BIOL 2044 - Healthcare infections
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
pathophysiology
within hours bacteria colonise patients
3 types of risk factors
IATROGENIC
invasive procedures (intubation, indwelling vascular lines, catheters
antibiotic/prophylaxis use
ORGANISATIONAL
contaminated water supplies, contaiminated air conditioning systems
staffing and physicaly patient layout
PATIENT RISK FACTORS
how severe the illness is
underlying immuneocompromised state
surface cleaning problem
most surfaces are not smooth - will have draw marks, scratches where pathogens can colonise
stainless steel is not so easy to clean
terminal cleaning (filling the room with hydrogen peroxide gas) is not actually effective against MRSA
superbugs
bacteria which are resistant to antibiotcs
many braod spectrum antibiobic resistances
MRSA
BRE - resistant to vancomycin
C. diff spores hard to kill
gram negative reistant bacteria (ESBL) - extended spectrum beta lactamase
beta lactamase is the enzyme produced by bacteria which gives them resistance to a range of beta lactam antibiotics
bacteria that have the enzyme:
acinobacterium baumanii
E. coli
P. aeruginosa
klebsiella pneumonia
new dehli metallo beta lactamase class B
ESKAPE group
the following can survuve days and weeks on surfaces and are the major pathogens prioritised by WHO:
Enterococcus faecium
Staphylococcus aureus
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Actinobacter
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Enterobacter

KPC
klebsiella pneumonia carbopenemes
resistant to lots of antibiotics
copper as an antimicrobial
used to sterilise drinking water and wounds
outer electron very reactive - mobilises this electron in redox reactions
supresses helicobacter pylori, legionella pneumophilia
antifungal, antiviral properties
on copper MRSA is completely killed within 40 mins
kill times on dry surfaces are a lot more rapid than on wet surfaces
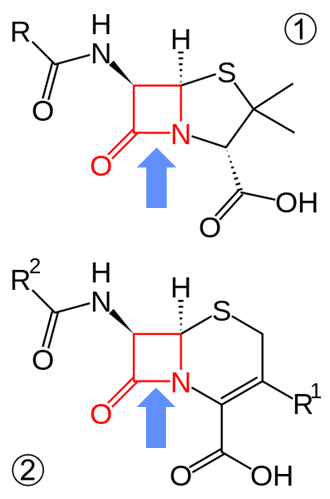
antibiotic resistance
some bacteria have beta lactamases which cleave the lactam ring
cephalosporin was produces as broad spec antibiotic is a last resort —> as a result, bacteria modified BS beta lactamases which break down cephalosprins
then a 3rd gen cephalosporin was produced —> bacteria then evolved resistance to theres
carbapenemes developes which have modified rings/side chains and are used as a last resort —> KPC, NDM1 bacteria are now resistant
New Dehli Metallolactase 1
namy people in india had these resistant pathogens which survived very well on surfaces
E. coli plasmid
CtxM which gives cephoxatine resistance
other resistant genes around it
if the plasmid is mibilised then the spread of more than one resistance gene
cells exposed to sstainless steel have in tact plasmids but those exposed to copper have broken plasmids
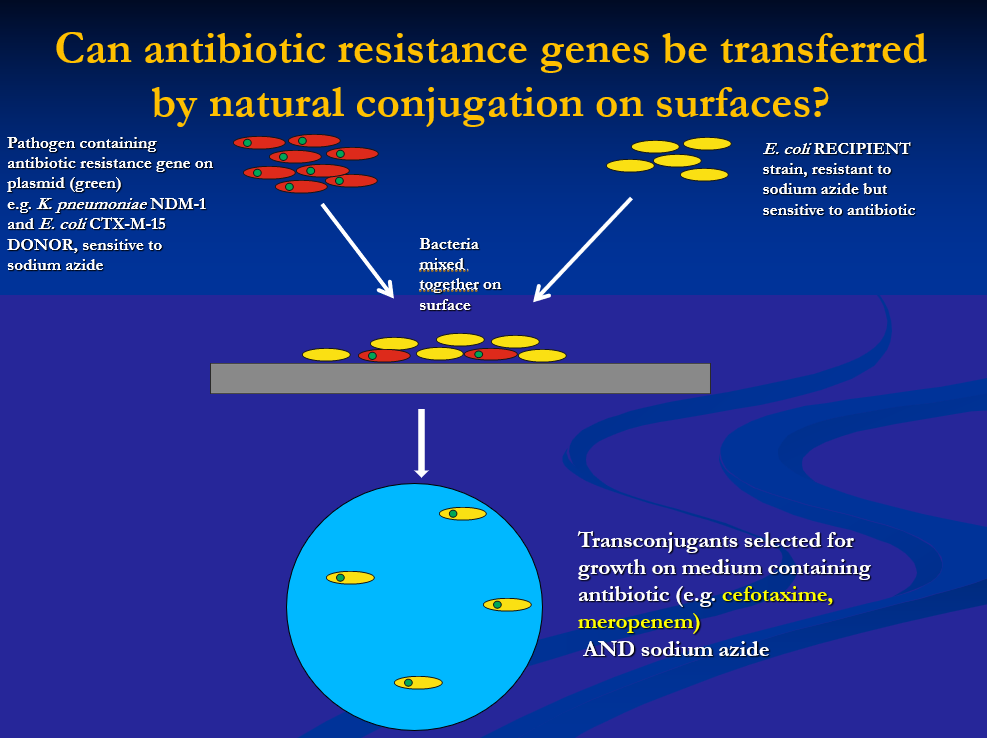
can we demonstrate transferred resistance?
pathogen with resistance gene and resident E. coli on surface together, then culture bacteria of residents on antibiotic covered plates
if capable of horizontal gene transfer you will get conjugates which rea resistant
transfer is good in suspension but not on copper
copper abolishes gene transfer
plasmid material is destroyed on copper
cell wall of bacteria
cell walls degrade when placed on copper
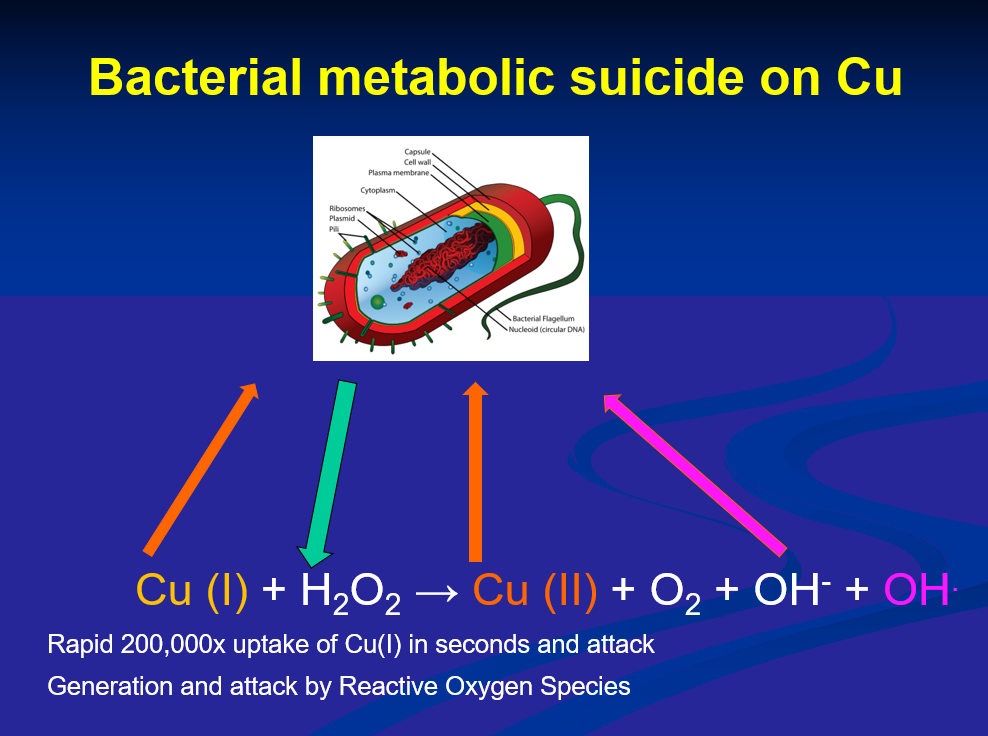
can measure metabolic state - stainless steel bacteria from ETC can measure metabolic activity
on copper respiratory activity is stopped
copper also disrupts membrame electrical potential in gram negative bacteria
when bacteria lands on copper surface it directly interacts with copper, particularly Cu1 and destroys
membrane
nucleic acid material
respiratory chain
H2O2 from side metabolism of bacteria converts Cu1—>Cu2 and generates oxygen radicals which accelerates copper kill
in a dry state kill is faster due to more hydroxyl radicals produced