DNA Cloning and Restriction Enzymes in Genomics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
DNA cloning
The mass production of identical copies of a segment of DNA.
Cloning vector
An artificially constructed DNA molecule that can replicate in a host organism, e.g. a modified bacterial plasmid.
Recombinant DNA
Foreign DNA combined with a vector.
Transformation
The introduction of recombinant DNA into a host.
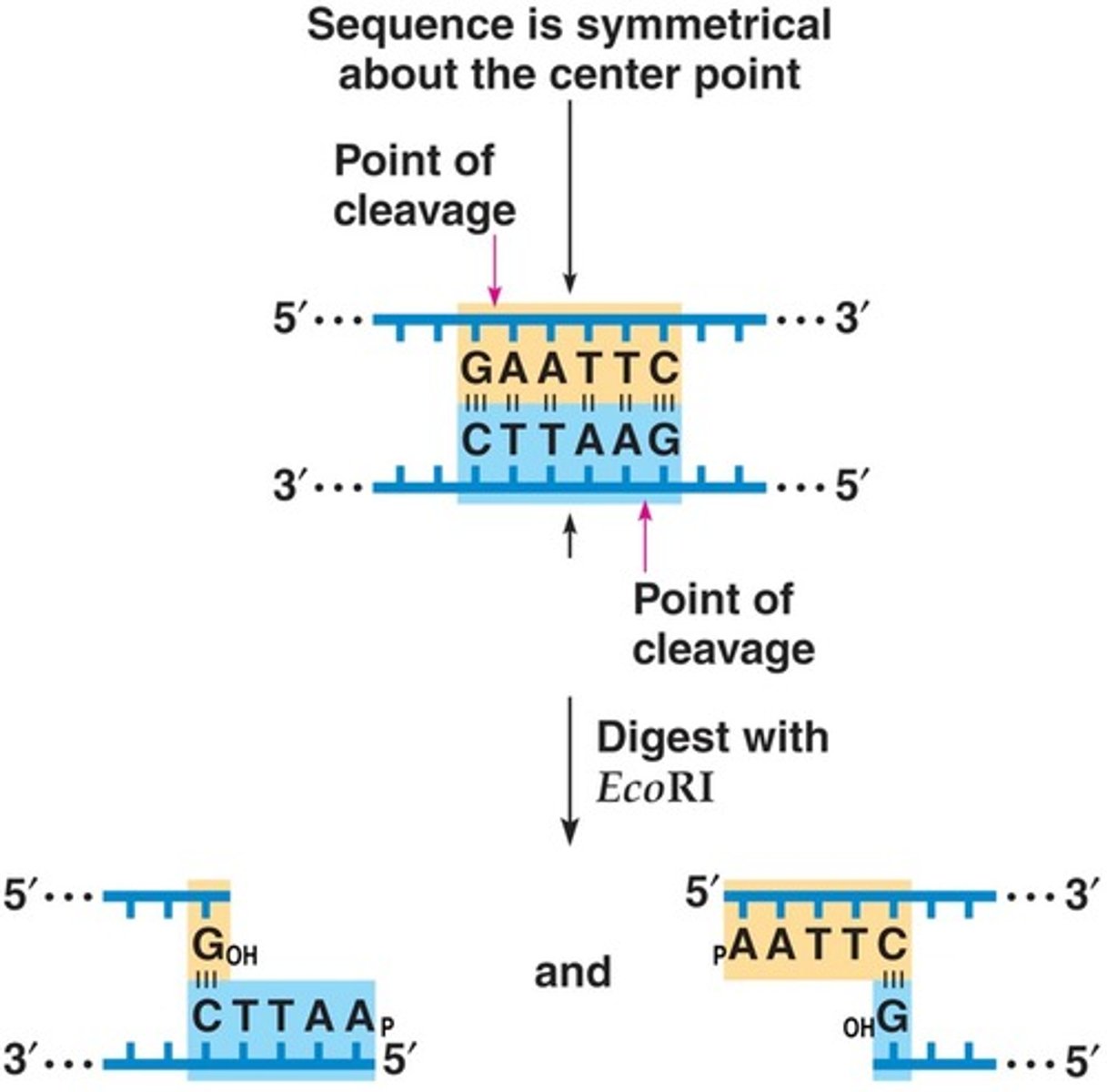
Restriction enzymes (RE)
Enzymes that recognize and cut a specific DNA sequence.
Palindromic sequence
A sequence that reads the same on the top strand (5'®3') as it does on the bottom (5'®3').
Staggered cuts
Cuts made by some REs that give overhanging or sticky ends.
Flush cuts
Cuts made by some REs that give blunt ends.
Methylation
The process by which restriction sites in bacterial DNA are protected from REs.
EcoRI
A specific restriction enzyme named after Escherichia coli strain RY13.
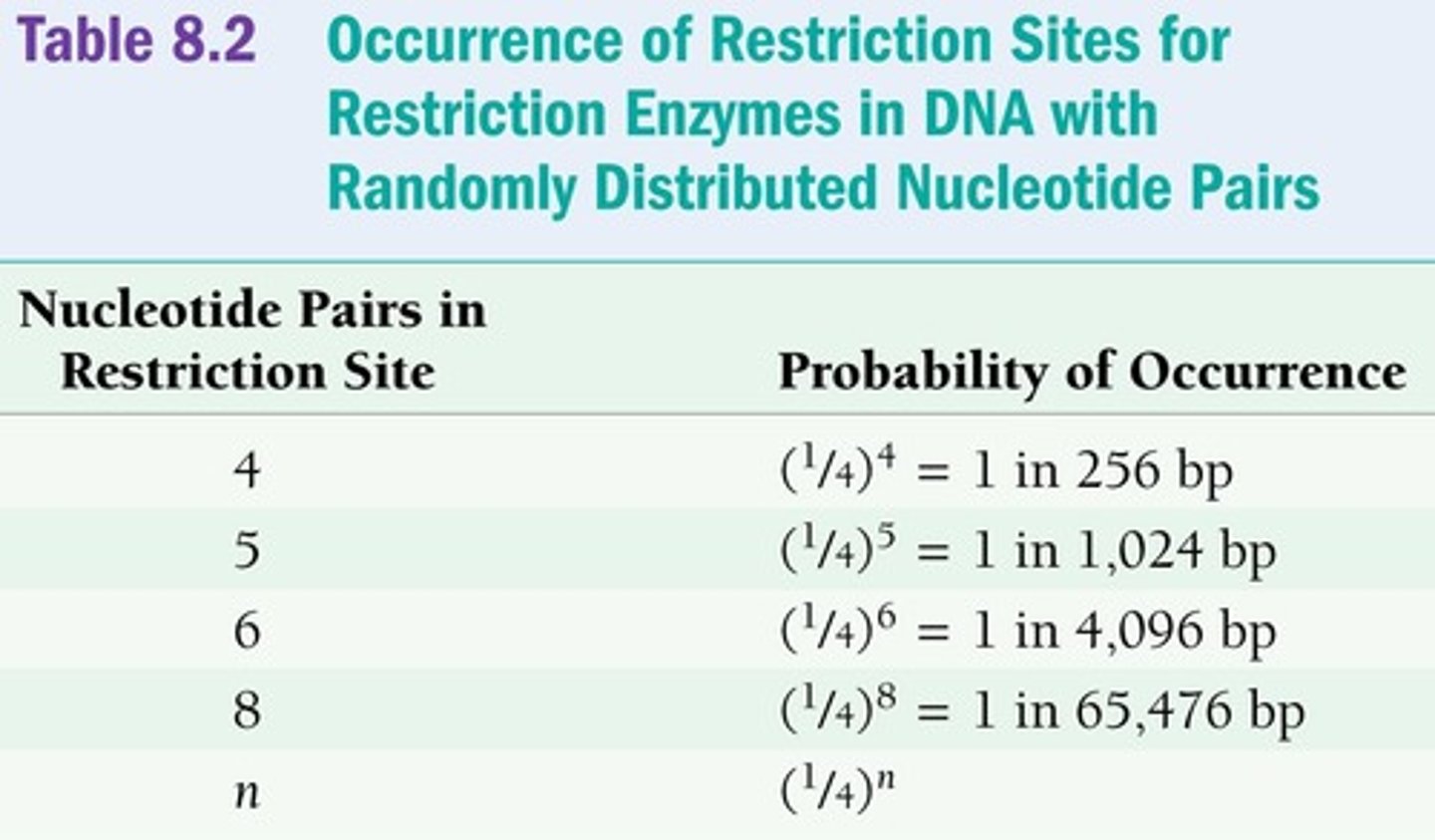
Frequency of occurrence of RE sites
The number of cuts a RE makes in a DNA molecule depends on how often the recognition sequence occurs.
Probability of a specific base
In an organism with random distribution of bases, the probability of a specific base at a given position is 1⁄4.
Frequency of a particular restriction site
Calculated as (1⁄4)n where n is the number of base pairs in the recognition sequence.
Example of Sau3AI
Recognizes the sequence GATC.
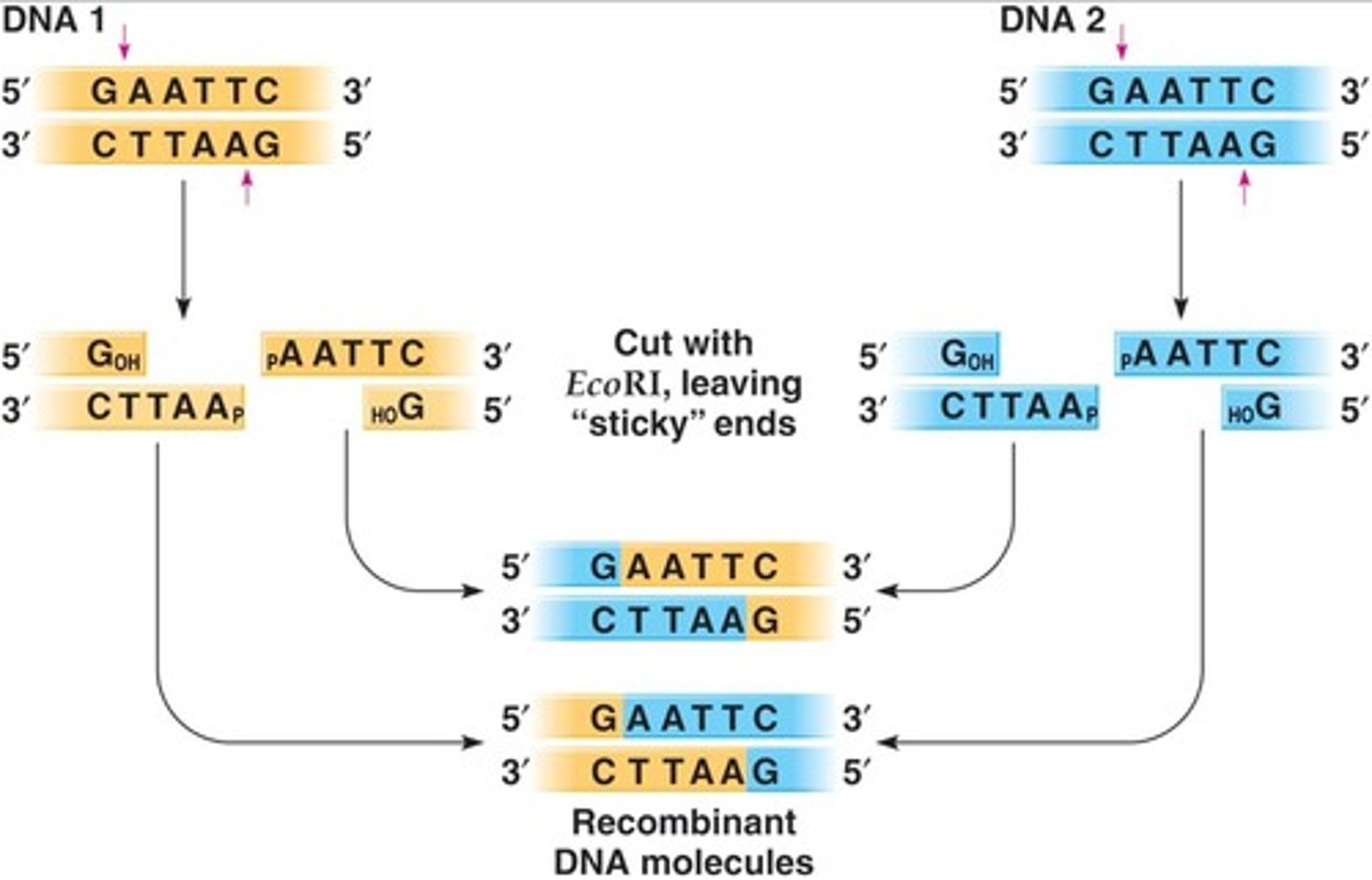
Ligation
The joining of two DNA fragments, forming phosphodiester bonds.
Blunt-ended DNA
DNA fragments that can be ligated together, although it is harder for them to find each other.
Ligase
An enzyme that joins DNA fragments and forms phosphodiester bonds.
Applications of cloned DNA
Includes mapping genes, sequencing, mutating, transforming cells, making proteins, and studying its function.
Single-stranded overhangs
Can be at either the 5' or the 3' end of DNA fragments.
Cloning procedure step 1
Isolate DNA from an organism.
Cloning procedure step 2
Use restriction enzymes to cut DNA into fragments.
Cloning procedure step 3
Ligate fragments into a cloning vector.
Cloning procedure step 4
Introduce recombinant DNA into a host.
Cloning procedure step 5
The host will replicate the DNA and pass copies to its progeny.