Bio- Cell Transport
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
When were Microscopes for developed and used
The 1600s
Who coined the term cell while observing dead cork cells
Robert Hooke in 1665
Who is the Father of Microbiology and was the first to use a microscope to study microorganisms?
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
What are the three ideas in The Cell Theory
All Living things are made of one or more cells.
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
What are the two Major Classes of Cells
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
What is significant to Prokaryotic Cells?
Smaller Simpler
Lack a nucleus and most other organelles
What is an example of Prokaryotic Cells?
Bacteria & Archaea
What is significant about Eukaryotic Cells
Have a Nucleus surrounded by a membrane and other membrane-bound organelles.
More Complex
What is an example of Eukaryotic Cells?
Fungi, Protists Plants & Animals
How do Plant cells look compared to Animal Cells
Plants are rectangular Animals are circular
What 3 Organelles do plant cells have that animal cells don’t?
Chloroplast, Cell Wall, and a Large Central Vacuole.
What do both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells have in common?
They Have plasma membranes, ribosomes, and genetic material (DNA).
What is the Plasma Membrane?
The Plasma Membrane regulates substances moving into and out of a cell.
What is Plasma Membrane composed of?
Phospholipids (Heads and Tails)
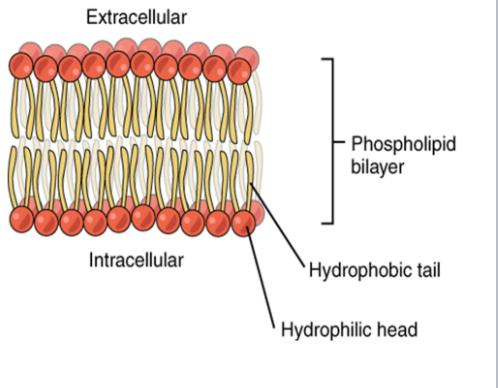
What is the phospholipid Bilayer?
A fluid-like membrane and act as Selectively permeable membrane.
What does it mean to be selectively Permeable Membrane?
A Selectively Permeable Membrane allows some substances to cross more easily than others and blocks some altogether.
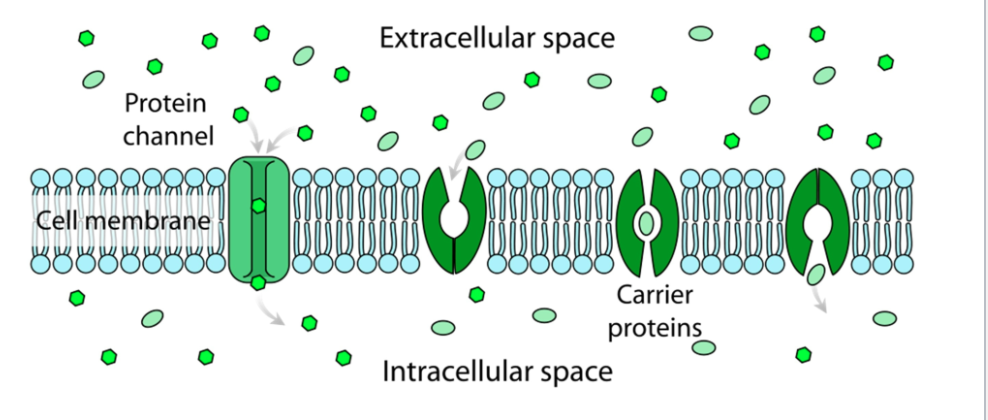
What are the three primary ways substances cross the membrane??
Passive Transport (no energy required)
Active Transport (requires energy)
Vesicle Transport (for large molecules)
What are the two different types of Passive Transport
Simple Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion
What is Simple Diffusion?
It just passes through selectively permeable membrane. (GHOST)
What is Facilitated Diffusion
The transport protein provides a path for certain molecules to pass through
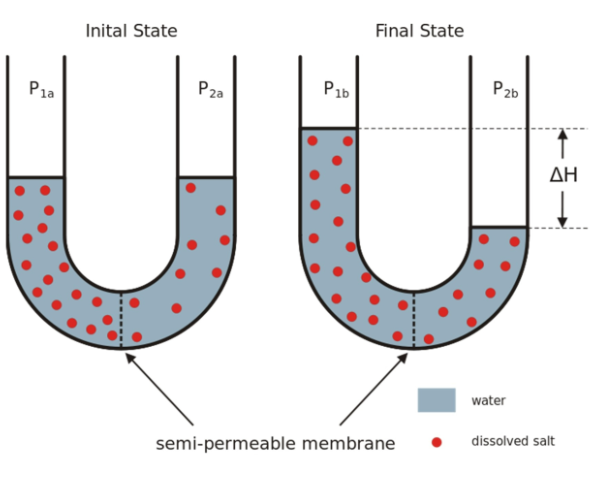
What is the Passive Transport of water across selectively permeable membrane called?
Osmosis
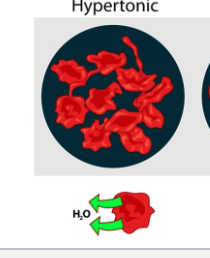
What are the three different types of Osmotic Solutions
Hypertonic
Isotonic
Hypotonic
What is a Hypertonic solution?
Solution with higher concentration of Solute
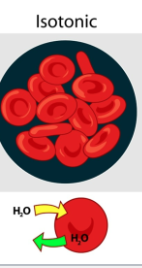
What is an Isotonic Solution
Solutions with equal concentration of solute.
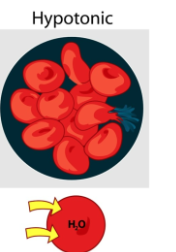
What is an Hypotonic Solution?
Solution with lower solute concentration
How is osmosis different in plant cells?
The plant cell wall helps maintain the cell shape

What is a Protein Channel?
The Protein that different types of molecules go through in facilitated diffusion.
When does active transport occur?
When a cell uses energy to move a molecule across the membrane. low to high
How do you transport large molecules?
they are packaged in vesicles
Moving products out is called what moving products in is called what
exocytosis and endocytosis
Where the Nucleus
surrounded by Nuclear membrane
What does the nucleus contain?
DNA
What is in the center of the Nucleus
Nucleoulus
What does the Nucleolus make?
Ribosomes
What is the cytoplasm
where all the other organelles are.
What do Ribosomes do
it is the sight of protein synthesis?
Where are ribosomes located?
Some are on rough er and some are suspended in the cytoplasm
What is ER
a network of membranes that manufactures, modifies and transports cells products
What are the 2 types of ER
Rough ER and Smooth ER
What does Rough ER do?
has ribosomes on the surface and modifies and transports proteins
What does Smooth Er do?
it doesn’t have ribosomes and it makes things like lipids
What is the Golgi Apparatus
Products from ER travel in vesicles to the Golgi Apparatus
It modifies stores and routes proteins to their destinations.
What are Vacuoles
Membrane bound sacs in the cytoplasm that store undigested nutrients and in plants it stores water
What are Lysosomes?
Membrane-bound sacs taht contain digestive enzymes that break down molecules
What are some fncs of Lysosomes?
Digest nutrients and Nourish the cell
Destroy harmful bacteria
Recycle damaged organelles w/o harming the cell
What is the path of cellular products?
Produced at ribosomes on Rough ER then travel to Golgi Apparatus then travel by vesicle to plasma membrane then products are released by exocytosis
What are Cytoskeleton Fibers
Microtubules
Microfilaments
intermediate filaments
What are Microtubules
straight hollow tubes of protein that give shape and rigidity
What are Microfilaments
Thinner solid rods of protein that enable the cell to move or change shape
What are intermediate filaments
rope like filaments taht provide stability
what is the Flagella
long thin whip-like structures composed of microtubules
What are Cilia
short microtubules move fluids over the cell