Cooling system
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What can happen if cooling system does not work properly?
without a properly operating cooling system, an engine can “self-destruct” in minutes.
Internal parts can overheat, causing the engine to seize (rotating assembly no longer rotates freely)
What are the six types of cooling systems?
Engine, supercharger, turbocharger, high voltage (HV) battery, HV motor generator, and HV power control module.
Internal combustion engines (ICE) generates a lot of heat from the power stroke (4500 degrees Fahrenheit) Where does all that heat go?
1/3 of heat goes out the exhaust
1/3 goes to through the cooling system
1/3 of the heat powers the engine
What is heat transfer?
Heat will transfer whenever there is a difference in temperature.
What are the three ways heat is transferred?
1) conduction - through solid objects
2) convection - through liquids and gasses
3) radiation - through space
What are the 4 jobs of the cooling system?
Remove excess heat from engine
maintain constant engine operating temperature
helps a cold engine quickly reach operating temperature
provides heat to the passenger compartment
What are the 12 parts of the heater core?
heater core
thermostat
upper radiator hose
expansion overflow tank
radiator pressure cap
radiator
lower radiator hose
fan
water pump
water jackets
heater hoses
coolant
What is flat rate?
standard set time a job should take to complete for a specific make, model, year, and specific part being replaced.
Give an example of flat rate:
2014 F-150 water pump flat rate = 1.7 hrs
every .1 is 6 minutes
this job should take the mechanic 1 hour and 42 minutes to complete.
If the shop charges customers $160 hr, this job would cost the customer $221 labor + parts, fluids, tax, and shop fees.
What is the heater core?
Small size radiator inside the passenger compartment. Located behind the dash in the A/C box.
As hot coolant goes through heater core, the blower motor blows air through the heater core, picking up the heat. This then allows you to have hot air in the passenger compartment during winter.
What is the flat time? (system based)
Part cost = $ 80-$100
Flat rate = 6-12 hours
Total = $1,000-$1,400
Thermostat function and operation:
Function: controls coolant flow through the radiator. The thermostat is the part that allows the engine to warm-up quickly and helps the engine maintain a constant temperature.
Operation of the thermostat: when the engine is cold, the thermostat is closed, and will not let coolant leave the engine. When the coolant gets hot enough, the thermostat will open and let the coolant flow to the radiator and begin to cool down.
Flat time for thermostat?$350
Part cost = $5 - $15
Flat rate = 1-2 hours
total = $200 - $350
Thermostat:
located at the end of the upper radiator hose where it plugs into the engine. Underneath the thermostat housing.
Heat range: temperature the thermostat will open at.
Average heat range is 185 degrees Fahrenheit
Bypass hose- allows coolant to flow when the thermostat is closed. This allows coolant to heat of evenly.
Thermostat problems:
does not open - engine overheats quickly
stays wide open - engine stays cold
stuck half-way open - overheats in the summer and takes a long time to warm up in the winter. Heater may not work very well.
Powertrain control module (PCM) monitors thermostat operation.
Types of hoses:
heater hoses - similar to a garden hose. Sized according to the inside diameter of the hose. (I.D.); 1/2”, 5/8”, 3/4”, 7/8”, and 1”. Sold by the linear foot as $1-$2
Molded - pre-formed; best used for radiators. Most hoses come this way. Set shape for a specific vehicle. (costs $20 to $75)
Hose problems:
clamps to loose, or to tight
cracking
stiffness; brittleness
soft spots
kinking
bulging at the clamps
What is a caution you should know when removing hoses?
When removing hoses, do not bend back and fourth to remove. Twist the hose to remove.
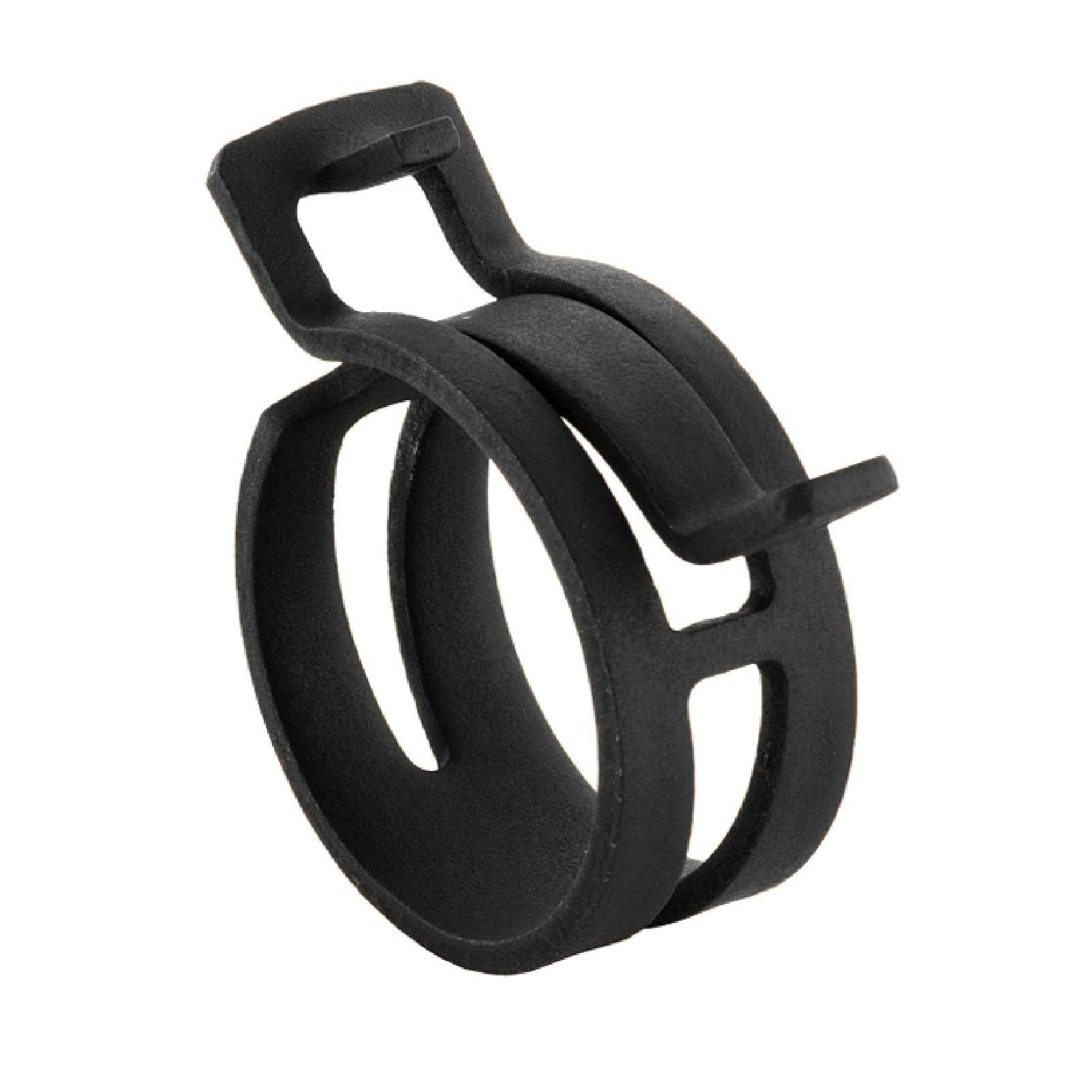

what type of clamp is this?
spring clamp
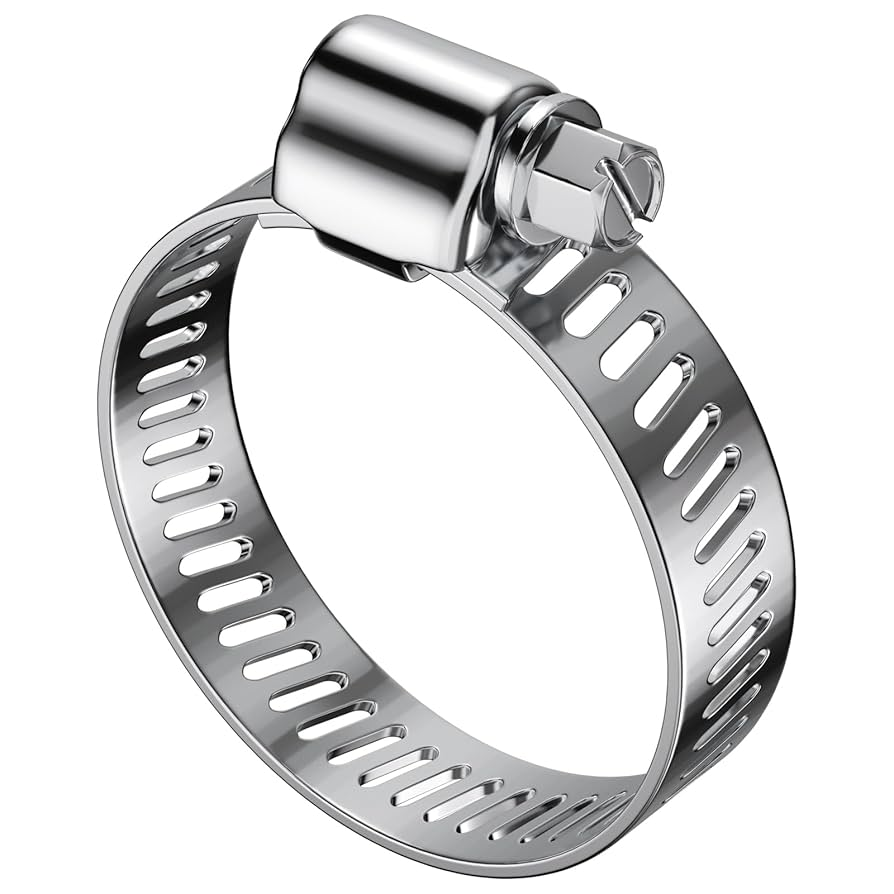

what type of clamp is this?
worm
explain the overflow/surge/expansion tank:
as coolant heats up, it expands.
the overflow tank allows extra coolant from radiator to be stored and not dumped on the ground.
There are two types pressurized and non-pressurized
Explain a closed cooling system:
a system that refills itself.
system must be completely full to operate properly. No air space!!
How does a overflow/surge/expansion tank operate?
As coolant gets hot it expands and pushes out the overflow tube and goes to the overflow tank.
After engine has been shut off, coolant cools down and contacts. As it lowers in the radiator it creates a vacuum.
This will pull the coolant back out of the overflow tank and refill radiator.
How do you check a overflow/surge/expansion tank?
check overflow tank when cold. Coolant should be at cold mark.
Check after engine is hot coolant should be at hot mark.
Make sure you see coolant in the overflow tank. It can get dirty and you cannot tell where the coolant is.
What are the two jobs of the radiator pressure cap?
Controls the amount of pressure in the cooling system.
Prevents a vacuum from forming in the radiator as the coolant cools.
What is the law of pressure when it comes to radiator caps:
For every pound of pressure on the cooling system, the boiling point is raised 3 degrees.
15 lb. Cap will raise the boiling point 45 degrees.
Water boils at 212 degrees Fahrenheit. SO the coolant in the cooling system could be at 257 degrees Fahrenheit!!
How and what to do for a radiator cap check:
check radiator cap for a dry, cracked, or brittle rubber gasket.
compress spring to make sure it is okay.
What is a caution you should be aware of when it comes to the radiator cap?
DO NOT attempt to remove the radiator cap when engine is hot. Always check upper hose for pressure to see if engine is hot.
What does a radiator cap look like?
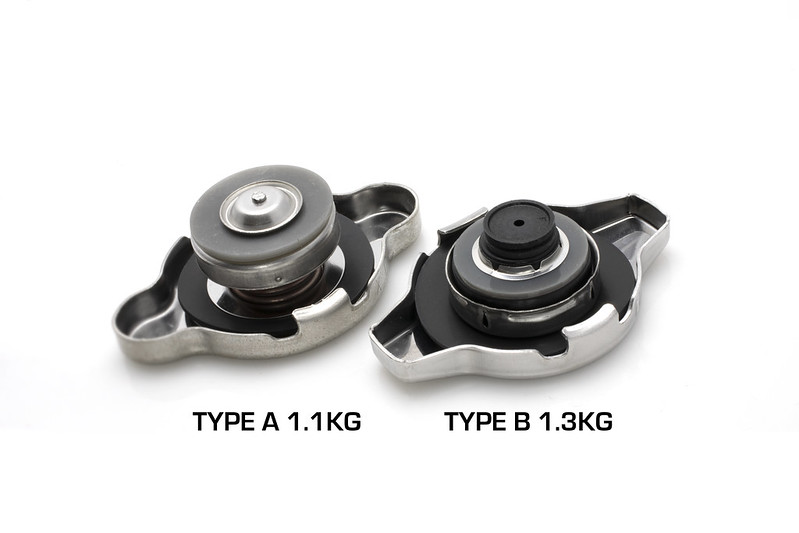

Explain radiators:
designed to remove heat from the coolant.
cost: $100-$400
Flat rate 1-3 hours
heat can be controlled by the amount of fins and tubes in the radiator. These are called cores.
What are the two types of radiators?
down flow - coolant travels from top to bottom.
cross flow - coolant moves from side to side . (came out because of low profile cars).
What does a flow down radiator look like?

What does a cross flow radiator look like?
6 basic parts of the radiator?
top tank (left or right tank)
core (tubes and fins)
bottom tank (left or right tank)
drain (petcock)
filler neck
hose connections
Radiator problems:
leaks - loss of coolant, or overheating. (damage to the core).
Clogged tubes - overheating
Damaged/clogged fins - does not allow air to flow through, causes overheating. (grass rocks, sticks, etc.)
explain the water pump:
Water pump - a device that circulates coolant, driven by the drive belt off the crankshaft pulley, timing chain, or electric motor.
Flat rate = 1.5-9.5 hours
cost new = $50 - $180
Cost rebuild = $45 - $80
Basic parts of the water pump:
Hub - front part that the fan and pulley bolts to.
Impeller - part with fins that moves the coolant.
Shaft - steel rod that holds impeller to the hub.
Bearings - allow the shaft to spin.
Seal - keeps coolant from leaking out along shaft.
Housing - foundation for all parts.
Parts that can wear out and how to check them in a water pump:
bearings - with engine off, hold fan or pulley and wiggle it back and forth. If it moves it is bad.
Seal - look for signs of leakage at vent in water pump housing. Corrosion at vent hole could indicate leaking.
Drive belts:
Serpentine/Drive Belts - used to drive several components using the crankshaft pulley. Components driven by fan belts.
water pump
fan
power steering pump
alternator
AC compressor
2 types of belts:
V-belt - first types used. Cost $5 to $15. Usually needs 3 to 5 different belts. Flat -rate .1 to .2 per belt.
Serpentine - used on newer cars. Cost - $20 to $ 40. Flat-rate is .1 to .5. Needs only one belt to run everything.
Fan belt problems and symptoms:
loose tension - squealing noise, or overheating.
Cracking - squealing when load is applied.
Glazing - Squealing when load is applied.
Damaged/missing pieces - Squealing worse and some components may not work.
Problem vs. Symptom:
Symptom - things we can hear, see, feel, and smell coming from the car.
Problems - the things that create the symptoms. Cannot always see the problem.
What is Anti-Freeze:
ethylene glycol base liquid. Poisonous and hazardous to the environment. Should not dump on ground. Use 50% mixture with distilled water (loss of minerals in water) in engine.
Cost - $20-$30 a gallon
Two main jobs:
1) Lowers the freezing point of coolant
2) Increase the boiling point
(when coolant additives go bad, coolant becomes acidic and electrolysis happens!)
4 jobs of additives:
clean the system
prevents corrosion
lubricates the water pump seal
prevents foaming
What is a note to make about Anti-Freeze:
Note: Cars use different kinds of anti-freeze. Make sure to verify what kind of anti-freeze is used in the car you are servicing.
What is a Refractometer?
Refractometer - Measures gravity of water/anti-freeze, this also includes a hydrometer which indicates the freezing point.
Water Jackets:
Passages in the engine block where coolant flows around combustion chamber, cylinder head, cylinder walls.
Fan:
driven off the drive belt or electric motor. Used to pull air across the radiator and aid in removing heat. Used during low vehicle speed.
Fan clutch:
A device that is hooked to the fan which keeps it from turning during cold engine temperatures. Also slow it down at high speed.
Electric Fans:
Commonly used on front wheel drive vehicles. Fans are driven by electric motors.
Fan Shroud:
Helps ensure fan pulls air through radiator core, not around it.
Heat Transfer Process: Where does the heat transfer to in the engine?
Heat is produced in combustion chamber.
Heat goes to cylinder walls.
From cylinder wall to water jackets.
Water pump circulates coolant.
Coolant flows into top radiator hose.
Top hose to top tank of radiator.
From top tank to core tubes.
From the tube(s) to fins.
From fins it flows out the air.
Fan and shroud increase air-flow through radiator.