Models of memory
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
memory model definition
a representation of how memory would work in the brain. A conceptual framework to understand it.
Multistore model of memory diagram
senses —> sensory register —> STM <—> LTM
each component stores,encodes and processes information in a different way but they operate simultaneously + interact
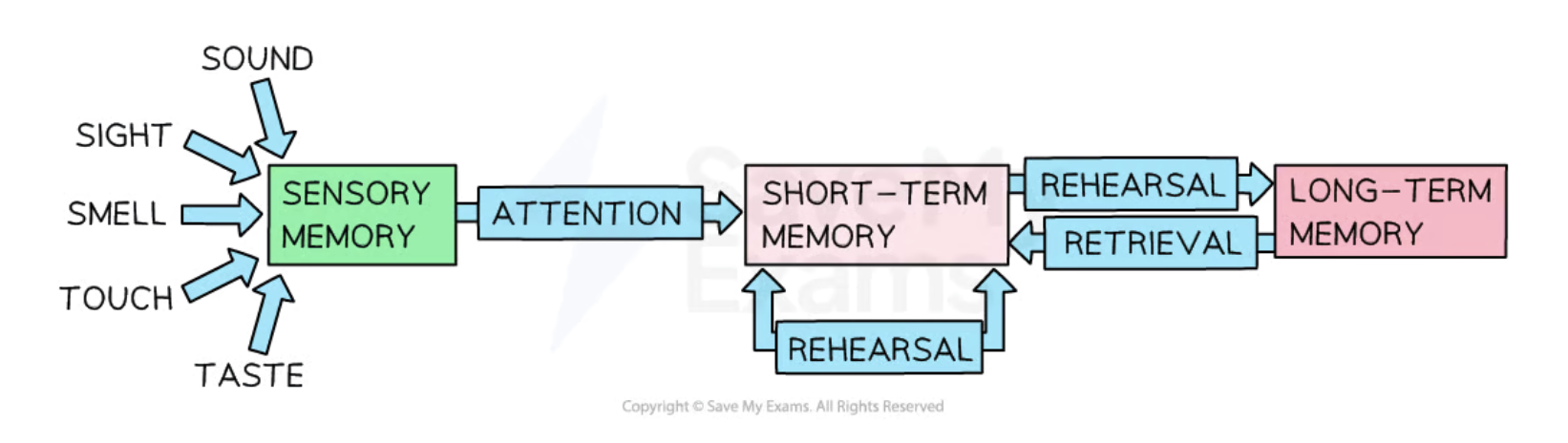
sensory register capacity,duration + encoding
capacity - very large/almost unlimited
duration - 0.3-4s → 0.5s
encoding - echoic + iconic
Short term memory capacity,duration + encoding
capacity - 5-9 items
duration - 18-30s
encoding - acoustic
Long term memory capacity,duration + encoding
capacity - unlimited
duration - lifetime (ranges from hours to life time)
encoding - semantic
encoding definition
the form information takes when it is stored in the brain
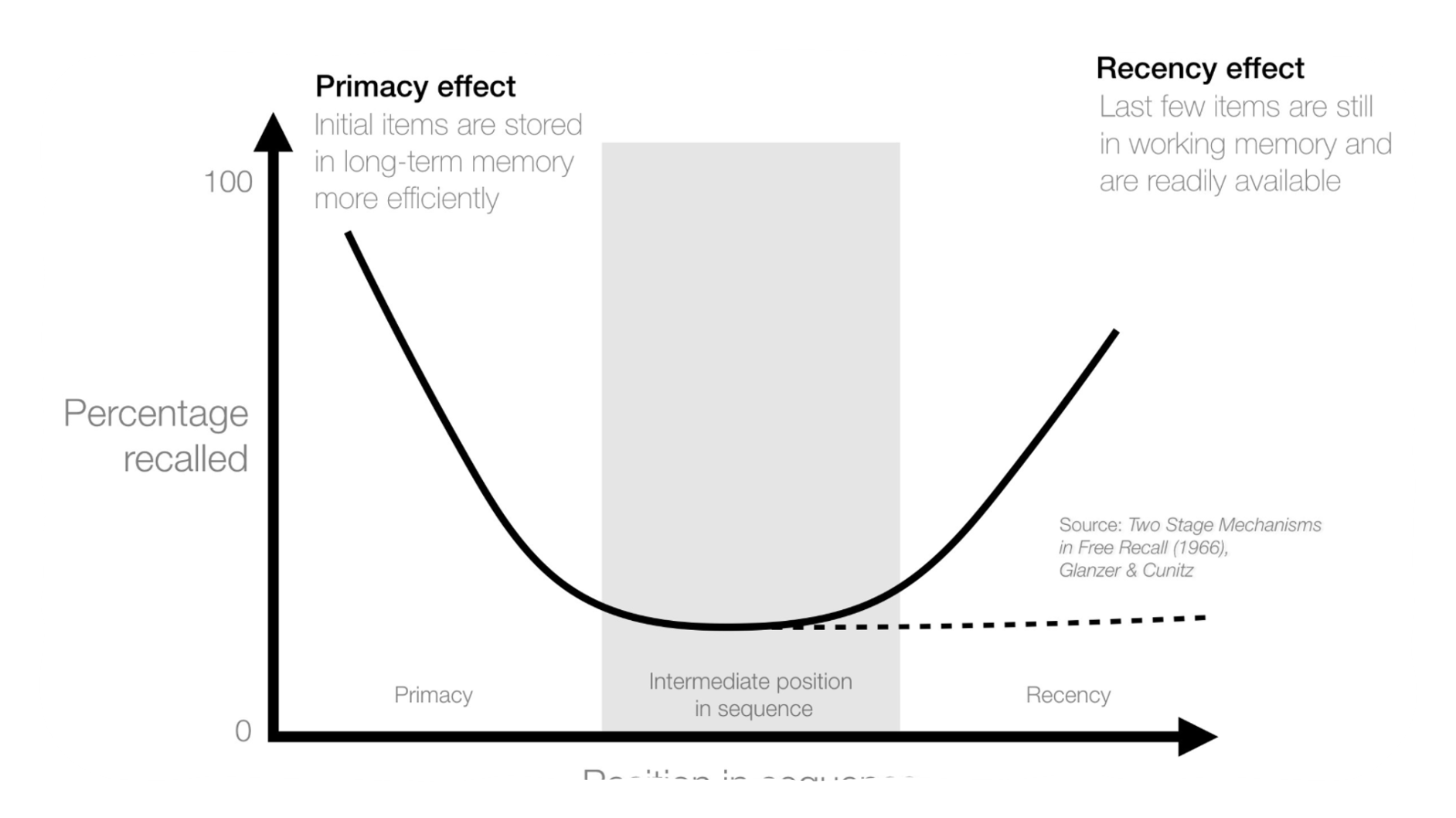
serial position effect
the effect an item’s position on a list has on how well it is recalled.
primacy effect : items at the start of the list are remembered well as they are rehearsed the most
recency effect : items at the end of a list are remembered well as they are still in the STM
why do we forget
decay - if we don’t rehearse/retrieve memories for a long time they will be lost
displacement : STM has a limited capacity and so when new information comes in some is forgotten if not rehearsed
interference : we forget because memories interfere with and disrupt one another.
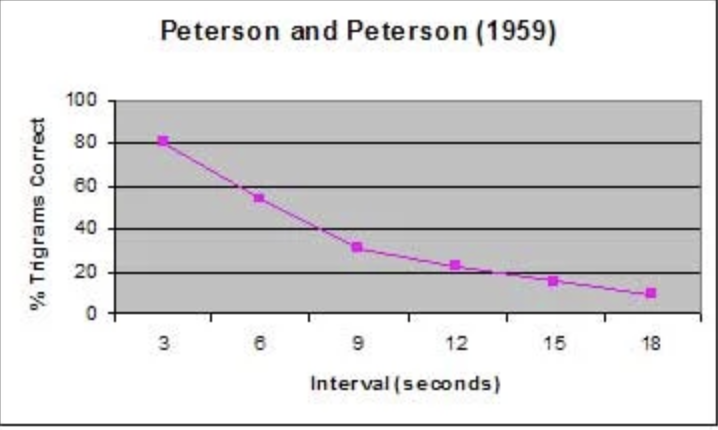
Peterson and Peterson Aim
to investigate the duration of short term memory
Peterson and Peterson procedure
24pp (psychology students)
lab experiment
pp were shown trigrams one at a time
after pp were shown trigram they had to count backwards in 3’s or 4’s from a specified random digit until they were shown a red light
trigrams then had to be recalled after intervals of 3,6,9,12,15 and 18 seconds
IV + DV of Peterson + peterson
IV- time interval when pp were counting (preventing rehersal)
DV - number of correct trigrams recalled
Peterson + Peterson findings
longer each pp had to count backwards the less accurately they were able to recall the trigrams
3s - 80% correctly
6s - 50%
18s - less than 10%
STM has a short duration of 18s
types of long-term memory
implicit memory → procedural/ classically conditioned memory
explicit memory → semantic/episodic memory
implicit memory
does not require conscious awareness
procedural memory : motor skills + actions
classically conditioned memory : reflexive responses learnt through association of two stimuli (UCS and CS).
explicit memory
memories we have conscious awareness of (we actively retrieve + think of them)
episodic - memories we personally experience
semantic - memory of facts and figures and general knowledge
Measurement - evaluating Multi store model
Strength : supported by controlled lab experiments with standardised procedures to measure memory which allow for replication + reliability
Limitations :
the tasks used often lack ecological validity → may not reflect how memory works in real life settings
Measuring the duration and capacity of memory stores may oversimplify a complex and interactive cognitive process.
Working memory model
more developed version of MSM
short-term memory is renamed to working memory
WMM distinguishes between different short term memory stores
central executive (CE)
controls slave systems by determining how resources will be allocated
information comes from LTM or sensory memory
very limited capacity (about 4 chunks of info which are stored in the episodic buffer)
allows us to switch attention between different inputs of information.
Phonological loop (PL)
2 parts - Articulatory control system, Phonological store
Limited capacity of 2 seconds worth what you can say out loud.
Phonological loop - (inner ear) → holds the sound/words you hear
articulatory control system - (inner voice) → words maintained by repetition that are heard or seen.
Visuospatial sketchpad (VSS)
temporary storage + manipulation of visual and spatial information.
VSS is important for tasks involving visual imagery, spatial reasoning and navigation.
Episodic Buffer (EB)
temporary store of information
links working memory to LTM
limited capacity of 4 chunks
maintains a time sequence of info
Strengths of WMM
brain scans show that different parts of the brain are active during verbal vs visual tasks → different parts of memory for visual + verbal tasks
model explains the execution of everyday tasks such as reading using the PL and navigating using the VSS
Weaknesses of WMM
model is complex → only one component of WMM can be tested at a time
does not explain memory distortion or the role of emotions in formation of memories
reductionist → looks only at STM and does not factor in SR and LTM.
Cognitive load theory
an educational theory that explains how the brain processes information during learning
focuses on the limitations of working memory.
what does the cognitive load theory suggest
working memory has a limited capacity + duration
Long term memory has an unlimited capacity
learning involves transferring info from working memory to LTM
learning is hindered if too much info is presented at once → cognitive load
types of cognitive load
intrinsic load
extraneous load
germane load
intrinsic load
The complexity of the material itself.
Intrinsic load can't be eliminated but can be managed by breaking material into smaller steps.
Extraneous load
The way info is presented; unnecessary effort caused by poor instructional design.
Extraneous load should be minimized by presenting info clearly and in an integrated way.
Germane load
The effort involved in processing, constructing, and automating schemas.
Germane load is desirable—it's the "good" load that supports deep learning.