Exercise science
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is anatomical position?
The universal reference point
What is the transverse plane?
Divides body into top and bottom
What is the frontal plane?
Divides body into front and back
What is the sagittal plane?
Divides body into left and right
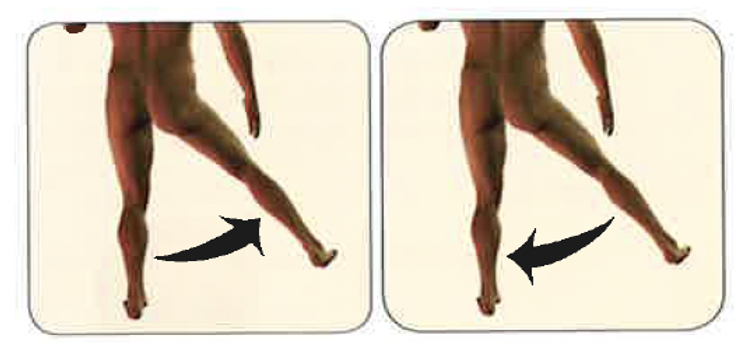
What is abduction?
Moving away from the middle of the body
What is adduction?
Moving towards the middle of the body
What does medial mean?
Nearer to the middle
What does lateral mean?
Farther from the middle
What does superficial mean?
Nearer to the surface
What is an example of the transverse plane?
Golf/baseball swing
What is an example of the frontal plane?
Jumping jack
What is an example of sagittal plane?
Walking, running, cycling
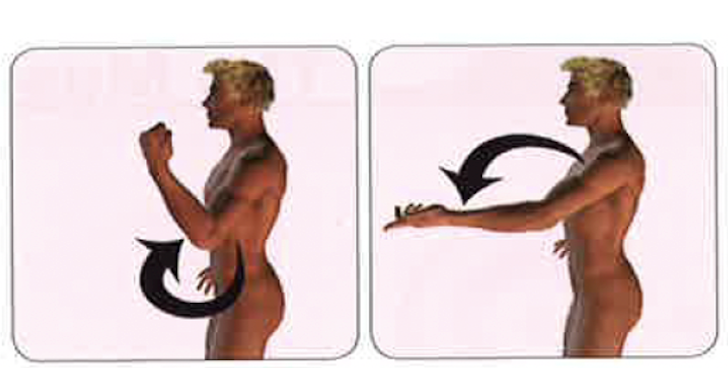
Flexion/extension
Sagittal plane (elbows, knees, hips, fingers, toes, and spine)
Abduction/ adduction
Frontal plane (shoulder, hip, wrist)
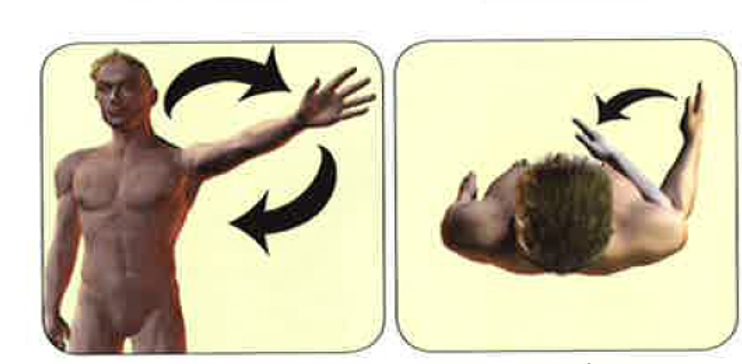
Circumduction/rotation
Ball and socket joints
Pronation/supination
Proximal and distal radioulnar joints in the forearm
Inversion/eversion
Foot
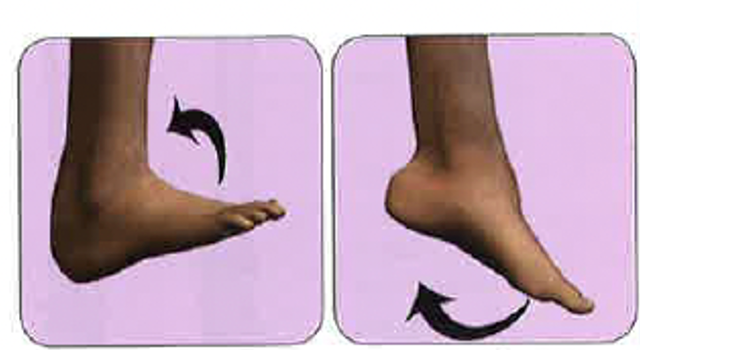
Dorsiflexion/plantar flexion
Foot
Features of bone
Rigid framework, protection, acts as levers
Long bone & function
Arm and leg bones: acts as levers
Short bone & function
Wrist and ankle: absorbs shock
Flat bone & function
Skull and ribs: protective
Sesamoid bone
Patella (inside tendon): produce leverage
Irregular bone
Vertebrae: unique functions
What is hydroxy appetite?
Combination of calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, and water : contributes to stiffness and strength
What is collagen?
A structural protein: gives bone flexibility, lost with age
What is the composition of a bone?
Hydroxy appetite, collagen, and water
What is the epiphysis?
The end of the bone
What is the diaphysis?
The middle of the bone
What is the epiphyseal plate?
Becomes the epiphyseal line and how you grow
What are the types of muscle?
Cardiac, skeletal, and smooth
What are examples of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle?
Cardiac: heart, skeletal: bicep, smooth: intestines & arteries
What is a tendon?
Attach muscle to bone, strong fibrous tissue at the end of each muscle
What is a ligament?
Attach bone to bone, can sprain
What is a joint?
Where 2 bones meet
What are the features of a fibrous bone?
Least mobile and absorbs shock
What are the features of a cartilaginous joint?
Semi movable
What are the features of a synovial joint?
Most mobile (shoulder & knee)
What is an intrinsic ligament?
Inside a joint capsule (ACL)
What is an extrinsic ligament example?
MCL
What is a hinge joint?
Movement in one plane only (elbow, finger, knee)
What is a pivot joint?
One bone rotates around one axis (forearm during pronation & supination)
What is a plane joint?
Gliding action is the only movement allowed forward-backward, side to side (wrist)
What is a condyloid (knuckle) joint?
Flexsion-extension, abduction-adduction, circumduction all possible (all except thumb)
What is the saddle joint?
Flexsion-extension, abduction-adduction, circumduction all possible (thumb joint)
What is the ball and socket joint?
Movement in all planes: greatest range of motion of any joint type (shoulder and hip)
What are the features of cardiac muscle?
Most fatigue resistant, has own intrinsic beat, heart contraction/beating
What are the features of skeletal muscle?
Attached to bone, middle fatigue resistant, motor nerve control
What are features of smooth muscle?
Blood vessels and organs, slow uniform contractions, least fatigue resistant
What is the humerus bone?
The arm bone, shoulder to elbow
What is the femur bone?
From hip to knee, largest bone
What is the tibia bone?
Shine bone
What is wolfs law?
Bones adapt to stresses put on them, strengthening with increased stress (like exercise) and weakening with inactivity
What way to arteries move?
Away from the heart
What way to veins move?
Towards the heart
Flow of the heart
Goes in through the inferior or superior vena cava into the right atrium, through the tricuspid valve, into the right ventricle, through the aortic valve and out the aortic artery. Goes in through the pulmonary vein into the left atrium through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle, into the pulmonary valve and out the pulmonary artery.
What is the one part of the heart that is insulated?
Septum
How to find cardiac output?
CO= Stroke volume (volume of blood pumped each beat) * heart rate (number of beats per minute)
What is the max cardiac output?
220- age
Arteries generally carry
Oxygenated blood
Veins generally carry
Deoxygenated blood
What is a capillary?
Site of exchange: 1 cell thick, 10 billion in body
What is the fick equation?
VO2= CO (a - VO2)
What is A-VO2 (bus analogy)?
Bus is RBC, ppl are oxygen, how many ppl who get off is A-VO2 difference, driven by the number of capillaries you have
What does exercise science study?
How the body adapts physically, psychologically, and metabolically to exercise and physical activity
Type 1 muscle fiber
Most fatigue resistant, red in color, slow twitch
Type 2x muscle fiber
White in appearance, fewest mitochondria, most explosive
Is muscle fiber type modifiable?
No
What is phase dialation?
The opening of blood vessels
What is a semi lunar valve?
Controls blood flow from ventricles to major arteries
What is a atrioventricular valve?
Located between an atria and ventricles
What texture is the inside of bone & why?
Spongy: helps with shock absorption
Flexion/extension photo
Abduction/adduction photo
Circumduction/rotation photo
Pronation/supination photo

Inversion/eversion photo
Dorsiflexion/plantar flexion photo