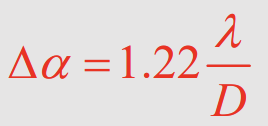Fourier and Optics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does a Fourier series allow you to do?
Find the frequencies present in a function of time, f(t)
How do you find the frequencies present in a function f(t) when f(t) is periodic?
Use a Fourier series
How do you find the frequencies present in a function f(t) when f(t) is non-periodic?
Use a Fourier transform
What does a Fourier series represent?
Any periodic function as an infinite sum of sine and cosine waves
If f(x) is an even function, which, if any, out of a0, an, bn are zero?
bn = 0 for even functions
If f(x) is an odd function, which, if any, out of a0, an, bn are zero?
a0 = 0, an = 0 for odd functions
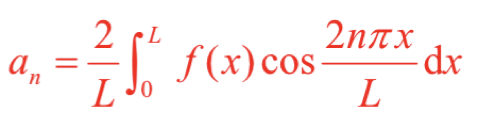
If the function f(x) is even, then is this integral odd or even?
Overall even because even function*even function = even function
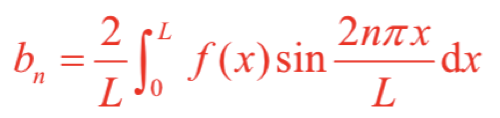
If the function f(x) is odd, then is this integral odd or even?
Overall even because odd function*odd function=even function

What can this be simplified to?
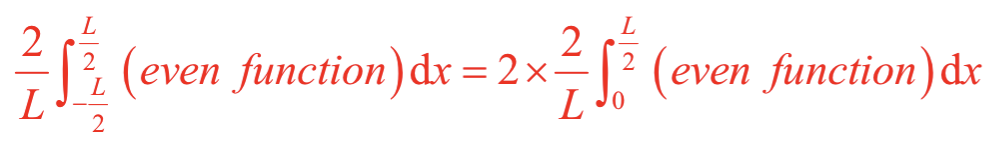
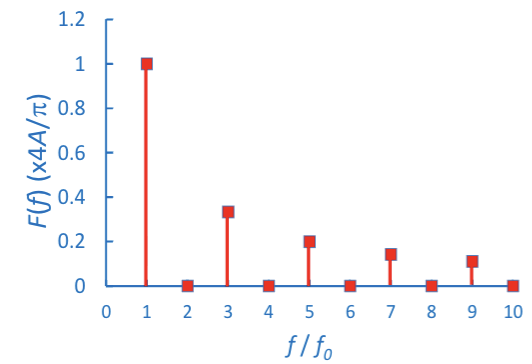
What does this graph plot?
This graph plots the harmonics on the x axis (first, second, third harmonics etc) against the amplitude of each harmonic on the y axis
What is the definition of a Fourier transform for a function of time?
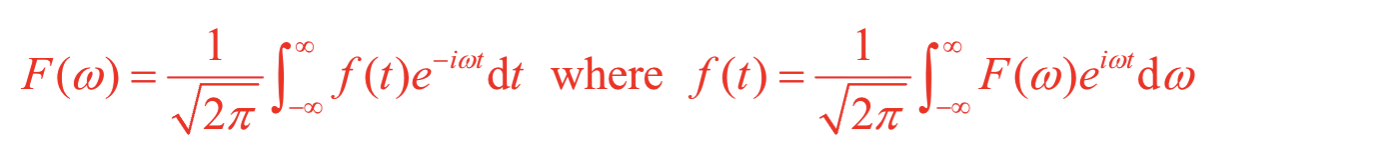
What is the definition of a Fourier transform for a function of distance?
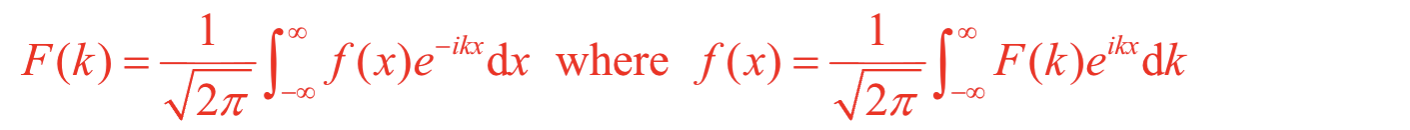
What is the equation for wavenumber, k?
k = 2π/λ
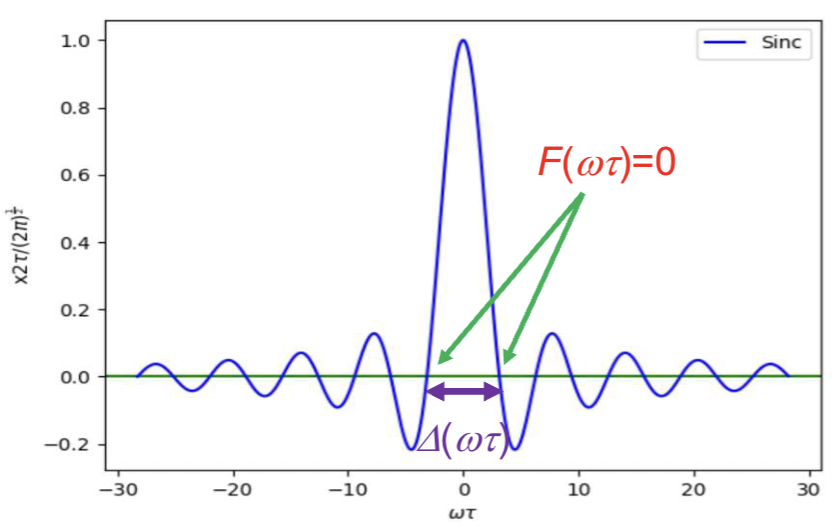
How do you measure the width of the sinc function?
Measure the the distance between the two points where the function crosses 0, width = Δ(ωτ)
What is the physical significance of Fourier transforms?
Tells us how much of each frequency component we would need to use to construct the original voltage pulse
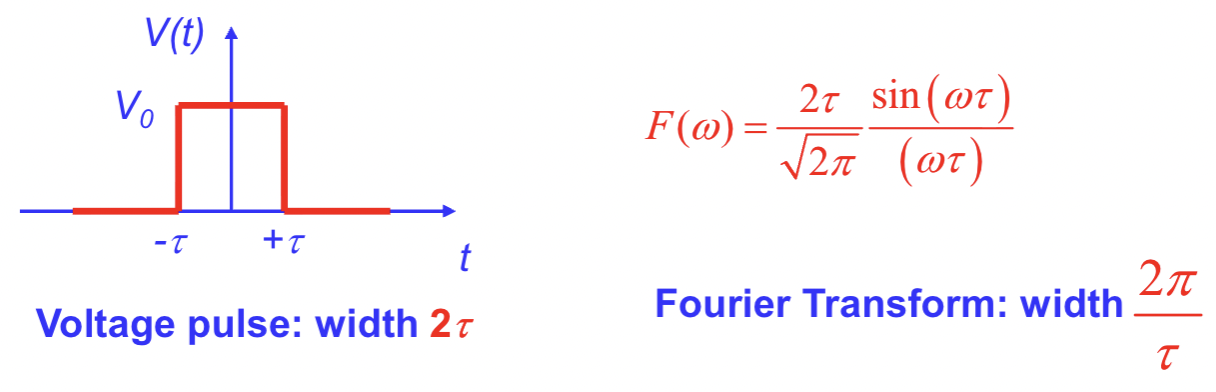
What do Fourier transforms tell us?
The frequency components present in any signal and their amplitudes
How are the width of the original function f(x) and its Fourier transform F(k) related (i.e. what’s their proportionality like)?
Width of the original function f(x) and its Fourier transform F(k) are inversely proportional
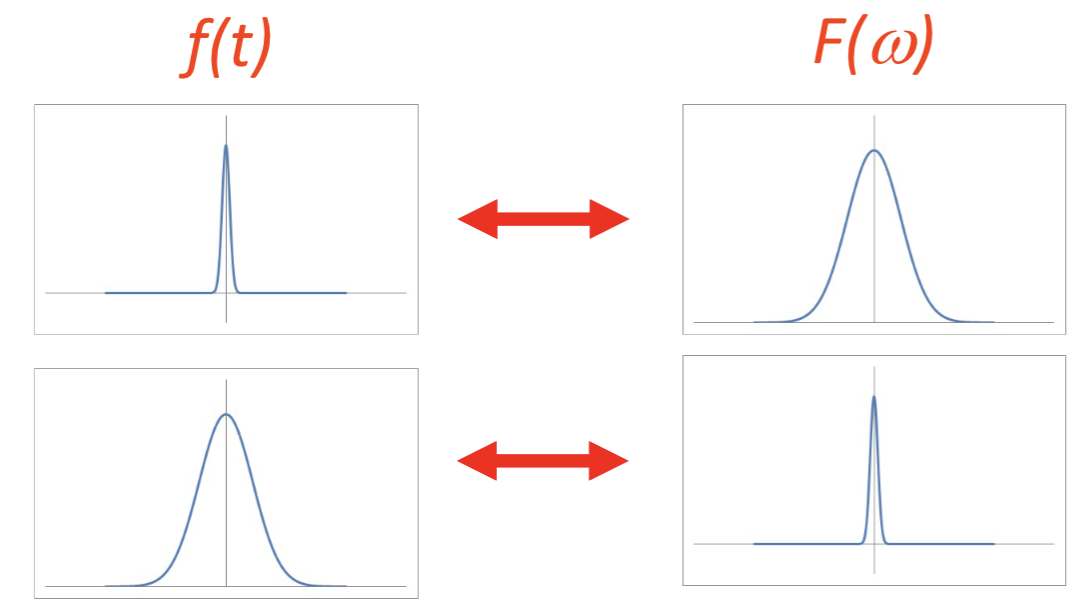
Describe the relationship shown here
The broader f(t), the narrower F(w) and vice versa
For a pulse of light, what are the main frequencies present in the range of?
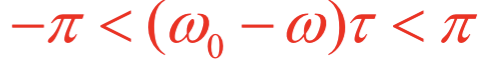
What is the condition for symmetry A for a Fourier transform?
f(x) is generally a real function but may have odd or even but possibly neither symmetry
What are the three conditions in symmetry B for a Fourier transform?
If f(x) is even
If f(x) is odd
If f(x) is real and even
What is the equation for the Fourier transform for f(x) when f(x) is real and even?
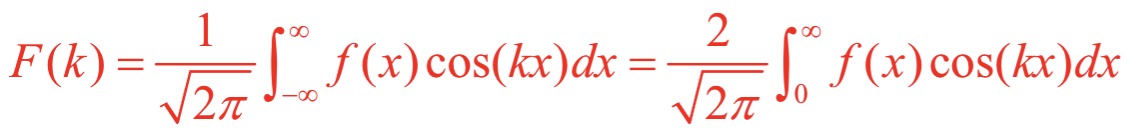
What is the equation involving cos and sin and i for the Fourier transform?
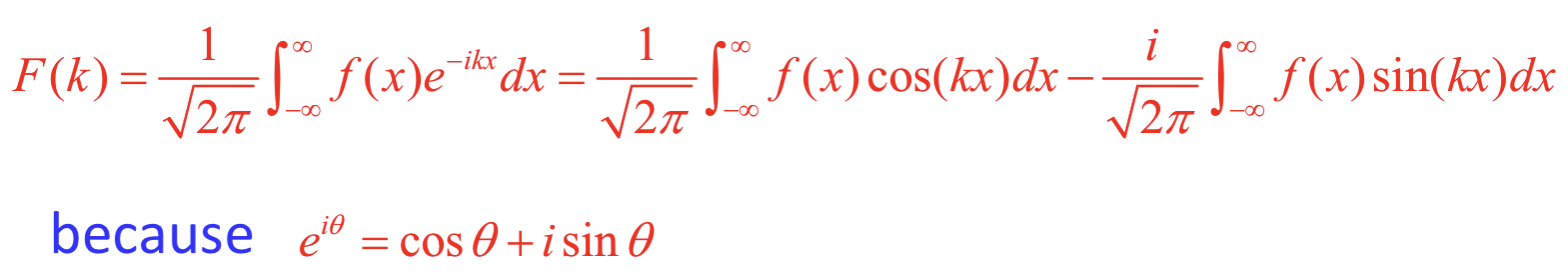
What are 4 applications of Fourier transforms?
Diffraction of light
Nuclear physics - scattering of electrons
Optical fibre data transmission
MP3 encoding
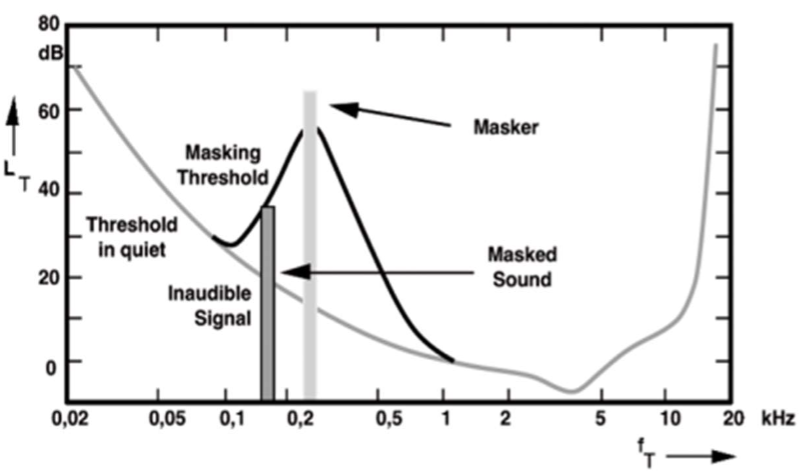
How does MP3 encoding work with Fourier transforms?
Transforms time to frequency - allows components that are too quiet to be audible or masked by louder nearby frequencies to be discarded
What is the Dirac delta function equation for a spike centred at x=0?
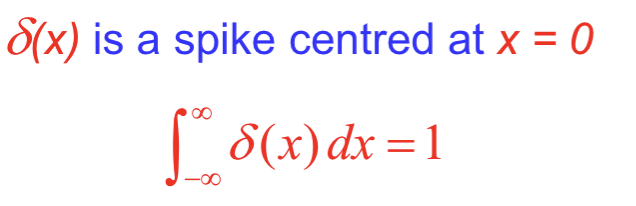
WHat is the Dirac delta function for a spike centred at x=x0?

What is the Dirac delta function B?

What are the 4 manual steps for calculating convolution and what is the definition? DELETE
The signal function is given by g(x) and the system response function is given by f(x)
Introduce a dummy variable u which enters the two functions as: f(u) and g(x-u)
For a given value of x calculate the overlap between the two function f(u) and g(x-u)
This is achieved by keeping x constant and integrating the product of the two functions between -∞ and + ∞ with respect to the variable u
In the figure the overlap will depend on the form of the two functions in the shaded region where they are both non-zero
As x varies the functions slide across each other
This will give a new function c(x) which gives the detected signal as a function of x and is a convolution of the functions f(x) and g(x)
A convolution function is therefore defined by the image
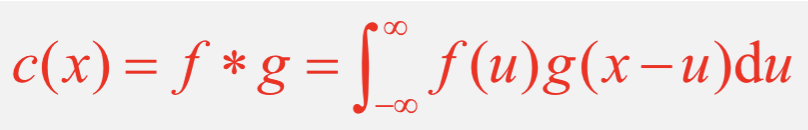
What is the definition of convolution? (wordy)
A mathematical process which takes two input functions f(x) and g(x) and produces a third output function
How do you find f(x) using c(x), g(x), and the result for C(k)?
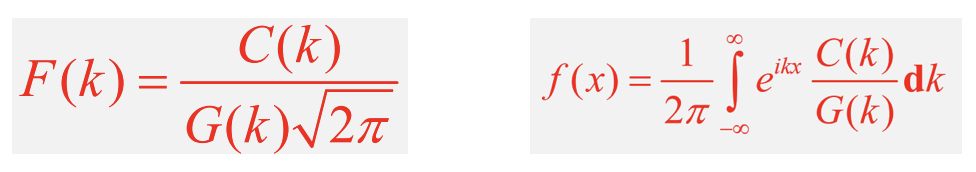
What is C(k) given by for 2 different Gaussian functions?
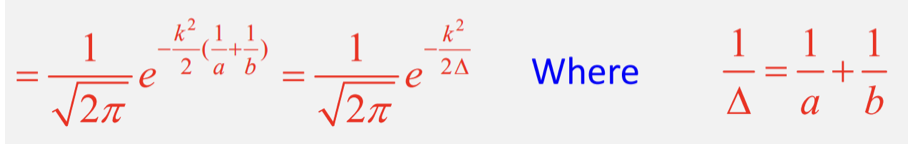
What is the equation for 1/Δ?
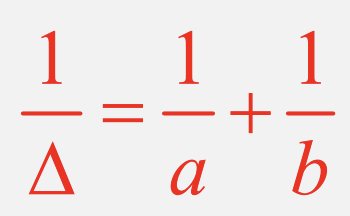
What is the condition for small aperture diffraction?
When light passes through a small aperture it is diffracted IF the wavelength is comparable or larger than the aperture size
What is Fraunhofer diffraction?
Where the waves incident on and leaving the aperture can be modelled as a plane
What is Fresnel diffraction?
Where the waves incident on and leaving the aperture CANNOT be modelled as a plane
What is the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern described by? (with lenses)
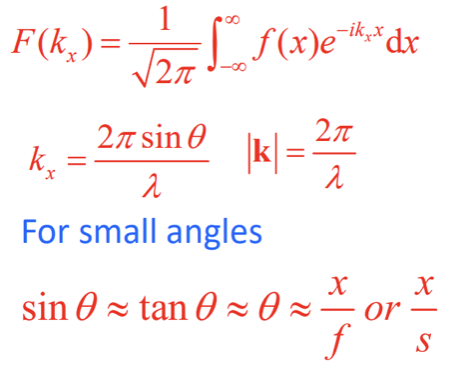
What are the 5 steps for finding the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern produced by an aperture?
Write down the function f(x) that describes the transmission of light through the screen - the aperture function. For a 2D aperture f(x,y)
Calculate the Fourier transform f(x) to give F(k(x))
Calculate |F(kx)|2
Substitute in for kx = (2πsinθ)/λ
Replace sinθ with x/f or x/s
Compare a square slit to a triangular slit for diffraction
Triangular slit produces a wider central maxima but weak subsidiary maxima
What is the equation for intensity for a square slit?
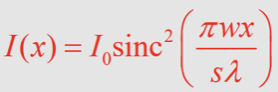
What is the equation for intensity for a triangular slit?
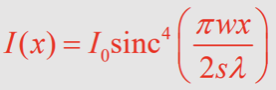
Under what condition can you consider an aperture as effectively one dimensional?
if the size in the other direction is much larger than the wavelength of light
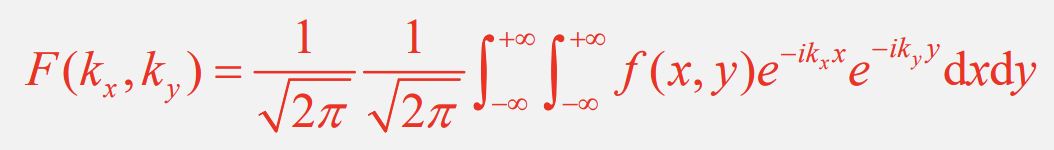
What does this equation mean?
It is the equation for 2D diffraction
What is the equation for 2D diffraction?
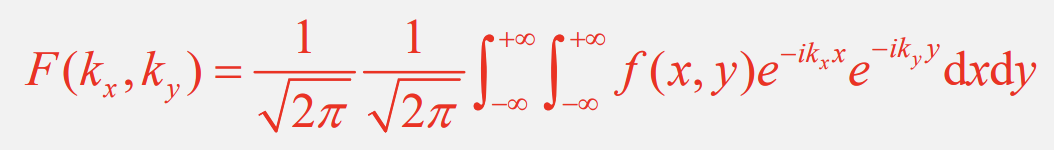
What is the equation for the width of an aperture in the x direction?
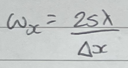
What is the equation for f(x,y), the diffraction by a rectangular aperture?
f(x,y)=g(x)h(y)
where g(x) and h(y) are both top hat functions of the widths 2a and 2b
What does diffraction by a circular aperture depend on?
The first order Bessel function J1()
Where do the first zeros of the Bessel function occur?
For arguments ~1.22π
Where do the first zeros of the sinc function occur?
At +-π
What is the effect of diffraction on spatial resolution of a telescope?
Diffraction as light passes through a telescope may prevent closely spaced objects from being separately resolved
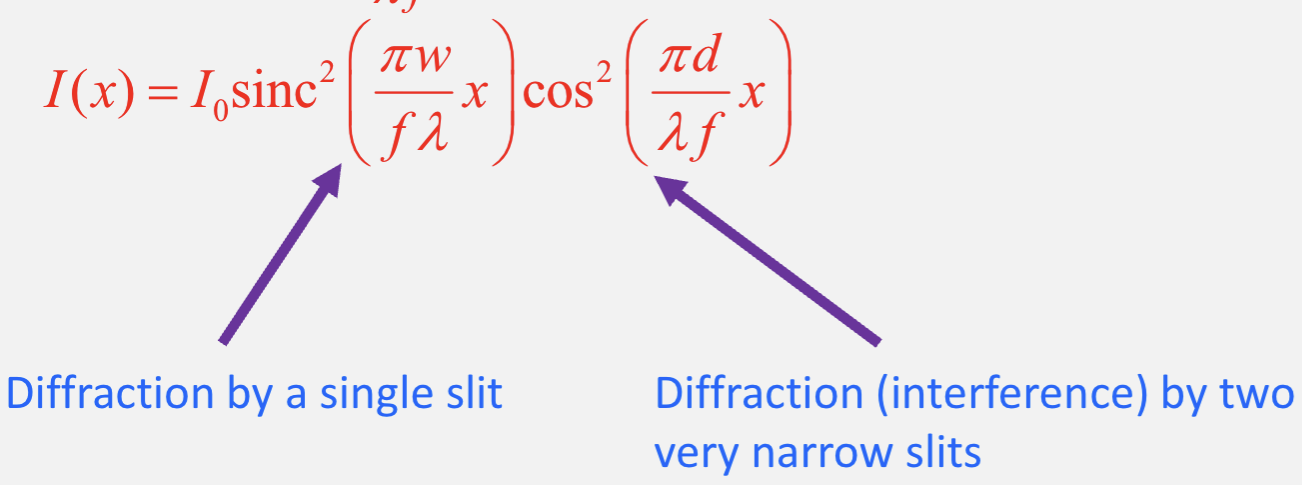
For two very narrow slits, what is the equation for the intensity of fringes?
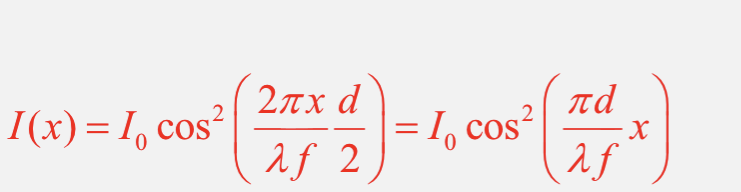
What is the equation for fringe spacing for two very narrow slits?
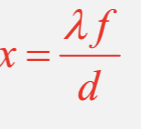
What is the equation for the intensity for two very narrow slits? and what does each component represent?
What is the equation for the diffraction grating width of main maxima?
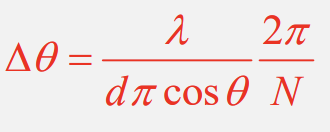
What is the Rayleigh criterion for spectral resolution and what can it be applied to?
Resolution is just possible when the maxima of one wavelength coincides with the first minima of the second wavelength(vertical yellow line)
Can apply to derive result for the resolving power of a diffraction grating
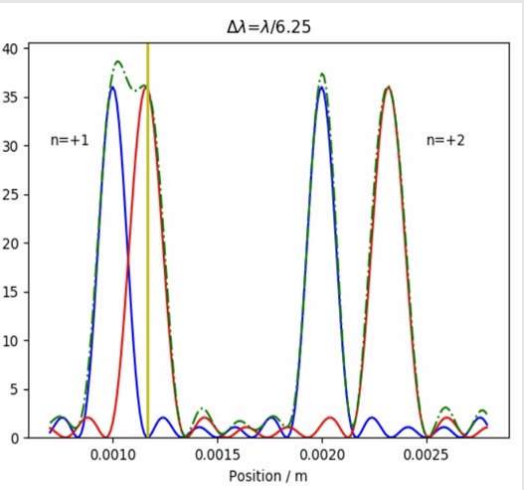
What is the equation for spectral resolving power?

What is the full equation for the resolving power of a diffraction grating and what do the symbols mean?
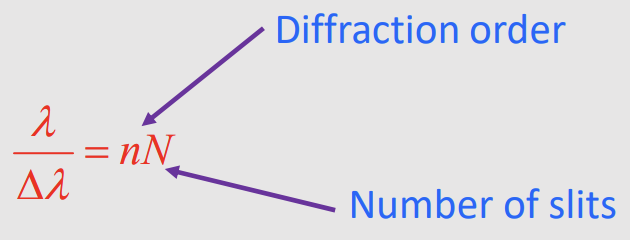
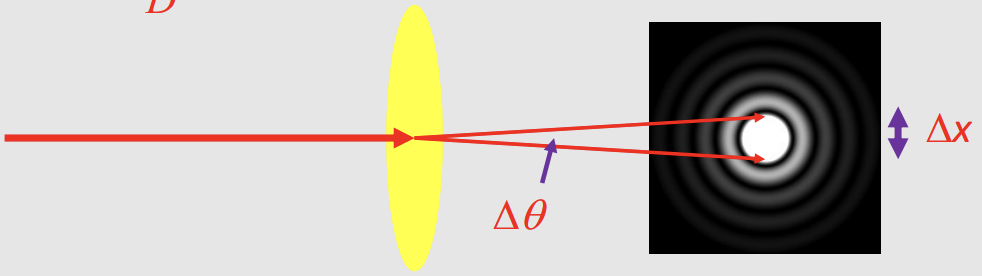
What is the equation for angular width of the maximum of the diffraction pattern?
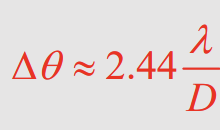
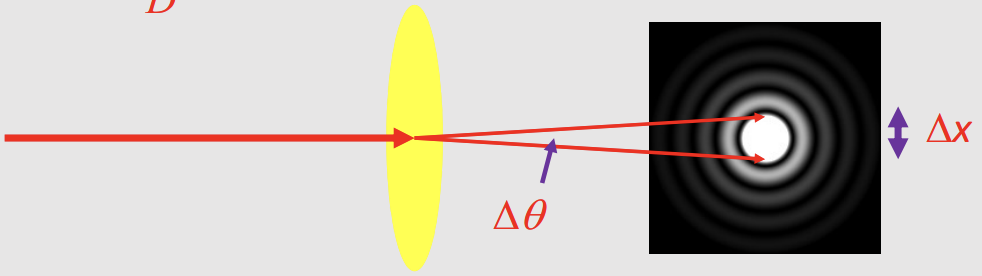
What is the equation for the spatial width of the maximum of the resultant diffraction pattern?
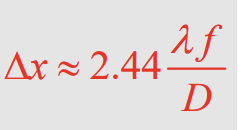
What is the equation for the angular resolution of an optical system with input aperture diameter D and imaging light of wavelength λ?