Laser Welding
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
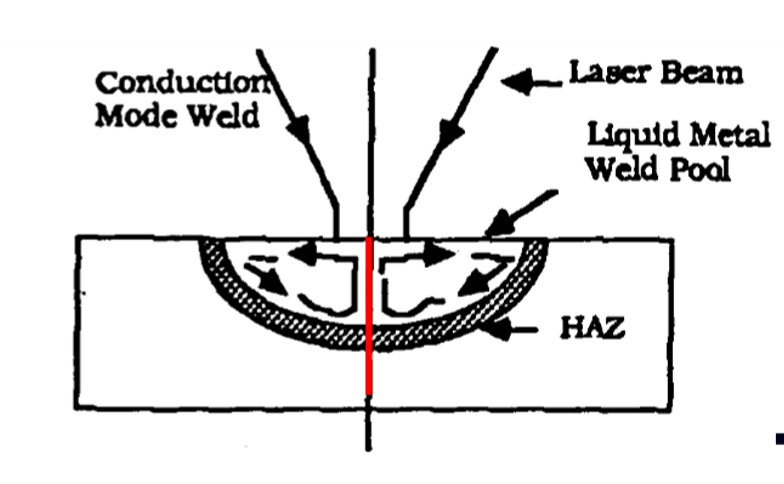
What is the principle of Conduction Limited Welding
The laser is absorbed at the surface (skin depth) only, and heat is transferred to the rest of the body by conduction
Melting only, no vapourisation
The melt pool is re-solidified behind the laser spot, joining 2 pieces together
Power Density
< 10^5 W
Advantage and Disadvantage
Adv: Low thermal damage
Disadv: Slow, Low efficiency
Applications?
Hardly used for metal welding, usually used for thin plastic film welding
Next type of welding?
Deep penetration (keyhole) welding
When the laser power density is >10^6……
fast vapourisation of metals occurs
Vapour pressure causes
the depression of molten metals and the formation of a keyhole
The keyhole acts as a ______ allowing for _______
black body, trapping the laser beam and allowing for very efficient laser-material energy transfer
The process is similar to _____ except ______
Similar to capourisation cutting, except the melt pool is not blow away but resolidified to join the 2 sheets
Temp and preressure is highest at:
The bottom of the keyhole
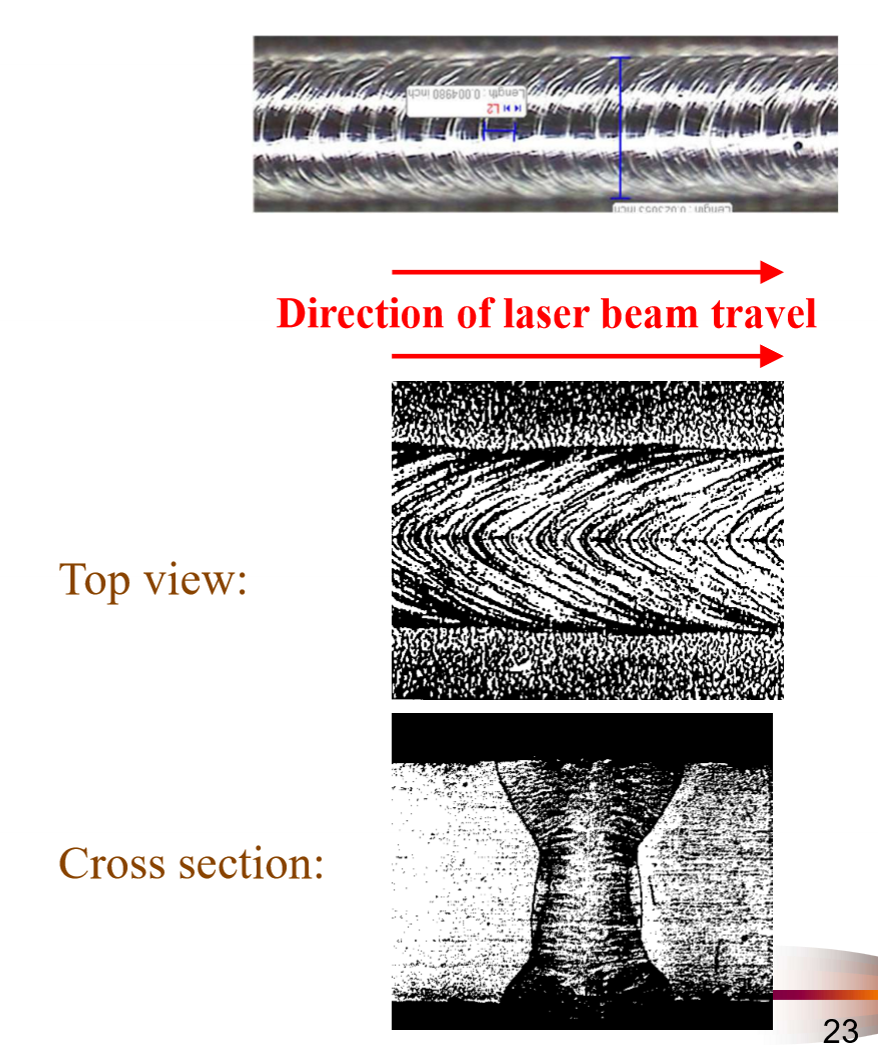
What are ripples?
Ripple like defects on the resolidified metal due to the natural oscillation frequency of the membrane
Equation?

Typical Lasers used for welding:
CO2 Laser, Fibre Laser, Nd:YAG Laser
Low order beam (ie TEM00) preferrer
Suitable materials:
All the same as arc welding can be used for laser welding
What is a plasma cloud?
When metal vapour and shroud gas is broken down into positive ions and electrons
When electron density reaches a critical value:
Avalanching breakdown occurs (large quantity of plasma formed)
_______ has to overcome ______ to start _____
Laser beam energy has to overcome ionisation potential to start ionisation
Minimum of ____ is required to generate breakdown
10^6 W/cm²
The degree of ionisation is
An exponential function describing material energy levels
Ionisation at comparable temps differs by order of ____ between metal and gas
_____ ionises first
e²
Metal ionises first
Plasma is high ________ that _____
Thus?
High temp, pressure and velocty that disturbs beam absorption
Thus, should be avoided (but practically not possible)
Plasma absorption coefficient to laserbeam relationship:
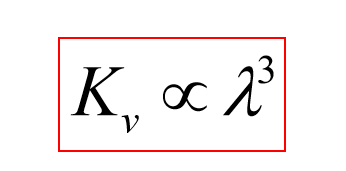
Therefore?
Shorter wavelength results in less beam absorption by plasma, meaning shorter wavelengths are desirable for laser welding
What happens in Laser Supported Combustion? (LSC)
Laser intensity between 10^6 & 10^7 W/cm²
Expansion of plasma is below sonic speed (slow, meaning it hovers over the weld pool)
Results in Beam Absorption of up to 30% (Plasma is transparent to beam)
The plasma lenses the original beam (meaning it is poorly reflected and further diminishes beam)
Plasma re-radiates the energy in the form of light
Plasma is confined to surface, meaning energy is transferred via thermal conduction and radiation
All of these effects result in the Weld Width Increasing, and the Penetration Decreasing
Cheeky Diagram:
What happens in Laser Supported Detonation? (LSD)
For Laser Intensity >10^7 W/cm²
Plasma detatches from the surface, travelling perpendicular to the surface at supersonic speeds
Plasma absorbs up to 50% of the beam (plasma is considered opaque to beam) - blocking the beam
Transfers energy to workpiece in form of re-emitted light, in a larger spot size
Weld is disrupted and stopped
When the plasma expands, the plasma density decreases, allowing the beam to reach the workpiece, resulting in more plasma formation - Results in periodic plasma formation
What happens when the Laser Intensity is >10^8 W/cm²
Plasma/Vapour pressure is too high, meaning expulsion of molten metals occurs (splattering)
Beam may be totally reflected
2 Types of Weld:
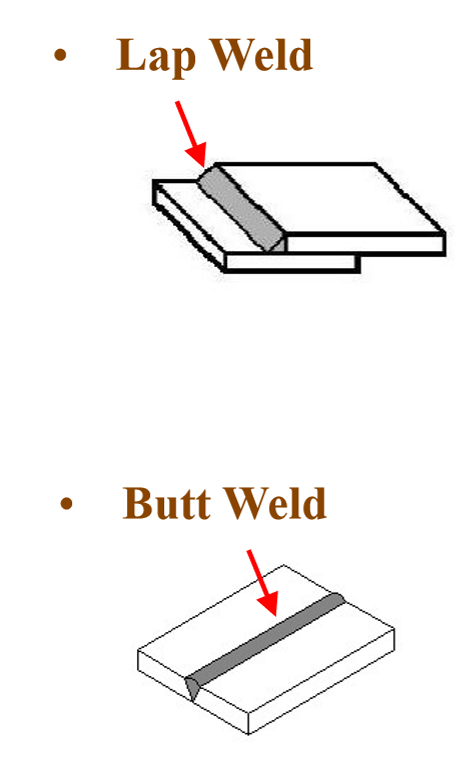
Formation of a good weld
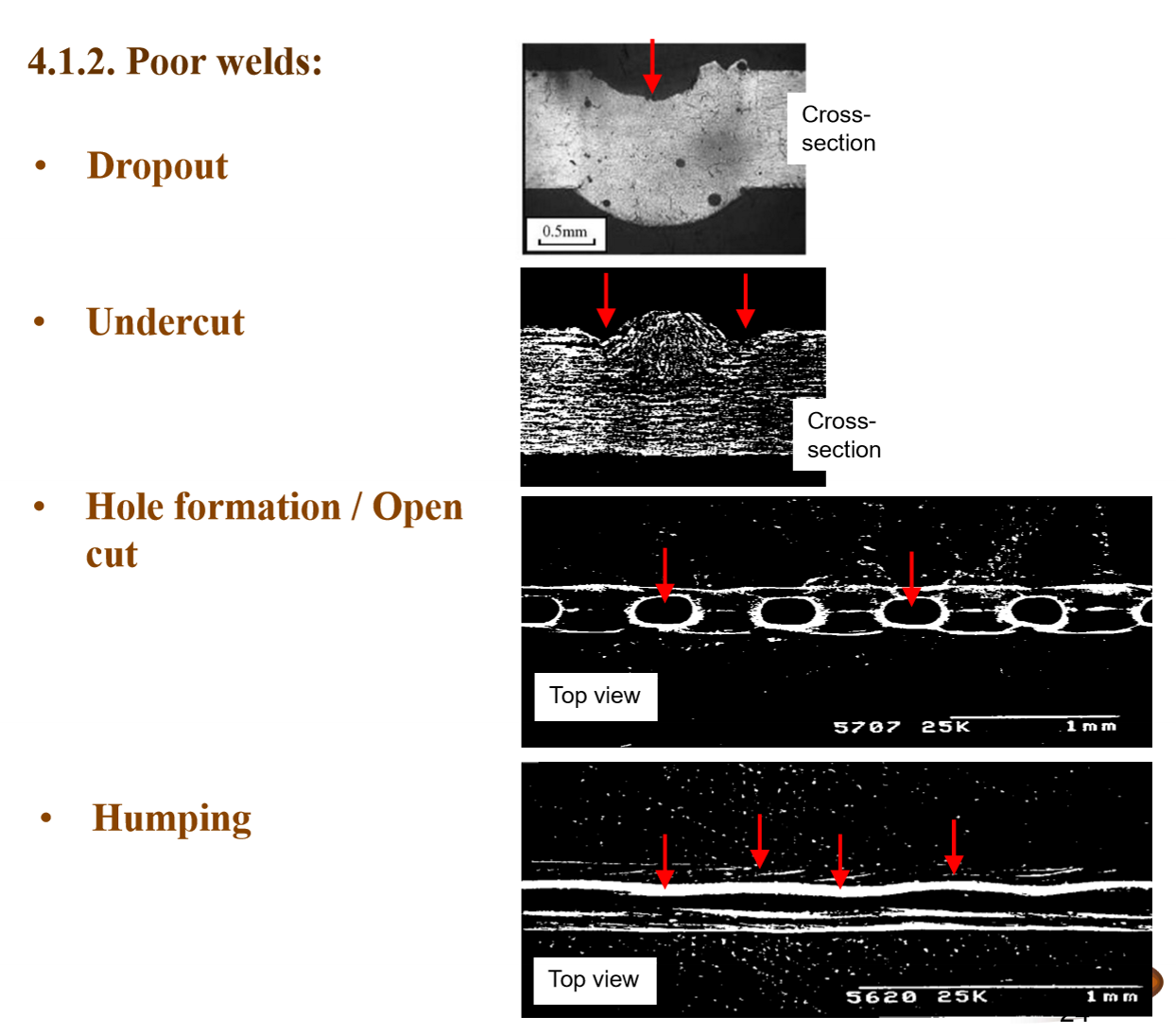
4 indicators of bad welds:
What two effects reduce porosity in welds?
Leaving a gap
Changing the material
Why does gap help reduce porosity?
Helps evaporation of vapours
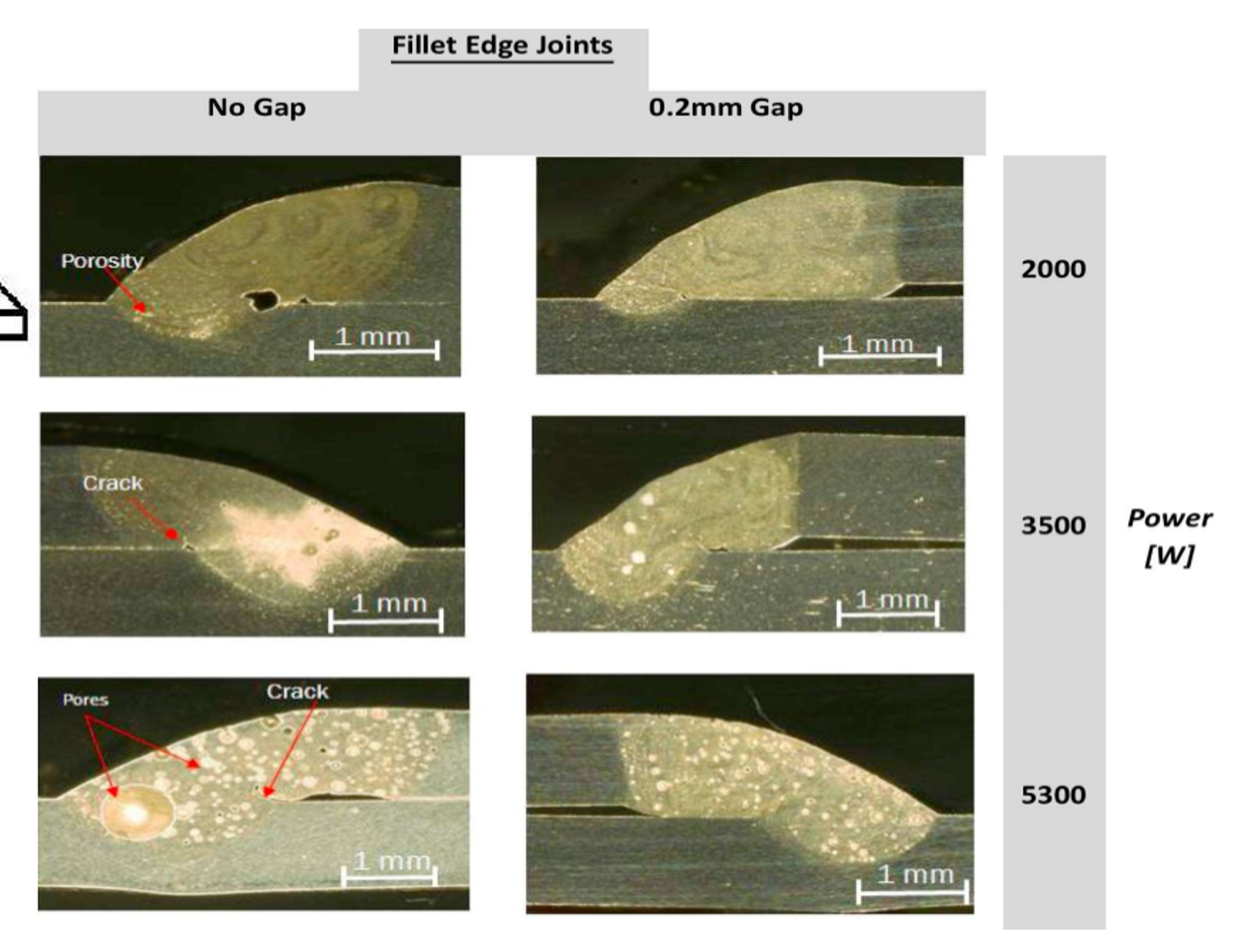

What materials reduce porosity
Al-Mg-Mn filler materials
Why does the filler material reduce porosity? (5)
Increases molten pool size
Slows cooling
Improves flow and degassing
Stabilises the keyhole
Adds alloy elements that reduce gas entrapment
Weld penetration depth relationship
H = Weld Pen Depth
P = Power
V = Cutting speed

How else can H be increased without changing P or V?
Increasing power density, by decreasing focal spot area, by reducing focal length
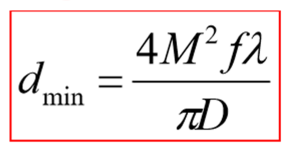
Too high welding speed also causes
Himpung (knowt wouldnt let me type it)
Undercut
Low speed causes
High HAZ
More Porosity
(Plasma inc)
What is the role of process gas? (3)
To cool and blow away plasma
To protect melt pool and hot work piece from atmospheric contamination + oxidation
To protect laser optics from metal vapour
It affects: (4)
Porosity of the weld
Absorption Coefficient
Weld pool melt flow patterns
Plasma Density
Adv of CO2 gas: (1)
Increases absorption by generating oxides at high temp
Limitations of CO2: (2)
Oxides may cause corrosion issues, (thus is not good for steel and titanium alloy welding)
Has a low ionisation threshold, producing more plasma :(
Adv of N2 (1):
Low Cost
Disadvantages of N2:
Low ionisation threshold (easy to ionise)
Ti-alloys are sensitive to N2 (ie not good at Ti Alloy Welding)
Ar Gas adv (2) and disadv (1)
Heavy(good for shroud)
Cheap
Low Ionisation threshold
He gas adv and disadv:
High ionisation threshold, meaning good for high welding penetration depth
Light (bad for shroud)
Expensive
Optimum gas:
High ionisation threshold (He) for plasma prevention
Heavy gas (Ar) for good shroud
Low cost (N2)
Why is O2 not used by itself
To avoid oxidation
At high power, _______ assist gas _____
He assist gas almost doubles penetration length
At lower power or higher welding speed, ______ so _____ is preferred
type of assist gas does not affect penetration depth, so Ar or N2 is preffered (low cost)
At longer wavelength (ie CO2 Laser) _______ thus _______ is preffered
Assist gas strongly affects welding penetration depth, thus He is preferred
At shorter wavelength (Nd:YAG, Fibre) ______ thus ______
Assist gas has less influence on welding depth, thus N2 or Argon is preferred
If the gas flowrate is too low:
Plasma shielding causes low penetration and porosity formation
If the gas flowrate is too high:
Gas flow widens keyhole, reducing multiple reflection effect, reducing beam absorptivity
Produces himpung
Weld penetration is increased by adjusting focal position to:
0.5-1.0 mm below the surface
Focusing above the surface leads to
Poor weld quality
Overview of Steels for Welding: (4)
Excellent Weld
Higher Tensile Strength
Higher Aspect Ratio
Corrosion resistance not affected/improved
Very good quality welds can be achieved provided ________
Sulphur and phosphorous levels are low (they promote grain boundary weakening/cracking)
High carbon steels require care to avoid _____
______ can be used to avoid ____
Weld cracking
Preheat can be used to avoid cracking
Low alloy steels can be used but _____- is an issue and _____ can be used to help
hardness can be an issue (may lead to cracking), preheat can be used to help
What can occur when zinc coated sheets are welded?
Zinc vapour is produced, which could cause porosity issues
(May lea
______ and _______ steels weld well but _____
Austenitic and Ferritic Stainless Steels weld well, but Martensitic steels develop brittle and hard behavior
Aluminum welds can be poor quality due to: (5)
High reflectivity (leading to low absorption and back reflectivity causing damage to optics)
High thermal conductivity resulting in crack
Porosity Generation (due to gas from surface oxidation layer)
Lower joints tensile strength
Low melting temp and high fluidity, which can cause dropout of weld seam
How to increase Beam Absorption and reduce back reflection? (5)
Using shorter wavelength laser source
High intensity
Tilting surface to Brewsters angle and using p-polarised beam
Tilting surface to prevent back reflection
Use surface coating or sand-blasting
How to reduce dropout and porosity? (2)
Filler wire to modify composition and microstructure
Use a mixed beam (e.g. an excimer laser) to remove oxidation layer
How to prevent Cracking? (1)
Preheating workpiece!!
Adv of Ti-alloy welding?
Good quality weld with fine grais
What is essential?
Prior material cleaning
Weld pool shielding
Summary of welding properties: (remember if you cba with rest)
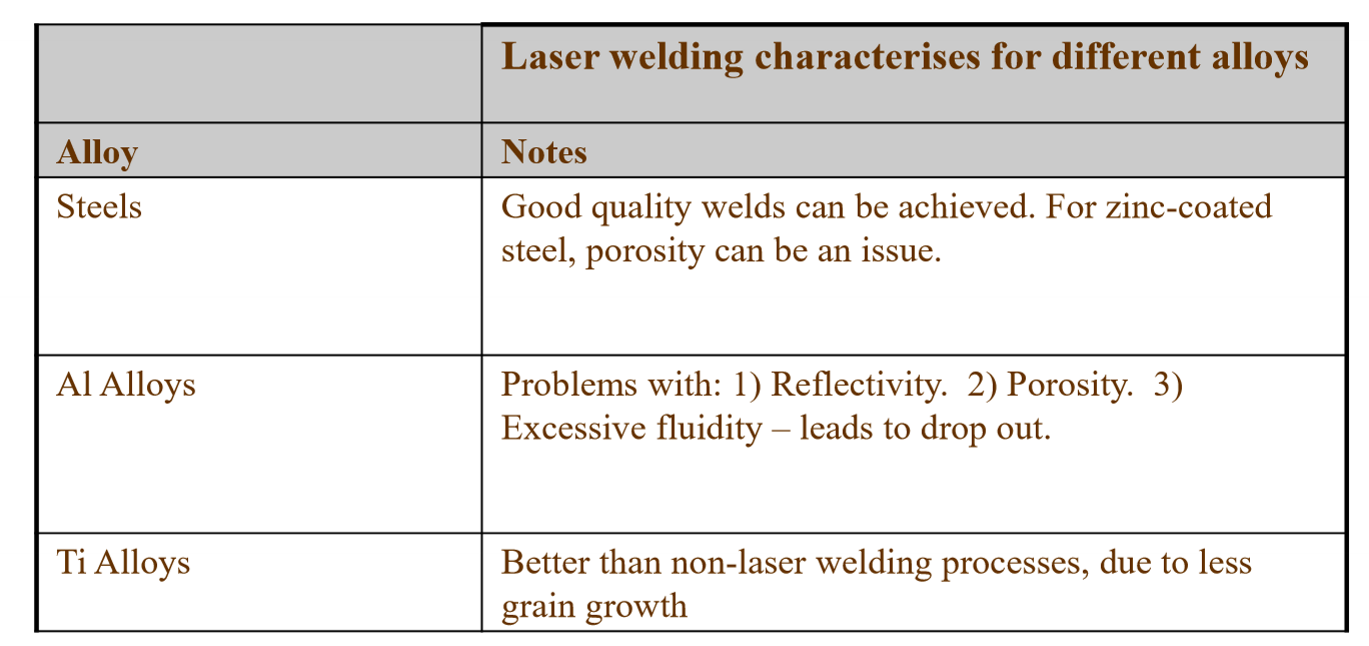
4 main types of weld:
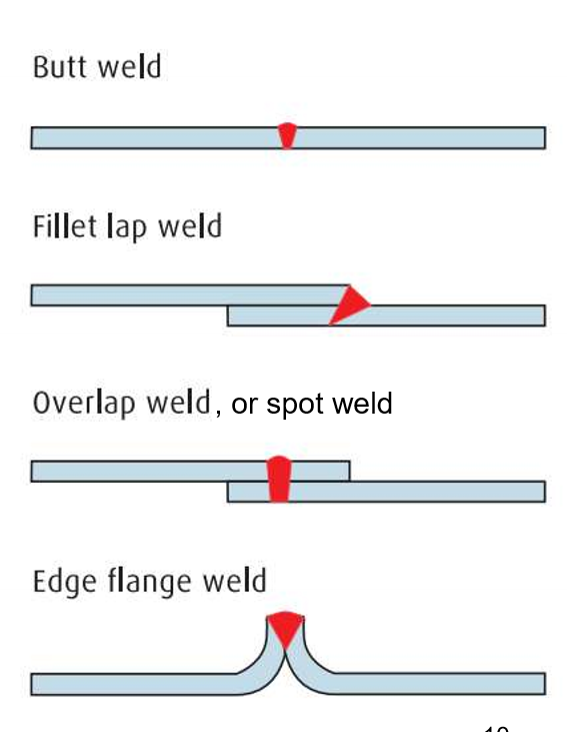
Welding of _____ may require specific geometries
Cylinders
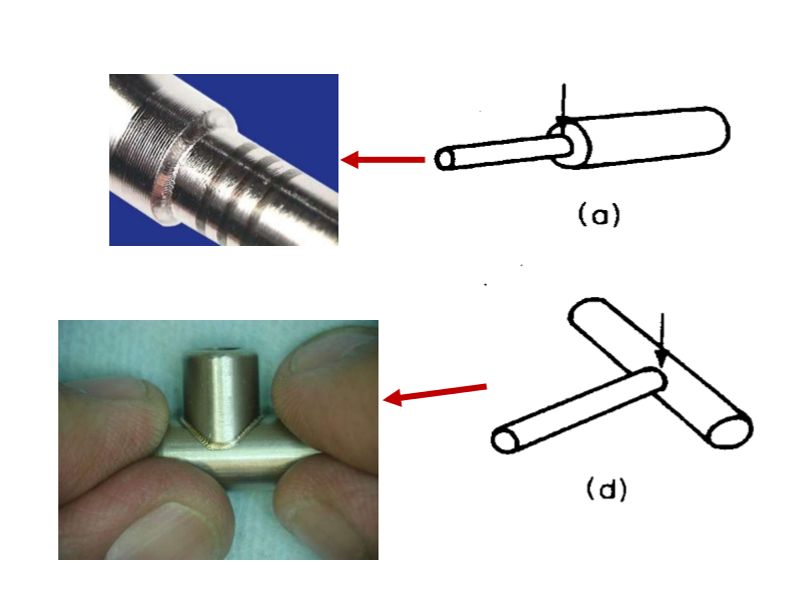
Designing a laser welding process also involves designing of a ___ to provide a ____
jig to provide a suitable clamp force