Earths Structure and internal energy sources
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
Last updated 8:15 AM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1
New cards
Describe the structure of the earth
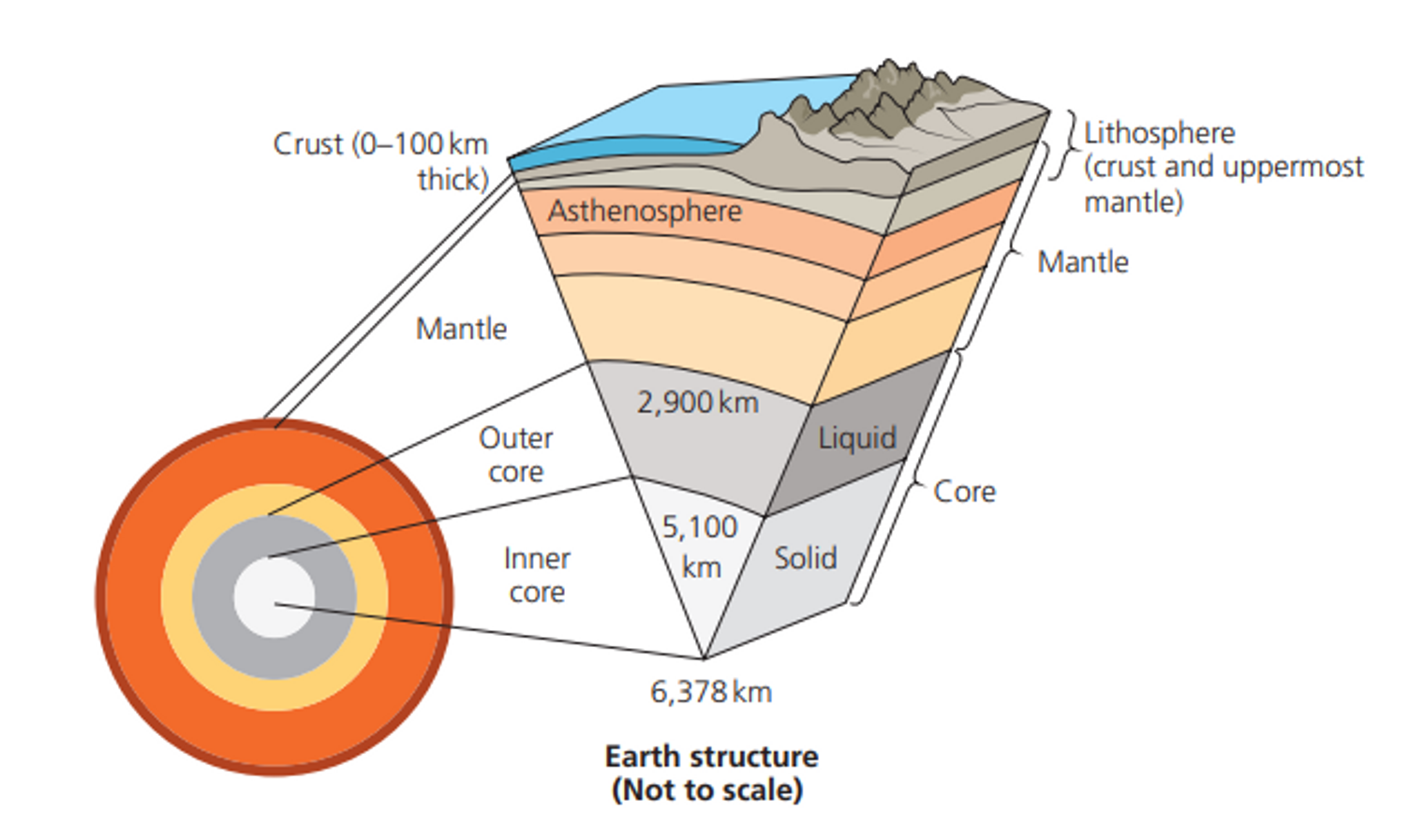
2
New cards
Describe Oceanic crust features
1. Alternative name
2. geology
3. thickness
4. density
1. Alternative name
2. geology
3. thickness
4. density
* known as Sima
* Primarily basalt
* 4-7 km thick
* denser than continental
* Primarily basalt
* 4-7 km thick
* denser than continental
3
New cards
Describe Continental crust features
Describe the asthenosphere
* known as Sial
* Primarily granite
* 20-70 km thick
* less dense (will not undergo subduction)
* known as Sial
* Primarily granite
* 20-70 km thick
* less dense (will not undergo subduction)
4
New cards
Describe the asthenosphere
Upper Mantle:
* Weaker, plastic rocks
* constantly moves due to convection currents
* Weaker, plastic rocks
* constantly moves due to convection currents
5
New cards
Describe the earths core
* Outer Core:
* liquid
* mainly iron
* Inner Core
* Solid
* iron-nickel alloy
* temperatures up to 4,700
* liquid
* mainly iron
* Inner Core
* Solid
* iron-nickel alloy
* temperatures up to 4,700
6
New cards
Describe the lower mantle
Weaker, plastic rocks
700-3,000km deep
700-3,000km deep
7
New cards
2 sources of internal energy
Radiogenic, Primordial
8
New cards
Explain how primordial heat occurs
Left over from the formation of the earth. The heat lost by the Earth as it continues to cool from its original formation,
9
New cards
Explain radiogenic heat
produced by the radioactive decay of isotopes in the mantle and crust.
The radioactive decay of elements results in the production of daughter isotopes and release of particles and heat energy, or radiogenic heat
* Actively produced
The radioactive decay of elements results in the production of daughter isotopes and release of particles and heat energy, or radiogenic heat
* Actively produced
10
New cards
Distribution of energy:
Internal heat is transferred from the ____ __via _________, into the mantle where it is moved on by__ ________. Afterwards, the heat escapes through__ _______ ___________ (heat carries in molten rock through the crust )
Internal heat is transferred from the ____ __via _________, into the mantle where it is moved on by__ ________. Afterwards, the heat escapes through__ _______ ___________ (heat carries in molten rock through the crust )
core, conduction, convection, volcanic advection