Kingdom Bacteria (Eubacteria)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Bacteria Basic Information
they are unicellular micro-organisms ranging in length (few micrometers to half a milimeter)
come in a variety of different shapes
found in almost all ecosystems on earth
Why is bacteria important
it’s important to many nutrient cycles and are important decomposers of organic material
found all over earth and even covering and living in the human body
some bacteria is pathogenic and cause disease
Bacteria History
Bacteria first observed by Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
bacteria is greek for small stuff
Robert Koch and Louis Pasteur first to discover that bacteria caused diseases
first antibiotic used to treat bacterial disease was made by Paul Ehrlich (used to treat syphilis)
Evolution of bacteria
thought by some to be the first forms of life abt 4 billion years ago
believed that domain Archaea and Eukarya evolved from bacteria
poor fossil record, scientists unable to determine from what bacteria evolved
Morphology (study of living organisms)
bacterial cells are prokaryotic
lack a nucleus and complex organelles
have a cell membrane and a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan (combo of protein and carbohydrate)
making it different from cell wall of Archaea and Eukaryotes
Morphology continued
bacteria use flagella or pili for movement and interaction with the enviorment
shapes:
bacillus- rod
coccus- sphere
spirillus- spiral
vibrio- boomerang
spirochaetes- tight coils
prefixes are added to the shapes to indicate the living arrangement of the bacteria
strepto: chain of bacteria
staphylo: grape like cluster
More about bacteria cell wall
gram stain: type of stain used to visualize bacteria cell wall structure
cell wall structure:
bacteria are classified as gram-positive or gram-negative based on chemical and physical properties of their cell wall
gram + bacteria: thick layer of peptidoglycan in cell walls, retains crystal violet stain (appears purple)
gram - bacteria: thinner peptidoglycan layer and lipoproteins and an outer membrane, allowing crystal violet to be washed out during decolorization step (appears pink/red), harder to treat with antibiotics/ more infectious, more common pathogen
bacterial reproduction
bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission
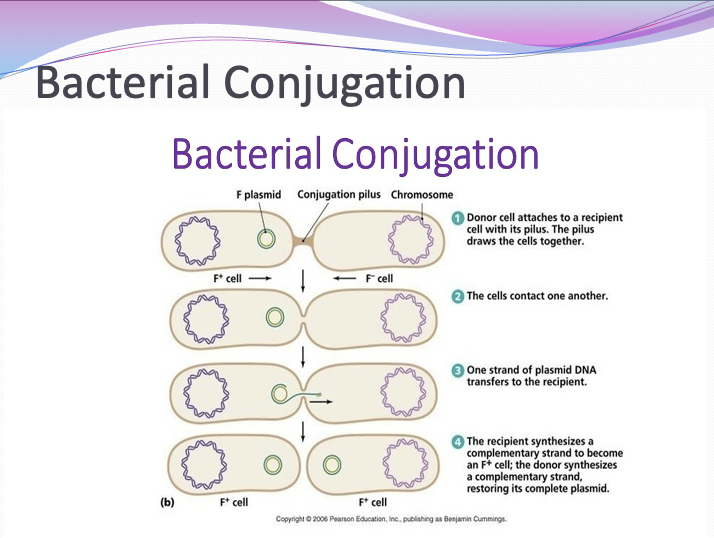
conjugation - way to mutate
some bacteria exchange some of their DNA through a conjugation tube to another bacterium (pilus)
usually plasmid DNA not genomic DNA
plasmid DNA: small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell, physically separated from chromosomal DNA, replicates independently
Bacterial Groth
lag phase: bacteria adjust to new environment and grow slowly
log phase: exponential growth
stationary phase: bacteria reach carrying capacity of the environment
death phase: logarithmic death of bacteria as nutrients get used up
endospores- sneaky particles
small spore that develops in some bacterium, includes genetic material and a protective coat
initiated in response to nutrient deprivation'
allows bacterium to produce a dormant and highly resistant cell to preserve the cells genetic material in times of extreme stress
Obtaining energy
Photosynthesizers
significant fraction of worlds photosynthesis is carried out by bacteria
cyanobacteria are blue-green bacteria that contain chlorophyll in their cell membrane
cyanobacteria are thought to have made earths oxygen
Chemoautotrophs
breakdown chemicals found in soil; use those chemicals for nutrition
bacterias waste products act as fertilizer and helps with agriculture
handful of soil has up to 10 billion bacterial organisms
Heterotrophs
most types of eubacteria are heterotrophic
together with fungi, serve as primary decomposers for the environment by releasing nutrients back to soil after living things have died
Bacterial interactions
mutualism: interaction where all parties benefit
(ex: nitrogen fixing bacteria in the soil as well as the naturally occurring bacteria in our gut)
parasitism: interaction where one party benefits and other is negatively affected
(bacteria cause disease in many organisms, these bacteria are pathogenic
Pathogenic bacteria
body = wealthy for bacteria
bacteria have evolved in various ways of entering the body and taking what they need to survive
competition for resources in body can result in you being ill
bacteria is harmfull in two ways
bacteria can metabolize (weaken) their host by using different parts of the body as their food source
tuberculosis ie less common bacterial infection of lungs
mycobacterium tuberculosis is bacteria that uses lung tissue as food source
warm moist environment allows bacteria to reproduce and populate the lungs
bacteria cause disease by secreting chemical compounds called toxins into their environment
humans affected most when food is not properly prepared / cooked (food poisoning)
most types of toxin bacteria can be killed by boiling water and cooking food at rec temp
kitchen and antibacterial products help rid our house of these pests
treatment of bacterial diseases
antibiotics used to treat bacterial diseases
work by punching holes in the cell walls of bacteria to allow bodies natural defense to be more effective OR prevent bacteria from reproducing
Antibiotic discovery
Alexander Fleming noticed fungus growing on a petri plate that was growing bacteria
bacteria did not grow near fungus
concluded fungus secreted a substance that killed bacteria
called secretion penicillin
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria
problem 1
bacteria multiplies quickly (7-10 day course of antibiotics might not kill all the bacteria)
bacteria that remain become resistant and may mutate their DNA and reproduce more cells
new cells are resistant to antibiotic and make it harder to treat infection next time
problem 2
society related, people not taking prescribed course of pills
stopping too early gives opportunity for bacteria not yet killed by antibiotic to reproduce and create resistant cells
problem 3
overuse of antibacterial soaps may do more harm than good
bacteria found our skin can become resistant to antibacterial chemicals in soap
antibiotic resistance main reasons
overuse for treatment of things not caused by bacteria
improper use of prescription by patient
natural selection
created “superbug” term for bacterium that cannot be destroyed by antibiotics
bacteria and technology
food preparation: lactobacillus is used in making pickles. soy sauce, etc
bioremediation: cleaning up toxic chemicals in environment by breaking them down into less toxic products
biologically safe pesticides: specific to the pest and dont harm plants, humans pollinators, or non-pest species
bioengineering: used to reproduce specific genes quickly to mass produce their protein products (insulin)
good things about bacteria
act as decomposers
live within our digestive tract (probiotics)
many foods we eat are processed by bacteria (olives, cheese, buttermilk)
used in mines to breakdown surrounding rock and leave behind the ore/metal
bacteria classification
