HSC 214 anatomy lab final
1/1008
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1009 Terms
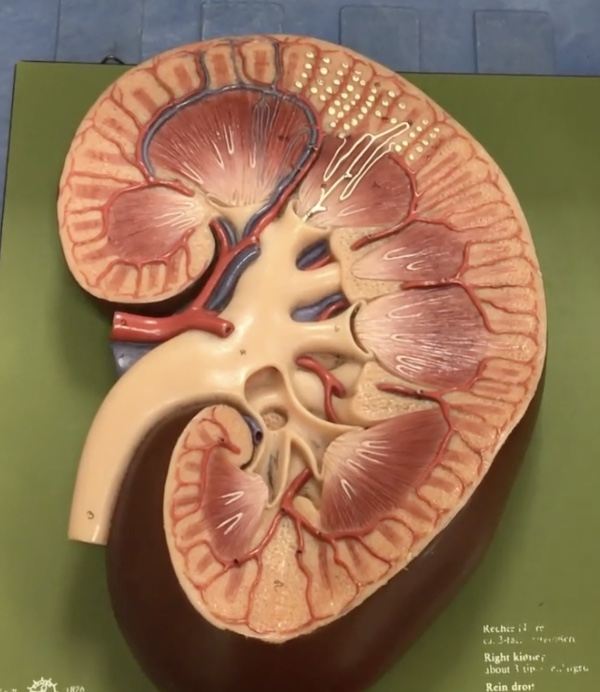
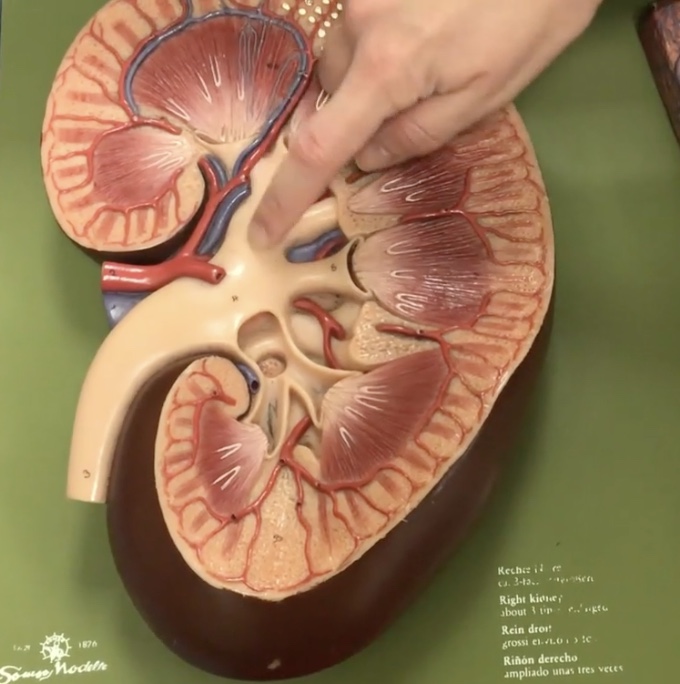
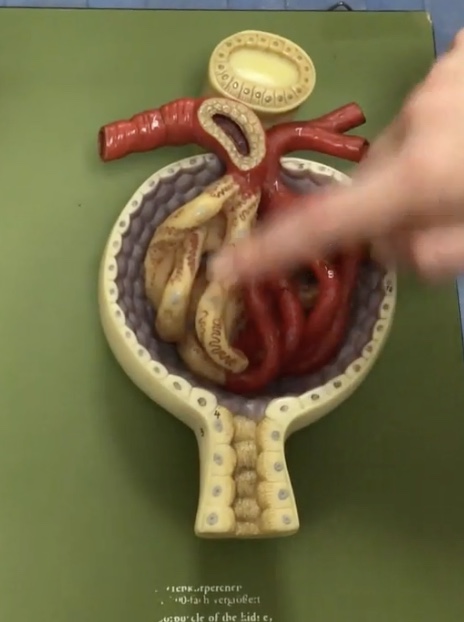
Kidney
Description: Bean-shaped structures located retroperitoneal
Function: Responsible for blood filtration and urine formation
Renal fascia
Description: Extraperitoneal connective tissue surrounding the kidneys and adrenal glands
Function: N/A
Renal capsule
Description: Inner, fibrous layer coating the kidney
Function: Maintains kidney shape and protects kidney from trauma
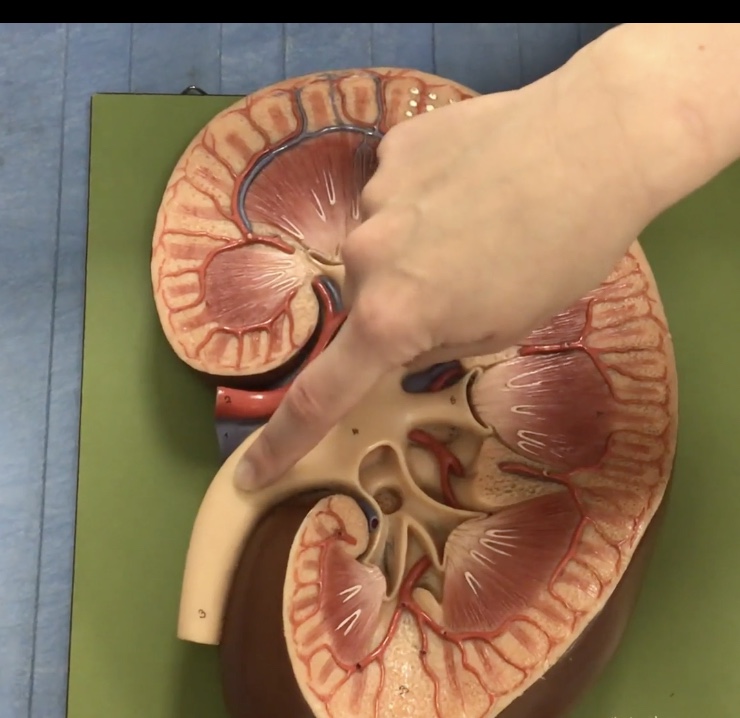
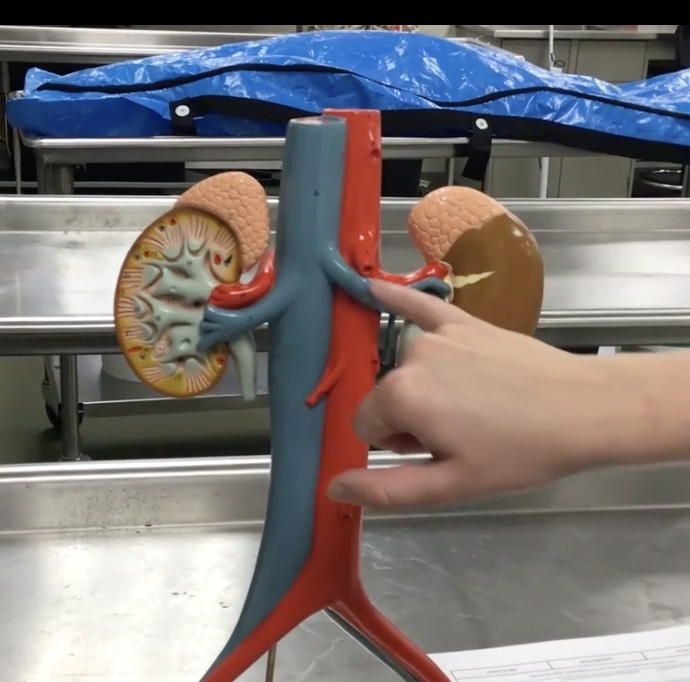
Hilum of kidney
Description: Concaved (indentation) medial border of kidney
Function: Where the renal arteries, veins and renal pelvis enter/leave the kidney
Renal pelvis
Description: Funnel-shaped tube narrowing into ureters
Function: Collects urine from the major calyces
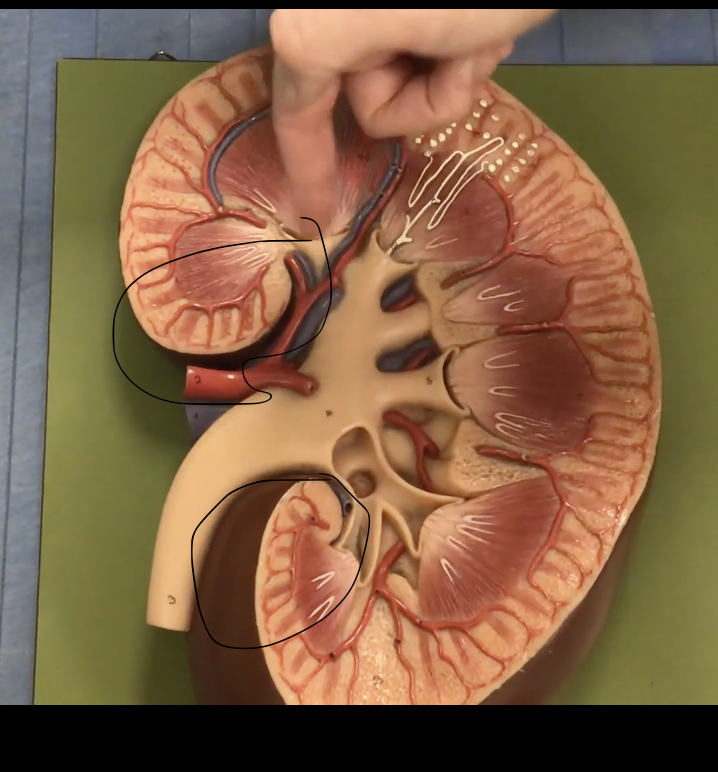
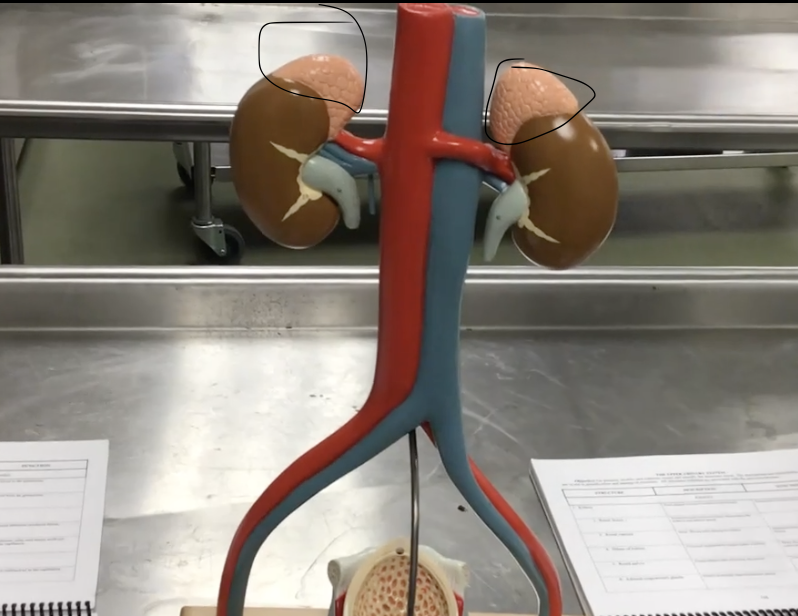
Adrenal (suprarenal) glands
Description: Paired, pyramidal shaped endocrine glands
Function: Secretes hormones (corticosteroids and androgen) and catecholamine’s (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
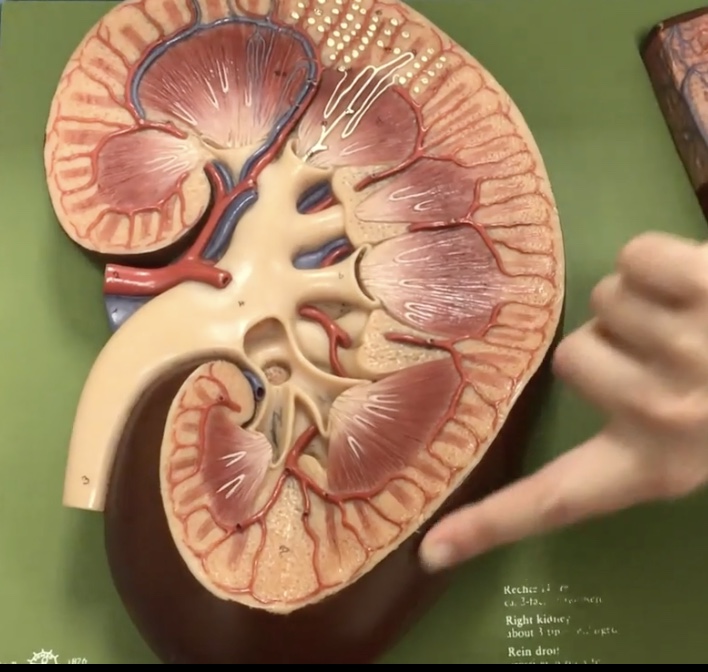
Renal cortex
Description: Outer part of kidney surrounding medulla
Function: Contains renla corpuscles and renal tubules where reabsorption and secretion occur
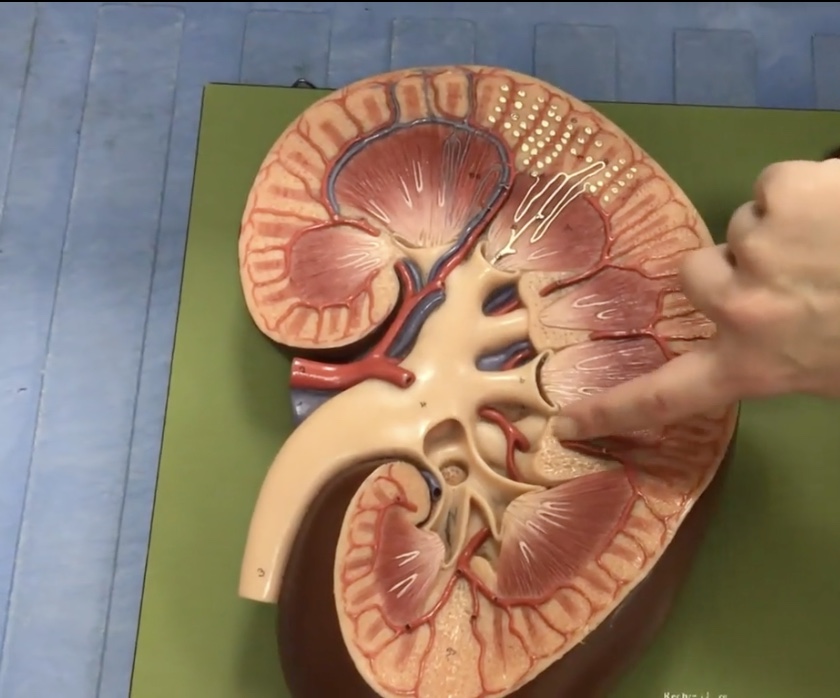
Renal columns
Description: Extensions of cortex between renal pyramids
Function: Divides the medulla into renal pyramids and contains interlobar arteries
Renal medulla
Description: Inner part of kidney
Function: N/A
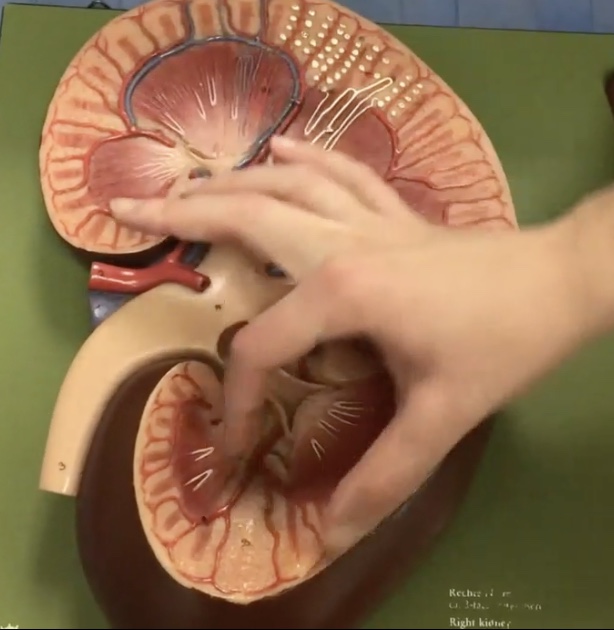
Renal pyramids
Description: 8-10 cone-shaped masses that compose most of the medulla
Function: Contain collecting ducts that drain urine into the minor calyx
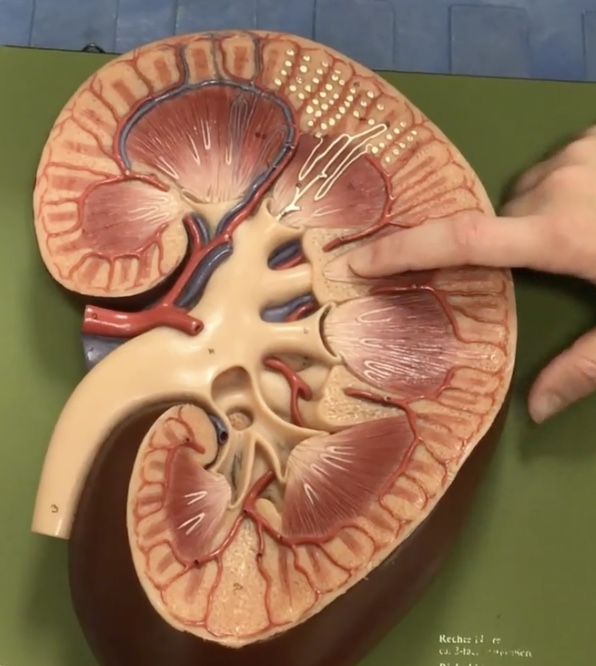
Renal papillae
Description: Tip of renal pyramid
Function: Releases urine into the minor calyx
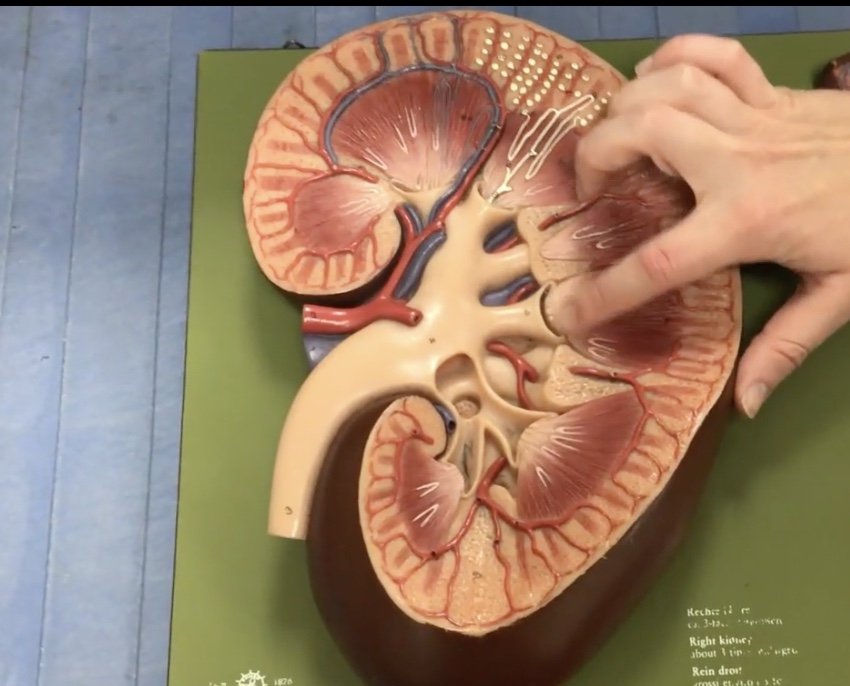
Minor calyx
Description: Smaller collecting ducts at renal papillae
Function: Drains urine from the renal papillae and collecting ducts
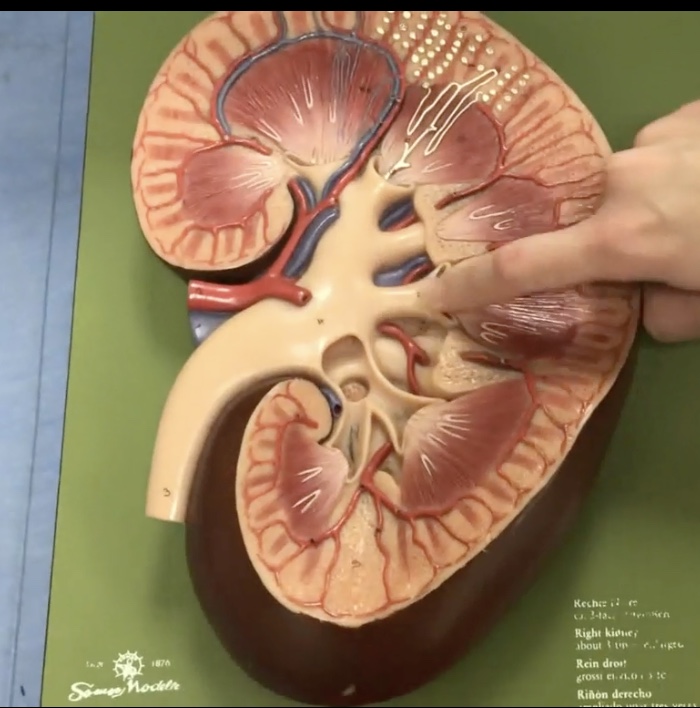
Major calyx
Description: Larger collecting ducts which form from minor calyces
Function: Drains urine from the minor calyx to the renal pelvis
Afferent arteriole
Description: Vessel carrying blood into the renal corpuscle
Function: Supplies blood to the glomerulus
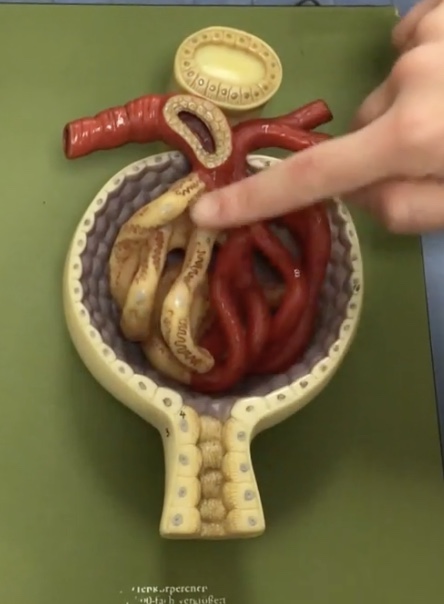
Efferent arteriole
Description: Vessel carrying blood out of the renal corpuscle
Function: Drains blood from the glomerulus
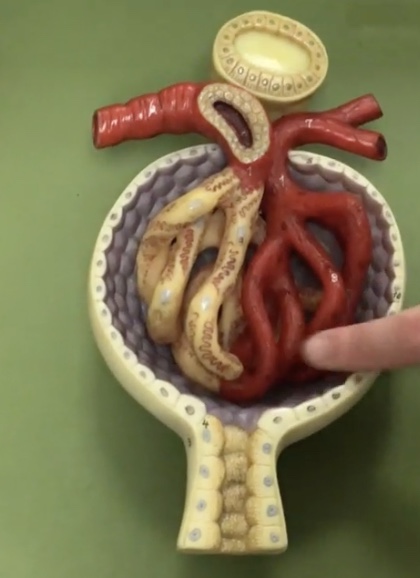
Renal corpuscle
Description: Enlarged region of nephron containing the glomerulus and glomerular capsule
Function: N/A
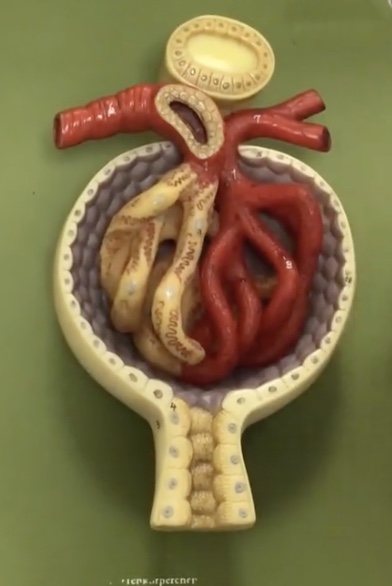
Glomerulus
Description: Capillary network within the renal corpuscle
Function: Site of glomerular filtration, produces filtrate
Proximal convoluted tubule
Description: Tube between glomerulus and loop of henle
Function: Where water, glucose, salts, and amino acids get reabsorbed to the capillaries
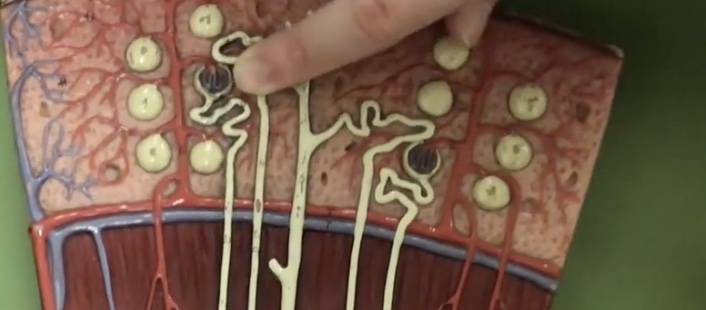
Loop of henle
Description: U-shaped tube extending from the proximal convoluted tubule
Function: N/A
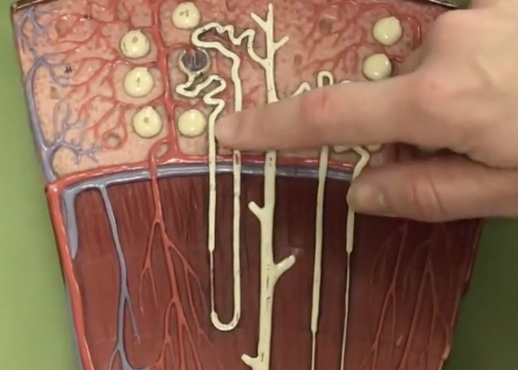
Descending limb
Description: Tube traveling toward the renal pelvis after the proximal convoluted tubule
Function: Where only water is reabsorbed to the capillaries (osmosis)
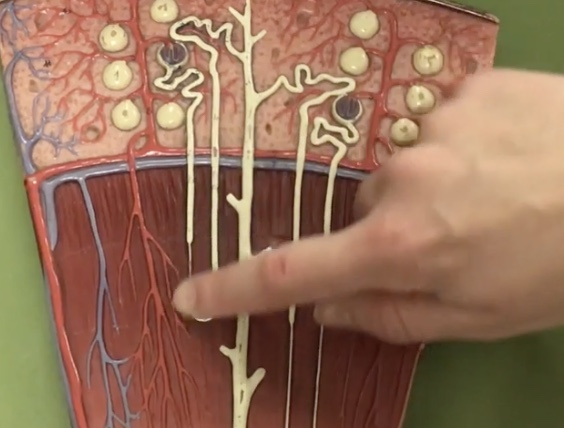
Ascending limb
Description: Tube traveling toward the cortex after the descending limb of loop of henle
Function: Potassium and sodium chloride (NaCl) only are reabsorbed to the capillaries (active transport)
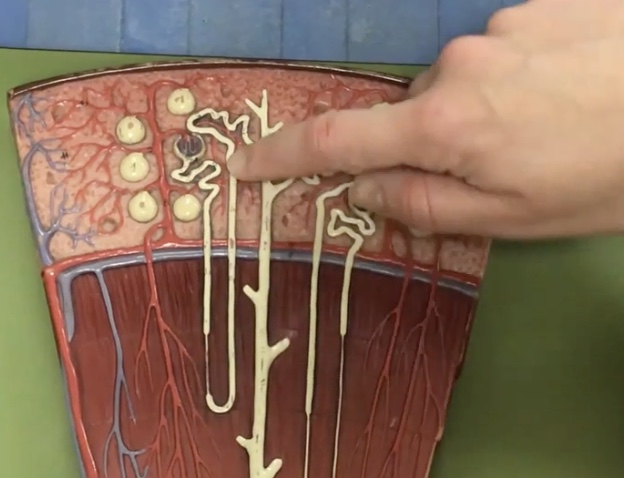
Distal convoluted tube
Description: Tube after the loop of henle connecting to the collecting duct
Function: Where potassium and sodium chloride ions continue reabsorption to the capillaries
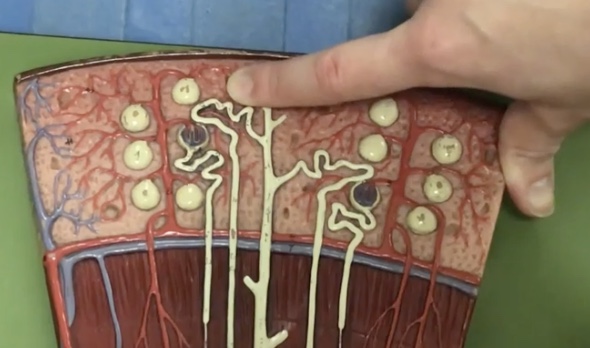
Collecting duct
Description: Duct after the distal convoluted tubule that travels through the renal pyramid, selectively permeable to water
Function: Depending on the need to conserve or eliminate water, the collecting duct absorbs water to change concentration of urine
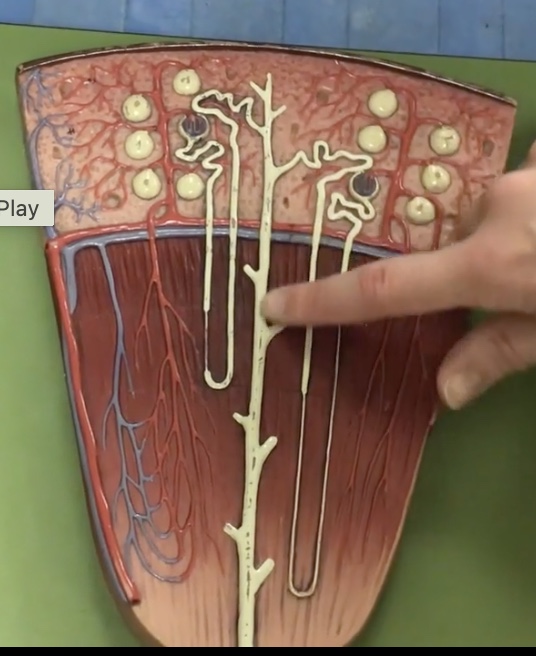
Papillary duct
Description: Duct at end of collecting duct in the region of renal papillae
Function: Releases urine to minor calyx
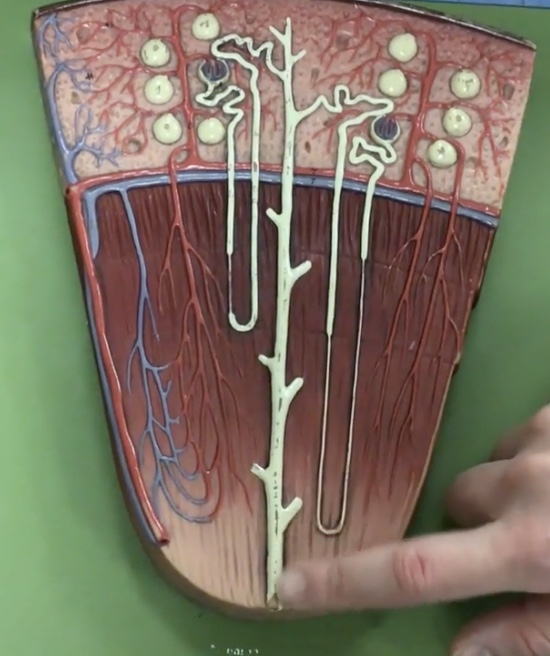
Renal arteries
Description: Short arteries arising from the abdominal aorta to enter the hilum of the kidney
Function: Supplies blood to the kidneys and adrenal glands. Located posterior to the renal veins

Segmental arteries
Description: Branches of the renal arteries near the renal hilum
Function: Branches into the interlobar arteries
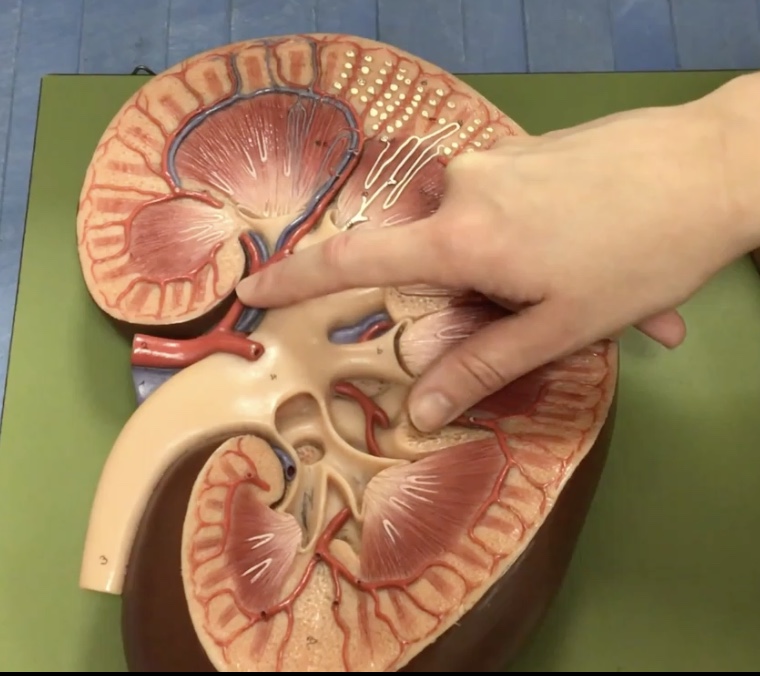
Interlobar arteries
Description: Arteries in the renal columns
Function: Branches into the arcuate arteries
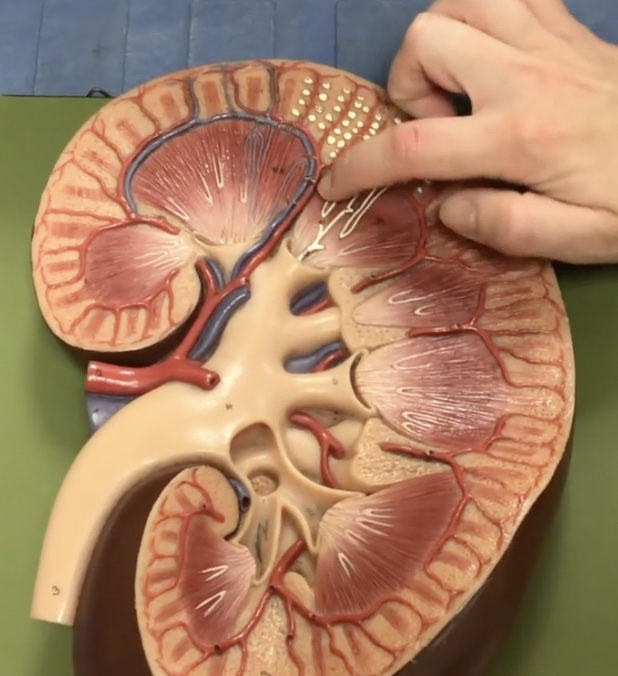
Arcuate arteries
Description: Arteries at the base of the renal pyramids
Function: Branches into the interlobular arteries
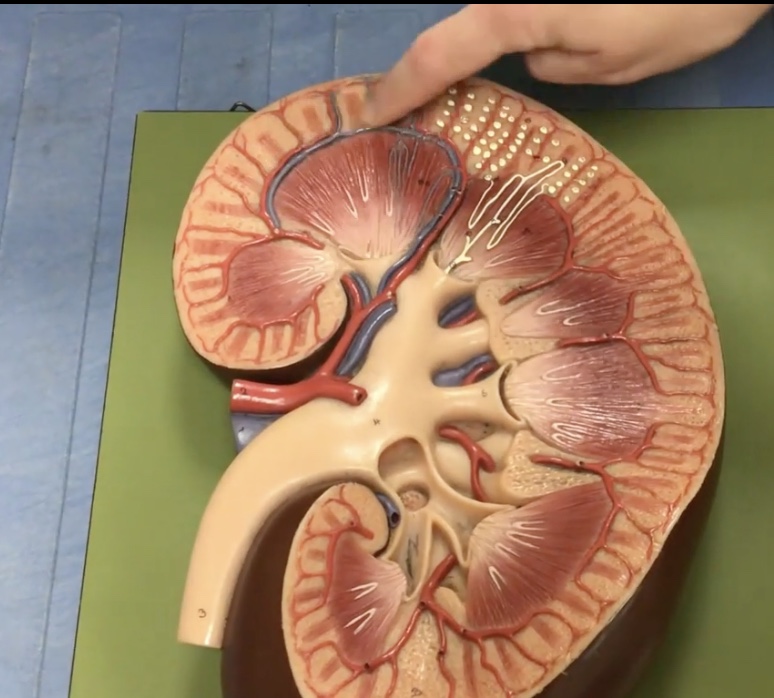
Interlobular arteries
Description: Arteries in the renal cortex
Function: Branches into the afferent arterioles
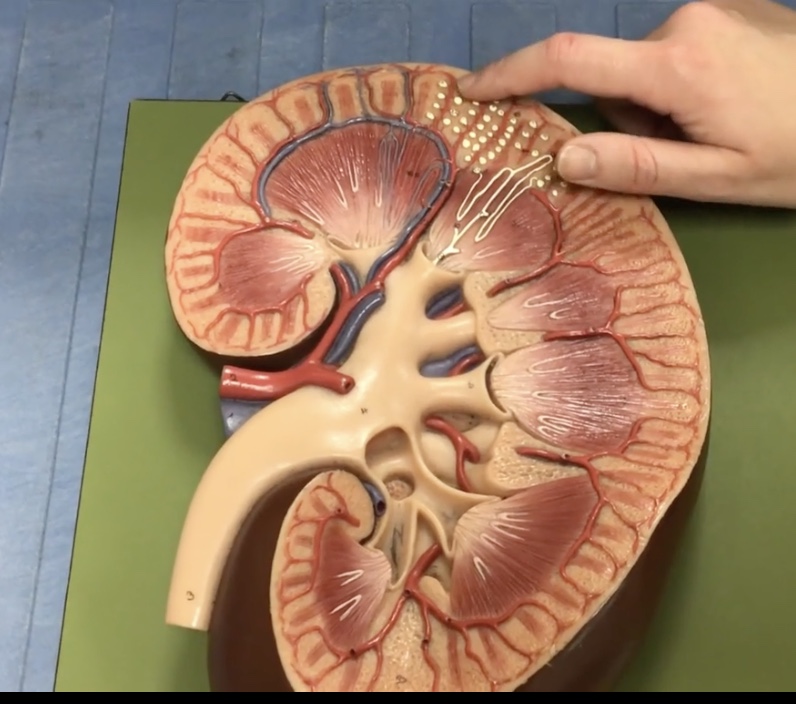
Interlobar veins
Description: Veins in the renal cortex
Function: Drains blood from the efferent arterioles
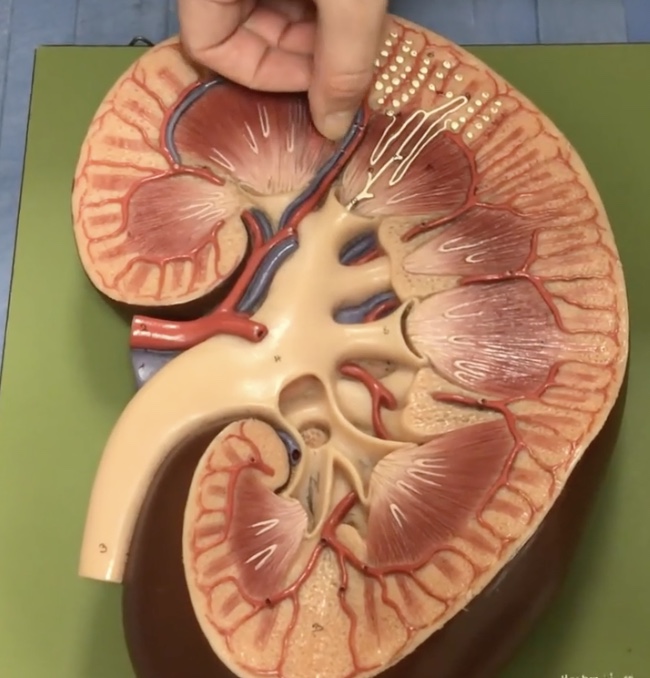
Arcuate veins
Description: Veins at the base of the renal pyramids
Function: Drains blood from the interlobular veins
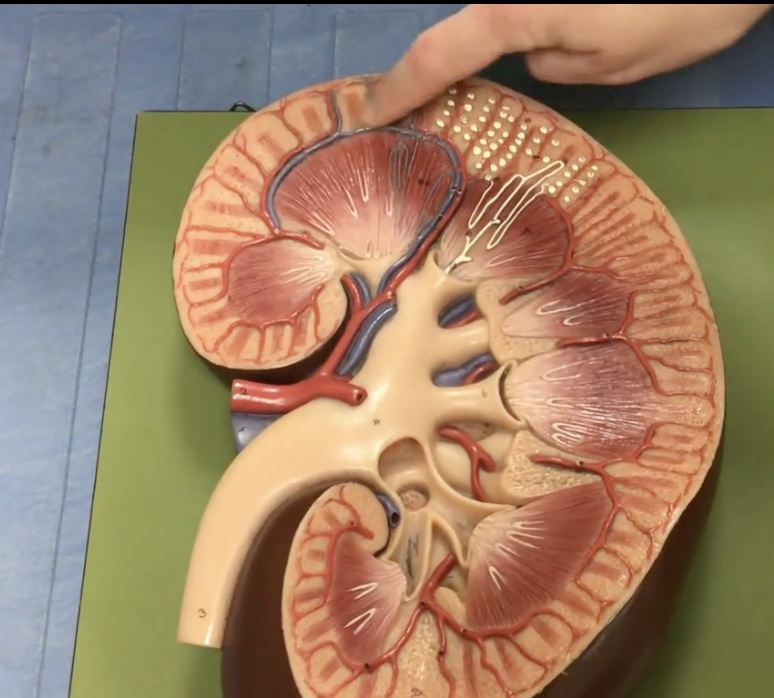
Interlobular veins
Description: Veins in the renal columns
Function: Drains blood from the arcuate veins
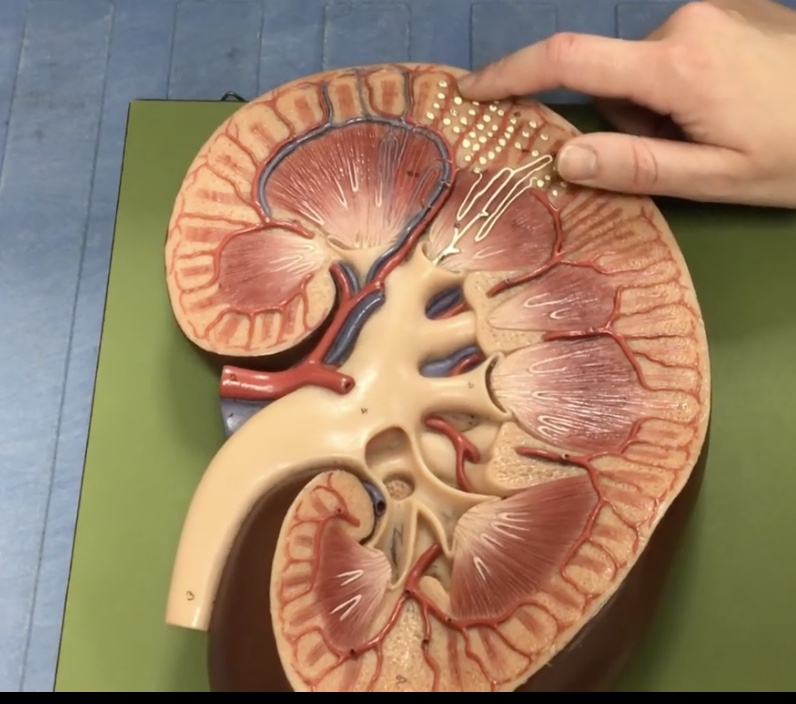
Urinary bladder
Description: Hollow, expandable organ posterior to the pubic symphysis
Relationship: Storage for urine
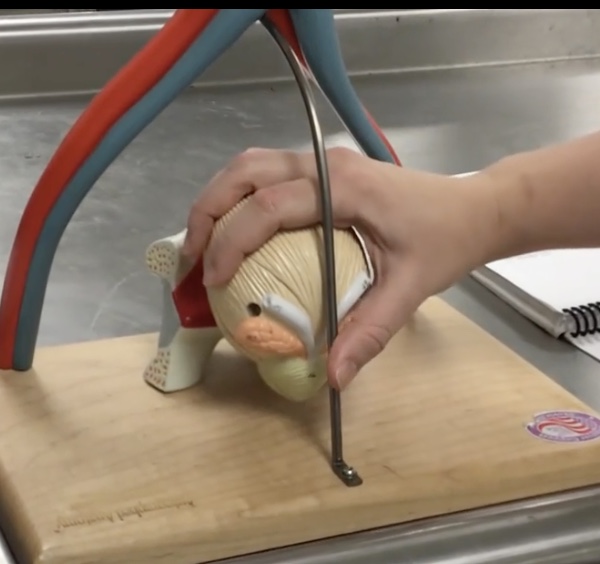

Serosa
Description: Visceral peritoneum covering the roof of the urinary bladder
Relationship: N/A
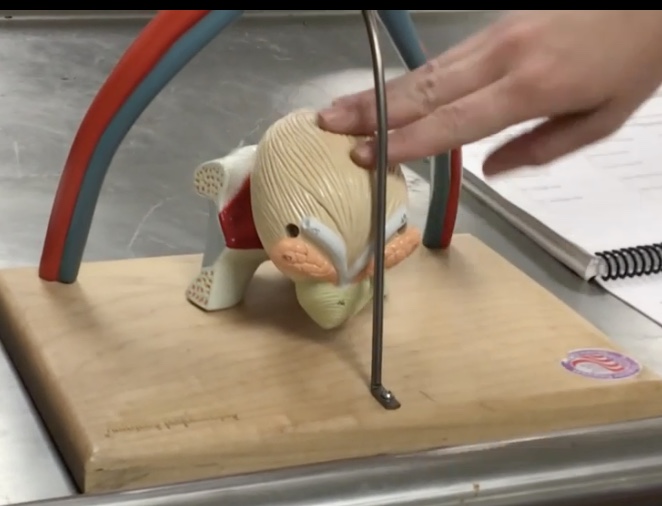

Detrusor muscle
Description: Smooth muscle layer of the urinary bladder
Relationship: When the urinary bladder expand, the parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the detrusor muscle to contract
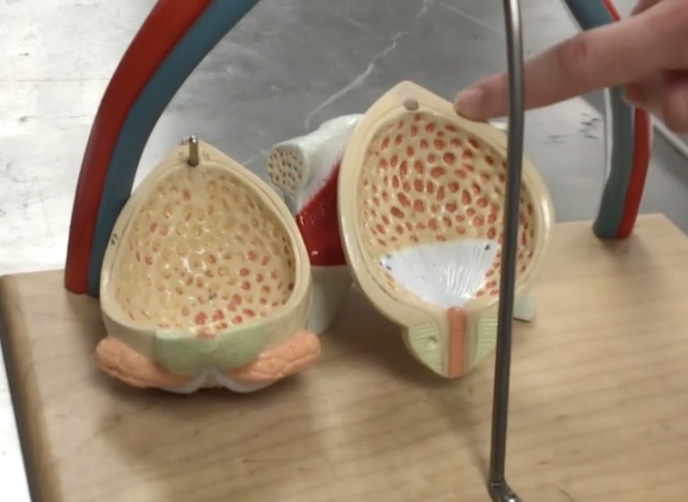

Rugae of urinary bladder
Description: Mucosal folds on the internal surface of the urinary bladder
Relationship: Allows for distension of the urinary bladder

Ureteral openings
Description: Openings of the ureters into the posterior inferior aspect of the urinary bladder
Relationship: Where urine enters the inferior portion of urinary bladder
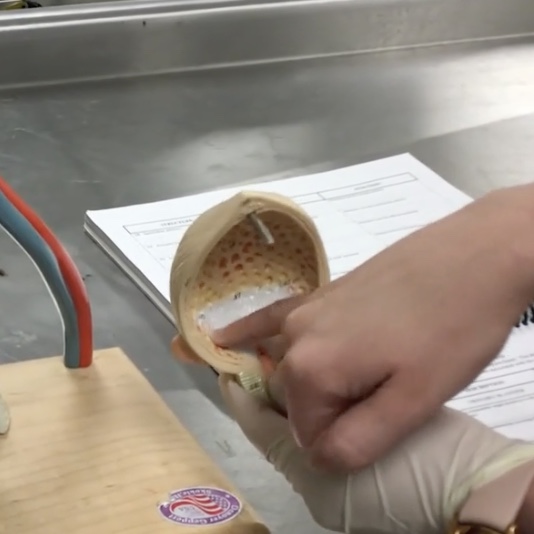

Trigone
Description: Smooth, triangular region on the internal surface of the urinary bladder
Relationship: Ureteral openings form the base and the urethral opening forms the apex

Urethra
Description: Duct draining the urinary bladder
Relationship: In females transports urine, in males transports semen and urine
Internal urethral opening
Description: Space at the apex of the trigone
Relationship: Where urine exits the urinary bladder

Internal urethral sphincter
Description: Smooth muscle (involuntary) compressing the internal urethral opening
Relationship: N/A
External urethral sphincter
Description: Skeletal muscle (voluntary) compressing the urethra
Relationship: N/A
Mons pubis
Description: Subcutaneous fat pad anterior to pubic symphysis
Relationship: After puberty, is covered in hair
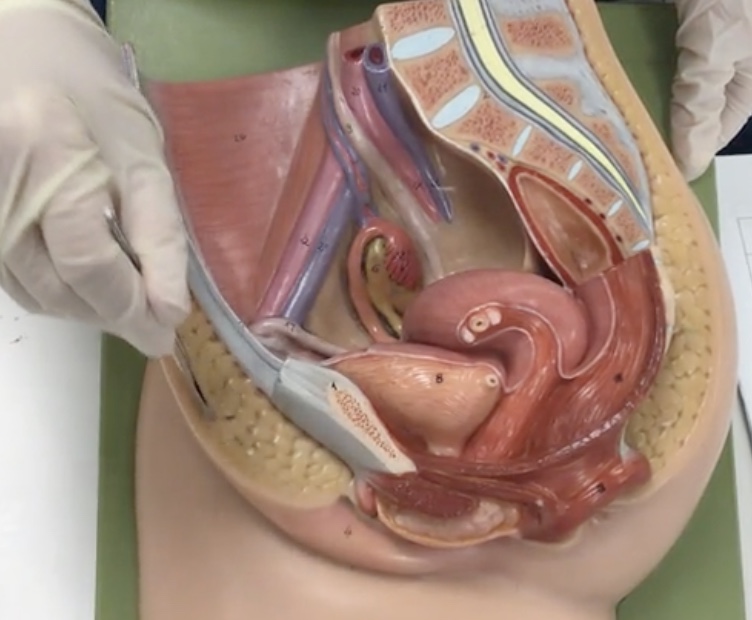
Labium majus
Description: Larger, hair covered folds created by subcutaneous fat
Relationship: Protects external genitalia
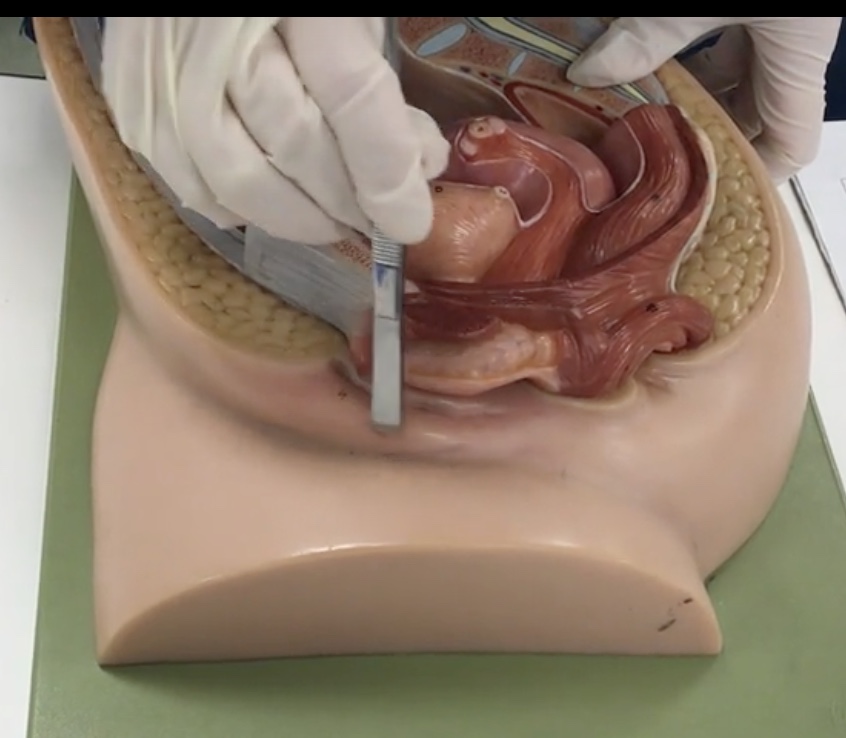
Labium minus
Description: Thin, hairless folds medial to labium majus
Relationship: Contains sebaceous glands
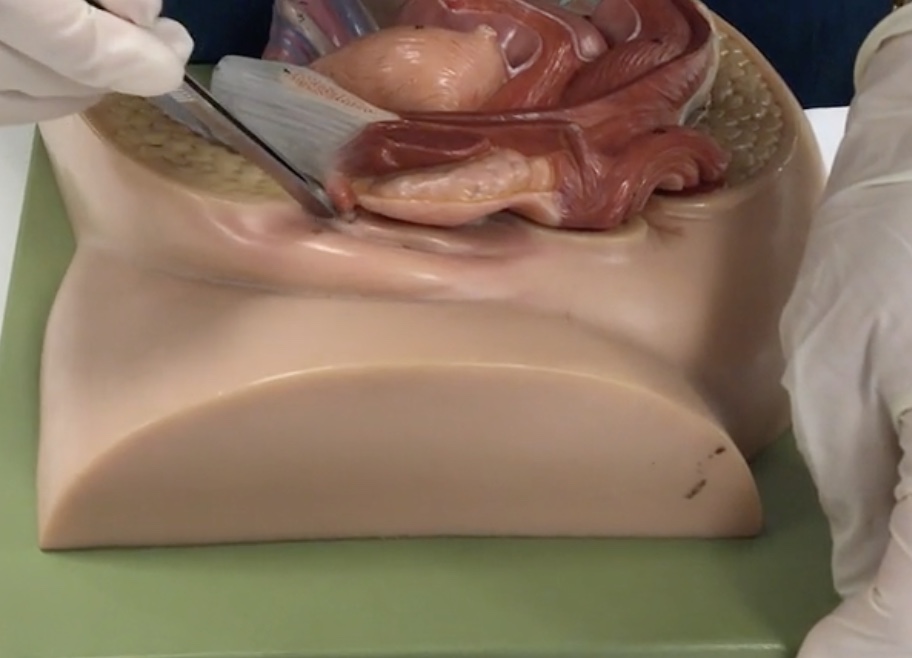
Clitoris
Description: Erectile tissue anterior to external urethral orifice
Relationship: N/A
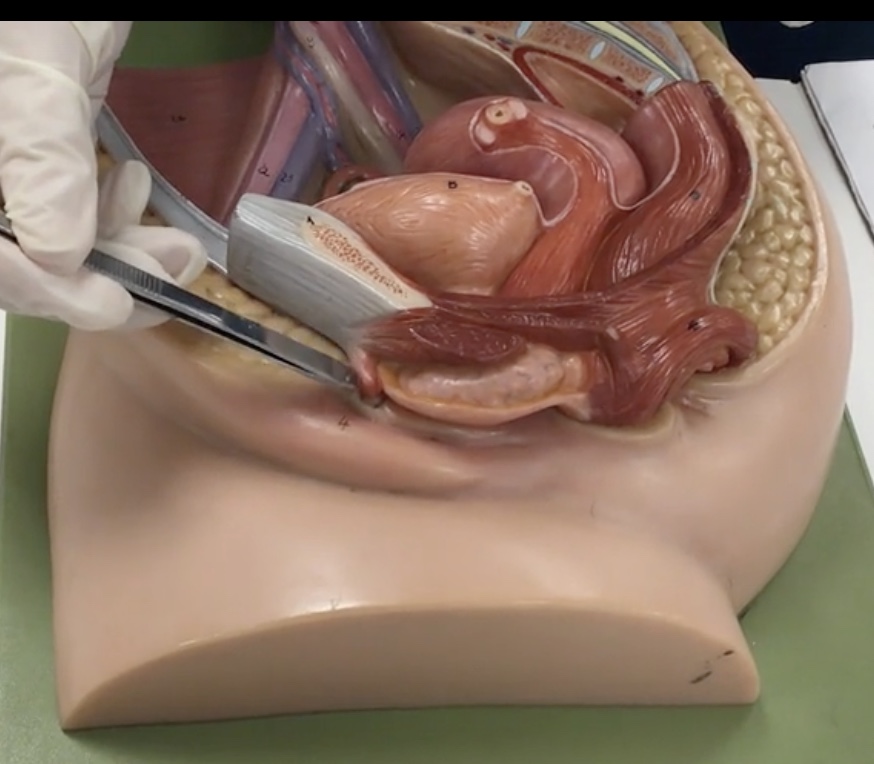
Vaginal orifice
Description: Inferior opening of the vagina
Relationship: Covered by the hymen
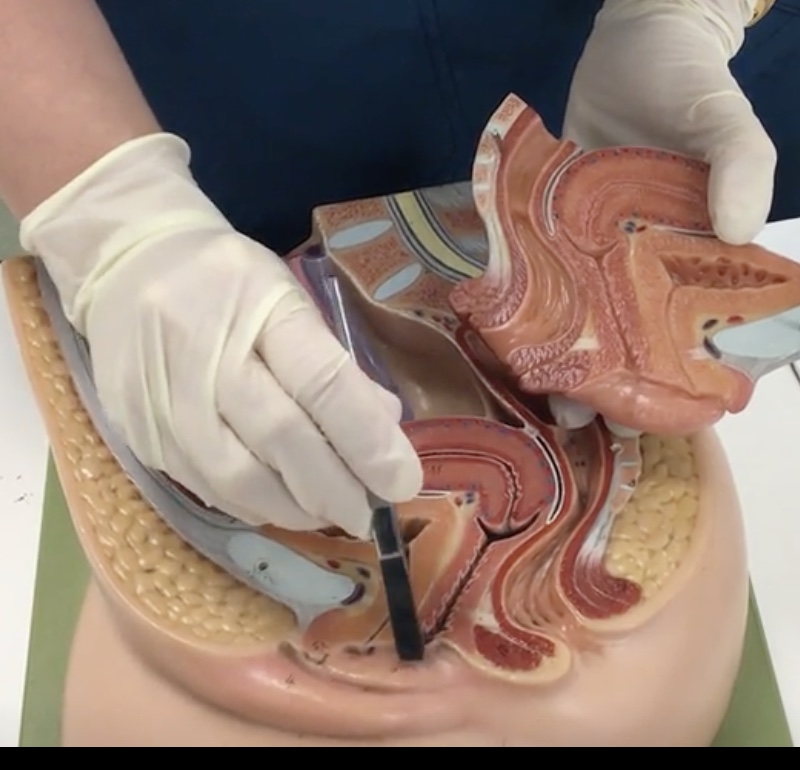
External urethral orifice
Description: Exit of urethra anterior to the vaginal orifice
Relationship: Exit for urine
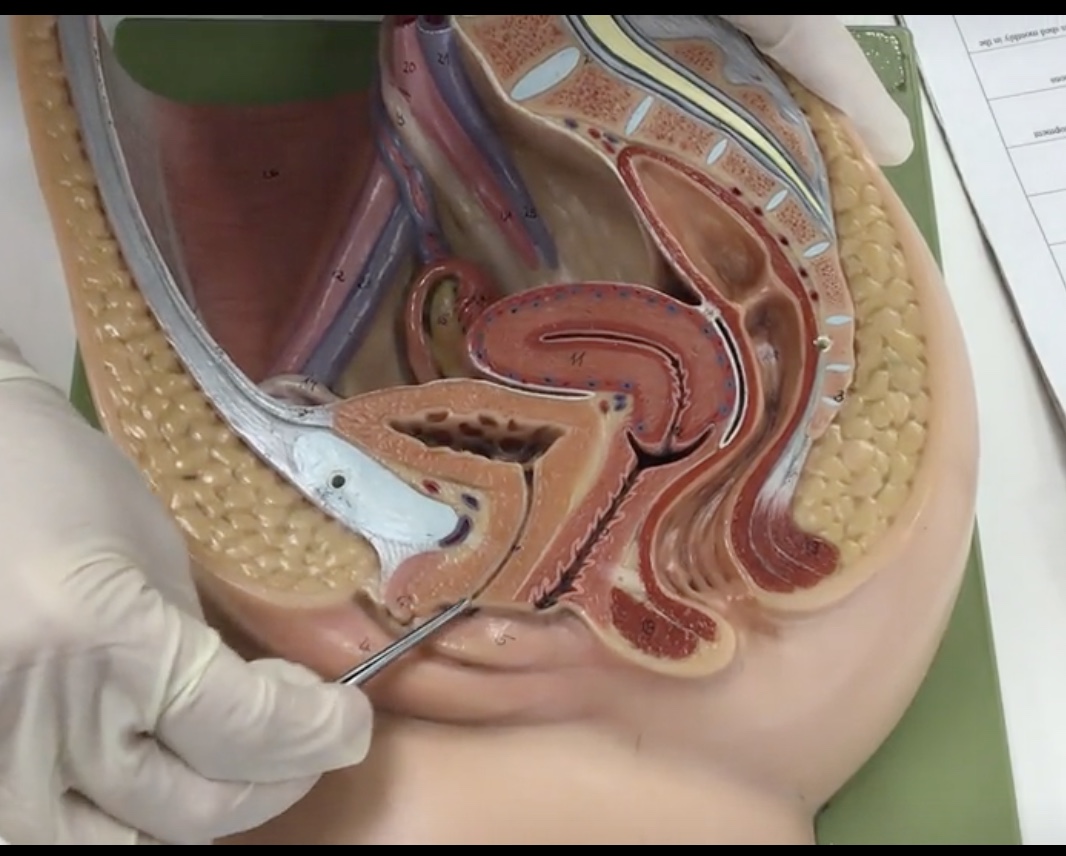
Ovaries
Description: Paired, female gonads that are small, almond shaped
Relationship: Where maturation of oocytes occur
Uterine (fallopian) tubes
Description: Thin, muscular tubes
Relationship: Transports mature ovum to uterus and common site of fertilization
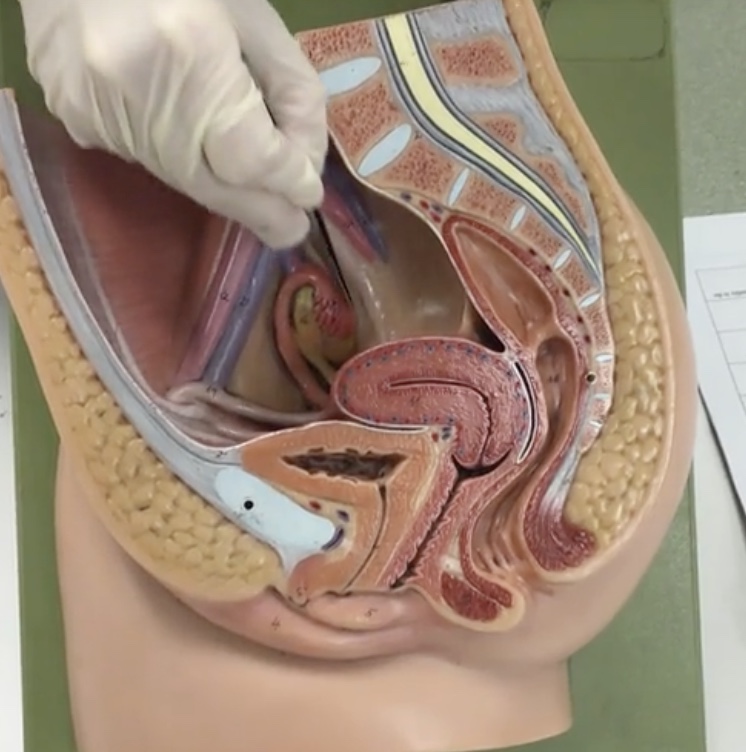
Fimbriae
Description: Mobile, finger-like projections at distal end of uterine tube
Relationship: Guide released ovum into the uterine tube
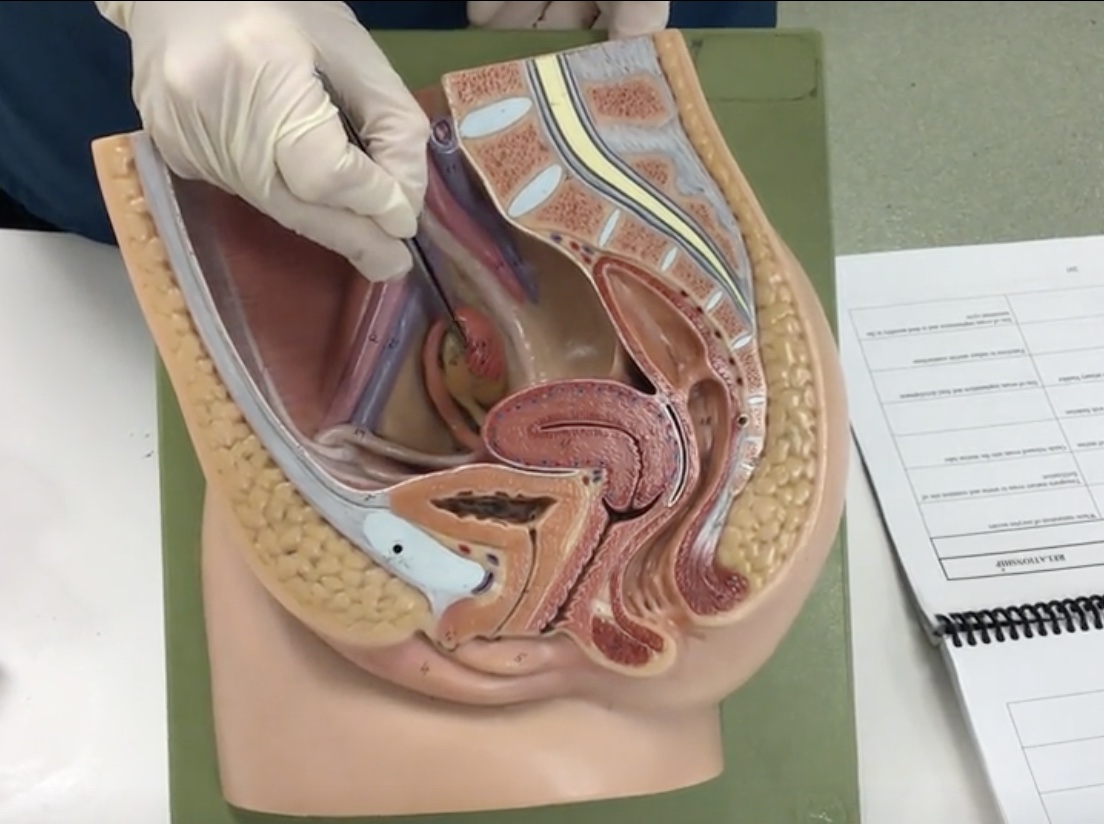
Infundibulum
Description: Funnel shaped opening of utuerine tube with fimbriae
Relationship: N/A
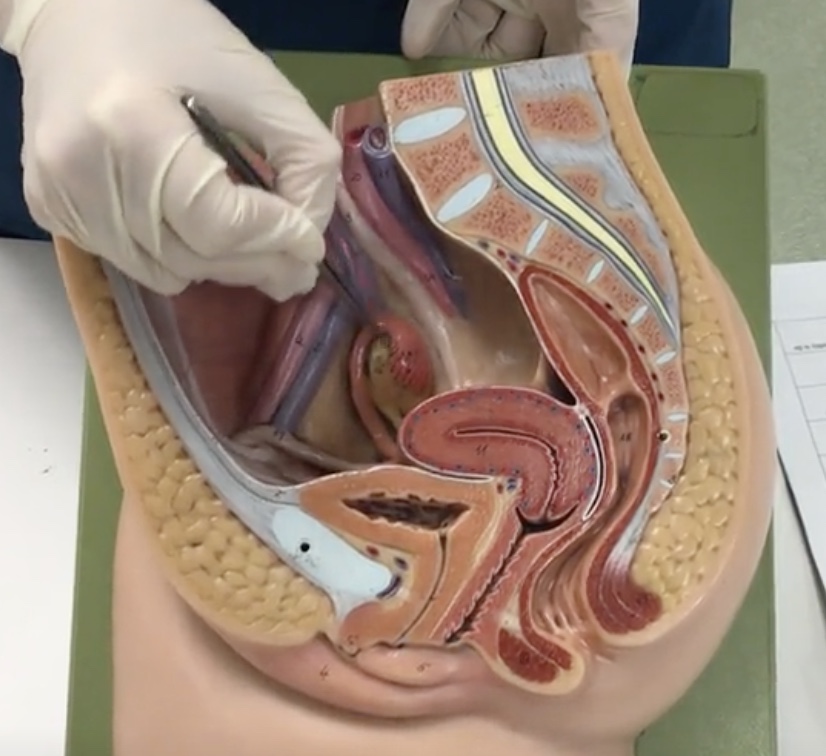
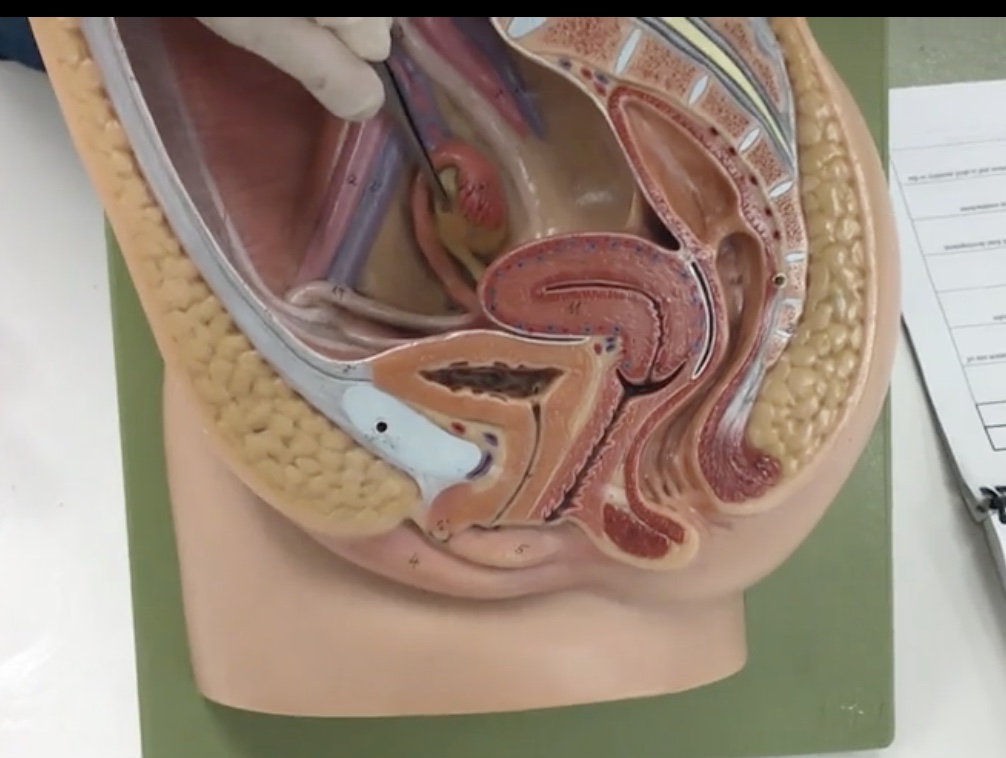
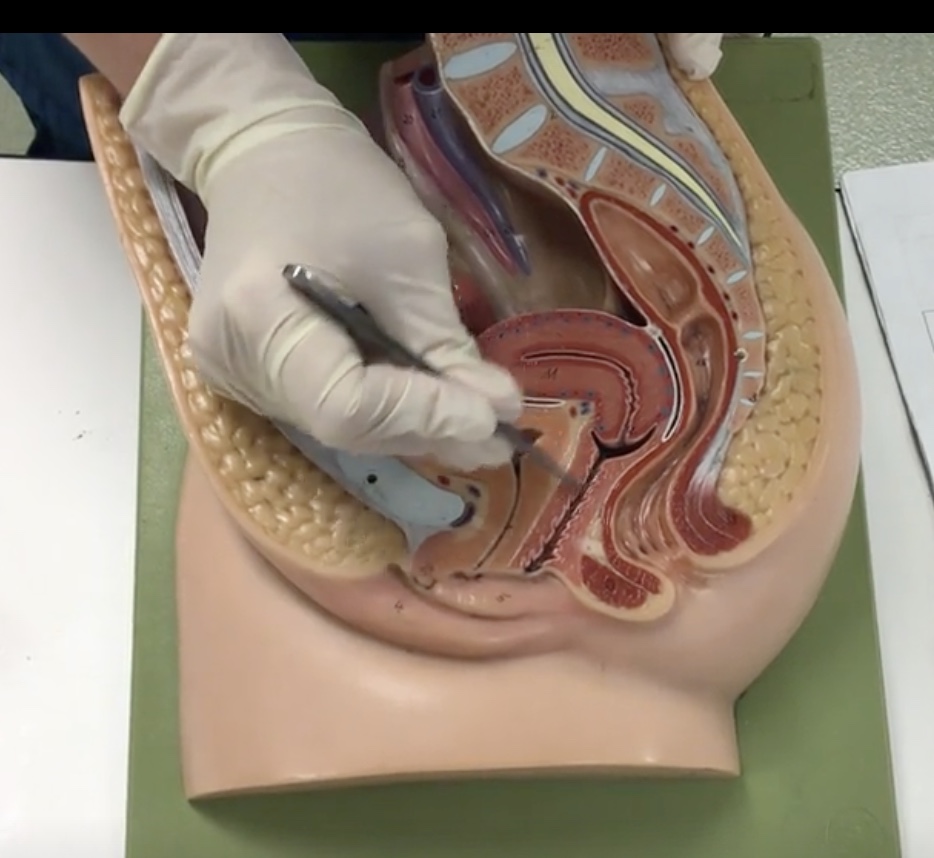
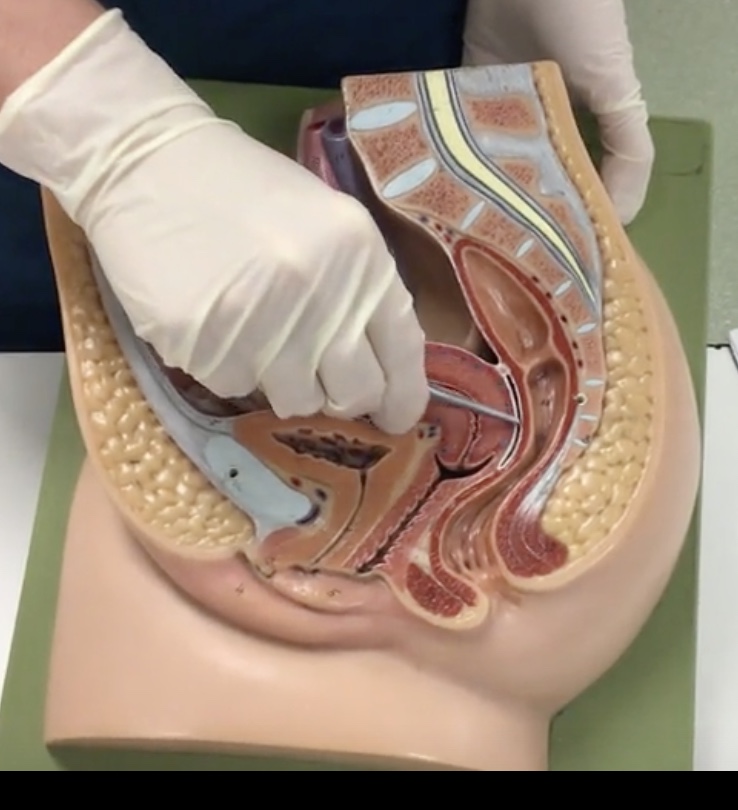
Uterus
Description: Pear shaped organ posterior to the urinary bladder
Relationship: Site of ovum implantation and fetal development
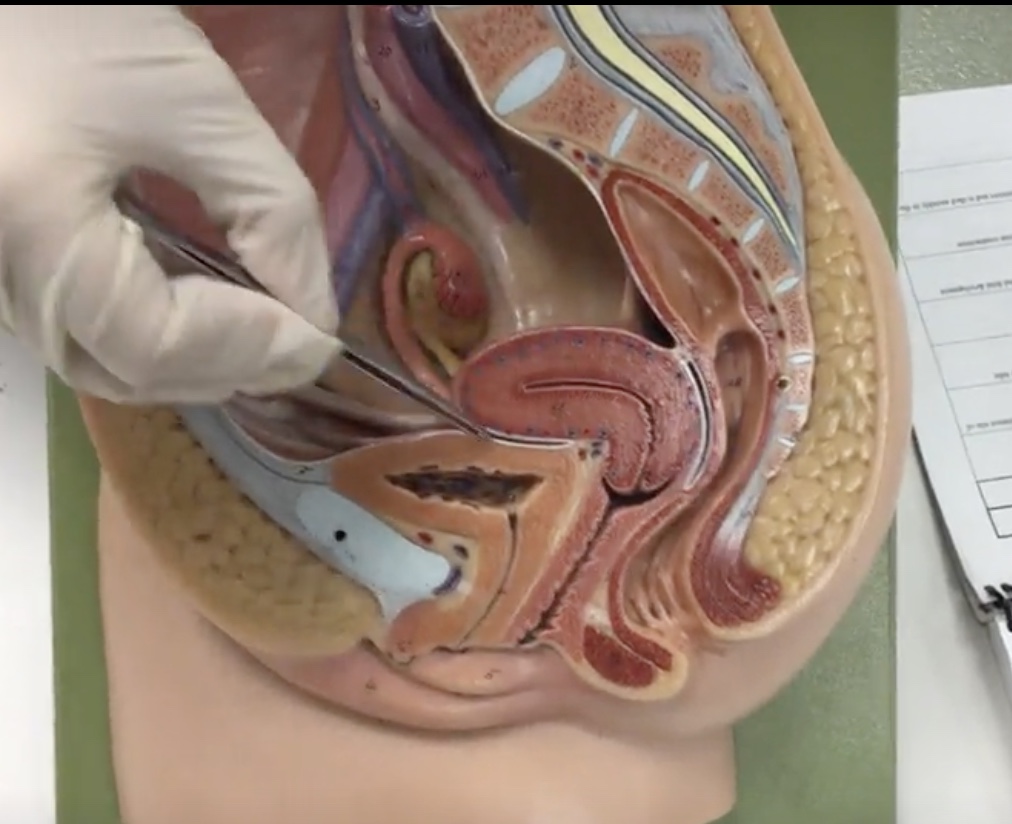
Myomentrium
Description: Thick, smooth muscle layer
Relationship: Functions to induce uterine contractions
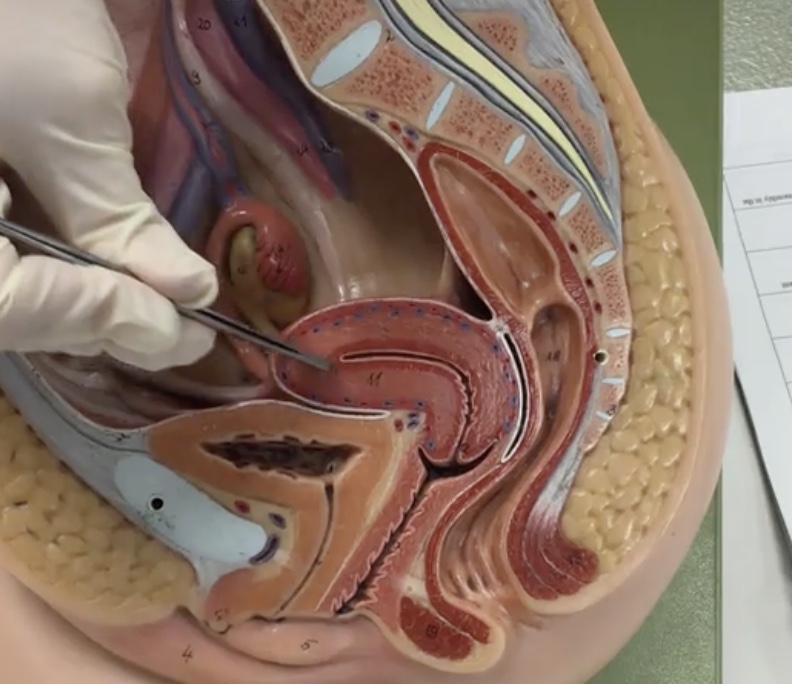
Endometrium
Description: Inner lining of uterus
Relationship: Site of ovum implantation and is shed monthly in the menstrual cycle
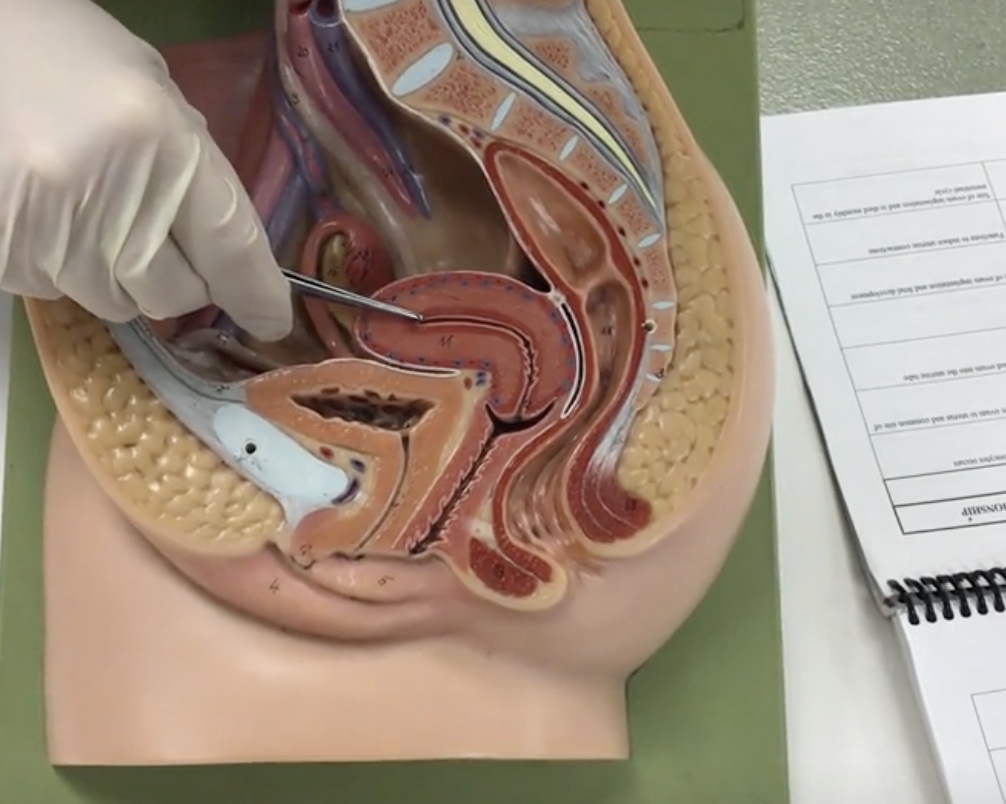
Fundus of uterus
Description: Wide, dome shaped portion of the uterus superior to openings of the uterine tubes
Relationship: N/A
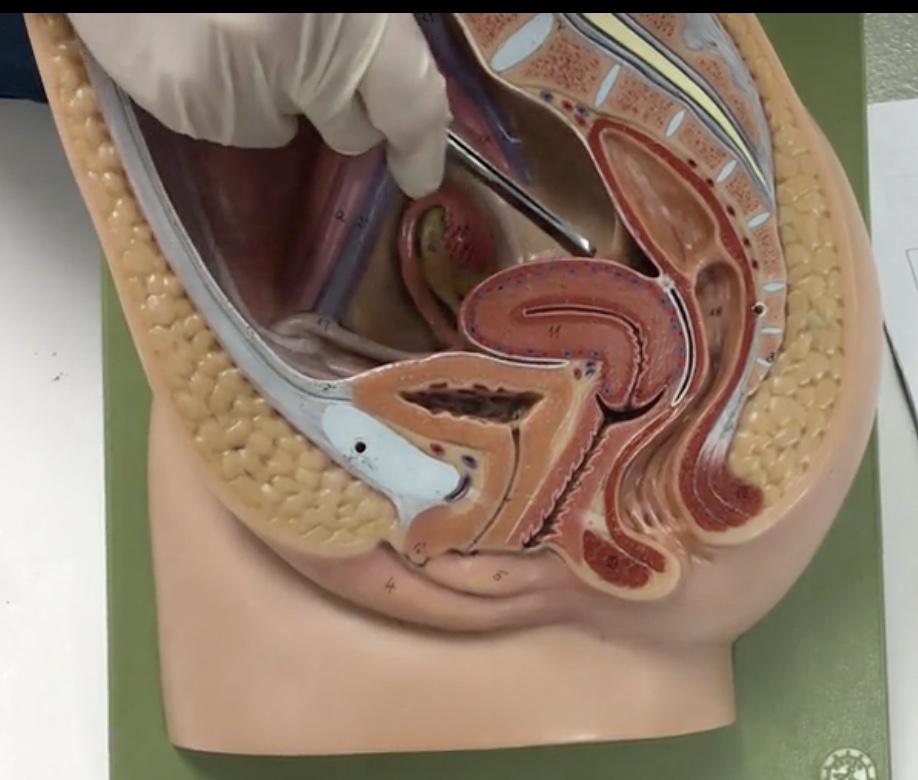
Body of uterus
Description: Narrow, middle portion of the uterus
Relationship: N/A
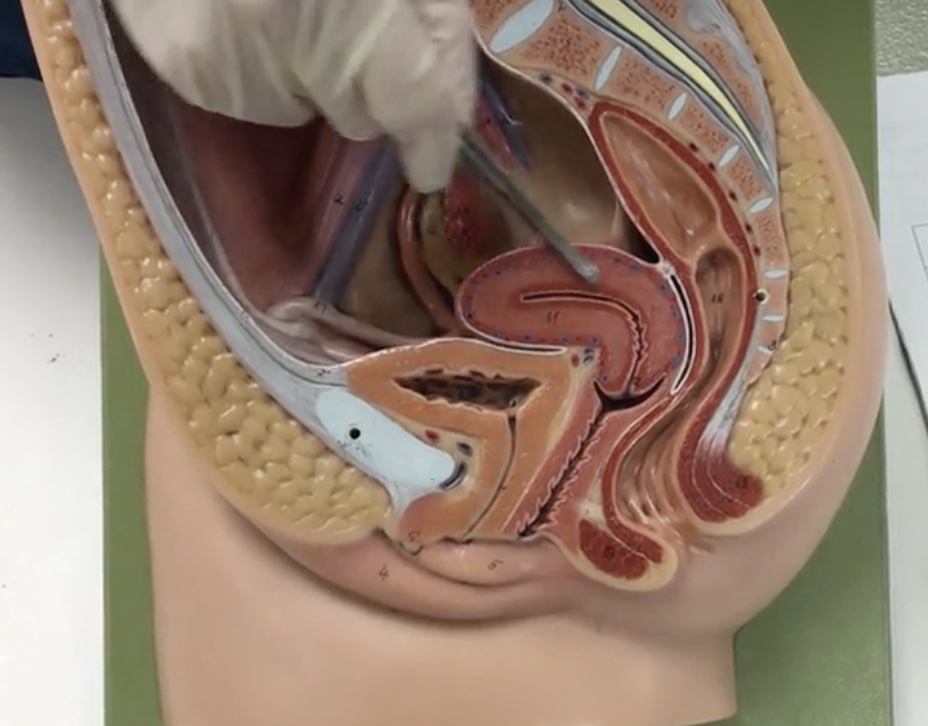
Cervix
Description: Cylindrical end of the uterus
Relationship: N/A
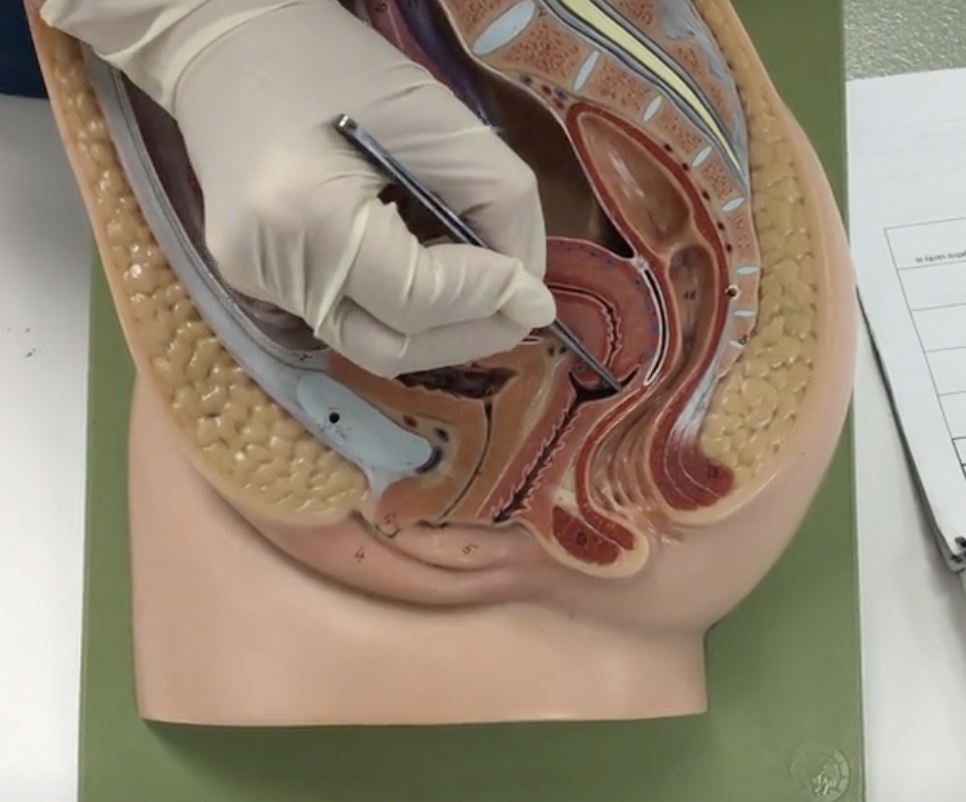
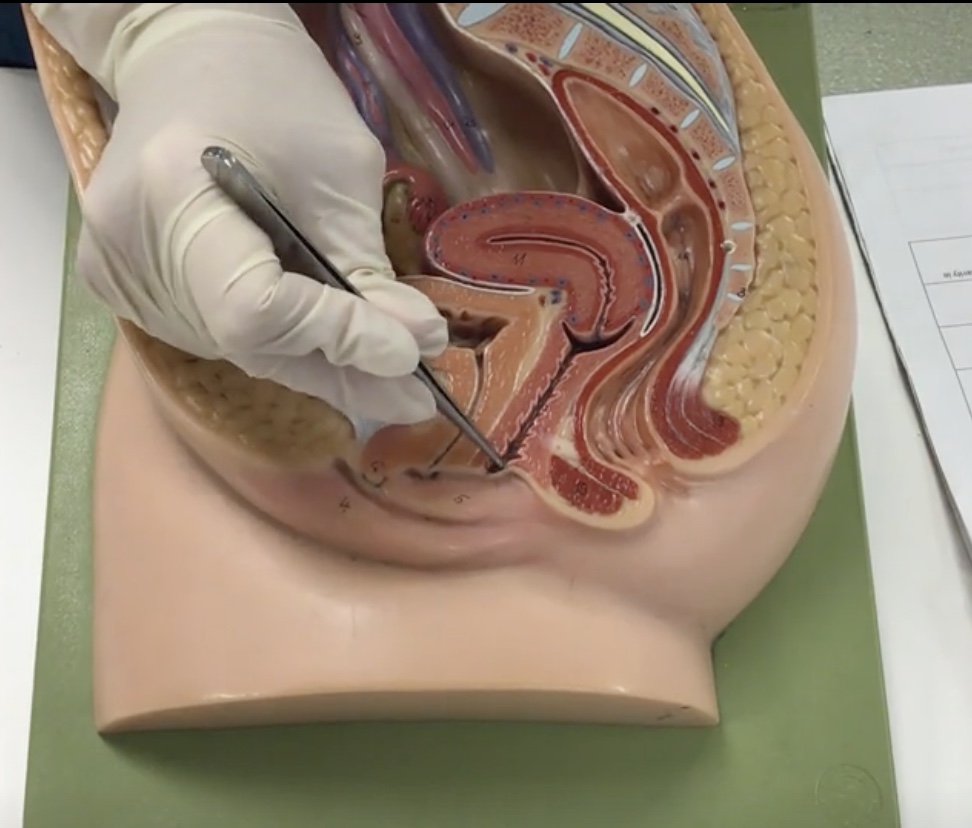
External OS
Description: Narrow opening in cervix
Relationship: Junction of the cervix and vagina
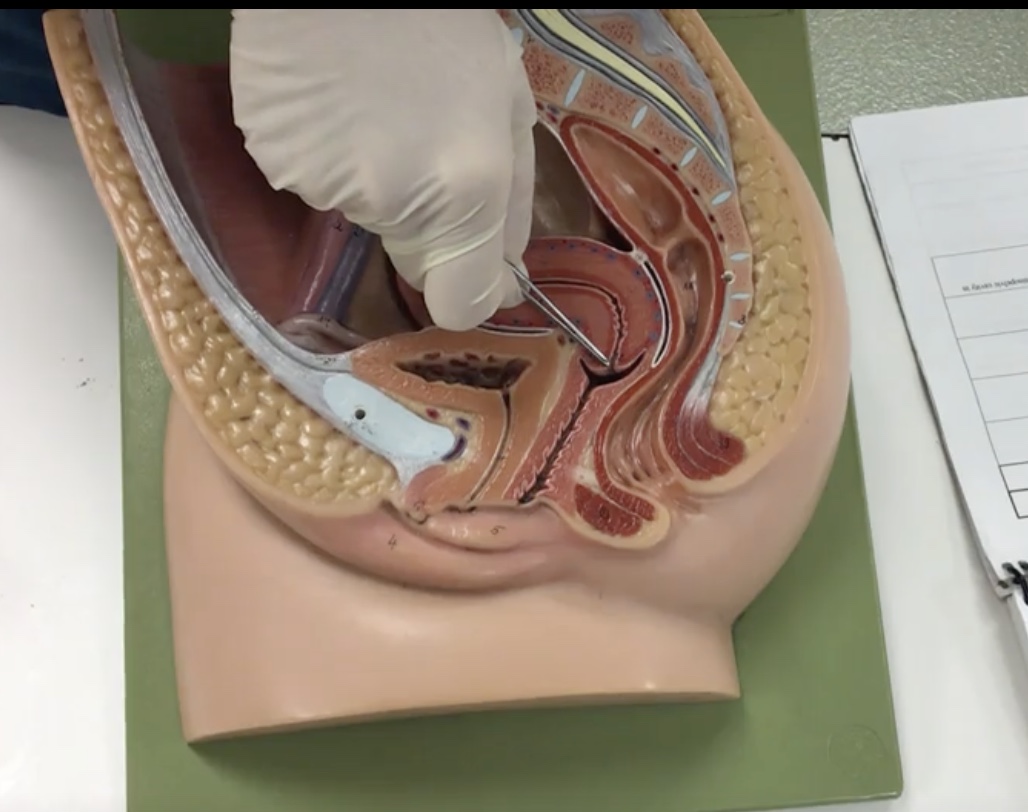
Fornix
Description: Recess surrounding cervix
Relationship: N/A
Vagina
Description: Muscular, hollow tube extending from the uterus to the vaginal orifice
Relationship: N/A
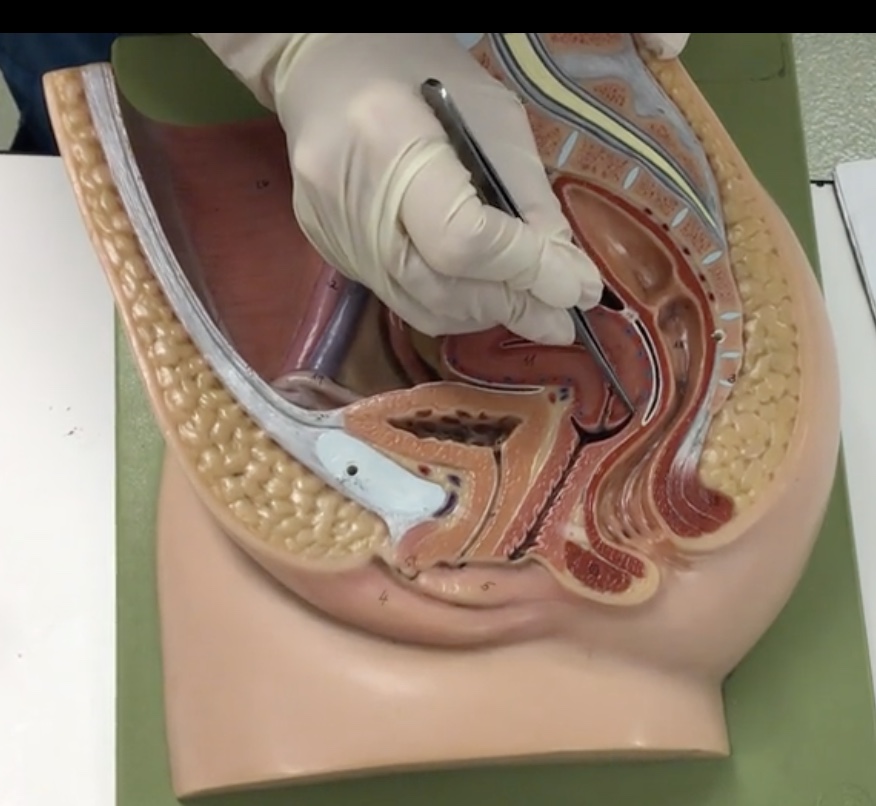
Hymen
Description: Thin, membranous covering vaginal orifice
Relationship: N/A
Round ligament of uterus
Description: Fibrous cord extending from the uterus to the inguinal canal
Relationship: N/A
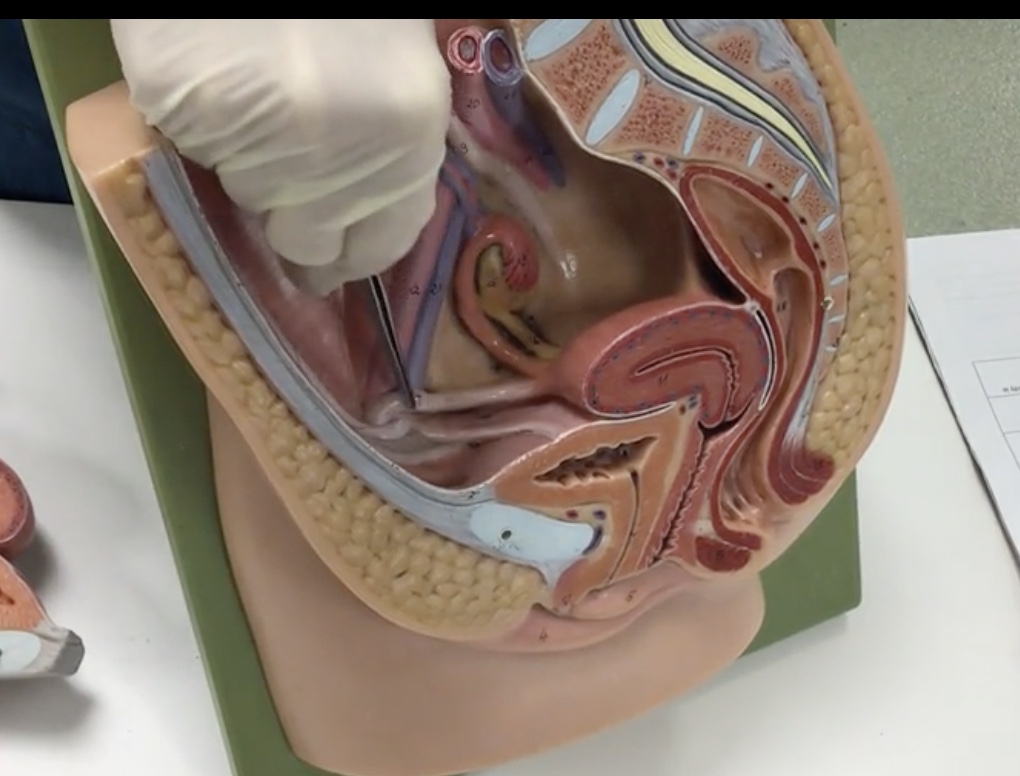
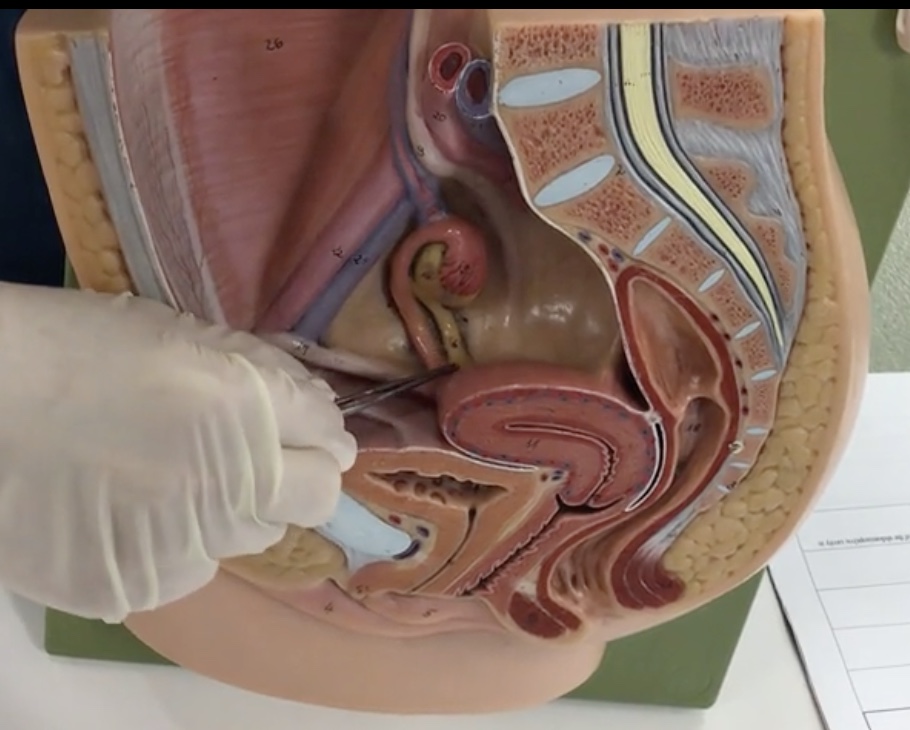
Broad ligament
Description: Double layer of peritoneum covering the uterus, uterine tubes, and ovaries containing blood vessels and nerves to the uterus
Relationship: N/A
Ovarian ligament
Description: Fibrous cord extending from the ovaries to the uterus
Relationship: N/A
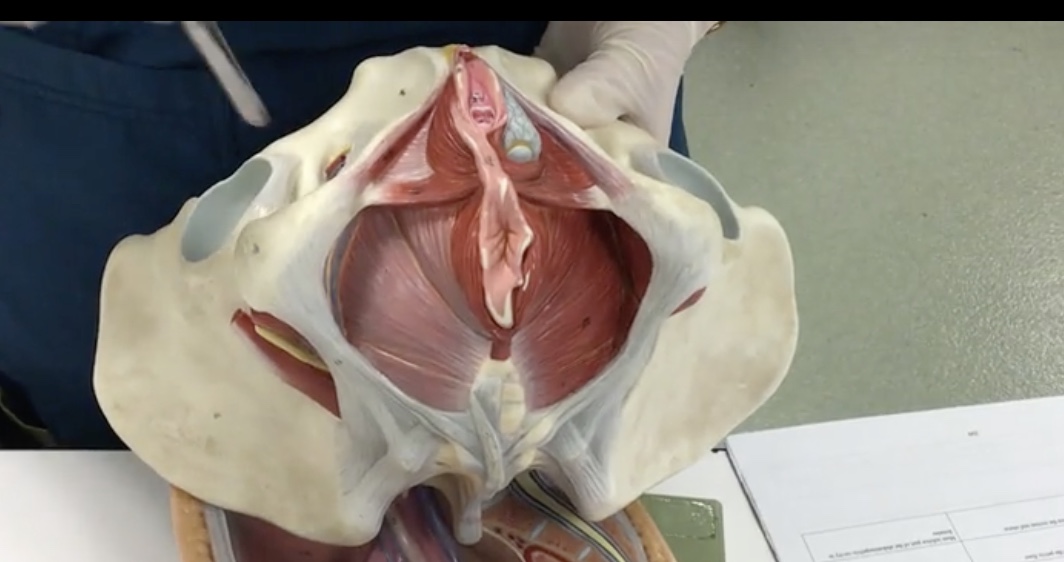
Levator ani muscle
Description: Group of muscles to the pelvic floor
Relationship: Supports pelvic viscera
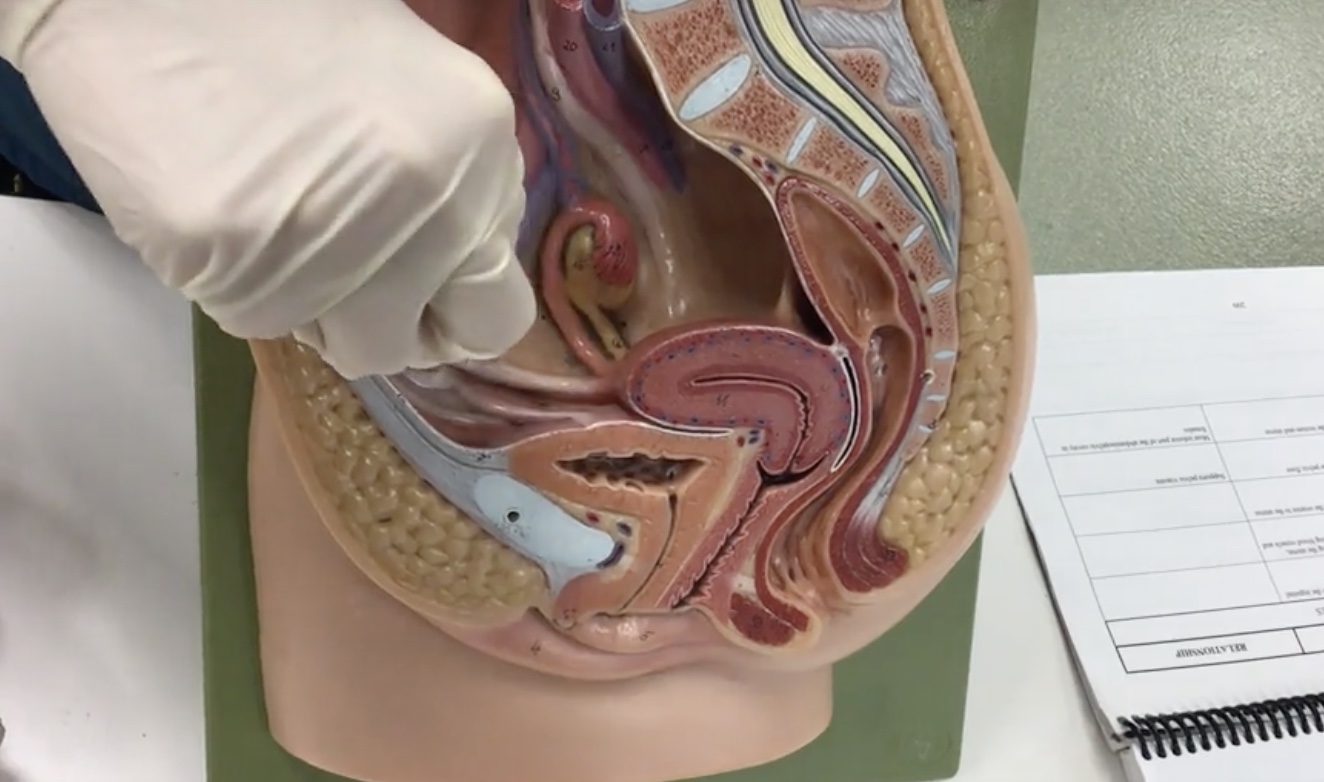
Rectouterine (douglas) pouch
Description: Recess between the rectum and uterus
Relationship: Most inferior part of the abdominopelvic cavity in females
Areola
Description: Pigmented skin surrounding the nipple
Relationship: N/A
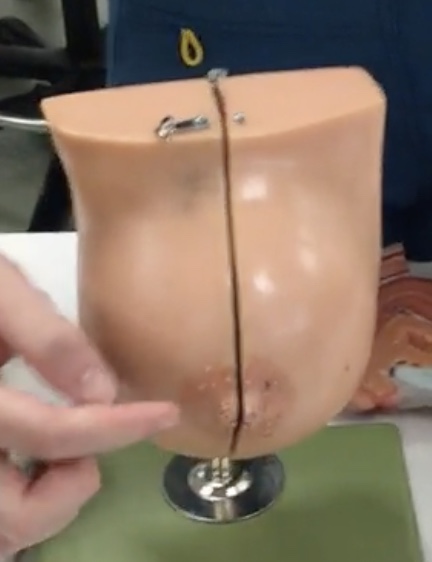
Nipple
Description: Elevation of skin at center of breast
Relationship: Contains smooth muscle
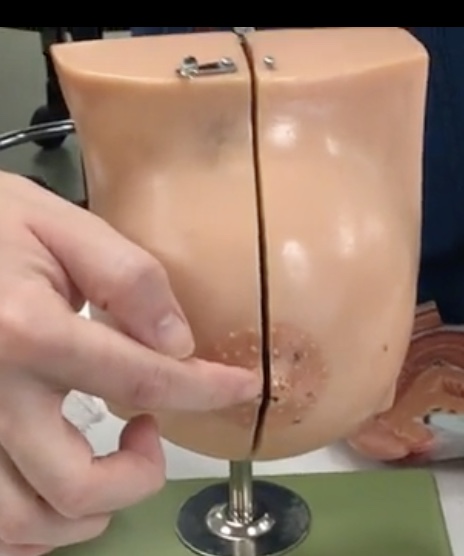

Pectoralis major
Description: Muscle deep to the pectoral fat pad
Relationship: Adducts and medially rotates the arm
Pectoral fat pad
Description: Conical-shaped fat pad
Relationship: Contains mammary glands
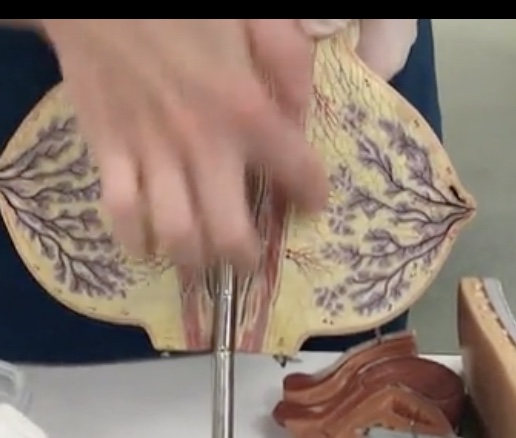

Axillary tail (process)
Description: Extension of fat in the superolateral breast
Relationship: Functions as fat storage
Suspensory ligaments
Description: Fibrous connective tissue connecting to the dermis
Relationship: Supports breast tissue
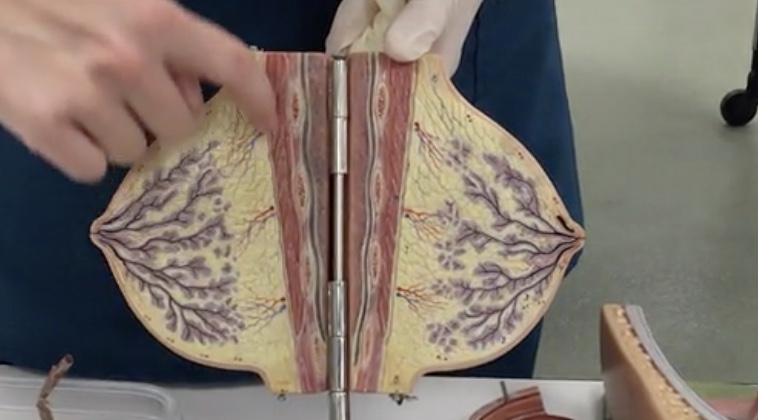
Mammary gland
Description: Milk producing gland
Relationship: N/A
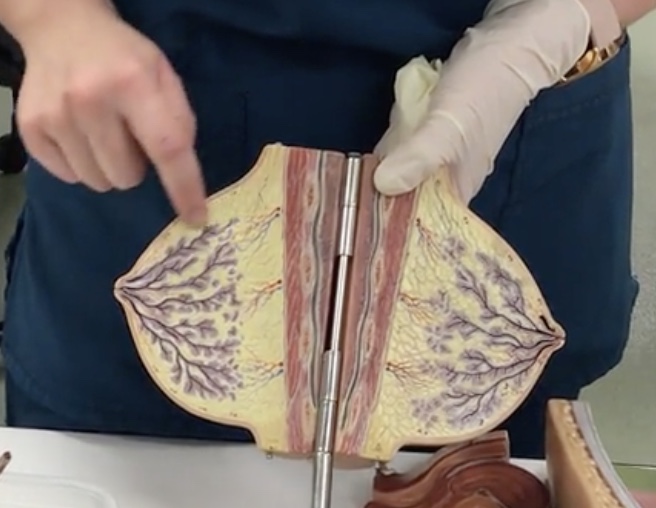
Secretory alveoli
Description: Small cavities lined by milk secreting cells
Relationship: Production of milk
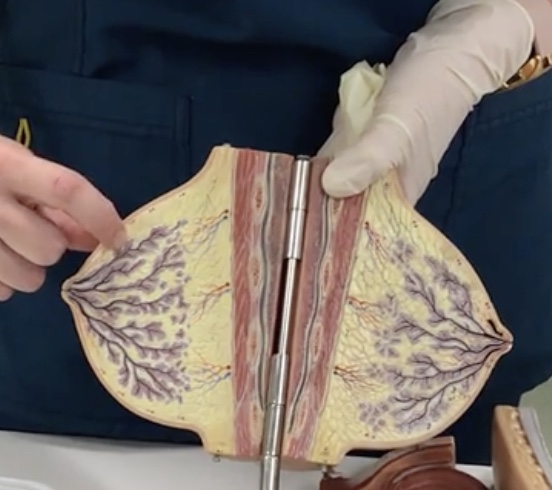
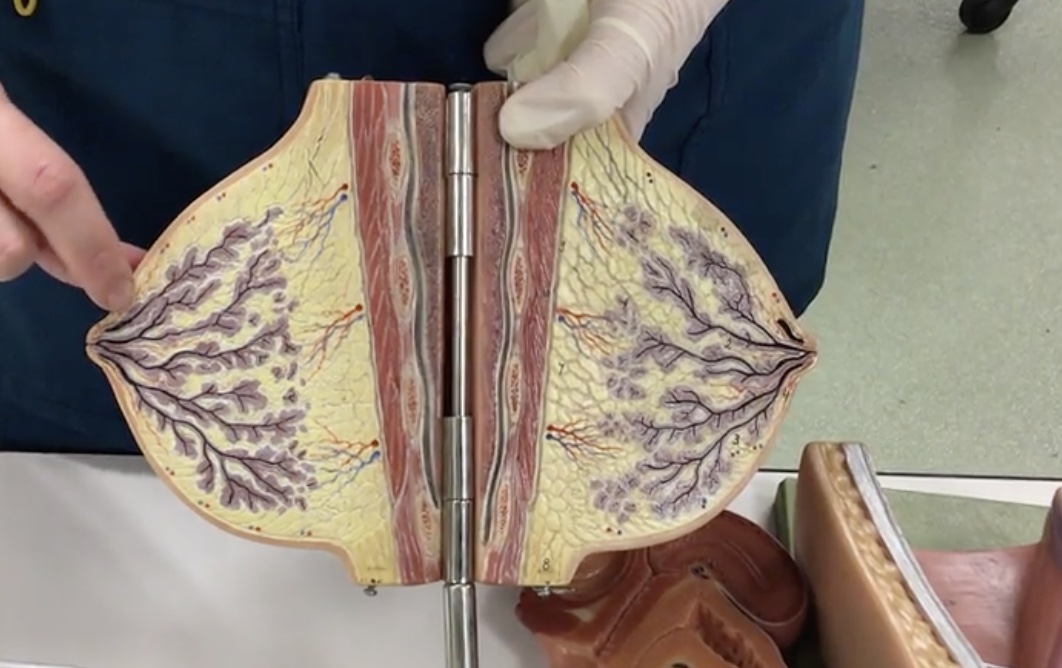
Lobules
Description: Groups of secretory alveoli
Relationship: N/A
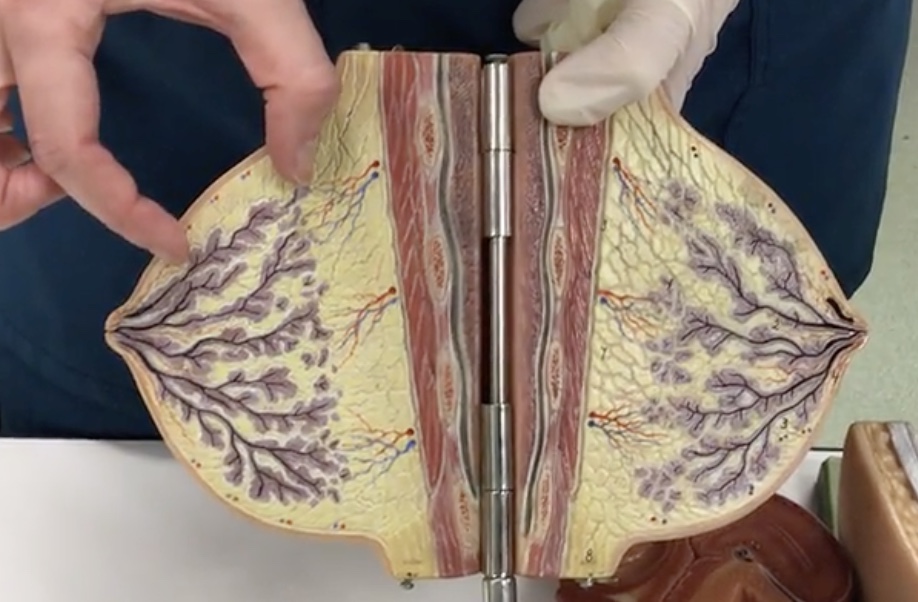
Lactiferous ducts
Description: Ducts connecting mammary glands to the nipple
Relationship: Transfers milk from mammary glands to the nipple
Penis
Description: Body of erectile tissues
Relationship: Transmits urine and semen
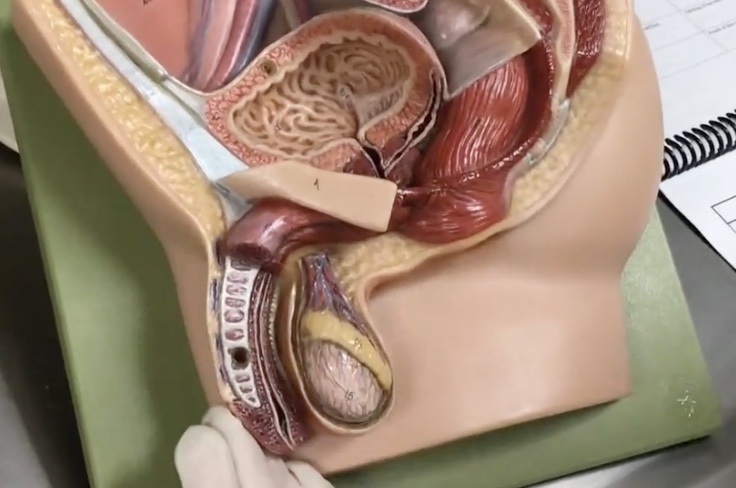
Glans penis
Description: Expanded tip of penis composed of corpus spongiosum
Relationship: Contains the spongy urethra
Prepuce (foreskin)
Description: Folds of skin covering glans penis
Relationship: Commonly removed (circumcision)
External urethral orifice
Description: Opening of the urethra in the glans penis
Relationship: N/A
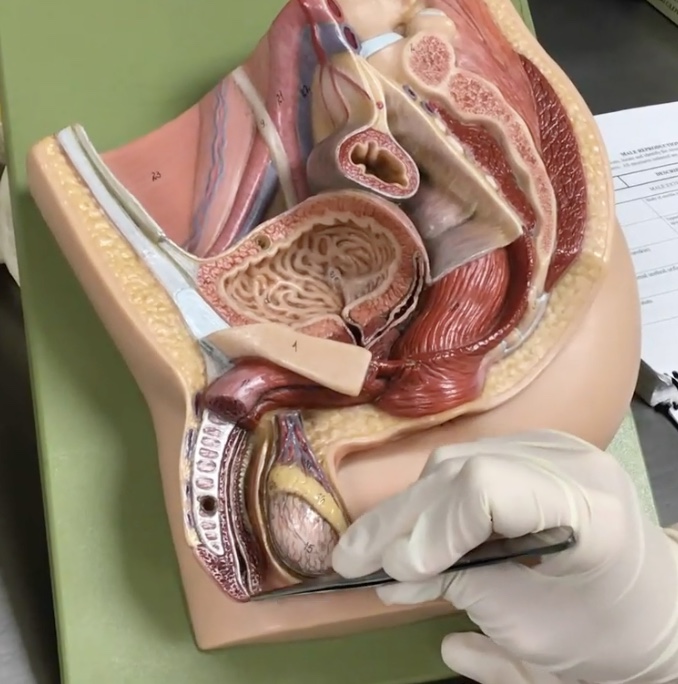
Scrotum
Description: Pouch of skin surrounding testis
Relationship: Contains the dartos muscle
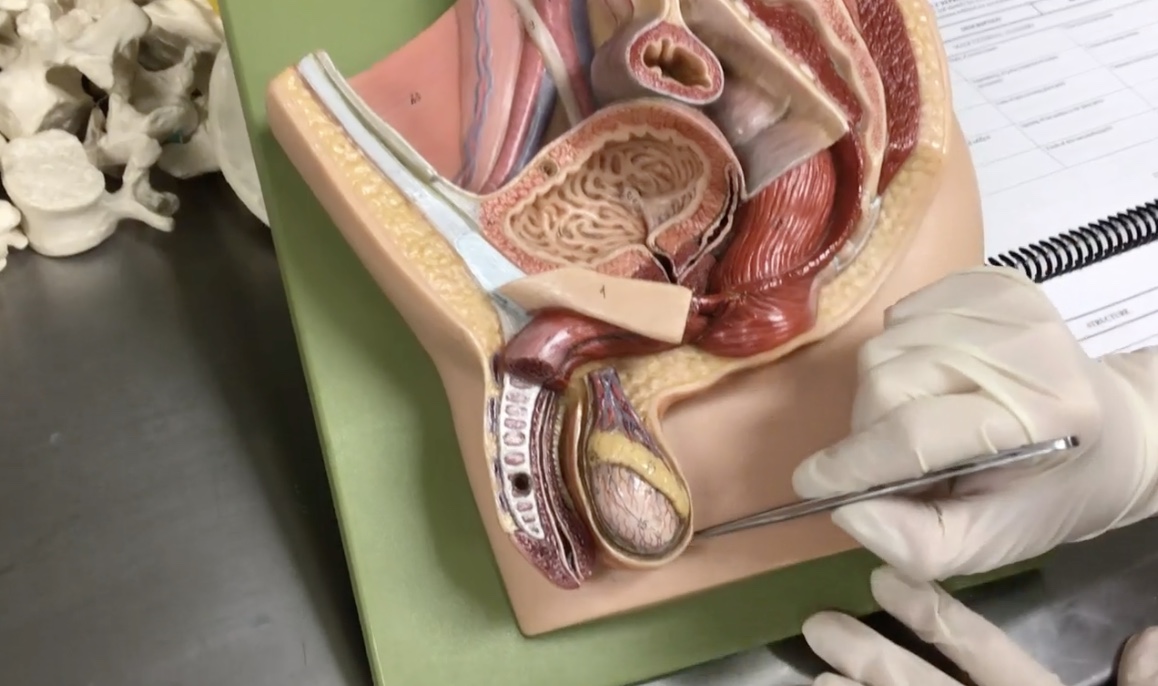
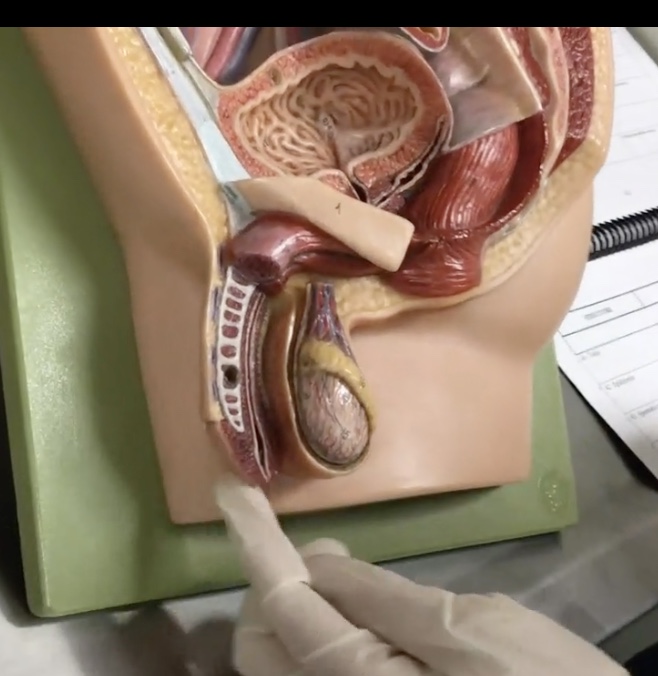
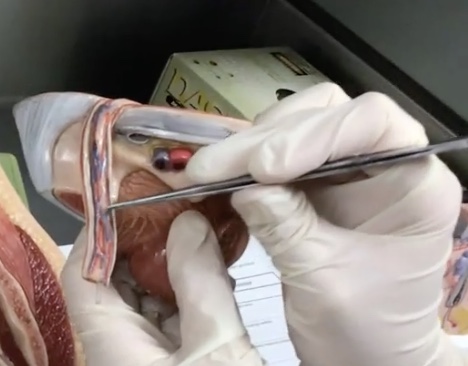
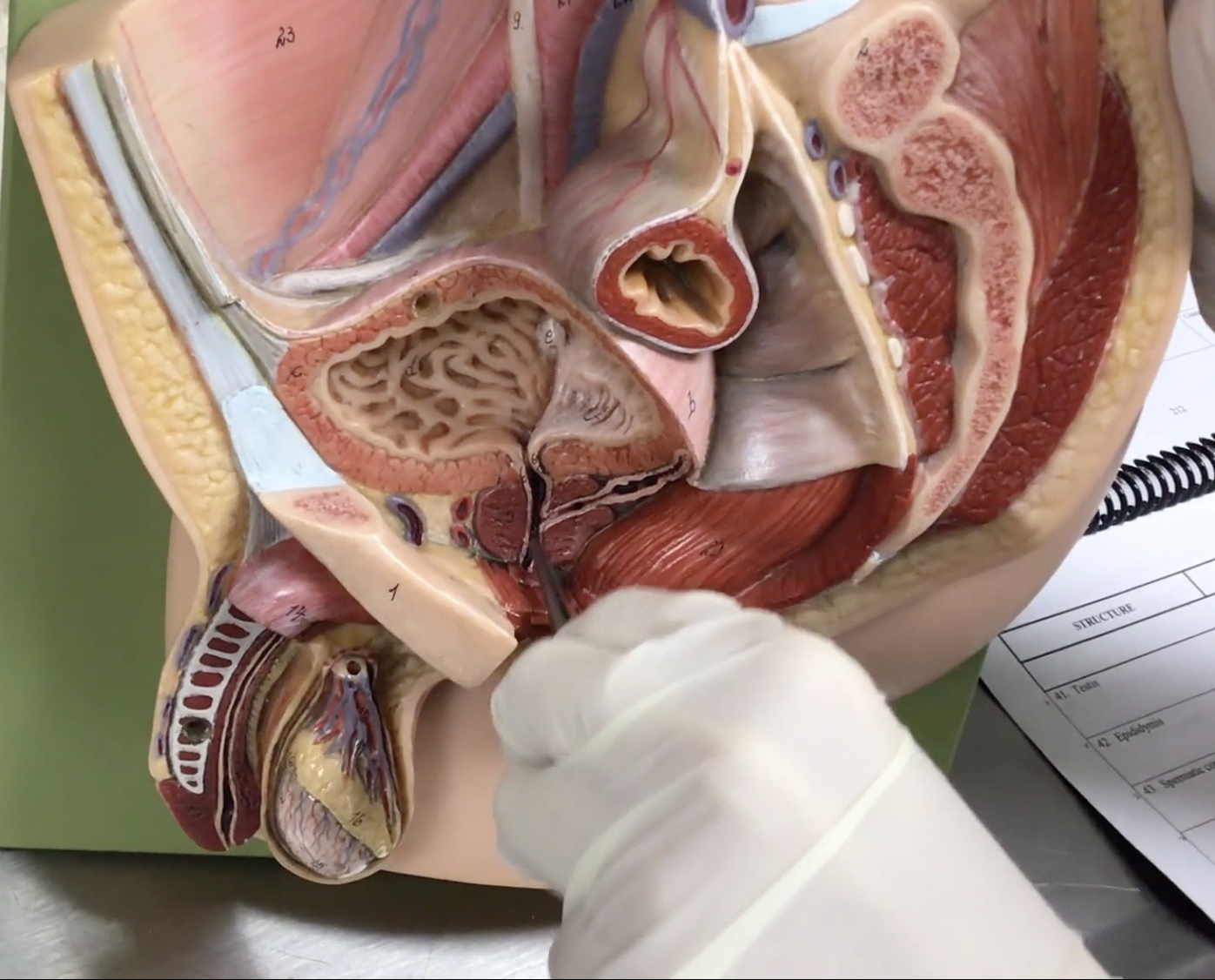
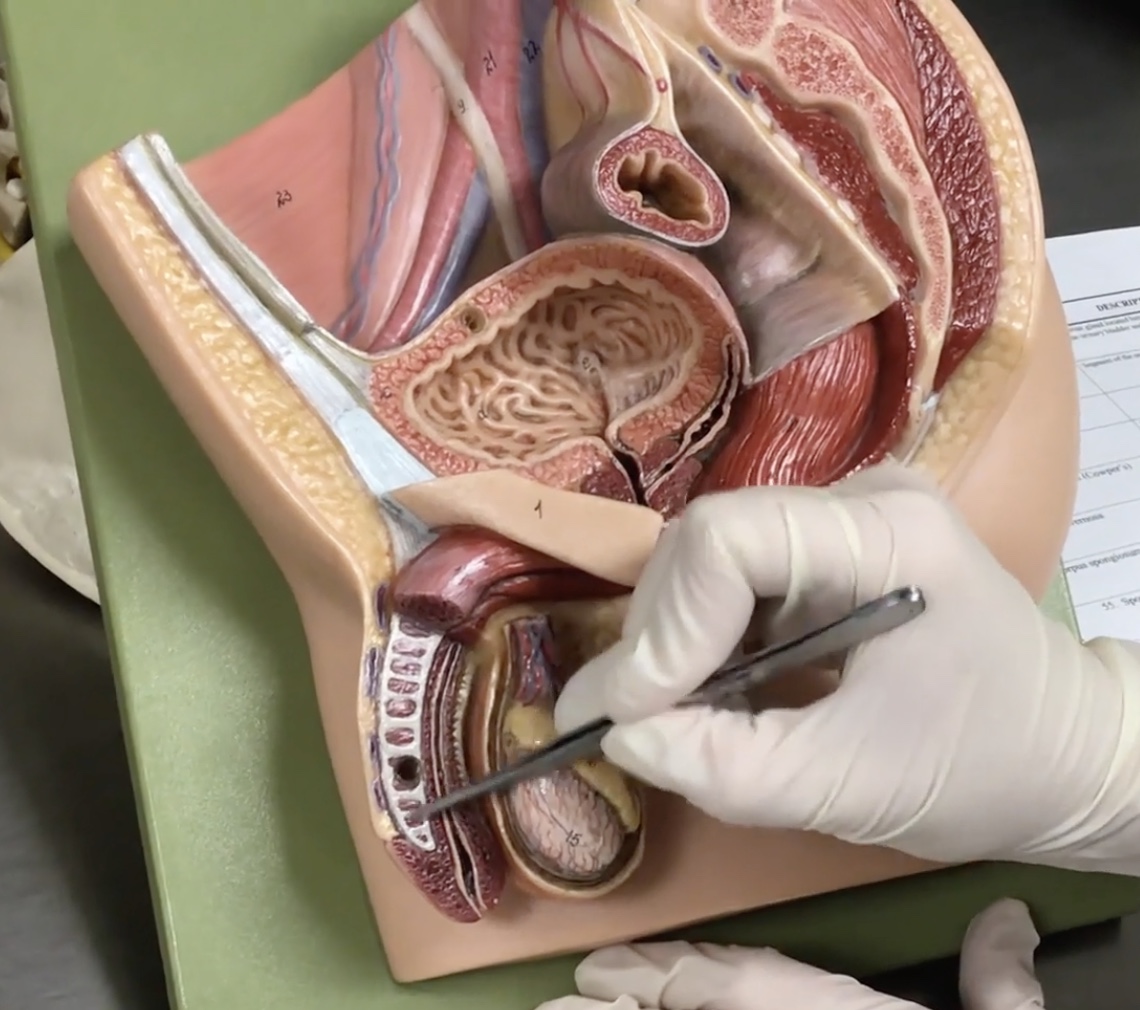
Testis
Description: Paired, oval-shaped male gonads located in the scrotum
Relationship: Produces sperm cells and sex hormones
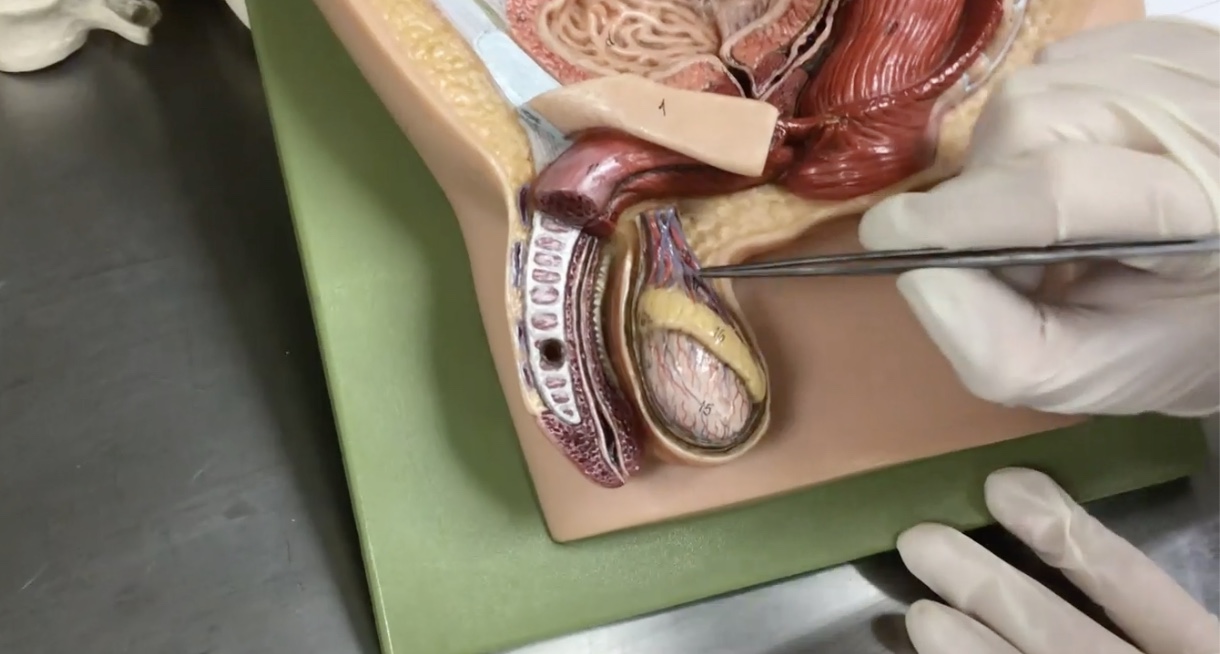
Epididymis
Description: Structure on the superior surface of testis in scrotum
Relationship: N/A
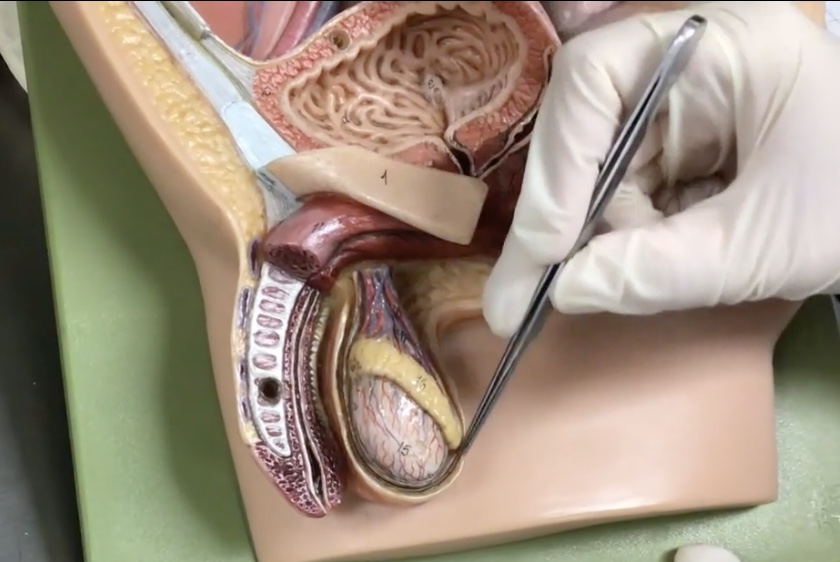
Spermatic cord
Description: Paired bundle of vessels extending from the deep inguinal ring to the testis
Relationship: N/A
Ductus (vas) deferens
Description: Tube-like structure of the spermatic cord extending from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
Relationship: Common site for vasectomies
Cremaster muscle
Description: Thin layer of skeletal muscle layer surrounding the testis
Relationship: Elevates the testis
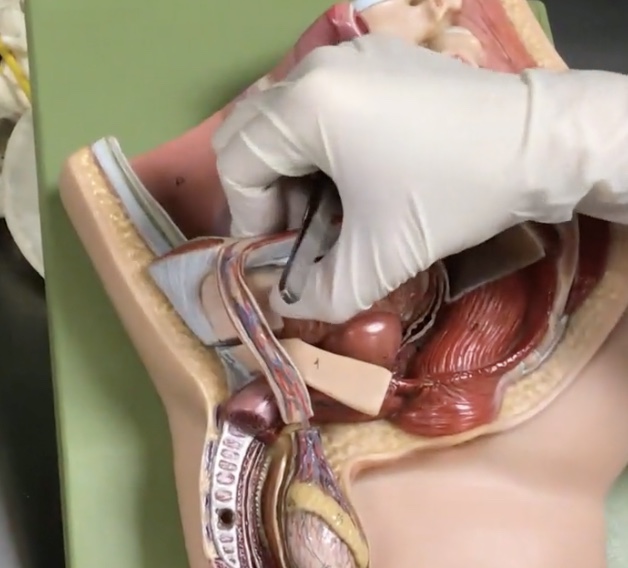
Seminal vesicle
Description: Paired, saclike gland on the posterior surface of the urinary bladder
Relationship: Connected to the ductus (vas) deferens and secretes seminal fluid
Ejaculatory duct
Description: Short, paired ducts within the prostate gland connecting the ductus (vas) deferens to the urethra
Relationship: N/A
Prostate
Description: Exocrine gland located between the inferior part of the to the urinary bladder and base of penis
Relationship: Contains the ejaculatory duct and prostatic urethra. Transmits both urine and seminal fluid
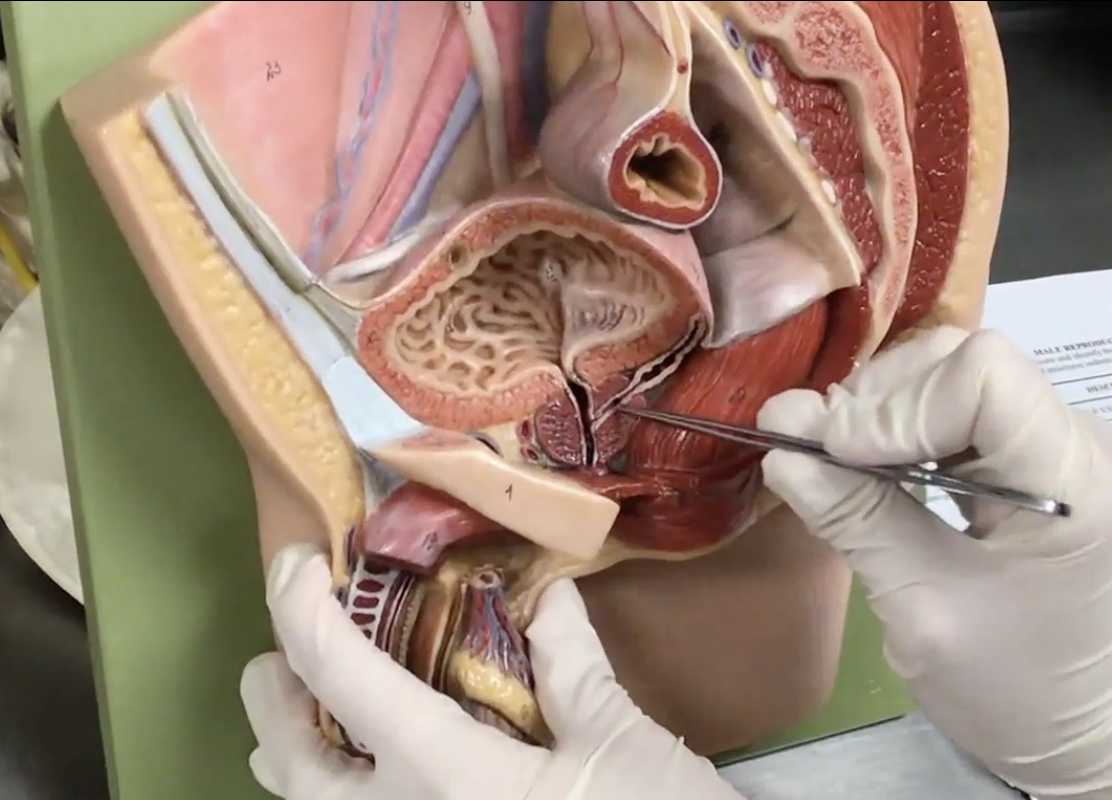
Prostatic urethra
Description: Segment of the urethra that passes through the prostate
Relationship: N/A
Urogenital diaphragm
Description: N/A
Relationship: Pelvic floor
Membranous urethra
Description: Urethra passing through the urogenital diaphragm
Relationship: Carries semen and urine
Bulbourethral (cowper’s) gland
Description: Exocrine gland located within the urogenital diaphragm
Relationship: N/A
Corpora cavernosa
Description: Two columns of erectile bodies of the penis
Relationship: N/A
Corpus spongiosum
Description: Midline erectile body of the penis
Relationship: Contains the spongy urethra
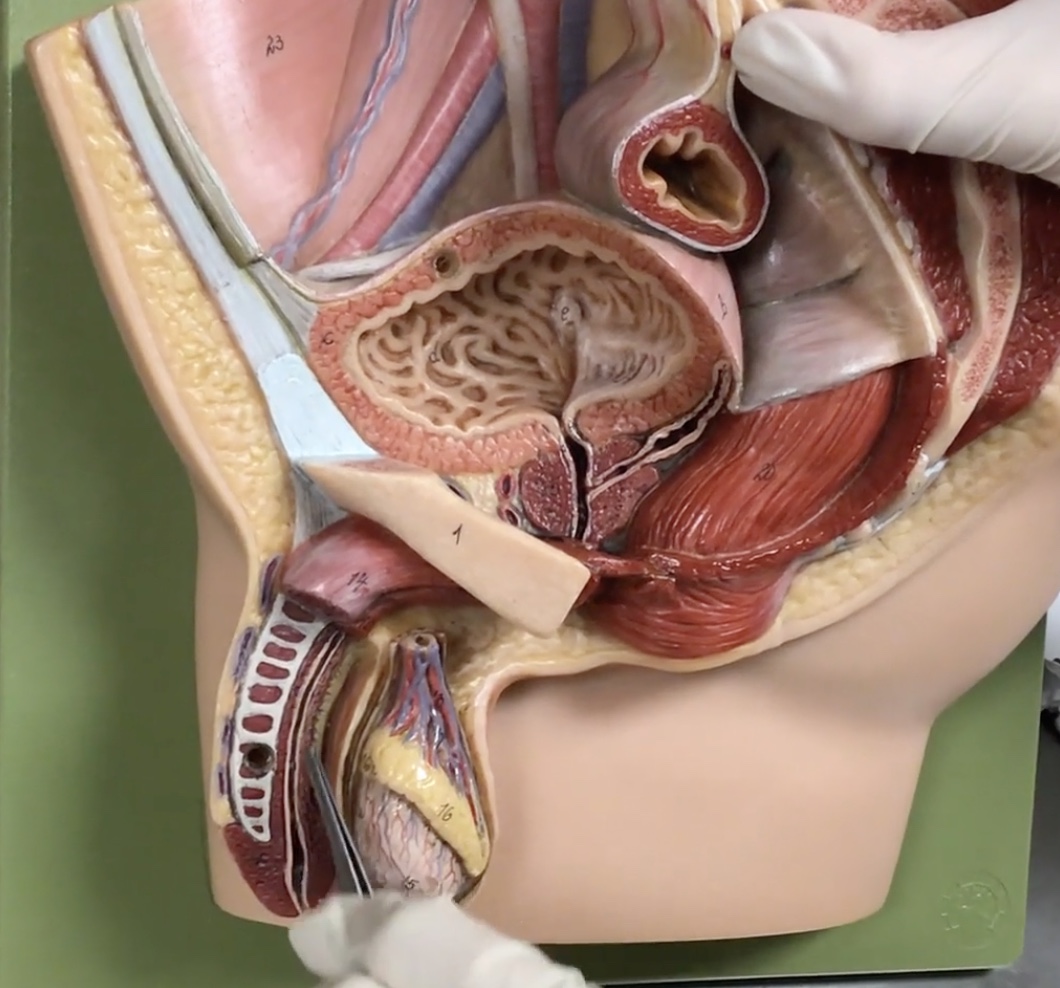
Spongy (cavernous) urethra
Description: Longest part of the male urethra
Relationship: Within the corpus spongiosum
Inguinal ligament
Description: Ligament attaching from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) to the pubis
Relationship: Forms the floor of the inguinal ligaments
Inguinal canal
Description: A tube-like passageway through the inferior abdominal wall muscles
Relationship: Passageway for the spermatic cord in males. Site of inguinal hernias in male
Superficial inguinal ring
Description: Superficial boundary of the inguinal canal
Relationship: Area of palpation for diagnosis of inguinal hernia