nervous system (copy)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
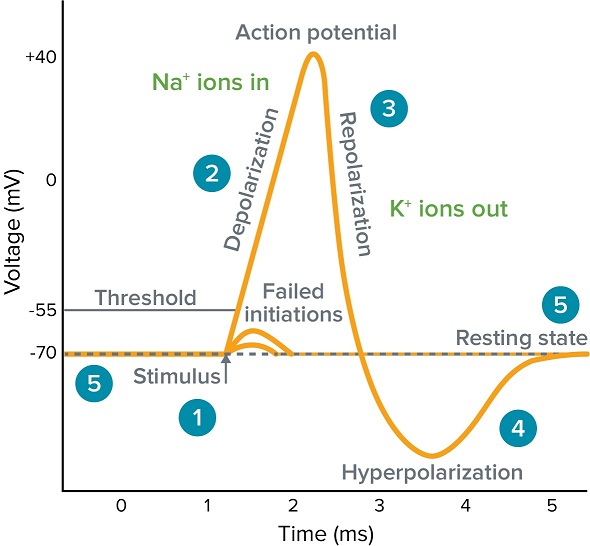
New cards
CNS
brain/spinal cord
2
New cards
peripheral nervous system
all parts of the nervous system external to the brain and spinal cord
3
New cards
autonomic nervous system
involuntary, stimuli transmitted to cardiac and smooth muscle
4
New cards
Myelin Sheath
allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells
5
New cards
neurilemma
protects neuron and regenerates nerves
6
New cards
neuroglia
nerve glue, provide developmental, physiological, and metabolic support for neurons
7
New cards
nerve impulse
neurons are not connected, travels down the axon membrane as an electrical action potential to the axon terminal
8
New cards
spinal cord
2 main functions- conducts impulses to and from brain, reflex center
9
New cards
efferent nerves
motor transmitters that carry impulses from the central nervous stem out to the muscles and glands
10
New cards
afferent
sensory transmitters that sends impulses from receptors in the skin, muscles, and joints to the CNS
11
New cards
repolarization
is the re-establishment of a polarized state in the cell after depolarization
12
New cards
polarized
when inside of a cell is more negatively charged than the outside it is…
13
New cards
refractory period
is the time between the completion of the action potential and repolarization
14
New cards
somatic reflexes
are involuntary stimuli transmitted to skeletal muscles from neural arcs in the spinal cord
15
New cards
depolarized
is more positively charged on the inside than the outside
16
New cards
salutary conduction
an action potential that rapidly skips from node to node on myelinated neurons is experiencing…
17
New cards
3 special characteristics of a neuron cell
lives long, amitotic, high metabolic rate
18
New cards
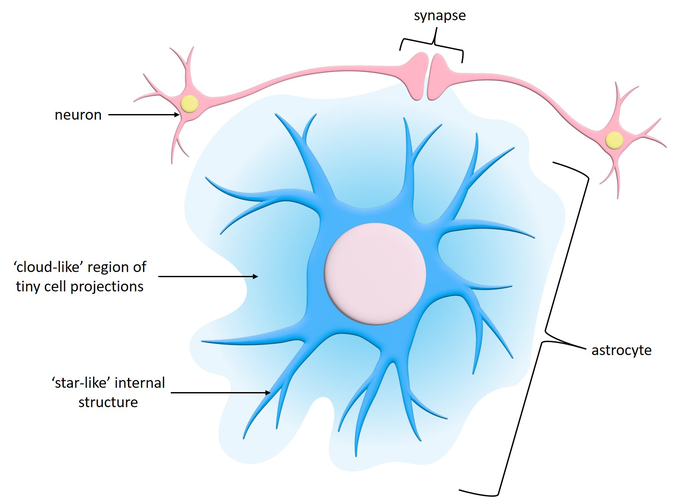
astrocyte (CNS)
most abundant CNS
19
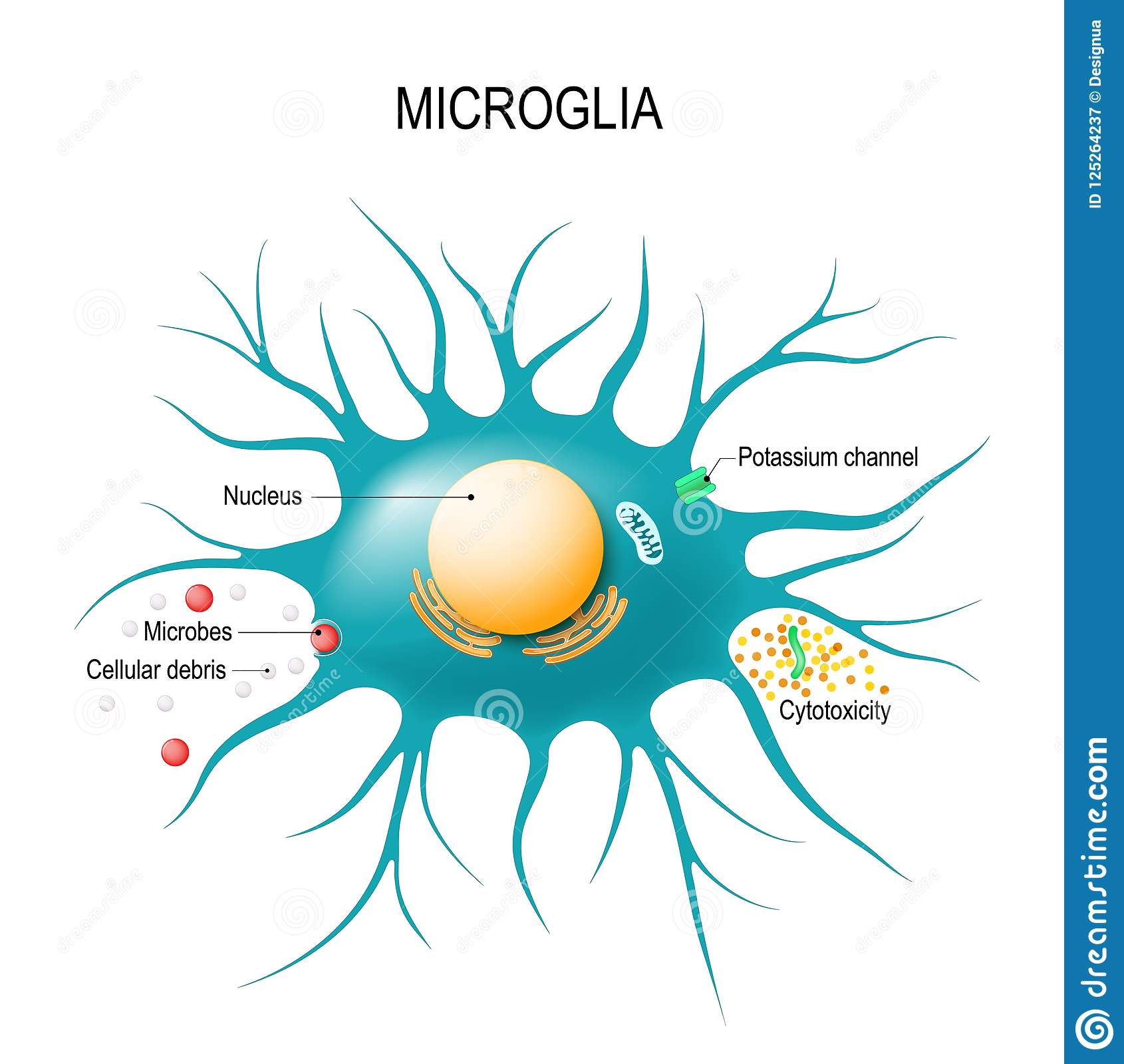
New cards
microglial (CNS)
change into macrophages-defenders, first to respond when something goes wrong in the brain
20
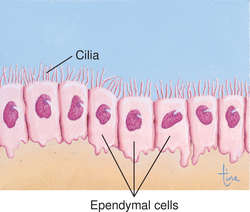
New cards
ependymal (CNS)
separate the CNS interstitial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid
21
New cards
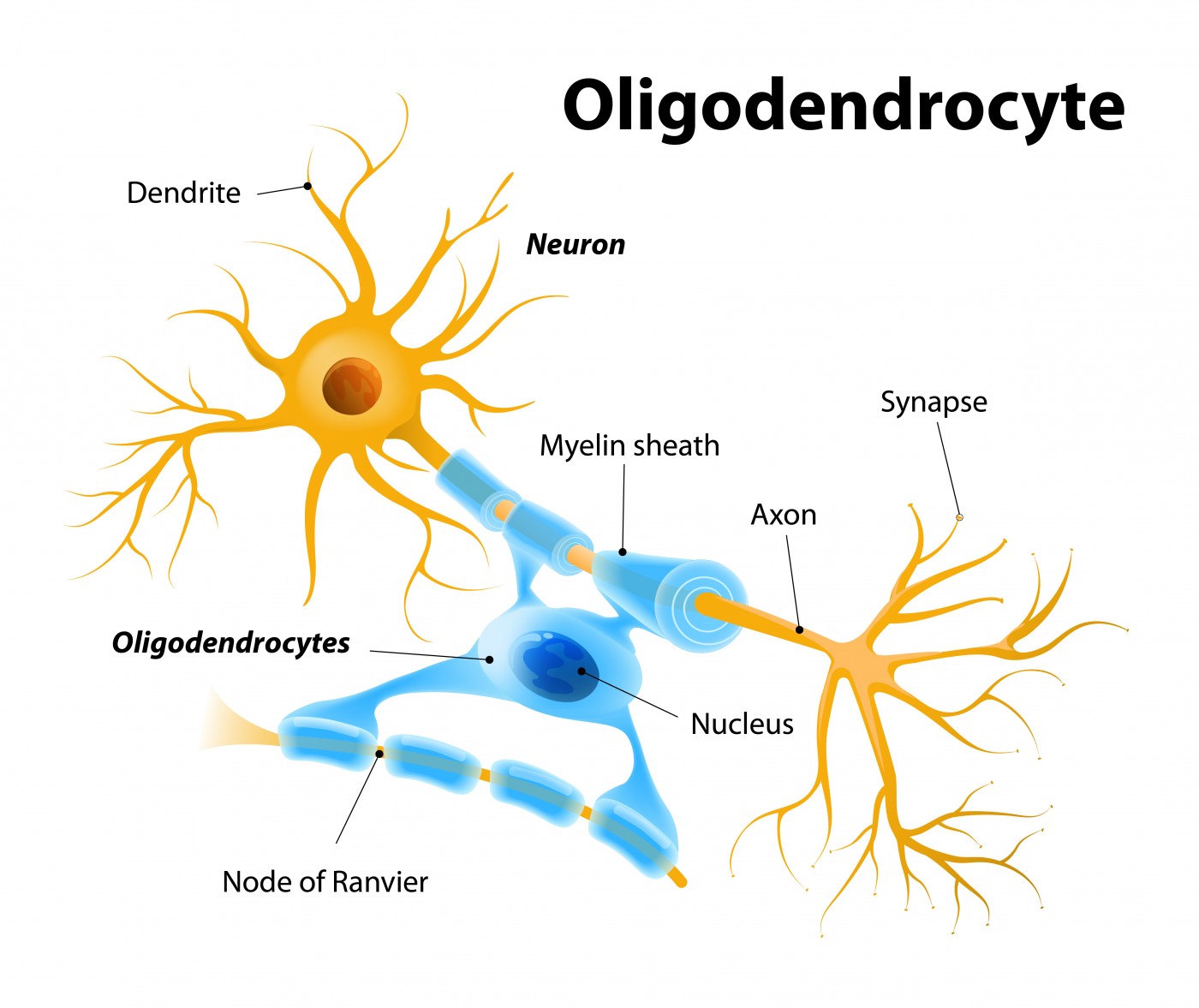
oligodendrocytes (CNS)
myelinating cells of the central nervous system
22
New cards
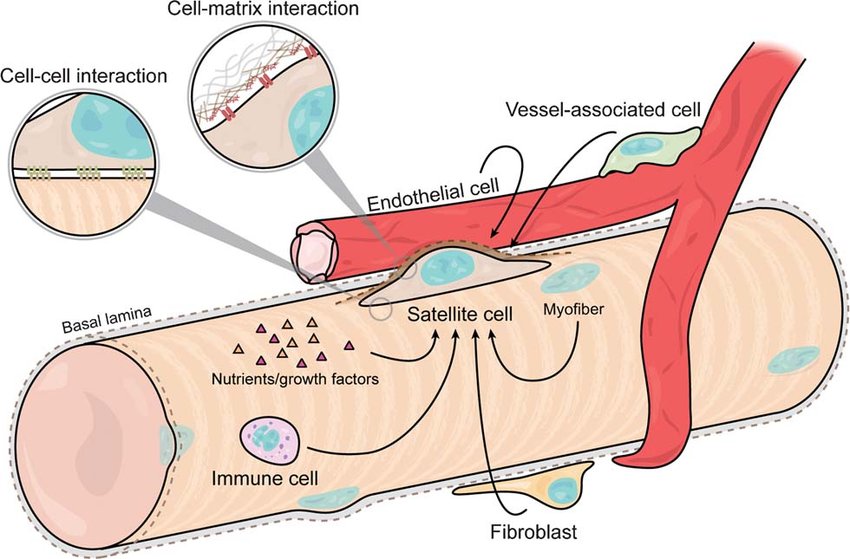
satellite cells (PNS)
surrounds neuron cell bodies in PNS
23
New cards
Schwann cell
wraps PNS fibers to form myelin sheath
24
New cards
sympathetic
fight/flight
25
New cards
parasympathetic
rest/digest
26
New cards
sensory
somatic/visceral, afferent
27
New cards
motor
muscle/glands, efferent
28
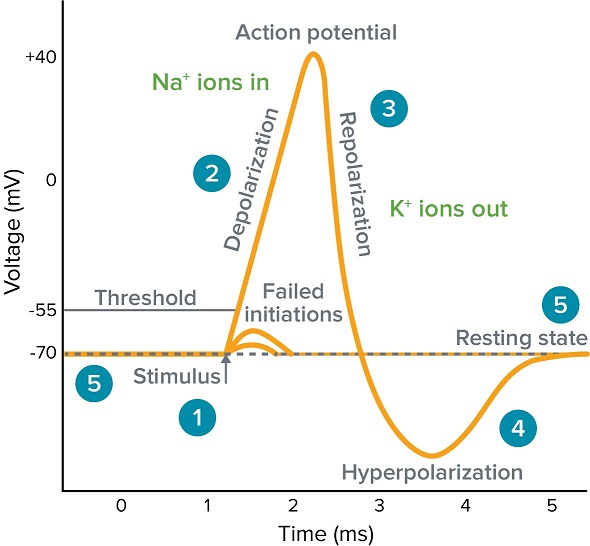
New cards
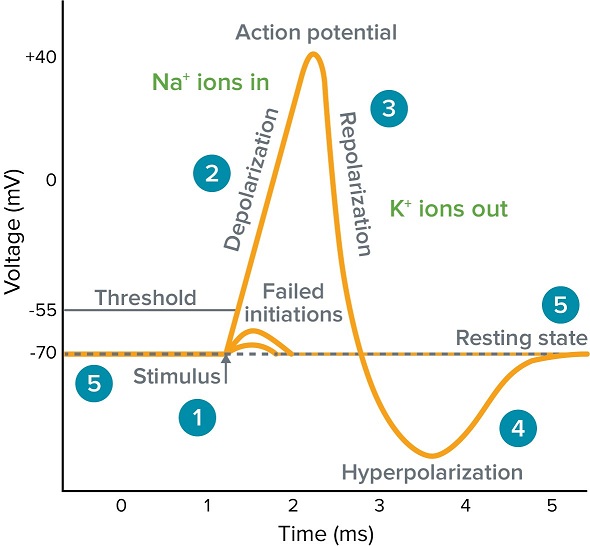
Na+ and K+ closed
\#5 - explain which ion channels are open or closed
29
New cards
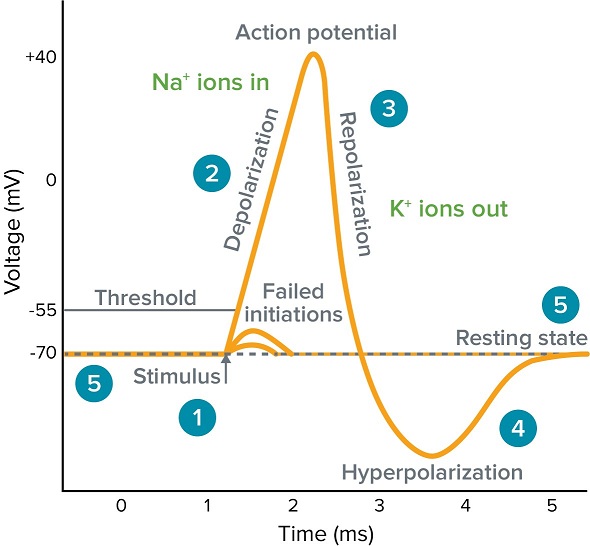
trigger for Na+ to open
threshold - explain which ion channels are open or closed
30
New cards
Na+ open, K+ close
\#2 - explain which ion channels are open or closed
31
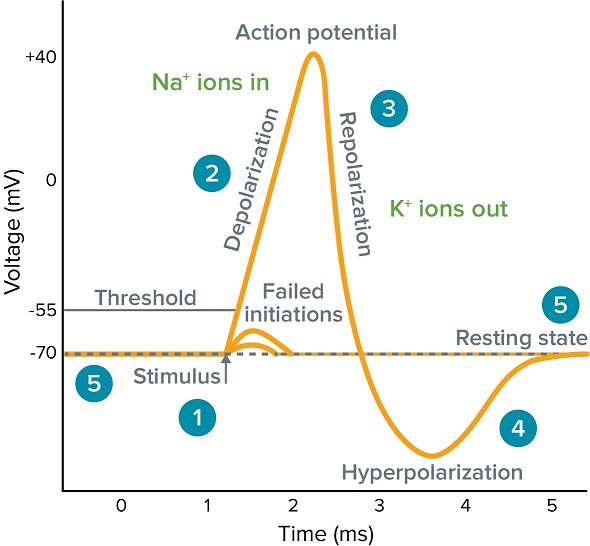
New cards
Na+ close, K+ open
\#3 - explain which ion channels are open or closed
32
New cards
K+ closing, Na+ reset
\#4 - explain which ion channels are open or closed