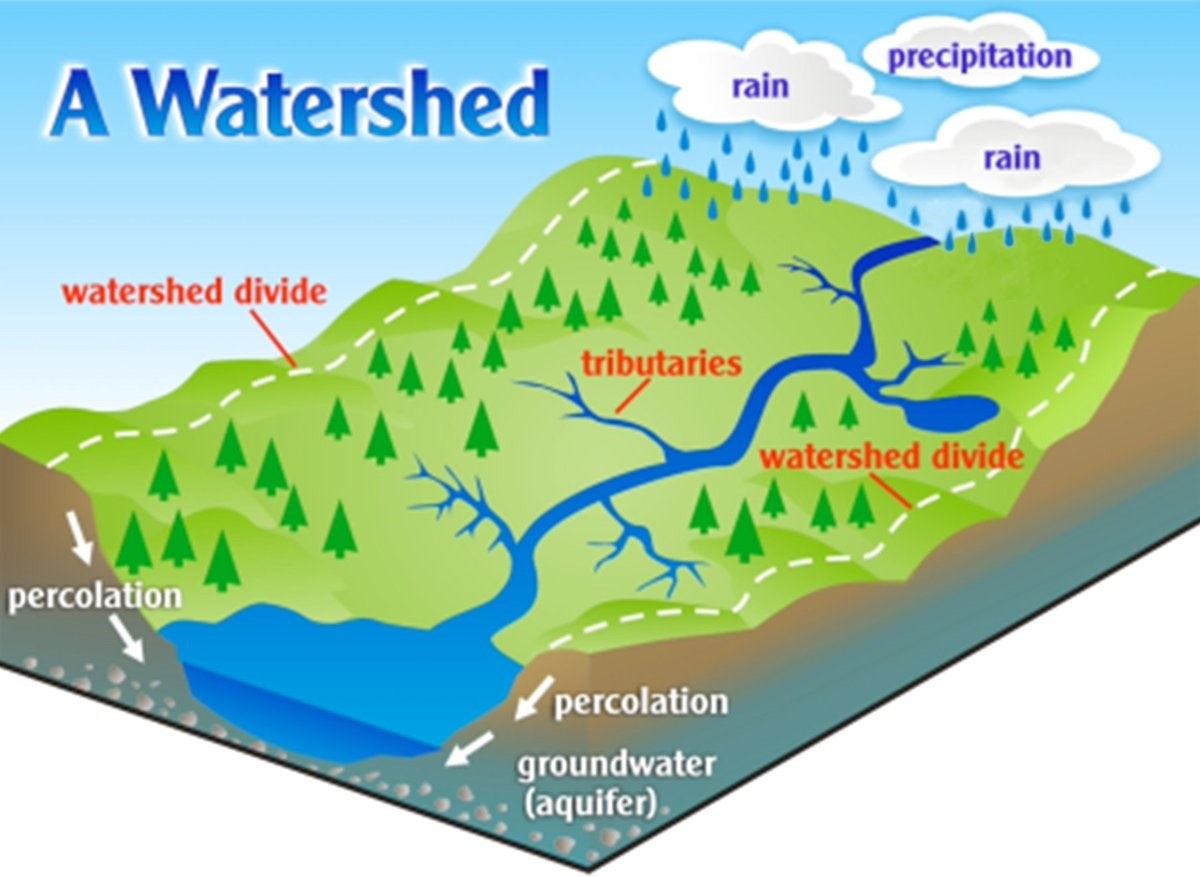
Watershed
an area of land that drains all the water that falls within it into a common body of water, like a river, lake, or ocean.