Lab 5: Muscle
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
what did we use to electrically simulate our nerves of our forearm?
Isolated stimulator
2
New cards
The hand dynamometer was used to examine what?
grip force and the ability to sustain it under different conditions
3
New cards
How is muscle connected to the bone?
through a tendon
4
New cards
What is a strong bundle of collagen fibers called?
a tendon
5
New cards
t/f two or more muscle work antagonistically
True
6
New cards
give an example of two muscles working antagonistically.
the tricep and bicep.
[when the bicep contracts/shorten, the tricep elongates]
[when the bicep contracts/shorten, the tricep elongates]
7
New cards
what are the components of muscles (smallest to largest)
myofilaments
8
New cards
what type of connective tissue covers muscle fibers?
Endomysium
[think.. endo = inner // muscle fibers are *IN* muscle fascicles]
[think.. endo = inner // muscle fibers are *IN* muscle fascicles]
9
New cards
what type of connective cells cover a muscle fascicle?
Perimysium
[think peri= perimeters ]
[think peri= perimeters ]
10
New cards
Epimysium covers what muscle structure?
skeletal muscle
[think.. epi= outer // outer as in whole muscle ]
[think.. epi= outer // outer as in whole muscle ]
11
New cards
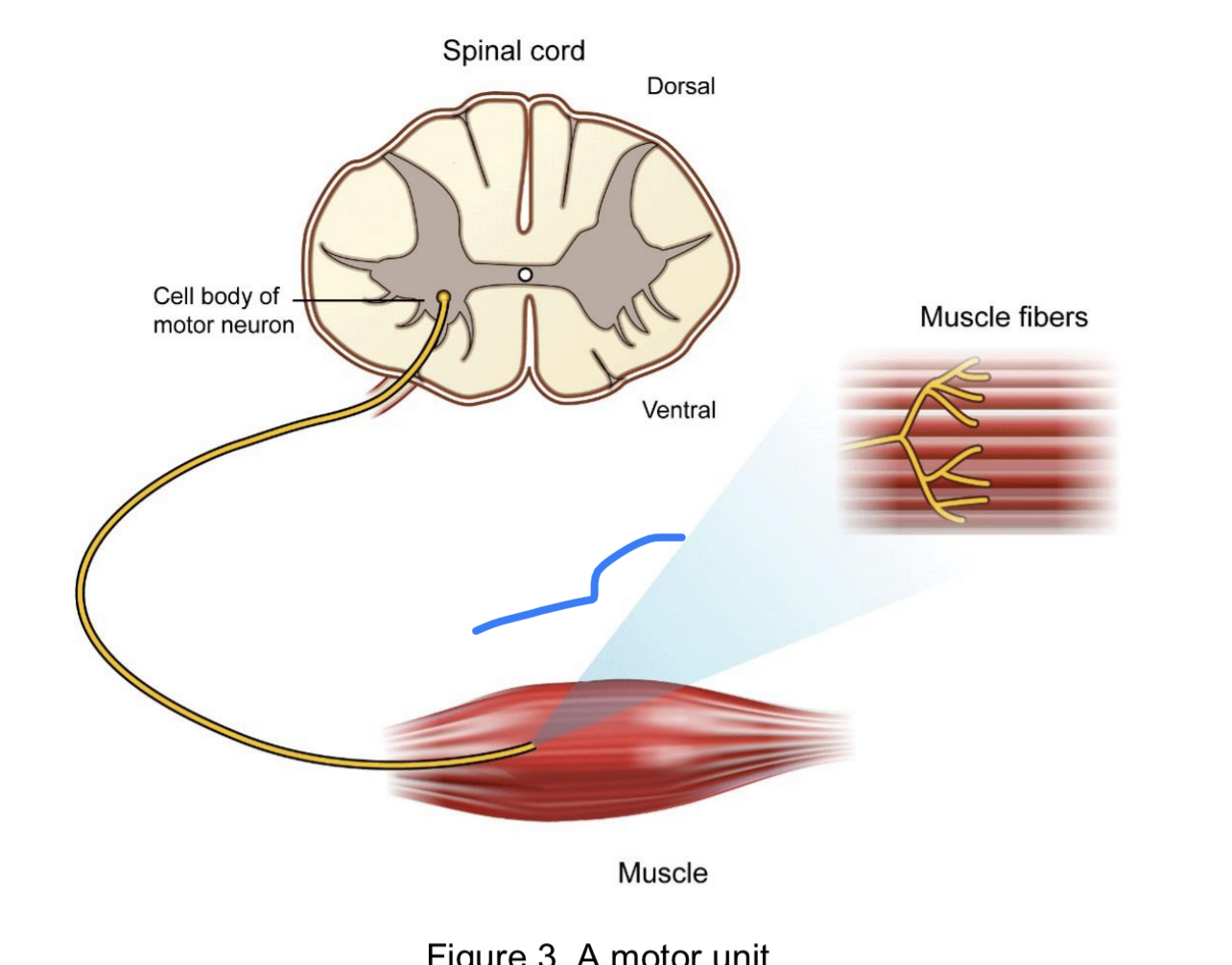
Describe what a motor unit is
a single motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervated
12
New cards
How do motor neurons affect action potentials in muscle fibers?
motor neurons release acetylcholine to induce action potential in muscle fibers
13
New cards
when acetylcholine is released what happens to the muscle fiber?
There is a brief increase of intracellular concentration of Ca2+
14
New cards
what is a twitch?
a single muscle contraction from a single stimulus
15
New cards
what is recruitment?
gathering of several motor units in order to create a strong contraction
16
New cards
what is summation?
rapid stimulation that does not allow a muscle to completely relax, thus creating a increased force.
[think... sum = adding ]
[think... sum = adding ]
17
New cards
what is tetanus?
several twitches with no time to relax in between, which creates a smooth contraction.
Summation leads to tetnaus
(looks like this ,--------, instead of this /\/\/\/\)
Summation leads to tetnaus
(looks like this ,--------, instead of this /\/\/\/\)
18
New cards
put these tissues in order from most inner to most outer
perimysium, epimysium, endomysium
perimysium, epimysium, endomysium
endomysium
19
New cards
connective tissue that surrounds muscle fascicles is called?
perimysium
20
New cards
t/f skeletal muscles are striated
True
21
New cards
the amount of stimulus necessary to elicit a maximal response in skeletal muscle is called what?
maximal stimuli
22
New cards
which procedure do we use to measure electrical activity of skeletal muscle?
electromyogram or electrocardiogram?
electromyogram or electrocardiogram?
ElectroMYOgram
[myo = skeletal muscle // cardio = cardiac msucle ]
[myo = skeletal muscle // cardio = cardiac msucle ]
23
New cards
contraction of a muscle leads to more minor activity in the antagonist muscle is called hat?
Coactivation
[think antagonist needs two... two = co]
[think antagonist needs two... two = co]
24
New cards
t/f in one of the muscle contraction labs, we measured the effects of a brief rest, visual feedback and verbal encouragement on grip force
True
[think of when zane reached 101% when we cheered for him]
[think of when zane reached 101% when we cheered for him]
25
New cards
t/f the speed at which an electrical impulse travels along a nerve is measured in m/s and is called contraction strength
false
[it is called electroneurography (EneG) or never conduction velocity (NVC) ]
[it is called electroneurography (EneG) or never conduction velocity (NVC) ]
26
New cards
Explain how motor neuron causes an action potential in a muscle fiber that results in contraction
-When an AP is fired in the motor neuron, Acetylcholine is released to bind with muscle fiber receptors
-Causes Na+ channels to open and Na+ defuses into the muscle fiber
-this depolarizes muscle fiber and creates AP
-Ap causes contraction
-Causes Na+ channels to open and Na+ defuses into the muscle fiber
-this depolarizes muscle fiber and creates AP
-Ap causes contraction
27
New cards
Define threshold stimulus
amount of voltage necessary to elicit a response from the muscle
28
New cards
Define Suprathreshold stimulus
a stimulus above threshold stimulus
29
New cards
Define Submaximal stimulus
the amount of voltage necessary to elicit a response above threshold but below maximum response
30
New cards
Define Maximal stimulus
stimulus necessary to elicit a maximal response