AP Chemistry Unit 6
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
The First law of Thermodynamics state (blank)
states can neither be created nor destroyed, it can only transfer or change forms.
Collisions between molecules will results in a transfer of their (blank), called (blank)
Kinetic energy
Heat Exchange
The more energetic particles will (blank) and the less energetic ones will (blank)
slow down
speed up
(blank); both samples will be at the same temperature, so their particles will have the same avg KE and net flow of heat will stop
Thermal equilibrium
In an (blank) process, heat is released from the system into the surroundings. The system gets (blank) and it’s surroundings get (blank)
Exothermic
cooler
warmer
In an (blank) process, heat is absorbed by the system from the surroundings; the system gets (blank) and the surroundings get (blank)
endothermic
warmer
cooler
Many Chemical reactions will absorb or release. called (blank)
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is associated with breaking or forming (blank) or (blank)
Chemical bonds or IMFs
Forming bonds or IMFs is (blank)
exothermic
Breaking bonds or IMFs is (blank)
endothermic
ΔH > 0
more energy is absorbed to break the bonds than released by forming bonds (endothermic)
The change or ΔH is the grand (blank)
total for all the bonds broken and formed in a reaction
ΔH < 0
If more energy is released by forming bonds than is absorbed to break bonds (exothermic)
You’ll feel warm near an (blank) reactions and cold near (blank) reactions
Exothermic
Endothermic
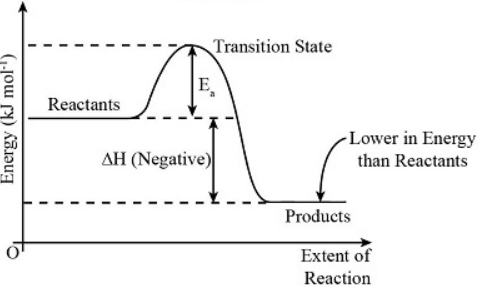
Exothermic Energy Profile
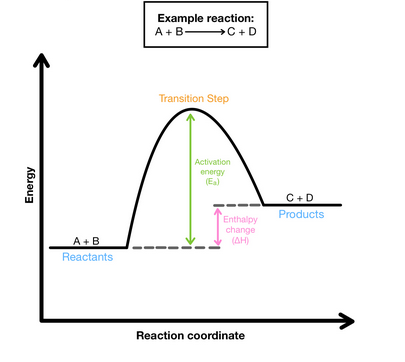
Endothermic Energy Diagram
A catalyst speeds up a reaction by providing the reactants with an (blank)
Alternate pathway
Enthalpy of formation is the (blank) in energy that takes plance when one mole of a compound is formed from its (blank) under standard state conditions
change
component pure elements
Enthalpy of formation equation
ΔH = ΔHproducts - ΔHreactants
Substances with (blank) are more stable than their elements
ΔH < 0
Combustion is always an (blank) process
exothermic
When a bond is formed, energy (blank) to the bond energy is released
equal
Bond energy equation
ΔH = Bonds Broken - Bonds formed
Hess’s Law Rules
if you flip the equation, flip the sign
if you multiply or divide, also do that for the enthalpy value
several equations when summed up make a new equation
Hydration energy is always (blank)
negative
Hydrogen bonding stretches out the IMFs make it a (blank)
Endothermic process
Ion-dipole forces form between seperated ions and water, making a (blank)
Exothermic Process
Phase changes change only the (blank)
Physical properties
A change in heat can change the (blank) or (blank) but not both
temperature
phase
Heat or enthalpy of transition is the (blank) associated with the changing phase of a compound
change in enthalpy
IMFs are strongest in the (blank)
solid phase
Enthanly of fusion is the energy that must (blank) to break those IMFs
absorbed (ΔH > 0)
Freeze is the (ΔH < 0)
The enthalpy of vaporization is the amount of heat associated with (blank)
vaporizing (ΔH > 0)
Condense (ΔH < 0)
Enthalpy of Subliminate is used to (blank) or (blank)
Solid to Gas (ΔH > 0)
Gas to Solid (ΔH < 0)
Enthalpy of fusion is the energy that is put into a solid to (blank)
Melt it
Enthalpy of vaporization is the energy that must be put into a liquid to (blank)
turn it into a gas
An Object with a larger specific heat can absorb a lot without (blank)
undergoing a large temperature change
Calorimetry Equation
q = mcΔT
Calorimetry experiments measure change in (blank) associated with some (blank)
temperature
chemical reaction
Solid to Liquid
Melting or fusion
Liquid to solid
Freezing
Liquid to gas
Vaporization
Gas to Liquid
Condensation
Solid to gas
Sublimation
Gas to solid
Deposition
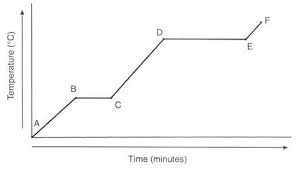
Label each one
A-B Solid
B-C melting
C-D liquid
D-E boiling
E-F Gas
A longer plateau means a larger (blank)
heat of transition
Substances with lower specific heats have (blank) since they require less heat to change their temperature
greater slopes
The intermolecular forces within a solid are more (blank) and therefore have (blank) than the forces within a liquid
stable
lower energy
When substance is changing phases, the temperature of that substance remains (blank)
constant