Hurricanes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is necessary for a Hurricane to form
Needs to be a goo mix of these factors
(1) Surface water greater than 27°C
(2) warm moist air
(3) weak upper level winds
(4) ~500km from equator so Coriolis Effect Happens
They form where there is warm surface water(in the open ocean where the water is that warm)
Moist air right above it
and weak winds in the upper level(that will not disrupt the rotation
There also needs to be far enough from the equator so the Coriolis effect happens
Low Pressure Zones
(2)Warm moist air
(3)Weak upper level winds.
Air flows upward and counter clockwise= Cyclone
Air is moving up, and picking up water from the ocean, and when it gets high enough and can’t hold the water is falls wound
In the northern hemisphere it is counter clockwise, so when the airs in pushing in it moves in a circles all the way up
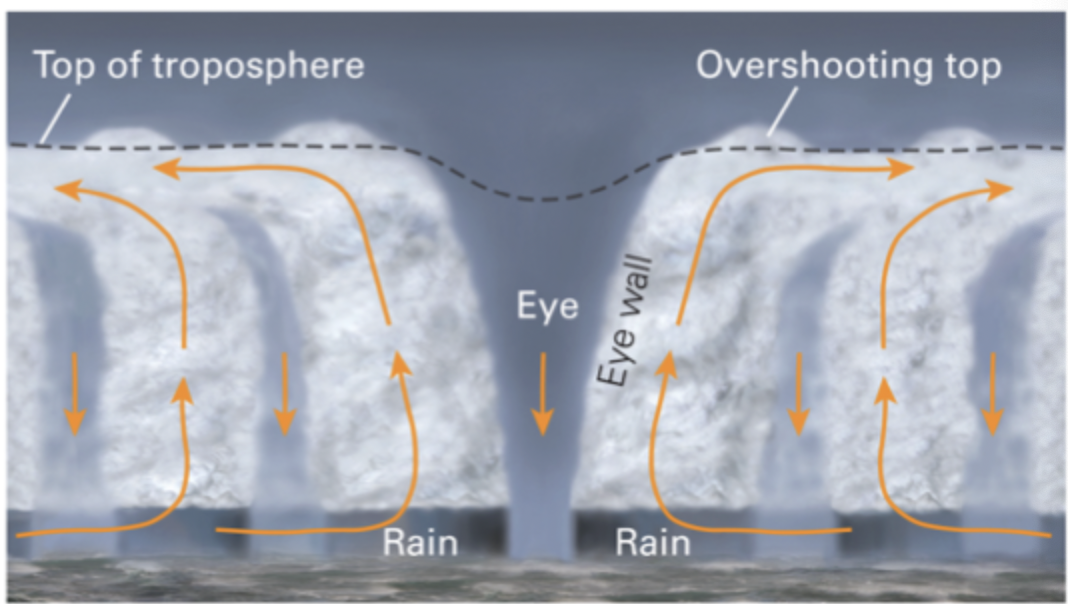
How a Hurricane Forms
winds flow into centre to updraft
once winds strengthen to 119km/h, they cant all reach the centere and the eye forms
the 119km/h is used to distinguished between a tropical storm and a hurricane
his to have moist air and weak winds in the upper levels
Areas with really strong updraft, some of the air overshoots the top and there are a bumps, there is sometimes chaotic movement
In the eye itself there is air sinking down, because there strongest updrafts surround it
What is a Hurricane Composed of?
Hurricane is a low pressure system but not every low pressure system is a hurricane
But the winds have to be a certain winds strength/speed
In the eye of a hurricane is very unsafe, and their may be blue skies above you
They are rings of thunderstorms within this system which is already rolling
Positive Feedback Mechanisms
storms create conditions that provide them with more energy
Positive Feedback #1:
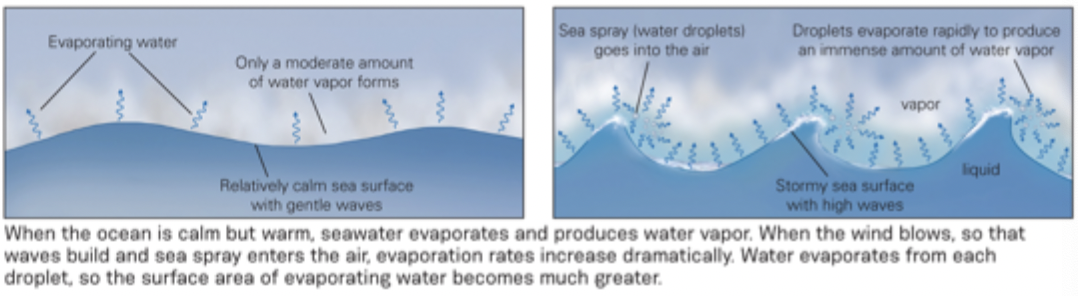
Sea Spray From wind increased evaporation by 100 -1 000 times. Increased evaporation creates more rising vapour molecules
Positive Feedback #2:
Updrafts carry vapour molecules into dry, upper troposphere
evaporation, and latent heat release, occurs in upper troposphere
When you have sea spray you push molecules back into the atmosphere
When the updrafts carry water in the atmosphere is cools down into rain( and this process releases heat
And to turn water into vapour it takes energy and when it turns back into liquid it releases that heat(energy) and that is a lot of energy and it revived the system, because it turns more water into gas
How Much Energy is Within a Hurricane?
The energy of the wind is half the global capacity, and the energy from a condensation is 200 times greater
Warm water bellow and warm air, and all of it gets warmer
To run our of steam land is often involved
Hurricane vs rain energy
energy released by cloud rain formation is 400x greater that energy of hurricane winds
Hurricane Geography
Coriolis Effect 500km from equator
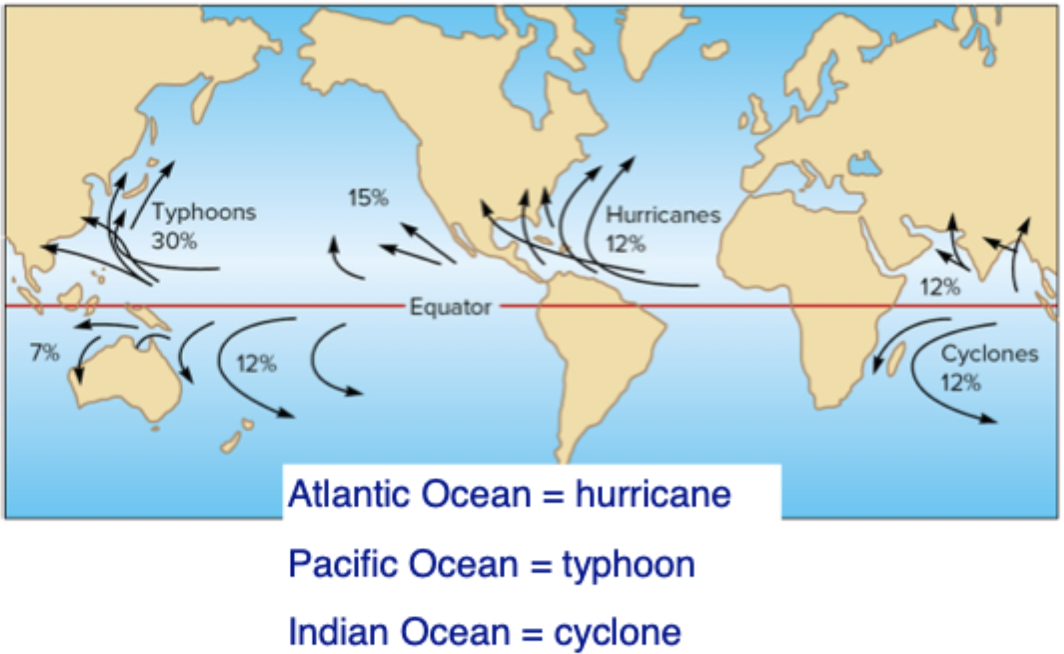
All of these storms are tropical cyclones
Depending on the ocean these storms have different names(why?historical and geographic reasons)
Image: The percentages of how many storms we get in these different places
The storms tracking show kind of move in a c pattern in Hurricanes, as well as an exclusion of polar regions
What are Streamlines
surface winds
How many North Atlantic Hurricanes Annually
How many hurricane we get varies
Through time
El Niño conditions: long term oscillating conditions; as effects that knock on another places; when they are present there are cooler sea surfaces in the tropical Atlantic, so there are fewer hurricanes;
El Niña conditions: El Niño is absent, there is lots of moisture, and warm surface water, so there is more frequent and stronger hurricanes
Iceland low= lots of rain,
The Bermuda high= lots of a c shape pattern of the winds
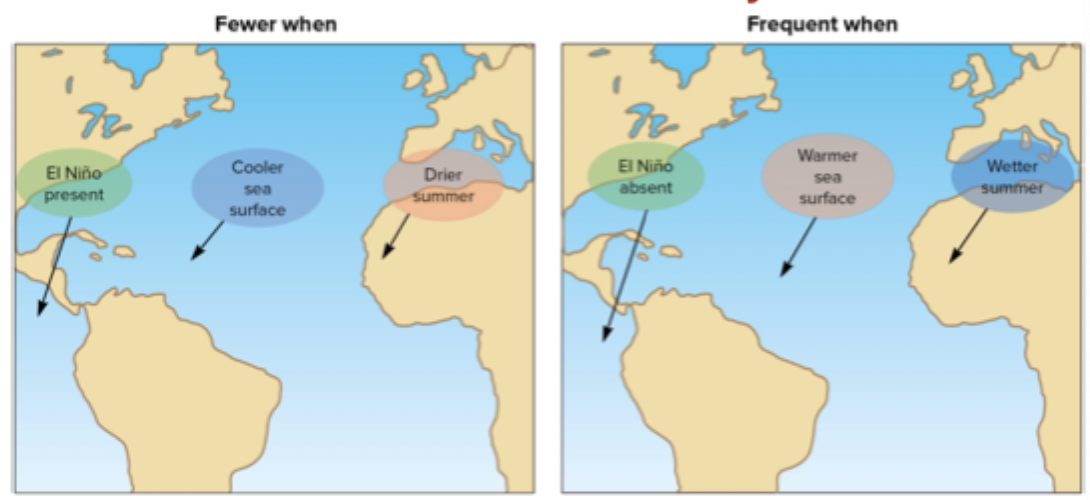
El Niña conditions
El Niño is absent, there is lots of moisture, and warm surface water, so there is more frequent and stronger hurricanes
El Niño conditions:
long term oscillating conditions; as effects that knock on another places; when they are present there are cooler sea surfaces in the tropical Atlantic, so there are fewer hurricanes;
Atlanti c Multidecadal Variability
Natural cycles in Atlantic temperatures influence frequency of hurricanes
There is variability to strength and frequency
There is a clear pattern in frequency oscillation climate change if it is affecting the frequency
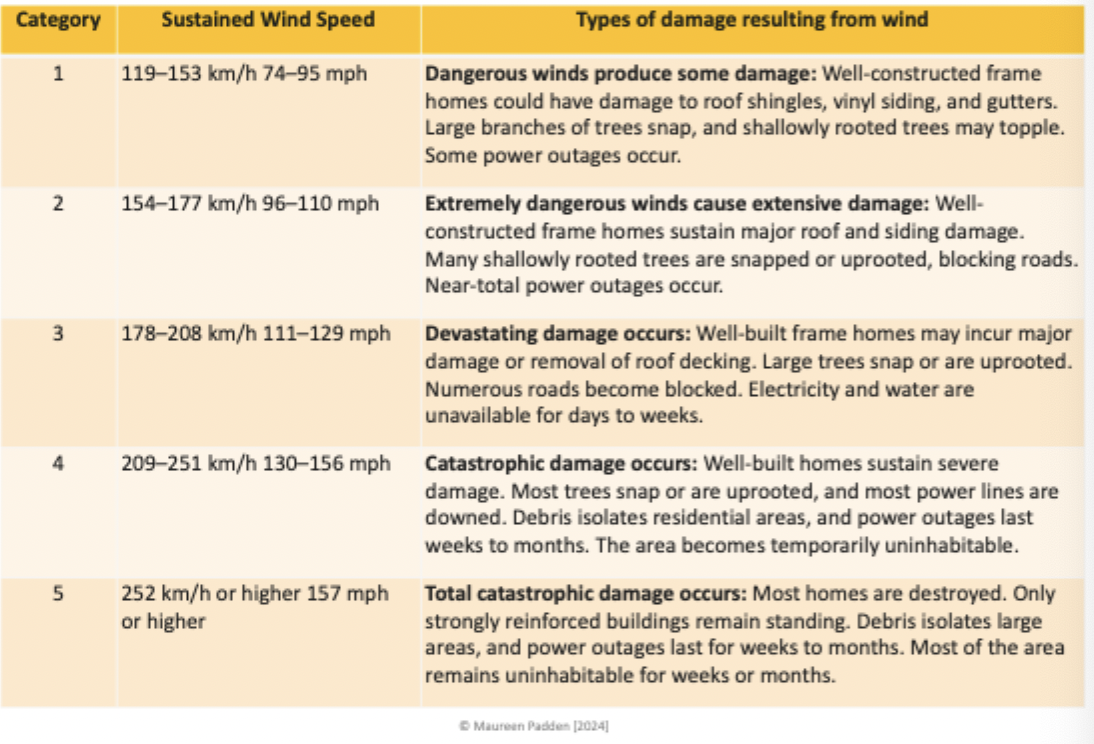
The Saffir Simpson Scale for Hurricane intensity
Intensity is a lot clearer
This one is based on wind speed
All of these are bad because winds have to all ready be 119km/h to be considered a hurricane
Winds is dangerous, but you also have to check on the water level(water gets pushed by the strong winds, and is another factor that makes hurricanes very. Dangerous
Not of the communities that are hit by hurricanes are costal, so getting to the basement is not a choice and ground level is also not safe
Best Choices to make when trapped in a Hurricane
Easiest way to survive a hurricane is to get out of the way, we can usually water them coming for us for days and weeks, so there should be well notice for you to get out of the area
If you have to stay mobile homes are very dangerous, you want a very strong house that is secured to the ground
Electricity may go out, so you want to have your own backups
If you are outside, get inside
Avoid bridges and over passed
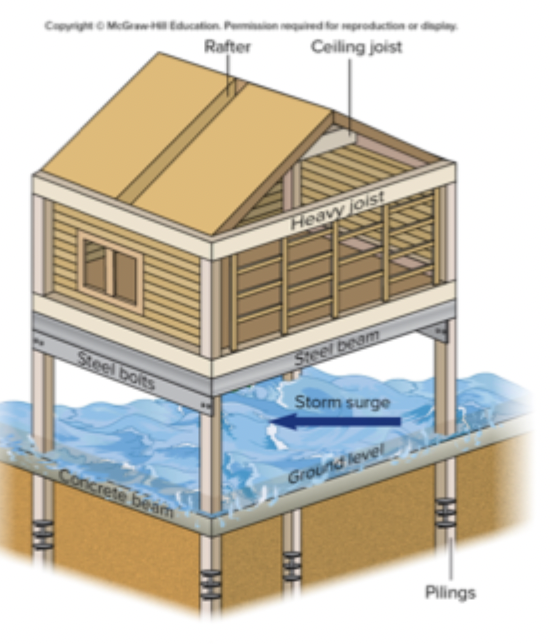
How to Build a Coastline Home
piling are driven into the ground
water can wash away from of the ground below the house without the entire house being washed away
The People Factor
Even after we put safety measures in place people are a big determinant is the actual safety, because it is their choice to do it or not
People will do things if you warn them, but nobody did everything on the list, most did something that involved shopping, but it is important to left them know with is more important on the list
Sometimes prep was in place but people still didn't o them i.e., storm shudders
Flooding is most dangerous in Hurricanes
Hurricane Sandy Statistics for after the Hurricane Warning…
90% made some preparations (extra water, gas in cars)
50% of people who owned storm shutters put them up
20% of people under evacuation orders planned to go
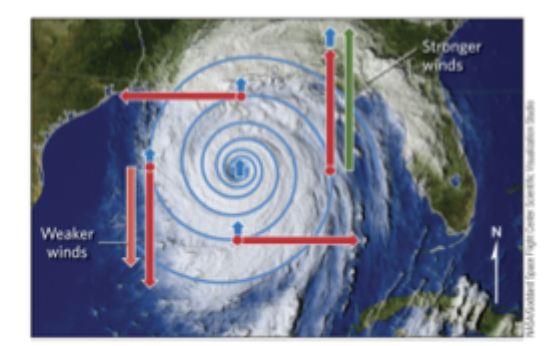
A Hurricanes Differing Wind Speeds
greater wind speeds are on the side of the storm where: rotation is same direction as forward motion
lesser wind speeds are on the side of the storm where: rotation is in opposite direction as forward motion
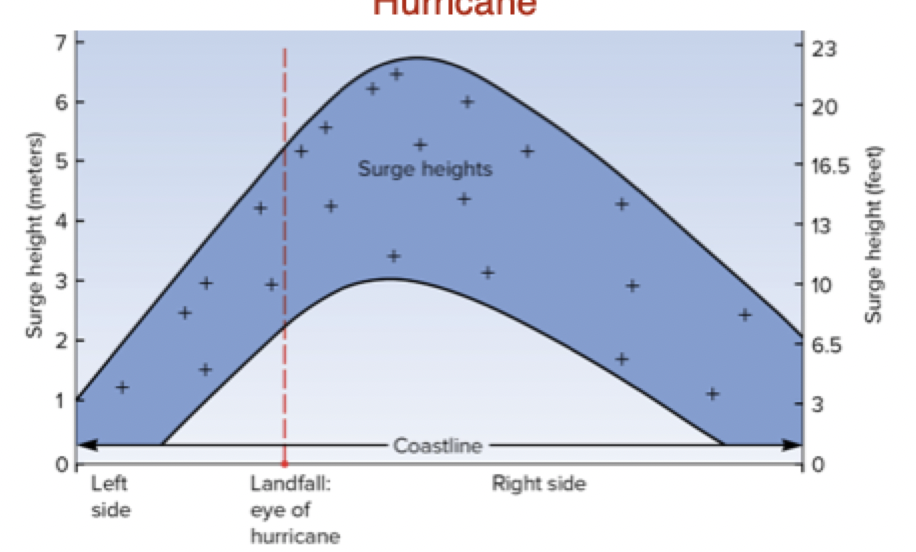
in the Northern hemisphere, highest winds speeds and largest storm surges observed in the N or NE quadrant
Storm Surge location relative to eye of Hurricane
highes to the right os t the eye as it hits lan becasye wind speed hughest
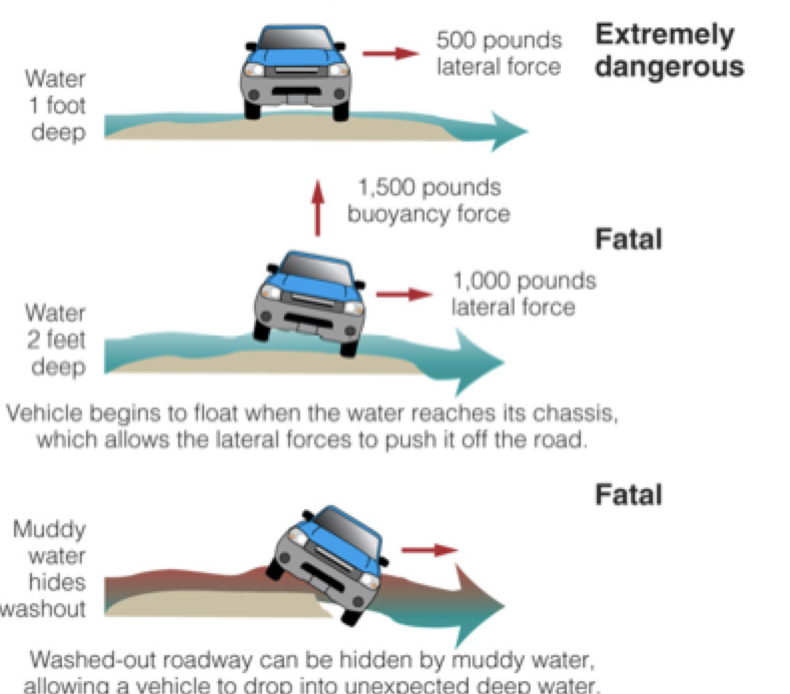
Driving through Flood Waters
Risk factor is flood water, do not drive through them
It doesn't take a lot of water (2 ft deep) to make the car float, cause you lose all control of the car
There is also a huge amount of lateral force
Case Study: Hurricane Katrina
Mississippi river coming in an a bunch a fragment water coming in sediments come doesn't the river, and hits the gulf of Mexico, and deposits their, and over time it builds up, but it is a deposit of watery sediment, and is still an active system, you need sediment to keep coming cause it will continually compact and push down, but putting buildings affects that so there has to be things put in place to keep it above water
The gulf of Mexico has sat water
With everything covered in water it is hard to do anything, so the first thing that had to do was dropping sandbag after sandbag t dry things up
Many people didn't know how of get out of town
Not good communication between responders,
Lot of people left with more transport
Deaths and Loses
1836 confirmed deaths due to hurricane Katrina, more than 1 million displaced, 39% of those who died were older than 75 years
Case Study: Hurricane Maria (2017)
Maria struck Dominica as a category 5 hurricane
No electricity, clean water, or communications, 31 people died
Tourism- based economy, lay in ruins
Dominica’s Slow recovery Widespread poverty Inaccessibility
Category five and stayed that way when it hit these places, and often parked during the hit, not a huge population, by the time the hurricane left there was not communication, not clean water, and co communication.
Case Study: Hurricane Maria (2017)
Puerto Rico, got hit it was category 4, no clean water and no coms after the hit, their was also a heat wave right after which cause even more issues and casualties; federal response was very sloe, fully a year after power was still not restored
nearly 3000 people died
Toursim based economy lays in ruins
Many schools close and the economy took a big hit
Lots of bitterness to the slow response to the disaster by the US
Indian Ocean and Southern Hemisphere Cyclones
Ganges River delta and Bay of Bengal are high-risk areas
Cyclones Bhola (1970) killed over 600 000 people
Cyclones in later years killed hundreds of thousands
Millions at risk because of poor logistics
Once we have them we will have them again, their is more notice than other disasters, (almost to the hour accuracy), because they form n the ocean then are on the move
the cyclones in the Indian ocean and northern hemisphere bend right
In the bay of a Bengal all those populations are huge and live pretty in level with sea level