Muscle tissue types (Break FC)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
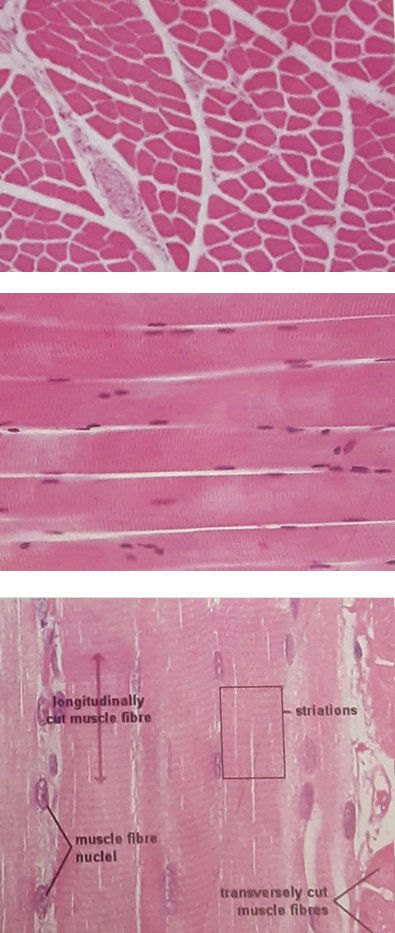
Skeletal Muscle
Attached to bony Skeleton
Elongated Fibers
Striated Appearance
Multinucleate
Voluntary Muscle
Subject to conscious control
Responsible for reflex contraction
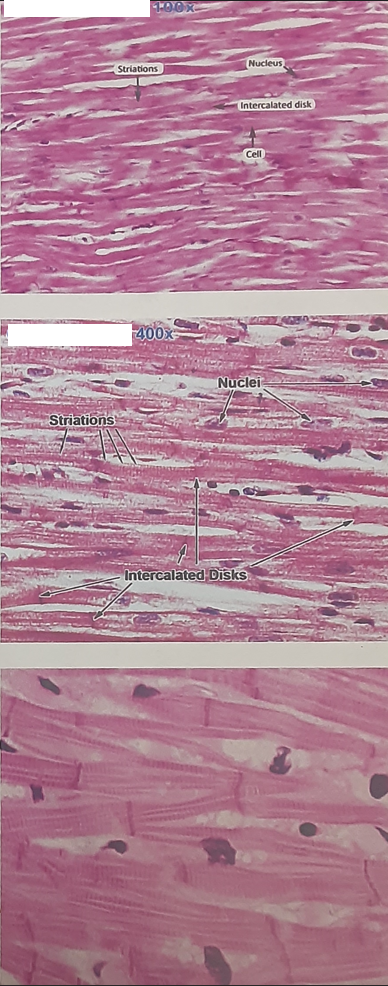
Cardiac Muscle
Found only in the heart
Branching fibers
striated appearance with intercalated discs
1-2 nuclei per cell
Involuntary muscle
Demonstrated autorhythmicity
Pacemakers
Stimulated by ANS and Hormones
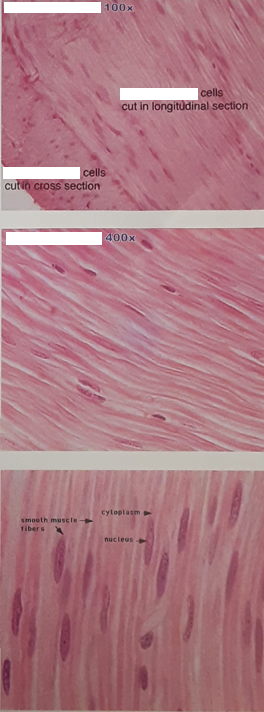
Smooth Muscle
Visceral: found in the walls of hollow organs
Blood vessels, Stomach, Respiratory Passages, Urinary bladder, ect.
spindle shaped cells
Non-striated appearance
Single nucleus
involuntary muscle
stimulated by ANS, Hormones and changes in ion levels
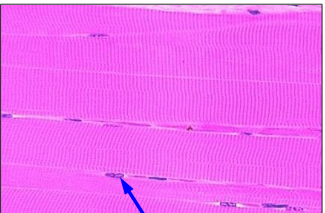
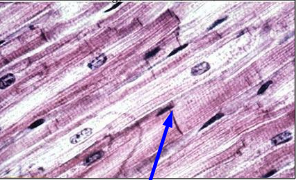
What type of muscle tissue is this?
What is the structure indicated by the arrow?
Is this tissue considered multinucleate?
Is this voluntary muscle tissue?
Is this tissue considered striated muscle?
Skeletal Muscle
nucleus.
yes.
Yes, skeletal muscle is voluntary muscle.
Yes.
What type of muscle tissue is this?
What is the structure indicated by the arrow?
Is this tissue considered striated muscle?
Is this tissue considered multinucleate?
Is this voluntary muscle tissue?
Cardiac
cell junction called intercalated disc.
yes.
No (but may occasionally have two nuclei)
No, involuntary.
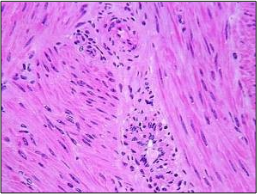
What type of muscle tissue is this?
Is this tissue considered striated muscle?
Is this tissue considered multinucleate?
Is this voluntary muscle tissue?
Where is this type of muscle found in the body?
Smooth muscle
No.
No.
No.
Uterus, wall of digestive tract, circulatory vessels, urinary, and reproductive organ.