Educational Psych final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:00 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory of Development Stage 1
Trust vs. Mistrust
* (0-1 year)
* Hope
* (0-1 year)
* Hope
2
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 2
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
* 1-3 years
* Will
* 1-3 years
* Will
3
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 3
Initiative vs. Guilt
* 3-6 years
* Purpose
* 3-6 years
* Purpose
4
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 4
Industry vs. Inferiority
* 6-12 years
* Competence
* 6-12 years
* Competence
5
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 5
Identity (ego) vs. Role Confusion
* 12-19 years
* fidelity
* 12-19 years
* fidelity
6
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 6
Intimacy vs. Isolation
* 20-25 years
* Love
* 20-25 years
* Love
7
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 7
Generativity vs. Stagnation
* 26-64 years
* care
* 26-64 years
* care
8
New cards
Erikson’s Theory of Development - Stage 8
Integrity vs. Despair
* 65-death
* Wisdom
* 65-death
* Wisdom
9
New cards
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development - Sensorimotor
* 0-2 years
* coordination of senses with a motor response
* sensory curiosity about the world
* language used for demands and cataloging
* object permanence developed
* coordination of senses with a motor response
* sensory curiosity about the world
* language used for demands and cataloging
* object permanence developed
10
New cards
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development - Preoperational
* 2-7 years
* symbolic thinking
* use of proper syntax and grammar to express full concepts
* imagination and intuition are strong, but complex abstract though still difficult
* conservation developed
* symbolic thinking
* use of proper syntax and grammar to express full concepts
* imagination and intuition are strong, but complex abstract though still difficult
* conservation developed
11
New cards
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development - Concrete Operational
* 7-11 years
* concepts attached to concrete situations
* time, space, and quality are understood and can be applied, but not as independent concepts
* concepts attached to concrete situations
* time, space, and quality are understood and can be applied, but not as independent concepts
12
New cards
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development - Formal Operations
* 11+
* theoretical, hypothetical, and counterfactual thinking
* abstract logic and reasoning
* Strategy and planning become possible
* concepts learned in one context can be applied to another
* theoretical, hypothetical, and counterfactual thinking
* abstract logic and reasoning
* Strategy and planning become possible
* concepts learned in one context can be applied to another
13
New cards

Be able to label the model
14
New cards
Disciplers Model - Growth
Maturation (in educational psych terms)
15
New cards
Disciplers’ Model - Thinking
Cognitive Development (in education psych term)
16
New cards
Disciplers’ Model - Relating
Social Connection (in educational psych terms)
17
New cards
Disciplers’ Model - Valuing
Affective Development (in educational psych terms)
18
New cards
Disciplers’ Model - Bible
Content Mastery (in educational psych terms)
19
New cards
Disciplers’ Model - Needs
Individual Differences (in educational psych terms)
20
New cards
Brain Labeling
Know the labels of brain
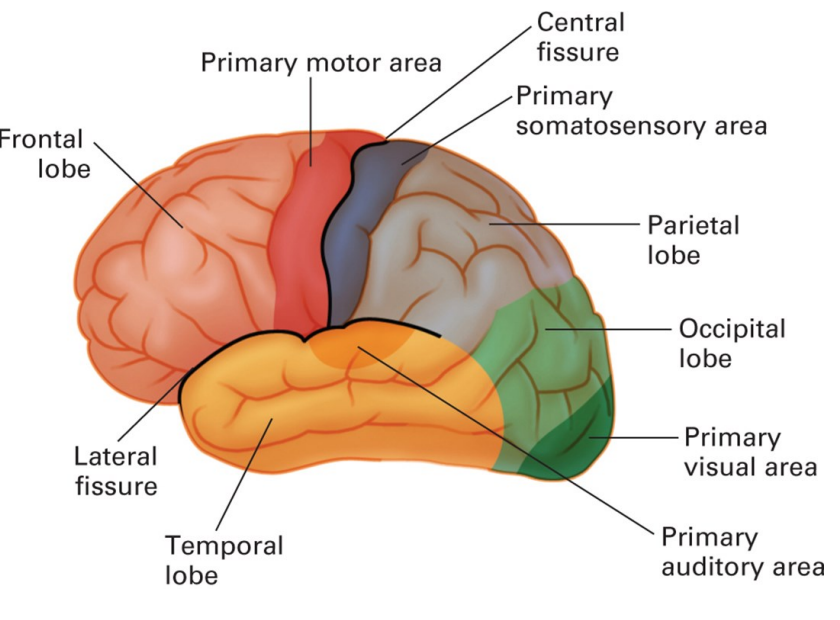
21
New cards
Frontal lobe
* higher level of thinking
* voluntary movement
* expressive language
* voluntary movement
* expressive language
22
New cards
Primary motor area function
* responsible for the initiation and execution of voluntary movements.
23
New cards
Central fissure function
* separates frontal and parietal lobes
24
New cards
Primary somatosensory area function
* integration of sensory and motor signals for skilled movement
* sensory receptive area
* sensory receptive area
25
New cards
Parietal Lobe function
* interpreting bodily sensations
* where body sensations of pressure, temperature, limb position and pain are processed
* where body sensations of pressure, temperature, limb position and pain are processed
26
New cards
Occipital lobe function
* responsible for vision and visual perception
27
New cards
Primary visual area
to receive, segment, and integrate visual information
28
New cards
Temporal Lobe function
responsible for hearing, language comprehension, memory and some emotional control
29
New cards
Lateral fissure function
separate the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
30
New cards
Neuron
Know labeling of neuron
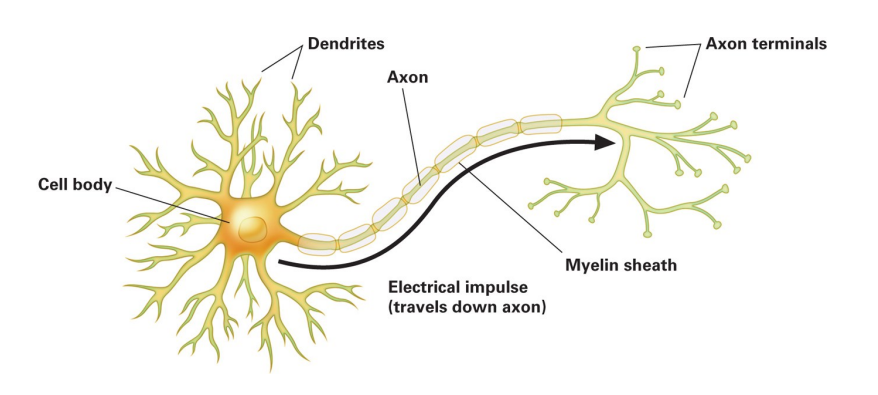
31
New cards
Neuron function
receives and conducts electrical impulses from the brain
32
New cards
Label subdivisions of Nervous System
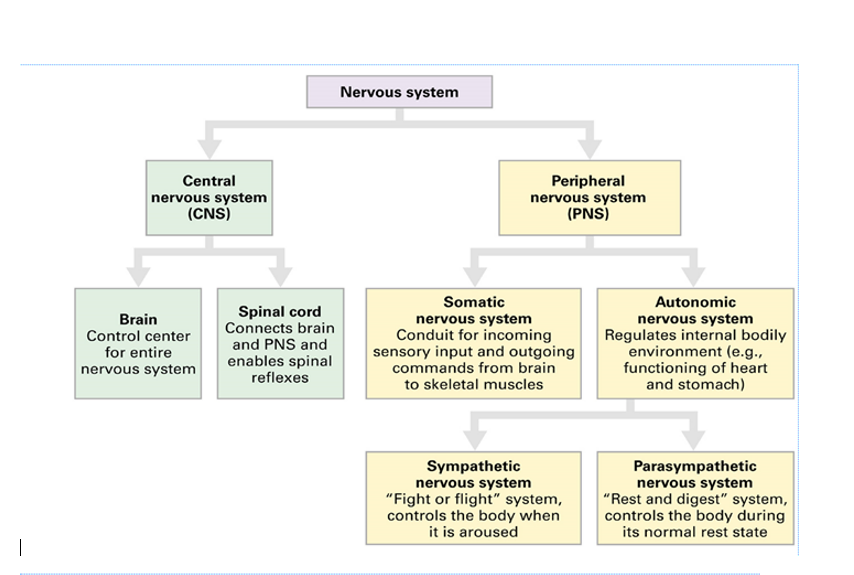
33
New cards
What is humanism?
A system of thought that centers on humans and their values, capacities, and worth.
34
New cards
Humanism’s beliefs about student learning
a system of thought that rejects religious beliefs
35
New cards
What is secular humanism?
humanism, with regard in particular to the belief that humanity is capable of morality and self-fulfillment without belief in God.
36
New cards
What is Christian humanism?
\
a philosophy advocating the self-fulfillment of humanity within the framework of Christian principles.
a philosophy advocating the self-fulfillment of humanity within the framework of Christian principles.
37
New cards
Abraham Maslow - Hierarchy of Needs
* theory of motivation
* children will make wise choices for their own learning with the opportunity
* allows children to select from choices of attractive and meaningful learning situations
* less teacher management is needed due to self-directed learning.
* children will make wise choices for their own learning with the opportunity
* allows children to select from choices of attractive and meaningful learning situations
* less teacher management is needed due to self-directed learning.
38
New cards
Carl Rogers - unconditional positive regard
* person-centered therapy approach
* teachers should trust students to do their best work to the best of their ability and provide opportunities for learning.
* respect students’ feelings and frustrations
* learn from students’ points of view
* students will take responsibility for their own learning
* teachers should trust students to do their best work to the best of their ability and provide opportunities for learning.
* respect students’ feelings and frustrations
* learn from students’ points of view
* students will take responsibility for their own learning
39
New cards
Arthur Combs - personal meaning/facilitator
* emphasized sharing personal views and less on objective problem solving
* meaning is not inherent in the subject matter; rather individual instills subject matter with meaning
* goal for teachers: to help students derive personal meaning/relevance of a subject
* emphasis on personal freedom over understanding, skill, and tangible achievement
* meaning is not inherent in the subject matter; rather individual instills subject matter with meaning
* goal for teachers: to help students derive personal meaning/relevance of a subject
* emphasis on personal freedom over understanding, skill, and tangible achievement
40
New cards
What is General motivation?
enduring and broad disposition to master a variety of learning situations (stable)
41
New cards
What is specific motivation?
energization toward a particular learning situation (unstable)
42
New cards
What is intrinsic motivation?
Based on internal origins from within the learner
43
New cards
What is extrinsic motivation?
Based on external origins outside of the learner
44
New cards
Behaviorism view of motivation
Motivation as direct reinforcement
* regulate future actions by controlling of consequences of present behavior
* Behavior modification - appropriate reinforcers for each student and then tie those to desired behaviors.
* Shaping - selectively using reinforcement strategies to move students toward particular goals
* regulate future actions by controlling of consequences of present behavior
* Behavior modification - appropriate reinforcers for each student and then tie those to desired behaviors.
* Shaping - selectively using reinforcement strategies to move students toward particular goals
45
New cards
Social learning view on motivation
Motivation as Providing Appropriate Models
* bandura - vicarious learning
* ripple effect
* bandura - vicarious learning
* ripple effect
46
New cards
Cognitive view on motivation
Motivation as Creating Curiosity
* Piaget - the tendency to maintain a balance between what we know, cognitive networks, and experiences of the world
* equilibration/disequilibration
* assimilation/accommodation
* social interactions prompt: thought-provoking questions and problem-solving activities and dilemmas.
* Piaget - the tendency to maintain a balance between what we know, cognitive networks, and experiences of the world
* equilibration/disequilibration
* assimilation/accommodation
* social interactions prompt: thought-provoking questions and problem-solving activities and dilemmas.
47
New cards
Information Processing view on motivation
Motivation as Increased Meaningfulness
* Piaget - a natural tendency to make sense out of experiences
* assimilation/accommodation to make the world meaningful
* attracting and holding attention (voice change, attractive displays, etc)
* Piaget - a natural tendency to make sense out of experiences
* assimilation/accommodation to make the world meaningful
* attracting and holding attention (voice change, attractive displays, etc)
48
New cards
Achievement theories views on motivation
Motivation as providing successful experiences
* success vs. anxiety
* locus of control (effort) and attribution
* success vs. anxiety
* locus of control (effort) and attribution
49
New cards
Weiner’s model of attribution
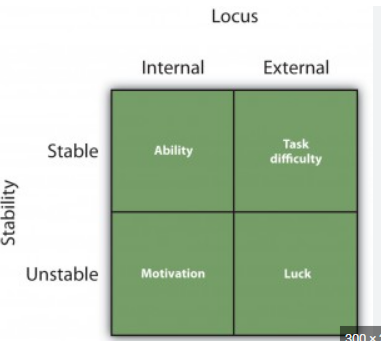
50
New cards
What is a neuron?
* A brain cell and primary functional unit of the nervous system
* communication with each other chemically
* 3 types (interneuron, sensory, and motor)
* communication with each other chemically
* 3 types (interneuron, sensory, and motor)
51
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
* reactionary
* responsible for “fight or flight” system that controls the body when it is aroused
* responsible for “fight or flight” system that controls the body when it is aroused
52
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
* calming
* responsible for “rest and digest” and control the body during its normal rest rate
* responsible for “rest and digest” and control the body during its normal rest rate
53
New cards
Hindbrain
* well protected central core of the brain
* includes the cerebellum, reticular formation, and brain stem
* responsible for most basic automatic functions of life (breathing and movement)
* includes the cerebellum, reticular formation, and brain stem
* responsible for most basic automatic functions of life (breathing and movement)
54
New cards
Limbic system
* plays a role in our survival, memory and emotions
* includes the hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, and basal ganglia
* includes the hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, and basal ganglia
55
New cards
Cerebral cortex
* thin surface layer on the left and right cerebral atmospheres
* regulates most complex behavior, including sensations, motor control, and higher mental processes.
* where perception, language, memory, decision-making, and all other higher-level cognitive processing.
* regulates most complex behavior, including sensations, motor control, and higher mental processes.
* where perception, language, memory, decision-making, and all other higher-level cognitive processing.
56
New cards
What is attention?
The cognitive process of selectively focusing on specific aspects of the environment while ignoring others. It involves concentrating and sustaining focus on a particular task or stimuli.
57
New cards
Brain structure in learning
What we focus on, where we place our mental effort, causes changes in the structure and wiring of our brains.
58
New cards
What is brain lateralization?
The division of tasks between the left and right hemispheres of the brain. Each hemisphere is specialized for certain functions such as language and spatial reasoning.
59
New cards
What is human functioning?
the sum total of functions and structures of the body and mind, the actions people perform, and the complex and socially-embed life activities they participate in