Intermediate Accounting
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Net Cash Flow Step 1
Net cash flow from operating activities
Operating Profit
Add depreciation
Add non-borrowing, non-current liabilities
Remove disposal gain/ add disposal loss
Add current asset movements and current liabilities movements excluding overdraft
Add deferred income
Add increase provisions/remove decrease in provisions
Subtotal cash generated from operations
Remove financial cost
Remove tax
Net cash flow
Depreciation Formula
Opening Depreciation - accumulated depreciation on disposal + x = Closing depreciation
Solve for x
Opening and Closing Cash
Opening cash = Balance Sheet Opening Cash - Opening Overdraft
Closing Cash = Balance Sheet Closing Cash - Closing Overdraft
Net Cash Flow
Net cash flow operating + Net cash flow investing + Net cash flow financial = Closing Cash - Opening Cash
PPE
Opening PPE at cost - Cost of PPE disposal + Revaluation + x = Closing PPE
Solve for x
Cash proceeds from PPE disposal
Cash proceeds from PPE disposal = Carrying Amount (±) Gain/Loss
Step 2: Investment
PPE + Cash Proceeds from PPE disposal + Remaining Non-current assets
Step 3: Financing
All borrowing Non-current liabilities + Equity excluding retained earnings + Dividends
Dividends
Dividends Paid = Opening Retained earnings + Profit after tax - closing retained earnings
Stock sales
Stock sales = Opening Stock Capital + Opening Share premium + x = Closing Stock Capital + Closing Share premium
Solve for x
Material usage variance
(AQ − SQ) × SP per unit
Fixed overhead spending variance
Actual FOH − Budget FOH
Sales price variance
(Act SP - Budg SP) * AQ
(Actual units sold - Budgeted units) × Standard contribution per unit
Standard selling price per unit - Standard variable cost per unit
Standard quantity per unit × Actual number of units produced
Total direct material and labour variances
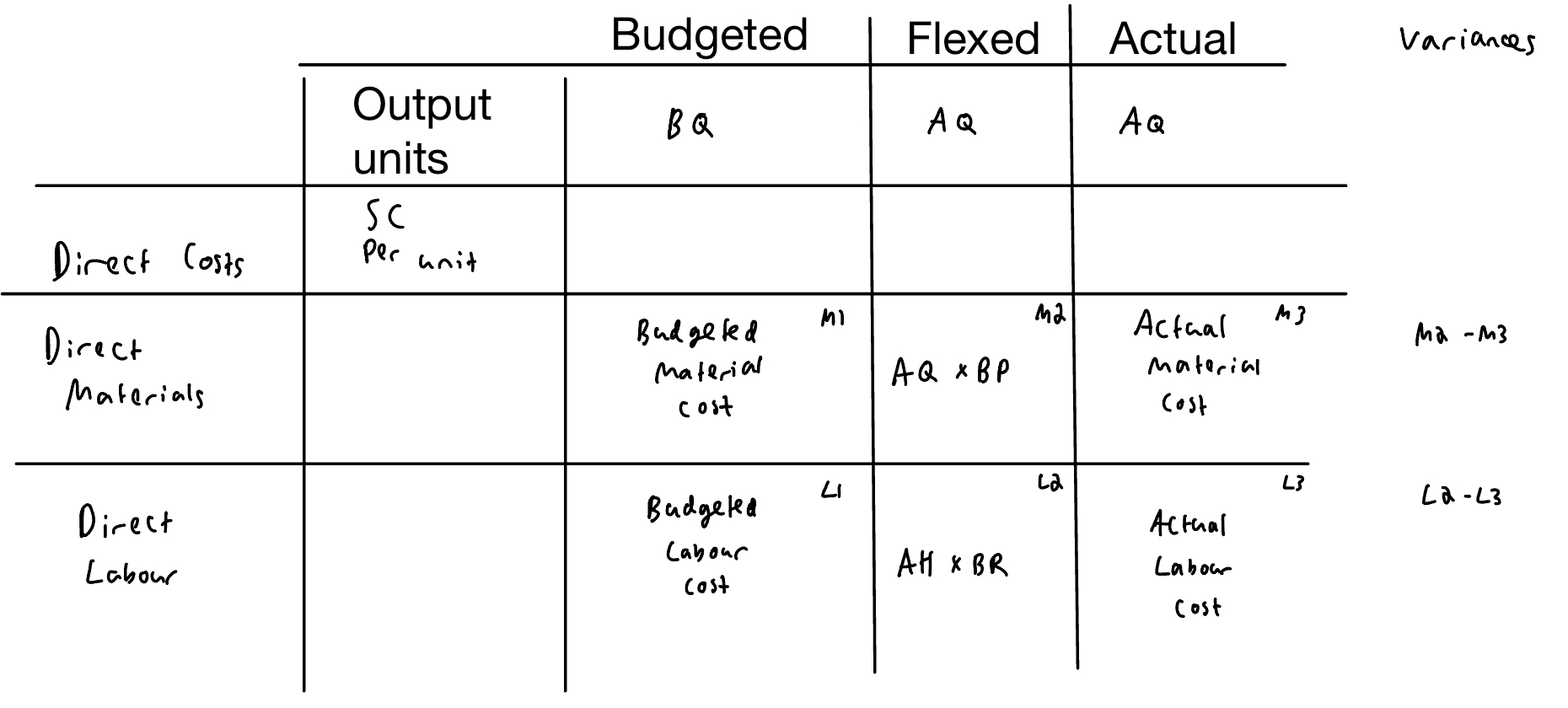
Material / Labour variance breakdown
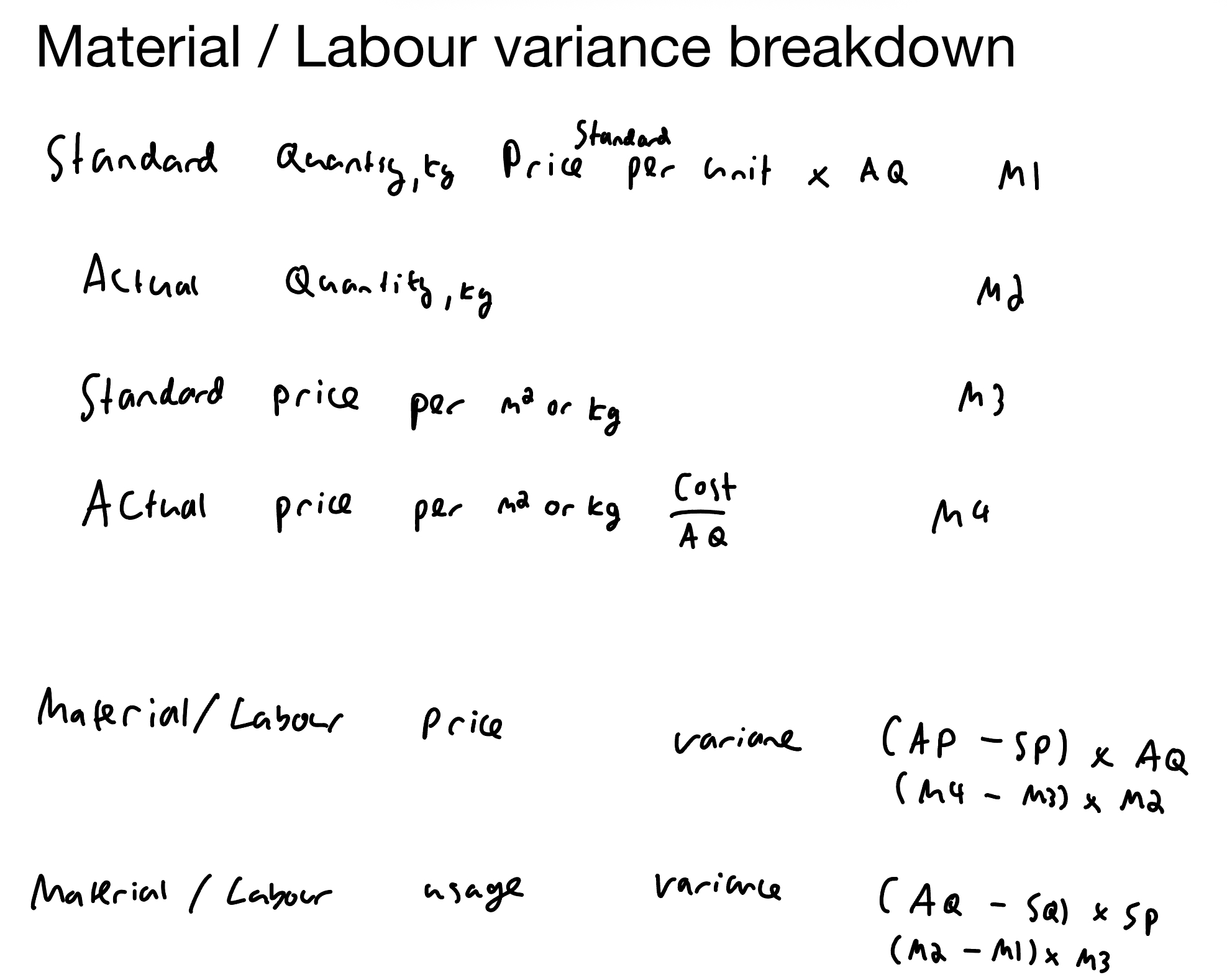
For direct material and labour breakdowns always use the actual count of either hours of quantity
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) formula
Average annual accounting profit ÷ Midpoint book value
Average annual accounting profit over project life
Total net cashflow over project life - Total Depreciation / Number of Year of project
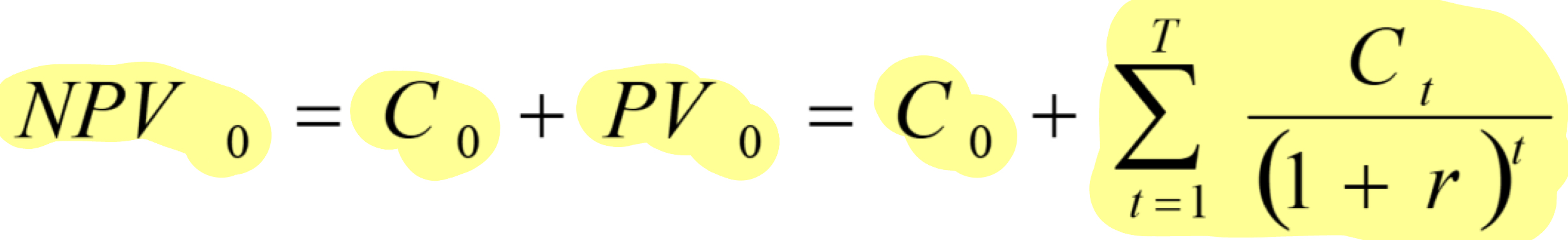
r in NPV formula
the cost of capital can be subbed in as r for projects. Cost of capital similar to interest rate, the rate of investing the money somewhere if you don’t invest in the project
Is NPV usually the most reliable
Yes
IRR limitation due to project length
When the IRR is high (the project is creating
significant surplus value) and the project life is long, the IRR will overstate the true return on the projec
What are relevent cash flows in investment projects
Relevant cash flows are cash flows that would only happen if the project was undertaken.
I.e if a cash flow will happen regardless of project decision, it is not relevant
NPV and Payback period net cash flow
Net cash flow per year = Profit/loss per year + annual depreciation
Tax Paid
Opening Tax liability/payable + Income statement Current Year Taxation + x = Closing Tax liability/payable
Solve for x
Standard fixed overhead absorption rate per unit
Budgeted fixed production overhead / Budgeted number of units
Do you add depreciation if it is included in distribution costs or on the income statement
Yes, you add depreciation regardless
How is overdraft thought of
Overdraft is thought as money owed
Midpoint book value
(Cost of Asset + Residual Value) / 2
Average annual accounting profitAverage annual accounting profit
(Total net cash savings/profit over project life − Total depreciation) / Project life in years