ELEMENTS OF THE SEA: OCR B A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY.
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:46 PM on 9/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
what is the equation for atom economy
the relative formula mass of the desired product x 100/ the relative formula mass of all the reactants used.
2
New cards
atom economy question example.

3
New cards
the relationship between atom economy and the efficient use of atoms in a reaction.
when deciding which reactions to use in a chemical plant, the percentage of reactant atoms ending up in the desired product is one factor that is taken into consideration - this is atom economy, the greater the atom economy the less waste.
4
New cards
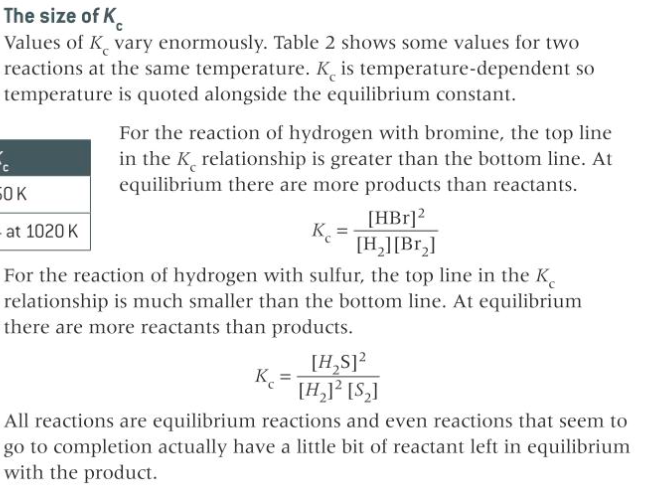
the explanation (given the necessary information) of the chemical processes occurring during the extraction of the halogens from minerals in the sea
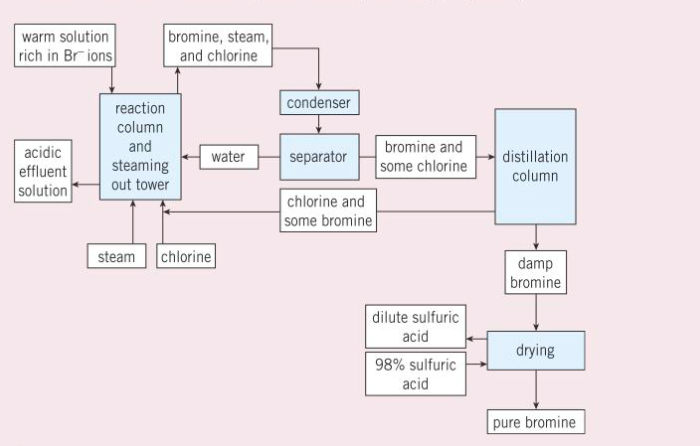
5
New cards
the listed half-equations for the different processes at the different electrodes
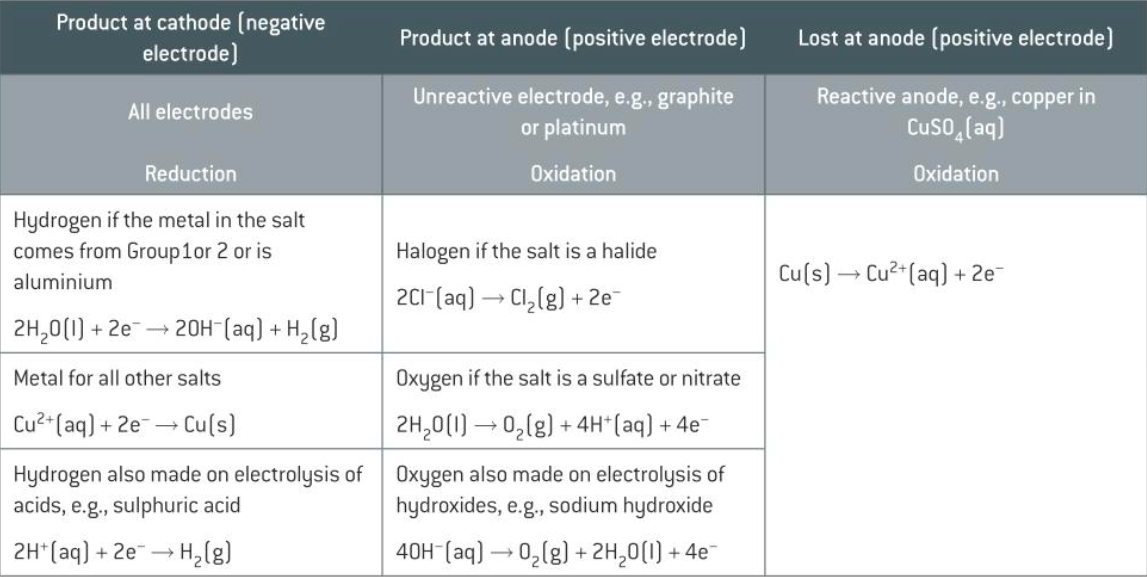
6
New cards
techniques and procedures in the electrolysis of aqueous solutions.

7
New cards
techniques and procedures in the electrolysis of aqueous solutions. (continued) (visual diagram).
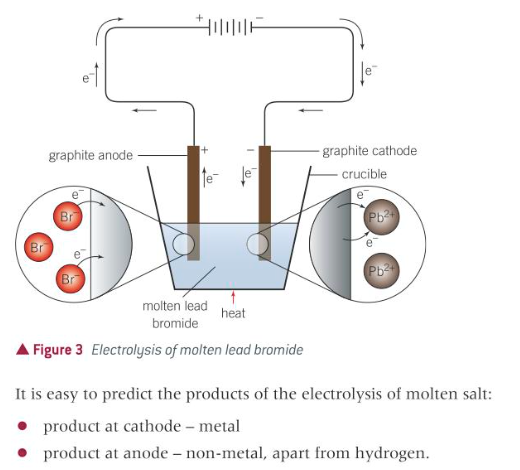
8
New cards
describe the electrolysis of solutions.

9
New cards
necessary physical properties of halogens
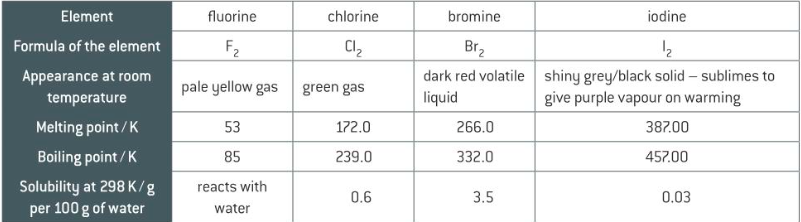
10
New cards
describe the relative reactivities of the halogens in terms of their ability to gain electrons
e.g. the fluorine atom is very small, so the attraction between the core and
the electron that competes is very strong. In chlorine, the outer shell is further from the core thus the attraction is less. So in turn fluorine gains an electron more readily.
the electron that competes is very strong. In chlorine, the outer shell is further from the core thus the attraction is less. So in turn fluorine gains an electron more readily.
11
New cards
the details of the redox changes which take place when chlorine, bromine and iodine react with other halide ions, including observations, equations and half-equations
examples of half-equation: CL2+2E- ---> 2CL- (REDUCTION)
2I- ----> 2E + I2. (OXIDATION).
2I- ----> 2E + I2. (OXIDATION).
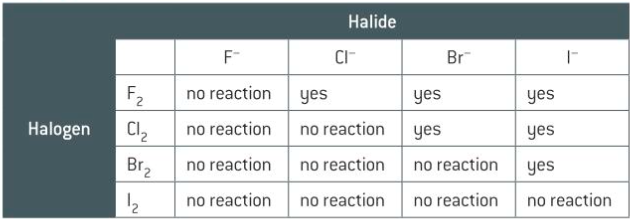
12
New cards
the reactions between halide ions (Cl –, Br– and I–) and silver ions (Ag+) and ionic equations to represent these precipitation reactions, the colours of the precipitates and the solubility of silver halides in ammonia

13
New cards
the properties of the hydrogen halides:
different thermal stabilities.
different thermal stabilities.
the thermal stability decreases as you go down group 7, HI is broken down easier than HCl, because the bond strength between hydrogen and halogen decreases as you go down group 7, less energy is needed to break the hydrogen bond.
14
New cards
describe the reactions of the hydrogen halides with ammonia

15
New cards
describe the acidity of the hydrogen halides

16
New cards
describe the reactions of hydrogen halides with sulphuric acid
the reactions of sulphuric acid and hydrogen halides are different due to the increasing strength of halide ions as reducing agents. HF and HCl do not react, sulphuric acid is reduced by HBr to make sulphur dioxide and by HI to make hydrogen sulphide.
17
New cards
describe the risks associated with the transport of chlorine.
chlorine is transported by liquid as more chlorine can be stored in a fixed volume under pressure, if the temperature/pressure becomes too high the tanks have pressure release devices designed to vent the tank and release some chlorine as gas. Tanks are lined with steel; the inside of the tanks must be dry so that chlorine doesn't react with water to produce corrosive acids. All unloading/loading is done through the protective housing at the top of the tank. On large chlorine tanks, there is an excess flow valve which is designed to close automatically if the angle valve that regulates the discharge of chlorine is broken or sheared off in the case of an accident; it is activated if the discharge of liquid chlorine exceeds some pre-determined value.
18
New cards
describe the risks associated with the storage of chlorine

19
New cards
describe the uses of chlorine
Water treatment: it is added to the water to kill bacteria and other pathogens.
Household bleach products: Used to kill bacteria on surfaces, the bleach (which is an oxidising agent) removes stains by breaking bonds in coloured chemicals to form colourless products.
Household bleach products: Used to kill bacteria on surfaces, the bleach (which is an oxidising agent) removes stains by breaking bonds in coloured chemicals to form colourless products.
20
New cards
what are the characteristics for dynamic equilibrium
when the closed system is at equilibrium the reactants and products are entering and leaving at the same rate.
- concentrations of reactants and products stay constant.
- forward and reverse reactions are both happening.
- the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal to each other.
- concentrations of reactants and products stay constant.
- forward and reverse reactions are both happening.
- the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal to each other.
21
New cards
what is equilibrium constant
For a general reaction
mA + nB ⇋ pC + qD
where
A and B are reactants,
C and D are products,
m, n, p and q are the number of moles.
The equilibrium constant Kc is
𝐾_𝑐=(〖[𝐶]〗^𝑝 〖[𝐷]〗^𝑞)/(〖[𝐴]〗^𝑚 〖[𝐵]〗^𝑛 )
mA + nB ⇋ pC + qD
where
A and B are reactants,
C and D are products,
m, n, p and q are the number of moles.
The equilibrium constant Kc is
𝐾_𝑐=(〖[𝐶]〗^𝑝 〖[𝐷]〗^𝑞)/(〖[𝐴]〗^𝑚 〖[𝐵]〗^𝑛 )
22
New cards
describe the relation of the position of equilibrium to size of K_c

23
New cards
the use of Kc to explain the effect of
changing concentrations on the position of a homogeneous equilibrium;
extension of the ideas of ‘opposing change’ to the effects of temperature and pressure on equilibrium position.
changing concentrations on the position of a homogeneous equilibrium;
extension of the ideas of ‘opposing change’ to the effects of temperature and pressure on equilibrium position.