3.2.5 (The Cardiac cycle)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is meant by the term cardiac cycle?
The sequence of events in one full heart beat
What are the 3 parts of the cardiac cycle?
Atrial systole
Ventricular systole
Diastole
What happens during Atrial systole?
Both the right and left atria contract together
The wall of the atria is thin so only a small pressure is generated by contraction
This helps to push the blood into the ventricles which stretches their walls and ensures they are full of blood
What happens during ventricular systole?
Both the right and left ventricles contract together
Contractions start at the apex of the heart so the blood is pushed upwards towards the arteries
The walls of the ventricles are thick to generate a high pressure by contraction to push the blood around the body to the lungs
what happens during diastole?
The muscular walls of all 4 chambers relax
Elastic recoil causes the chambers to increase in volume which allows blood to flow into the heart from the veins
what is the purpose of valves in the heart?
It is to ensure that blood flows in the correct direction so back flow doesn’t happen
How are valves controlled in the heart?
By changes in pressure of the chambers
Describe how pressure causes the movement of the atrioventricular valve during diastole and atrial systole
The pressure in the ventricles rapidly drops below the pressure of the atria
The blood in the atria pushes the atrioventricular valves opens
Blood entering the heart flows through the atria into the ventricles
The pressure increases in the atria and the ventricles as they fill with blood
The valve remains open while the atria contact, but close when the atria begin to relax
This happens due to a swirling action in the blood around the valves when the ventricle is full
Describe how pressure causes the movement of the atrioventricular valve during ventricular systole?
As the ventricles begin to contract the pressure of the blood in the ventricles begins to rise
When the pressure rises above that in the atria, the blood starts to move upwards
This movement fills the valve pockets
Describe how the pressure in the heart causes the movement of the semilunar valves during diastole
Once the ventricles have contracted, the heart muscle relaxes(diastole)
Elastic tissue in the walls of the ventricles recoil and stretches the muscle out again and returns the ventricle to its original size
This causes the pressure in the ventricles to drop quickly, which causes blood in the arteries to flow back towards the ventricles
The semilunar valves are then pushed closed by the blood collecting in the valve pockets which prevents blood from returning to the heart
What causes the beat that we can hear?
The semi lunar valves as it closes
Draw the graph for the pressure changing in the heart
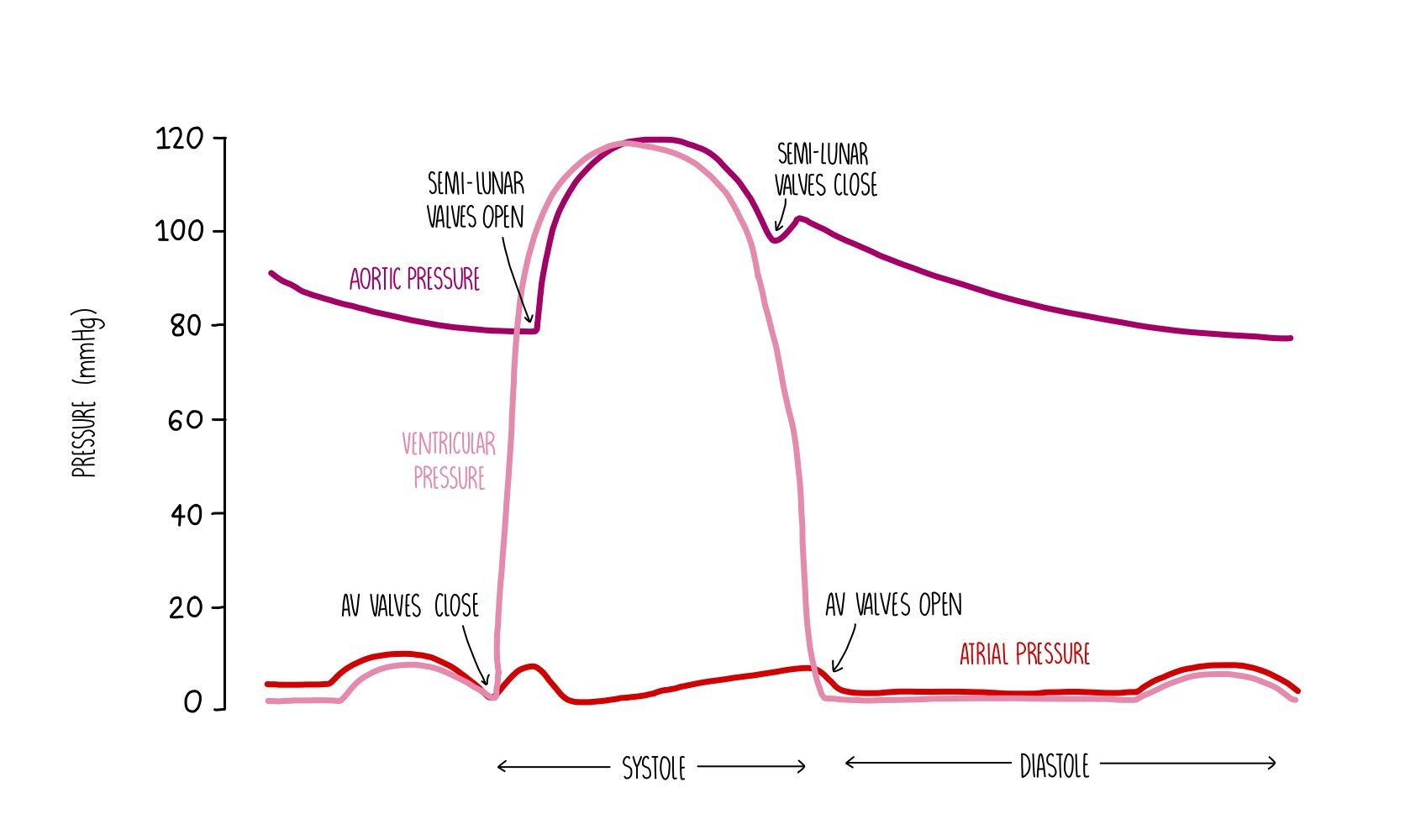
Describe how pressure changes across the blood vessels as it flows away from the heart
When blood leaves the heart, the elastic walls of the arteries stretch
As the blood moves along the aorta the pressure in the aorta begins to drop which is maintained by the elastic recoil of the walls
The further the blood goes along the arteries the more the pressure the drops due to the arteries getting wider and less friction being present