States of Matter + Atoms Elements and Compounds
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
227 Terms
Solids
Solids have a fixed volume and shape and they have a high density.
The atoms vibrate in position but can’t change location
The particles are packed very closely together in a fixed and regular pattern
Liquids
Liquids also have a fixed volume but adopt the shape of the container
They are generally less dense than solids (an exception is water), but much denser than gases
The particles move and slide past each other which is why liquids adopt the shape of the container and also why they are able to flow freely
Gases
Gases do not have a fixed volume, and, like liquids, take up the shape of the container
Gases have a very low density
Since there is a lot of space between the particles, gases can be compressed into a much smaller volume
The particles are far apart and move randomly and quickly (around 500 m/s) in all directions
They collide with each other and with the sides of the container
How is pressure inside a can created
Particles collide with each other and with the sides of a container
solid to liquid
melting
liquid to solid
freezing
liquid to gas
evaporation, boiling or vaporization
gas to liquid
condensation
solid to gas
sublimation
gas to solid
desublimation or deposition
Melting
when a solid changes into a liquid
Requires heat energy which transforms into kinetic energy, allowing the particles to move
Occurs at a specific temperature known as the melting point (m.p.)
Freezing
when a liquid changes into a solid
This is the reverse of melting and occurs at exactly the same temperature as melting, hence the melting point and freezing point of a pure substance are the same. Water, for example, freezes and melts at 0 ºC
Requires a significant decrease in temperature (or loss of thermal energy) and occurs at a specific temperature
Boiling
when a liquid changes into a gas
Requires heat which causes bubbles of gas to form below the surface of a liquid, allowing for liquid particles to escape from the surface and within the liquid
Occurs at a specific temperature known as the boiling point (b.p.)
Evaporation
occurs when a liquid changes into a gas and occurs over a range of temperatures
Evaporation occurs only at the surface of liquids where high energy particles can escape from the liquid's surface at low temperatures, below the b.p. of the liquid
The larger the surface area and the warmer the liquid surface, the more quickly a liquid can evaporate
Condensation
Condensation occurs when a gas changes into a liquid on cooling and it takes place over a range of temperatures
When a gas is cooled its particles lose energy and when they bump into each other they lack the energy to bounce away again, instead they group together to form a liquid
When substances are heated,
the particles absorb thermal energy which is converted into kinetic energy
basis of the kinetic theory of matter
When substances are heated, the particles absorb thermal energy which is converted into kinetic energy
Describe how a solid turns into a liquid
Heating a solid causes its particles to vibrate more
As the temperature increases, the particles vibrate so much that the solid expands until the structure breaks
Describe how a liquid turns into a gas through evaporation
Heating a liquid causes its particles to move more and spread out
Some particles at the surface gain sufficient energy to overcome the intermolecular forces
This is when a liquid starts to evaporate
Describe how a liquid turns into a gas through boiling
Heating a liquid causes its particles to move more and spread out
When the boiling point is reached, all of the particles gain enough energy to escape and the liquids boils into a gas
Heating and cooling curves are used to
show how changes in temperature affect changes of state
During a state change
there is no temperature chance
latent heat
the heat needed to cause a phase change to a specific amount of matter at a fixed temperature
A change in temperature or pressure affects the
volume of gases
As the air inside a hot air balloon is heated up
it expands and the balloon gets bigger. This is because the volume of a gas increases as temperature increases
the volume of a gas increases
as temperature increases. The density decreases as the volume increases so the balloon rises.
If you have a gas stored inside a container that is squeezed, the pressure
increases as you decrease the volume
Gaseous particles are
in constant and random motion
The pressure that a gas creates inside a closed container is produced by
the gaseous particles hitting the inside walls of the container:
How does temperature affect the volume of a gas?
Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of each particle. As the temperature increases, the particles in the gas move faster and spread out more. If the gas particles are inside a container, they will collide with the container walls more frequently. If the container walls are flexible and stretchy then the container will get bigger and bigger, just like the hot air balloon!
How does pressure affect the volume of a gas?
Pressure is about the number of particles in a given volume. Increasing the pressure means that there are the same number of particles but in a smaller volume. Conversely, decreasing the pressure means that there are the same number of particles but in a larger volume
When the pressure increases
the volume decreases. This means that the molecules collide with the container walls more frequently
Diffusion occurs in
gases and liquids, due to the random motion of their particles
Why does diffusion occur
because of the random motion of their particles
Diffusion
where particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Eventually the concentration of particles is even as the particles are evenly spread throughout the available space
Diffusion happens on
its own and no energy input is required
Diffusion occurs faster at
higher temperatures because the particles have more kinetic energy
Diffusion is faster in gases than
liquids
Why is diffusion faster in gases than in liquids?
because gaseous particles have more energy and move quicker than liquid particles
the diffusion of bromine gas and air
At the start, the orange-brown bromine gas is an area of high concentration
It diffuses from a high to low concentration
After 5 minutes, the bromine gas will have diffused from the bottom jar until it is evenly spread throughout both jars
The same can be said for the air, although it is less obvious as it is colourless
How molecular mass affects diffusion
At the same temperature, different gases do not diffuse at the same rate.
This is due to the difference in their relative molecular masses
Gases with a lower relative molecular mass are "lighter" which means that they Travel faster, travel further in the same amount of time
The reverse argument is true for gases with a high relative molecular mass, they Travel slower and Do not travel as far in the same amount of time
Diffusion of ammonia and hydrogen chloride
Ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride gas react together to form solid ammonium chloride. Ammonia molecules have less mass than HCl molecules so they diffuse faster and the product forms closer to the HCl end
Four substances are shown, in which of these substances are the particles closer together and moving slowly past eachother?
A) Ice
B) Air
C) Steam
D) Water
D) Water
A student noted the following observation in his book: The particles moved slowly from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Which process is being described?
A) Diffusion of a substance in a liquid
B) The particles of a solid when melting
C) A liquid being frozen
D) DIffusion of a substance through the air
A) Diffusion of a substance in a liquid
A small amount of bleach was accidentally spilled on the kitchen floor. After a while it was observed that the floor appeared to be dry and the room smelled of bleach. What processes have occured?
A) Evaporation and diffusion
B) Distillation and diffusion
C) Evaporation only
D) Diffusion only
A) Evaporation and diffusion
Characteristics of silicon (IV) oxide
very high melting point and boiling point and does not conduct in any form
Room temperature
between 20 to 25 degrees celsius
To be a metal
A substance must be a good conductor in all states and it must have a relatively high melting point
Aqueous sodium chloride
conducts as a liquid solution but not as a solid. The boiling point of water is elevated by the presence of sodium chloride and the melting point is depressed
an ionic compound conducts when
liquid but not solid, the melting and boiling point should also be high
chemical equation for the reaction of ammonia and hydrogen chloride
NH3 + HCl —> NH4Cl
Name the process by which ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases move in the tube
diffusion
What would be the result of an impure substance in a heating or cooling curve?
Lines would not be horizontal and the line would be lower
All substances can be classified into one of these three types
Elements
Compounds
Mixtures
What is an element?
a pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance. Every element is made up of its own type of atom. Made of atoms that all contain the same number of protons.
What is a compound?
A pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined
What is a mixture?
A combination of two or more substances (elements and/or compounds) that are not chemically combined
How can mixtures be seperated?
by physical methods such as filtration or evaporation
All substances are made of tiny particles of matter called
atoms which are the building blocks of all matter
Each atom is made of subatomic particles called
protons, neutrons, and electrons
Location of subatomic particles in an atom
nucleus - protons and neutrons
outer shells - electrons
proton mass and charge
mass - 1
charge - +1
neutron mass and charge
mass - 1
charge - 0
electron mass and charge
mass - 1/1840
charge - -1
atomic number (or proton number)
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
symbol for atomic number
Z
You can find out the number of electrons in an atom
by looking at the atomic number as the number of protons and electrons are the same
Nucleon number (or mass number)
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
symbol for nucleon number
A
The nucleon number minus the proton number gives you
the number of neutrons of an atom
protons and neutrons can collectively be called
nucleons
the mass number is always greater than the
atomic/proton number
We can represent the structure of the atom in two ways:
using diagrams called electron shell diagrams or by writing out a special notation called the electronic configuration
Electron shell diagrams
Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells (or energy levels) and each shell has a different amount of energy associated with it. The first shell can hold 2 electrons, the rest, up to 8.
The outermost shell of an atom is called
the valence shell and an atom is much more stable if it can manage to completely fill this shell with electrons
What is the electronic configuration of boron?
2, 3
electronic configuration of oxygen
2, 6
electronic configuration of calcium
2, 8, 8, 2
How does the electronic structure of an element relate to its location in the Periodic Table?
The number of notations in the electronic configuration will show the number of occupied shells of electrons the atom has, showing the period in which that element is in. The last notation shows the number of outer electrons the atom has, showing the group that element is in (for elements in Groups I to VII).
Rows in the periodic table are called
periods
horizontal lines in the periodic table are called
groups
how to know which period an element is in
The number of notations in the electronic configuration will show the number of occupied shells of electrons the atom has
how to know which group an element is in
The last notation shows the number of outer electrons the atom has
Period: The red numbers at the bottom show the number of notations
The number of notations is 3
Therefore the element has 3 occupied shells
Group: The last notation, in this case 7
This means that the element has 7 electrons in its outer shell
Element is therefore in Group 7
The noble gases
in group 8 or 0
All of the noble gases are unreactive as they have full outer shells and are thus very stable
Atoms want their shells to be
full
Why do atoms want their shells to be full?
It makes them more stable, in some cases atoms lose electrons to empty its shell so that the next shell below is full. Then they’d have the electronic structure of a noble gas.
electrons in the outer shell are also known as
valency electrons.
isotopes
Isotopes are different atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. This means that the mass number would change while the proton number would stay constant.
Why do isotopes share properties or same chemical characteristics
because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shells, and this is what determines their chemistry
The difference between isotopes is the neutrons which are neutral particles within the nucleus and add mass only
The difference in mass affects the physical properties, such as density, boiling point and melting point
What does the difference in mass affect in isotopes?
physical properties like density, boiling point and melting point because of the added mass from neutrons
Relative atomic mass
Atoms are so tiny that we cannot really compare their masses in conventional units such as kilograms or grams, so a unit called the relative atomic mass (Ar) is used
The relative atomic mass unit is equal to
1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom
Why does relative atomic mass have no units?
All other elements are measured by comparison to the mass of a carbon-12 atom and since these are ratios, the relative atomic mass has no units
relative atomic mass formula
(% of isotope A x mass of isotope A) + (% of isotope B x mass of isotope B)
100
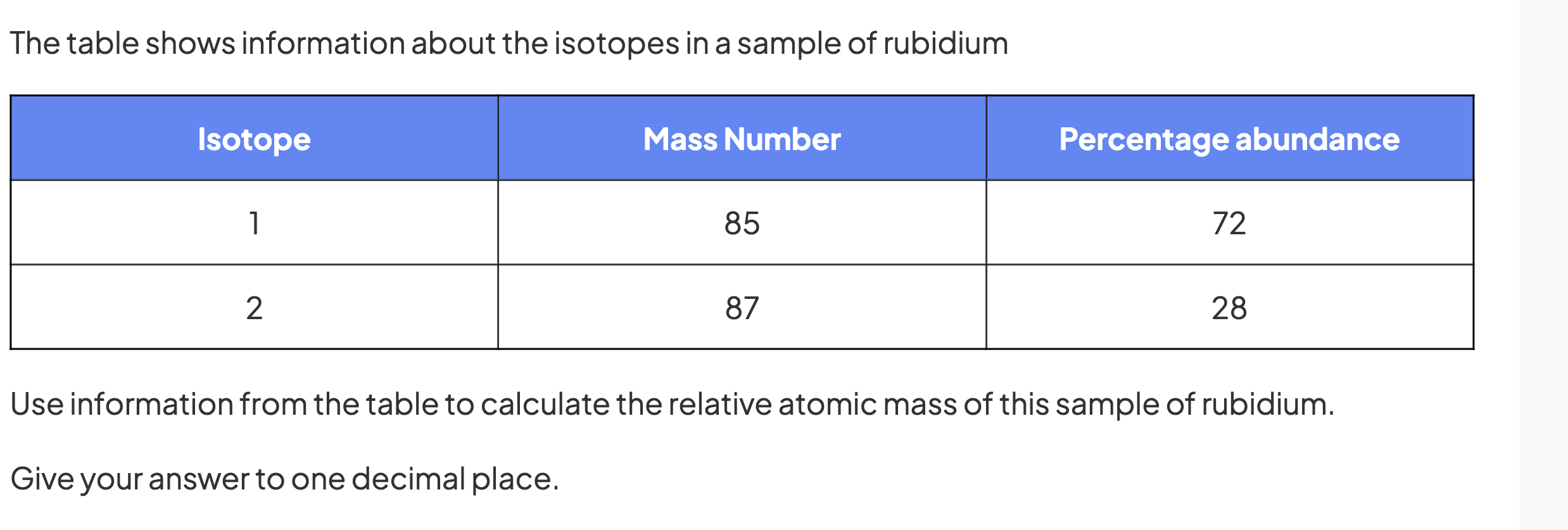
do this question
85.6
Is mass number and relative atomic mass the same thing?
No. mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom and it is a whole number value while relative atomic mass is the ratio of the mass of an element to the 1/12th of the mass of a carbon atom.
What is an ion?
an electrically charged atom or group of atoms formed by the loss or gain of electrons