Bioenergetics - 4.4
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Photosynthesis
An endothermic reaction in which plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Where does photosynthesis happen?
Takes place in chloroplasts in green plant cells
Contains pigments like chlorophyll that absorb light
How does photosynthesis get its reactants and what does it do with the products?
CO2 enters the leaf from the air via diffusion
Water reach the cells via the xylem
Oxygen is released as a by product
Glucose is used in the plant
Word Equation for Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + Water LIGHT —> Glucose + Oxygen
Symbol Equation for Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H20 LIGHT —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is glucose used for in plants?
Respiration
Cellulose
Amino Acids
Lipids
Starch
Respiration - Glucose
They break down the glucose to release energy
Cellulose - Glucose
Used to make cellulose to make strong cell walls
Amino Acids - Glucose
Combined with nitrate ions to make amino acids which eventually create proteins.
Lipids - Glucose
Convert the glucose into fats and oils that server as energy storage. eg. Seeds
Starch - Glucose
Used to store glucose for a later time. It is useful because it is compact,insoluble and easy to break down when needed.
Limting Factors Of Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll Concentration
Light Intensity
Carbon Dioxide Concentration
Temperature
Chlorophyll Concentration and affect on photosynthesis
These is not enough chlorophyll in the plant to absorb the light
This could be because of infection (TMV) , Environmental stress and lack of nutrients
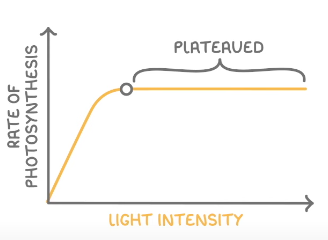
Light Intensity
Rate increases with light intensity up to a certain point
Light Intensity was the limiting factor as there was not enough energy so increasing it increases the rate
The graph then plateaus
This is because there is a different limting factor such as CO2 or temperature
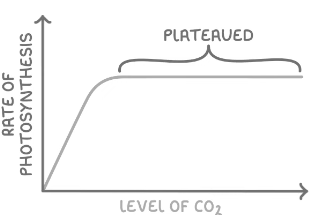
Carbon Dioxide Concentration
Rate increases with CO2 Conc up to a certain point
CO2 conc was the limiting factor as there was not enough as it is a reactant so increasing it increases the rate
The graph then plateaus
This is because there is a different limiting factor such as light intensity or temp
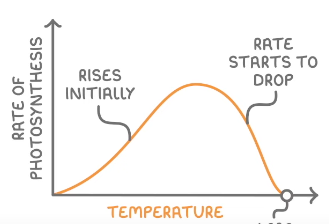
Temperature
Rate increases with temperature as enzymes can work quicker
This is because the particles have more energy and move faster so they react more frequently
Highest rate is at optimum temperature for enzyme
At high temp the rate decreases as bonds holding the enzyme together begin to break, and so the enzyme changes shape
Rate falls to zero as enzymes denature
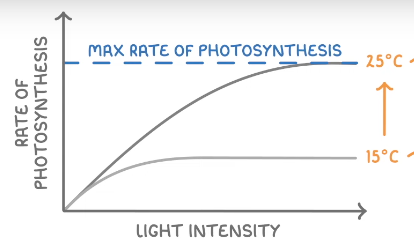
More than one Limiting Factor
Both lines show that as light intensity increases so does the rate
However the line then plateaus as temperature becomes the limiting factor
The line with the higher temp has a higher max rate of photosynthesis as it started to limit later on
How can farmers keep plants conditions ideal?
Temperature
Artificial Light
CO2 Concentration
General health of plants
Temperature - Plant Conditions
Greenhouses help to trap the suns heat and makes sure temp doesn’t become limiting
Light - Plant Conditions
When the sun goes down or when it isn’t bright enough farmers can supply the plants with artificial light for more photosynthesis time
CO2 Concentration + Temperature - Plant Conditions
Farmers can use paraffin burns to heat the greenhouse so temperature is not a limiting factor and it makes CO2 as a by product so CO2 conc is not a limiting factor.
General Health - Plant Conditions
Keeping plants enclosed in a greenhouse helps them to stay away from pests and diseases
Farmers can add fertiliser to the soil to provide minerals for growth
Greenhouse Costs?
Farmers only use greenhouses to improve condition so the plant grows faster/get a better yield
However it is expensive so it must be worth it
No need to supply stuff it does not need as that will be a waste of money
Variables for Photosynthesis Practical
IV: Light Intensity
DV: Amount of Oxygen produced
CV: CO2 Conc,Temperature,Size/Type of Pondweed (different chlorophyll quantity)
Inverse Square Law
light intensity = 1/distance 2 (inversely proportional)
Resipration
An exothermic reaction which releases energy from glucose and continuously occurs in living cells
Aerobic Respiration
Starts in the cytoplasm and occurs in the mitochondria
Uses oxygen to release energy from glucose molecules (by oxidising it)
Aerobic Respiration Word Equation
Glucose + Oxygen —> Carbon Dioxide + Water
Aerobic Respiration Symbol Equation
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ —> 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
Uses of Energy
Build up larger molecules from smaller ones (proteins to amino acids)
Allows for their muscles to contract
Mammals and Birds use energy to keep their body temp steady
Anaerobic Respiration
Only in the cytoplasm
Releases energy from glucose molecules without oxygen
Anaerobic Respiration Word Equation in Animals
Glucose —> Lactic Acid
Anaerobic Respiration Symbol Equation in Animals
C6H12O6 —> 2C3H6O3
Anaerobic Respiration Word Equation in Plants
Glucose —> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
Anaerobic Respiration Symbol Equation in Plants
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Oxygen Debt
Amount of extra oxygen the body needs after excercise to react with the build-up of latic acid and remove it from the cells.
Fermentation
Anaerobic Respiration in yeast cells
CO2 from fermentation makes the bread rise
Fermentation is the process the produces alcohol
Compare Aerobic and Anaerobic
Aerobic with O2 / Anaerobic without
Aerobic produces CO2 and H2O / Anaerobic produces lactic acid / ethanol
Anaerobic respiration quicker THAN aerobic
Aerobic releases more energy THAN anaerobic
Aerobic occurs in cytoplasm + mitochondria / Anaerobic occurs in cytoplasm only
Changes that happen to body after excercise
Heart rate increases BECAUSE pumps more blood / oxygen / glucose
Breathing rate increases BECAUSE more O2 in
Breathing rate increases BECAUSE more CO2 removed
Blood vessels dilate BECAUSE more blood to cells
Rate of AEROBIC respiration increases BECAUSE more energy released
Temperature increases BECAUSE respiration is exothermic / energy released to surroundings
More energy released to contract muscles
What does liver do with latic acid?
The liver oxidises lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water, or converts it back into glucose to be used for energy or stored as glycogen.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that happen in a cell or in the body
Controlled by enzymes
Metabolic Reaction that Occur in:
Both:
Respiration
Formation and breakdown of lipids into 3 x fatty acids and glycerol
Formation of proteins from amino acids
Animals:
Formation of glycogen
Breakdown of excess proteins to urea
Plants:
Photosynthesis
Formation of starch
Formation of cellulose
Combining nitrates with glucose to form amino acids