Ch. 11 - personality
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Freud
believed that we are only aware of a small amount of our mind’s activities
and that most of it remains hidden from us in our unconscious. The information in our unconscious affects our behavior, although we are unaware of it.
Bandura
proposed the idea of reciprocal determinism: Our behavior, cognitive processes, and situational context all influence each other.
Skinner
a prominent behaviorist, said that we demonstrate consistent behavior patterns, because we have developed certain response tendencies. believed that environment was solely responsible for all behavior, including the enduring, consistent behavior patterns studied by personality theorists.
Jung
interested in exploring the collective unconscious.
traits
characteristic ways of behaving
Myers-Briggs Type indicator (MBTI)
This questionnaire describes a person’s degree of introversion versus extroversion, thinking versus feeling, intuition versus sensation, and judging versus perceiving. Jung’s view of extroverted and introverted types serves as a basis of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI).
anal stage
psychosexual stage in which children experience pleasure in their bowel and bladder movements
analytical psychology
Jung’s theory focusing on the balance of opposing forces within one’s personality and the significance of the collective unconscious.
archetype
pattern that exists in our collective unconscious across cultures and societies
collective unconscious
common psychological tendencies that have been passed down from one generation to the next
congruence
state of being in which our thoughts about our real and ideal selves are very similar
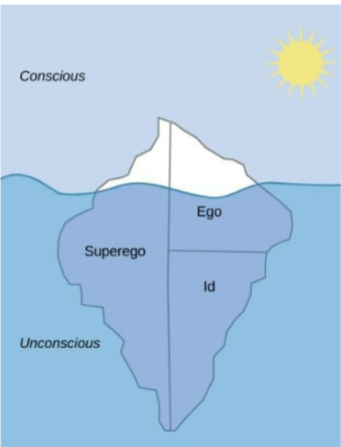
conscious
mental activity (thoughts, feelings, and memories) that we can access at any time
Contemporized-Themes Concerning Blacks Test (C-TCB)
projective test designed to be culturally relevant to African Americans, using images that relate to African-American culture
culture
all of the beliefs, customs, art, and traditions of a particular society
defense mechanism
unconscious protective behaviors designed to reduce ego anxiety
displacement
ego defense mechanism in which a person transfers inappropriate urges or behaviors toward a more acceptable or less threatening target
ego
aspect of personality that represents the self, or the part of one’s personality that is visible to others
Five Factor Model
theory that personality is composed of five factors, including openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism
genital stage
psychosexual stage in which the focus is on mature sexual interests
heritability
proportion of difference among people that is attributed to genetics
id
aspect of personality that consists of our most primitive drives or urges, including impulses for hunger, thirst, and sex
ideal self
person we would like to be
incongruence
state of being in which there is a great discrepancy between our real and ideal selves
individual psychology
school of psychology proposed by Adler that focuses on our drive to compensate for feelings of inferiority
inferiority complex
refers to a person’s feelings that they lack worth and don’t measure up to others’ or to society’s standards
latency period
psychosexual stage in which sexual feelings are dormant
locus of control
beliefs about the power we have over our lives; an external locus of control is the belief that our outcomes are outside of our control; an internal locus of control is the belief that we control our own outcomes
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
personality test composed of a series of true/false questions in order to establish a clinical profile of an individual
neurosis
tendency to experience negative emotions
oral stage
psychosexual stage in which an infant’s pleasure is focused on the mouth
personality
long-standing traits and patterns that propel individuals to consistently think, feel, and behave in specific ways. Shaped by upbringing.
phallic stage
psychosexual stage in which the focus is on the genitals
projection
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety disguises their unacceptable urges or behaviors by attributing them to other people
Projective test
personality assessment in which a person responds to ambiguous stimuli, revealing hidden feelings, impulses, and desires
psychosexual stages of development
stages of child development in which a child’s pleasure-seeking urges are focused on specific areas of the body called erogenous zones
rationalization
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety makes excuses to justify behavior
reaction formation
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety swaps unacceptable urges or behaviors for their opposites. I.e., reducing anxiety by adopting beliefs contrary to your own beliefs.
real self
person who we actually are
reciprocal determinism
belief that one’s environment can determine behavior, but at the same time, people can influence the environment with both their thoughts and behaviors
regression
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety returns to a more immature behavioral state
repression
ego defense mechanism in which anxiety-related thoughts and memories are kept in the unconscious. I.e., suppressing painful memories and thoughs.
Rorschach Inkblot Test
projective test that employs a series of symmetrical inkblot cards that are presented to a client by a psychologist in an effort to reveal the person’s unconscious desires, fears, and struggles
Rotter Incomplete Sentence Blank (RISB)
projective test that is similar to a word association test in which a person completes sentences in order to reveal their unconscious desires, fears, and struggles
selective migration
concept that people choose to move to places that are compatible with their personalities and needs
self-concept
our thoughts and feelings about ourselves
self-efficacy
someone’s level of confidence in their own abilities
social-cognitive theory
Bandura’s theory of personality that emphasizes both cognition and learning as sources of individual differences in personality
sublimation
ego defense mechanism in which unacceptable urges are channeled (redirected) into more (socially) appropriate activities (channels).
superego
aspect of the personality that serves as one’s moral compass, or conscience
TEMAS Multicultural Thematic Apperception Test
projective test designed to be culturally relevant to minority groups, especially Hispanic youths, using images and storytelling that relate to minority culture
temperament
how a person reacts to the world, including their activity level, starting when they are very young. It is biological and unchanging.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
projective test in which people are presented with ambiguous images, and they then make up stories to go with the images in an effort to uncover their unconscious desires, fears, and struggles
unconscious
mental activity of which we are unaware and unable to access
Galen’s theory of the four temperaments
4 Spectrums: Strong emotions, unchangeable temperaments, changeable temperaments, weak emotions
Choleric: Egocentric, excitable, exhibitionist, impulsive, histrionic, active
thrill seekers
mix of strong emotions and changeable temperaments
Sanguine: playful, easy going, sociable, carefree, hopeful, contented
chill
changeable temperaments and weak emotions
Phlegmatic: reasonable, principled, controlled, persistent, steadfast, calm
unchangeable temperaments and weak emotions
Melancholic: anxious, worried, unhappy, suspicious, serious, thoughtful
strong emotions and unchangeable temperaments
denial
a defense mechanism: refusing to accept real events because they are unpleasant.