Plant Roots, Water Potential, and Nutrient Transport in Biology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What are the four main functions of roots in plants?
1. Water uptake 2. Nutrient uptake 3. Store resources 4. Anchor plant to ground
What does water potential quantify?
The tendency of water to move due to osmosis, gravity, pressure, and matrix effects.
What is the water potential of the atmosphere?
-100 MPa
What is the water potential of leaves?
-1.5 MPa (driver: Ψp)
What is the role of primary macronutrients in plants?
They are required in high amounts for essential functions such as chlorophyll production, DNA synthesis, and enzyme activity.
List the primary macronutrients.
Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K)
What is the function of Nitrogen in plants?
It is essential for chlorophyll, proteins, and DNA.
What is the function of Phosphorus in plants?
It is integral to DNA, phospholipids, and ATP.
What is the function of Potassium in plants?
It helps maintain osmotic balance and enzyme activity.
What are secondary macronutrients?
Calcium (Ca), Sulfur (S), Magnesium (Mg) - required in lower amounts than primary macronutrients.
What is the role of Calcium in plants?
It is an important component of cell walls.
What is the role of Magnesium in plants?
It is the central metal ion in chlorophyll.
What are micronutrients?
Essential nutrients required in small amounts, such as Iron (Fe), Molybdenum (Mo), Boron (B), Copper (Cu), and Manganese (Mn).
How do cations and anions move through the soil to the root surface?
Cations are attracted to soil particles, while anions dissolve in soil solution.
What is cation exchange capacity (CEC)?
It is the soil's ability to hold cations, preventing nutrient loss and benefiting plant nutrition.
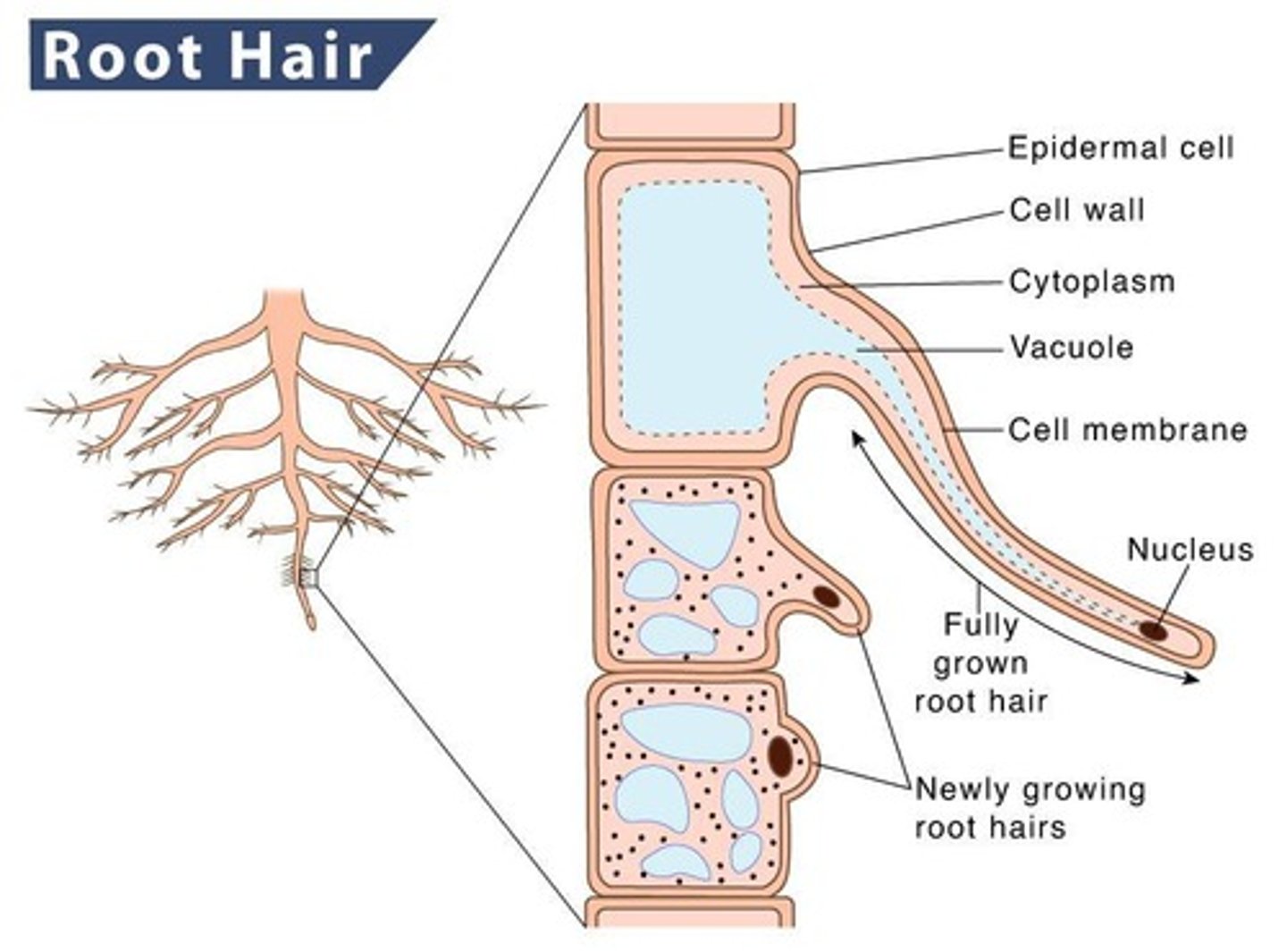
What is the role of root hairs in nutrient absorption?
They greatly increase root length and surface area, enhancing nutrient uptake.
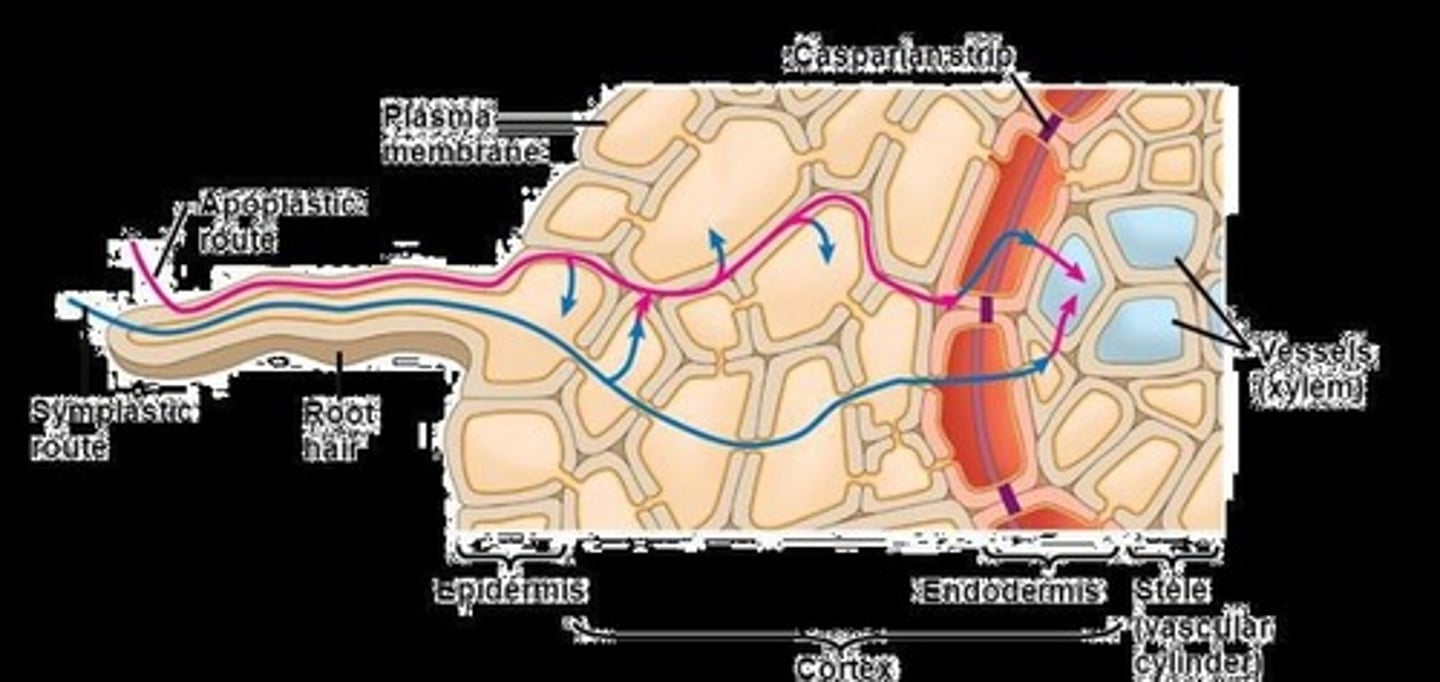
What are the two pathways for water and nutrients through the root cortex?
Apoplast (outside of cells) and Symplast (inside of cells).
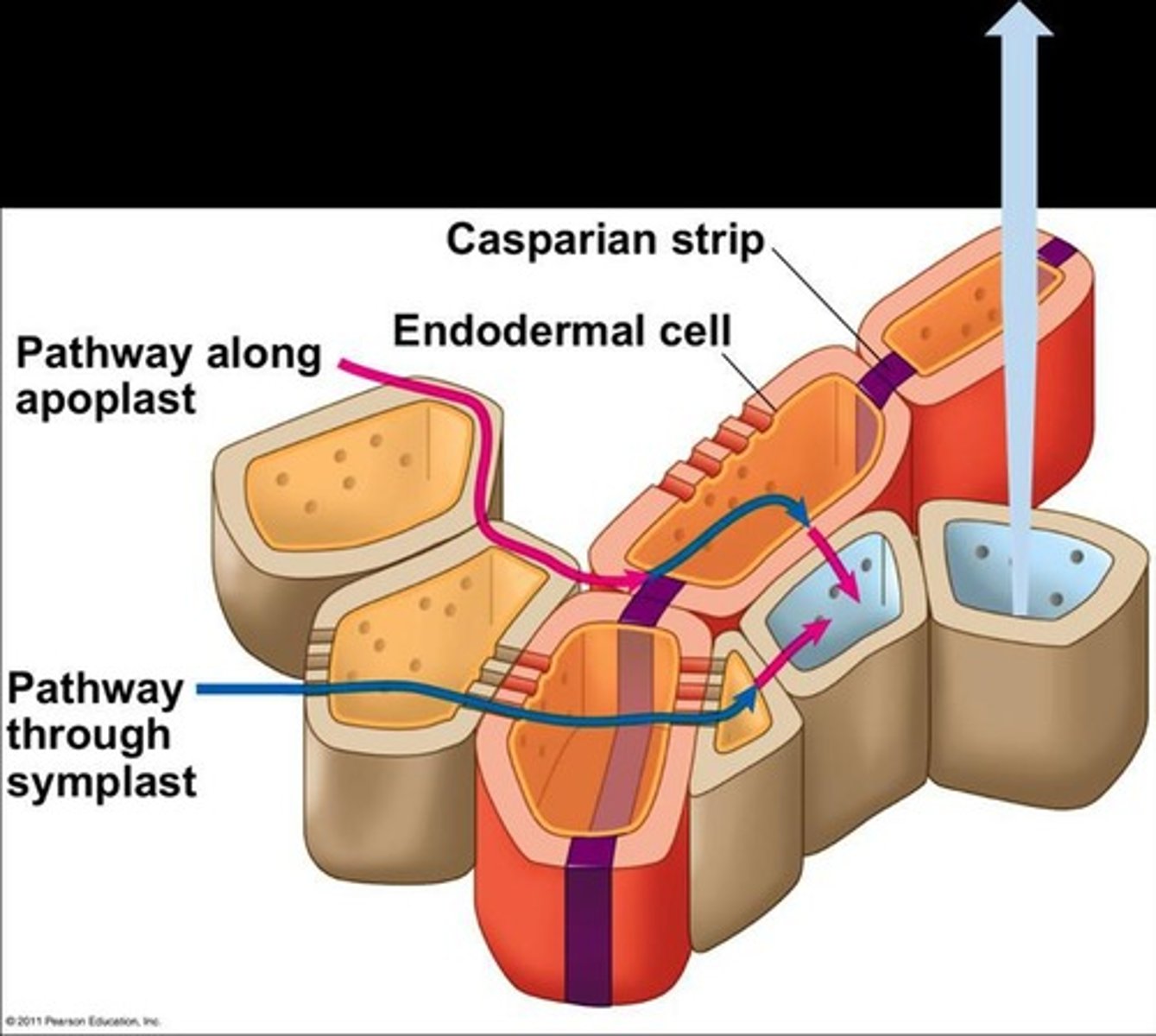
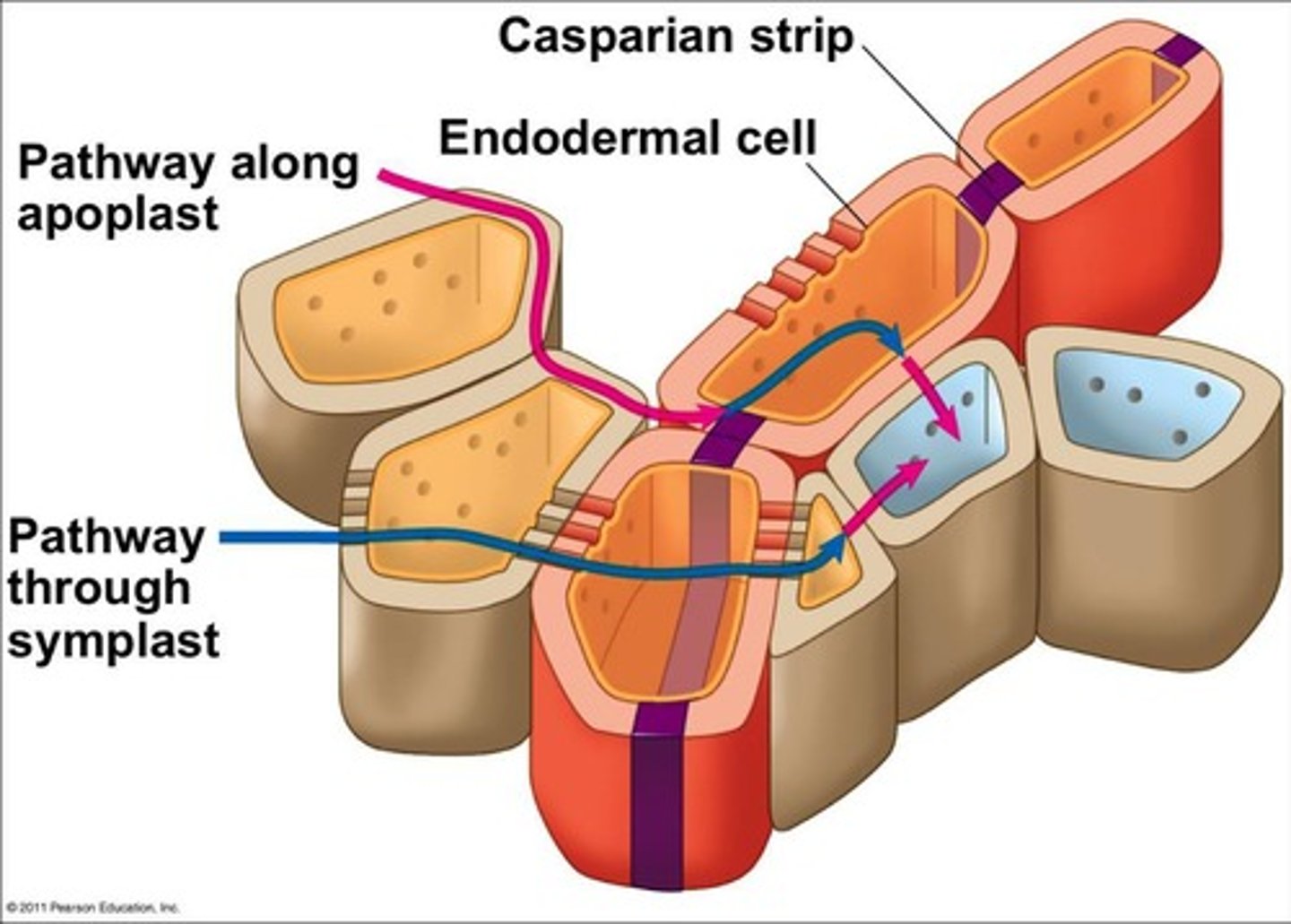
What is the Casparian strip?
A hydrophobic layer in the endodermis that forces water and solutes to cross cell membranes.
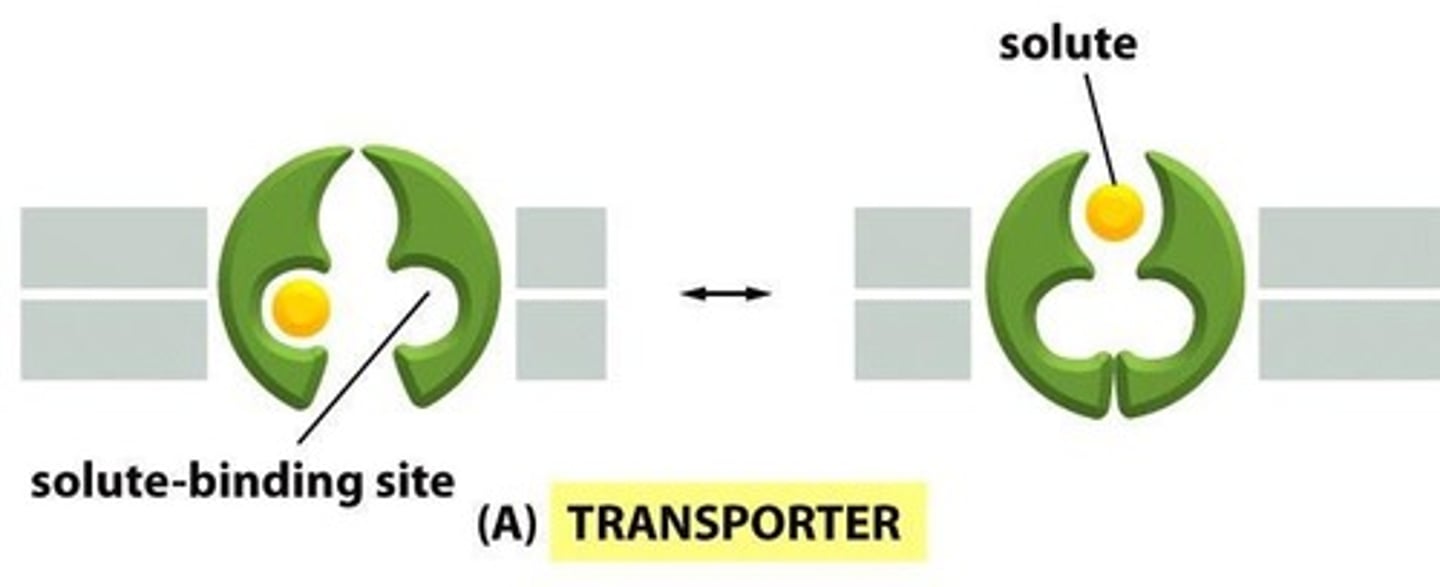
What are membrane transporters and channels?
Transporters bind and release solutes, while channels form hydrophilic pores for specific ions.
What is the difference between symport and antiport transporters?
Symport moves both molecules in the same direction, while antiport moves them in opposite directions.
What is mycorrhizae?
A symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots that enhances nutrient and water acquisition.
What percentage of plants form mycorrhizal relationships?
Over 80% of all plants.
What are the two types of mycorrhizae?
Ectomycorrhizae (ECM) and Arbuscular mycorrhizae (AM).
What is the role of ectomycorrhizae?
Fungi surround roots without penetrating root cells, commonly found in conifers and oak/beech.
What is the role of arbuscular mycorrhizae?
Fungi directly infect plant cells, commonly found in grasses and some trees.
What is the primary source of soil nitrogen?
Mostly from organic matter through mineralization and N2-fixation.
What is the primary source of soil phosphorus?
Mostly from minerals like apatite, released slowly through weathering.
What is the main function of roots in plants?
1. Water uptake 2. Nutrient uptake 3. Store resources 4. Anchor plant to ground
What is water potential (Ψ)?
Water potential quantifies the tendency of water to move due to osmosis, gravity, pressure, and matrix effects.
How is water potential measured?
Water potential is measured in pressure/tension units: Pascals (kPa or MPa).
What does a negative water potential value indicate?
Negative values indicate tension.
What are the three zones of root growth?
1. Division: actively dividing cells 2. Elongation: cells elongate and push root through soil 3. Maturation: cells stop growing and specialize.
What is the role of the apical meristem in root growth?
The apical meristem contains small, undifferentiated cells capable of cell division.
What is the function of root hairs?
Root hairs are extensions of single epidermal cells that greatly increase surface area for nutrient uptake.
What is the endodermis?
The endodermis is a layer of cells surrounding the vascular bundle that protects vascular tissue and controls transport of substances.
What is the permanent wilting point?
The permanent wilting point is when Ψsoil < -1.5 MPa for most herbaceous plants, indicating they cannot achieve Ψroot lower than -1.5 MPa.
What are the two pathways for water flow through roots?
1. Apoplast: outside of cells (through cell walls) 2. Symplast: inside of cells (through vacuoles/cytoplasm).
What is root pressure?
Root pressure is the pressure generated in the roots that pushes water up the plant, often occurring at night when soil is moist.
What is the relationship between soil particle composition and water potential?
Soil particle composition affects pore size; small particles create small pores that hold water strongly, while large particles create large pores that drain water easily.
What are the components of water potential in soil?
Ψsoil = Ψp + Ψg + Ψs, where Ψp is pressure potential, Ψg is gravitational potential, and Ψs is solute potential.
How does water flow in relation to water potential?
Water flows from areas of higher Ψ to areas of lower Ψ.
What happens to root Ψ if soil Ψ is at -0.033 MPa?
Root Ψ must be lower than soil Ψ to allow for water uptake.
What is the driving force behind the transpiration stream in xylem?
The negative Ψp (tension) in xylem pulls water from the symplast into the vascular system.
What occurs when stomata are closed in plants?
Guttation may occur, where root pressure pushes water up the plant, causing droplets to form.
What is the significance of the Casparian strip in roots?
It forces water and solutes to cross the cell membrane, allowing plants to control what enters the xylem.
What is the typical water potential of the atmosphere?
-100 MPa.
What is the typical water potential of leaves?
-1.5 MPa.
What is the typical water potential of xylem?
-0.6 MPa.
What is the typical water potential of roots?
-0.2 MPa.
What does the term 'guttation' refer to?
The process where excess water is expelled from the leaves of plants, often due to root pressure.
What is the role of vascular cambium in roots?
Vascular cambium is a meristem that contributes to the growth of xylem and phloem.
What happens during the maturation zone of root growth?
Cells stop growing and specialize into structures like root hairs, xylem, and phloem.