Chemistry - Unit 2 - atomic structure & Nuclear Chemistry
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass
mass cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged or transformed into different forms
What is the Law of Definite Proportions
any specific chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same fixed proportion by mass, regardless of its source or how it was prepared
What is the Law of Multiple Proportions?
if two elements can form more than one compound, then the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element will be in a ratio of small whole numbers
Define Atom
Basic building block of matter & the smallest unit of an element that retains the element’s properties.
Define Atomic Number
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table.
Define Isotopes
different "versions" of the same element
like different models of the same car
Which Greek philosopher suggested that matter was continuous?
Aristotle
The rays reflected in a cathode tube in early experiments were
deflected away from a negative plane
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, atoms…
of each element are identical in size, mass and other properties
Thomson
Scientist that concluded that all cathode rays are composed of identical negatively charged particles, which were later named electrons
Scientist who used gold foil experiment to study the nature of matter
Rutherford
Scientist who measured the charge of an electron and calculated that it has a mass of about one two-thousandth the mass of a proton (hydrogen atom)
Milikman
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ( What theory is this?
Dalton Atomic theory
Who performed the oil drop experiment?
Milikman
What scientist named the process by which materials, such as uranium atoms, emitting rays that darken photographic plates radioactivity?
Marie Curie
What is a radiosotope?
Isotopes of atoms with unstable nuclei
Radiation decay is a process…..
Where unstable nuclei release energy by emitting radiation to become more stable,
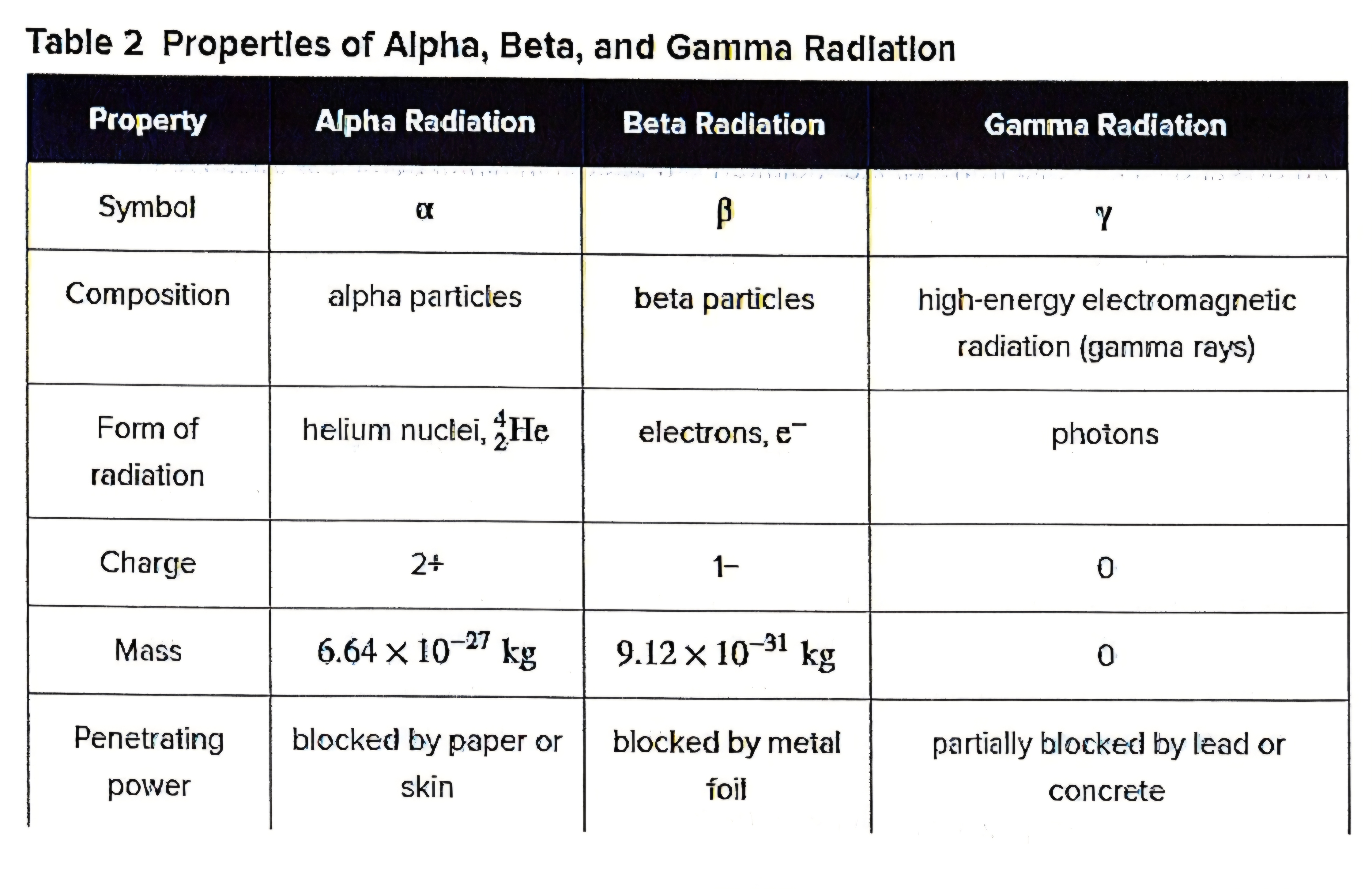
Refer to the table….:What type of radiation posses the most energy?
Gamma
What is NUCLEAR FISSION
a very heavy nucleus splits into smaller, more stable nuclei of intermediate mas
What is NUCLEAR FUSION ?
light-mass (small) nuclei combine to form a heavier, more stable nucleus
An atom of bromine has an atomic number of 35 and a mass number of 80. How many protons, neutrons and electrons does this atom have?
35p
35e
45n