Capacitance
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
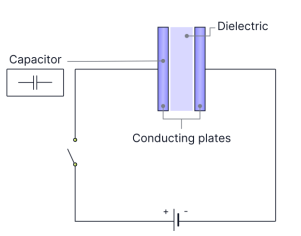
Explain how and why the conducting plates of a capacitor acquire charge when the switch is closed. 2 marks
electrons will accumulate from the negative terminal of the cell on to one of the plates. and the delocalised electrons from the 2nd plate are repelled to the positive terminal of the cell.
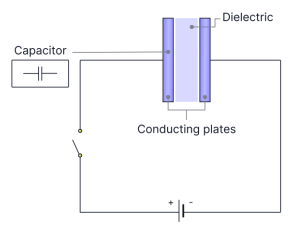
How does the rate of charging change as more and more charge is added to the plate?
the rate of charging decreases as the current decreases overtime.
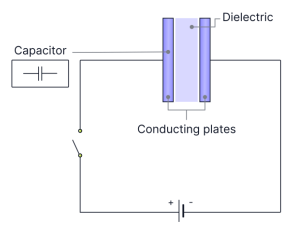
The cell is replaced with a resistor, and the switch is closed. Explain what happens.
the capacitor discharges, as electrons move from the negative plate around the circuit through the resistor in the opposite direction.
What determines the maximum charge stored in the capacitor? 1 mark
capacitors p.d
What is the resistance of the capacitor when it is fully charged? And what happens to the current?
it is infinite because it becomes very hard for electrons to go onto the plate when it is fully charged. As it’s p.d across it is equal to the power source, so the current reaches zero
What is the resistance of the capacitor when there is no charge?
zero ohms
explain the purpose of a capacitor
a device that store electrical charge in an electric field between two oppositely charged plates.
what is the unit for capacitance?
farad (F)
define capacitance
the charge stored per unit voltage (look at the equation)
explain how it explain in terms of particles what happens when an uncharged capacitor is connected to a cell (4 marks)
The electrons move from the negative terminal of the cell are attracted to the right plate. therefore the right plate becomes negatively charged
The charges from the left plate are attracted to the positive terminal of the cell. therefore the left plate becomes positively charged.
and the capacitor becomes fully charged
when the current is zero amps and the p.d across the capacitor is equal to the p.d across the cell

In a different circuit, a capacitor was charged to store 50 J of energy. How much energy would be stored in the same capacitor if twice the pd was applied across the capacitor?
E=200J
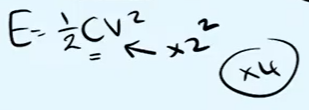

A capacitor is charged fully and then disconnected from the circuit such that there is no electrical contact between the plates. The distance between the plates is increased so that the pd becomes 3× larger. What happens to the energy stored in the capacitor?
the energy stored triples
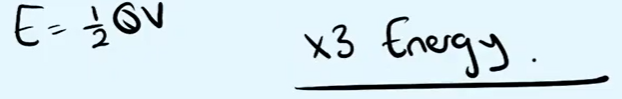

How do you know which equation to use for in questions.
Look for keywords in the question that relate to charge, potential difference, energy, capacitance. they will mention at least 2 or 3. And you must pick the ones that do not change.
e.g the capacitor is charging or discharging, not an equation with Q

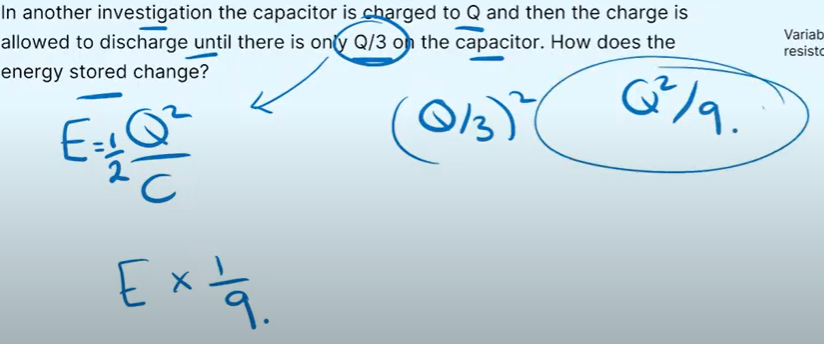
In another investigation the capacitor is charged to Q and then the charge is allowed to discharge until there is only Q/3 on the capacitor. How does the energy stored change?
E drops to one ninth

A capacitor charges until it reaches a voltage of V. The voltage is then doubled. How does the energy stored on the capacitor change?
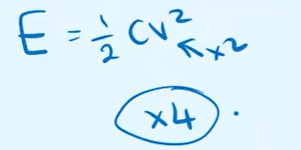
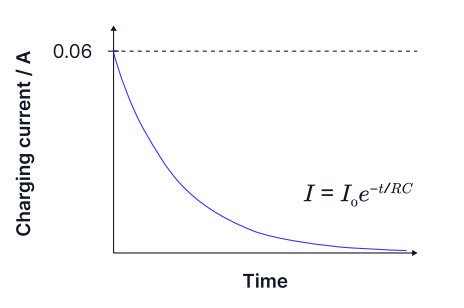
explain why the current decreases exponentially as the capacitor charges
How would the graph differ for a capacitor discharging?
the current decreases to 0 Amps as the rate of flow of electrons decreases as the electrons build up on the negative plate and the positive terminal of the cell.
It would remain the same
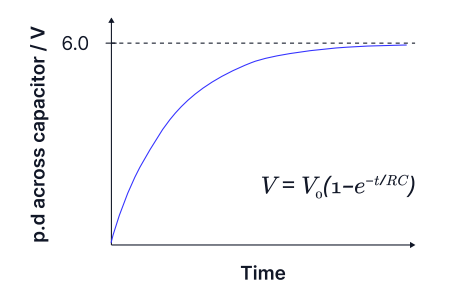
explain why the potential difference across the capacitor increases exponentially as the capacitor charges.
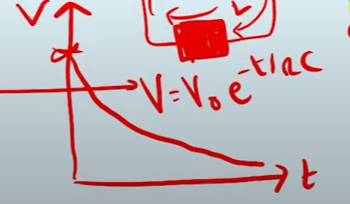
How would the graph differ for a capacitor discharging? what would the new equation be?
it increases until it’s equal to the potential difference across the cell of 6v
It would decrease overtime until zero.
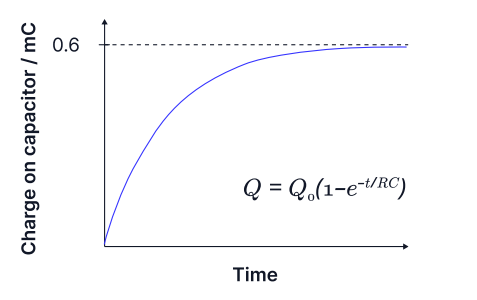
explain why the charge across the capacitor increases exponentially as the capacitor charges.
How would the graph differ for a capacitor discharging?
it increases until it reaches the maximum charge the capacitor can store within it’s electric field.
It would decrease overtime until zero.
A 0.03 F capacitor is fully charged by a 12 V supply and is then connected to discharge through a 900 Ω resistor. How much charge remains on the capacitor after 20 seconds?
0.17C

A 0.03 F capacitor is fully charged by a 12 V supply and is then connected to discharge through a 900 Ω resistor. What is the p.d. on the capacitor after 20 seconds?

A 0.03 F capacitor is fully charged by a 12 V supply and is then connected to discharge through a 900 Ω resistor. What is the discharge current after 20 seconds?

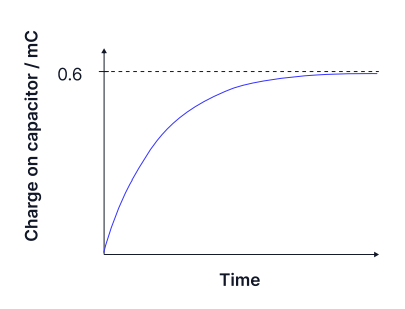
The graph shows the charging of a 4,700 µF capacitor through a 2,000 Ω resistor. How long does it take to charge to 0.3 mC?
t=6.5 seconds
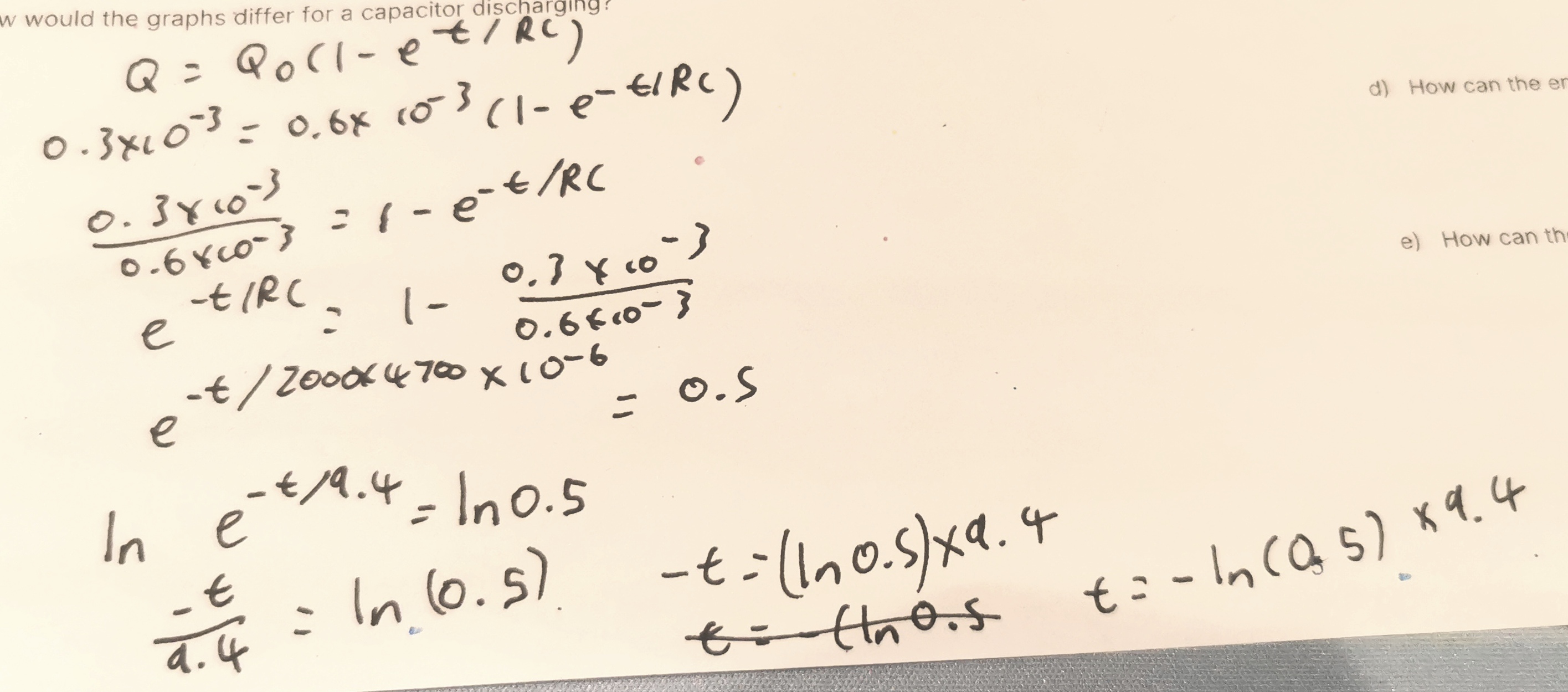
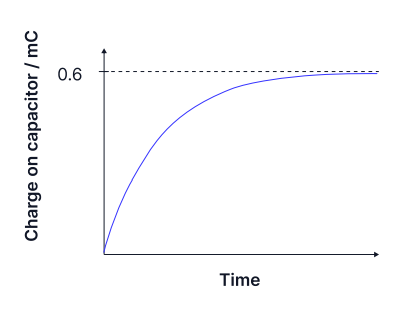
The graph shows the charging of a 4,700 µF capacitor through a 2,000 Ω resistor. How much energy was supplied by the cell?
1.9×10-11J
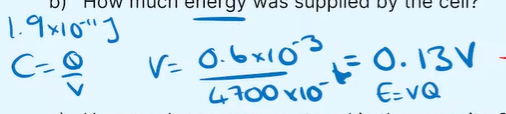
The graph shows the charging of a 4,700 µF capacitor through a 2,000 Ω resistor. How much energy was stored in the capacitor?
explain why there is less energy stored in the capacitor than the cell
less energy is stored in the capacitor due to the resistor.
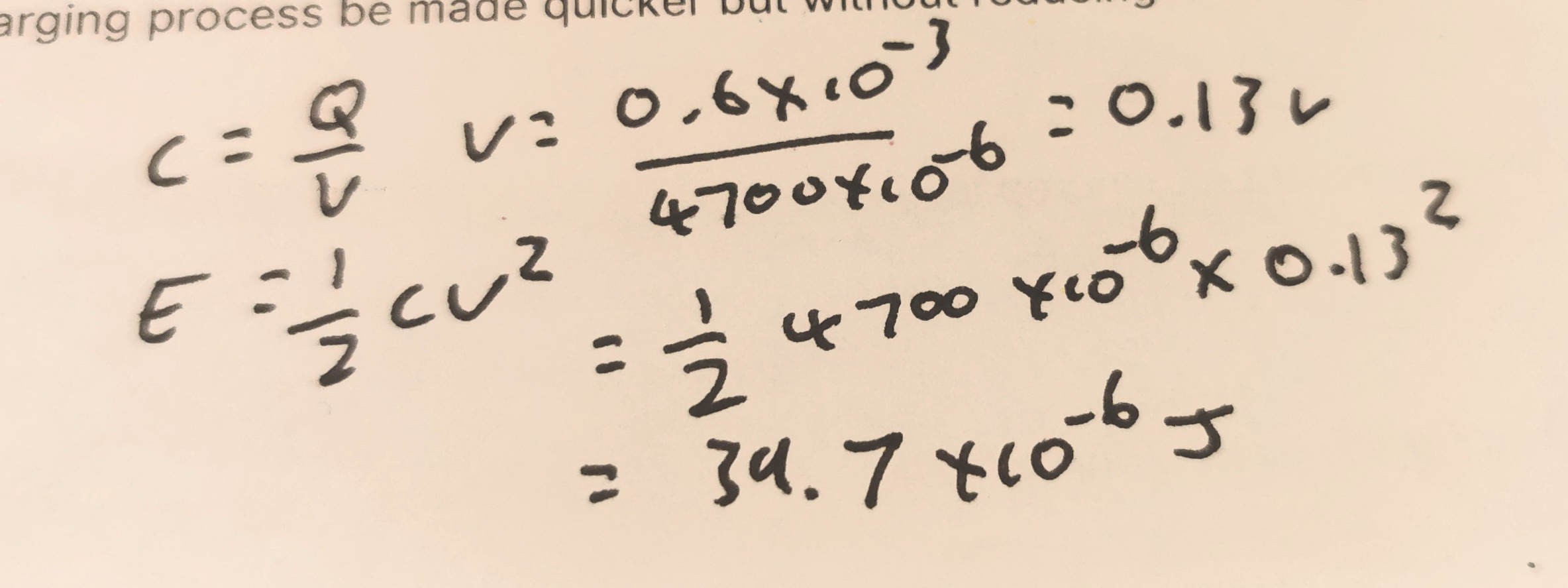
explain what the time constant is, include a value in your answer
how long it takes for the capacitance to drop to 37% of it’s original value