AP World History Unit 3 AMSCO Vocab
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Ming Dynasty
Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China.
Manchu
Federation of Northeast Asian peoples who founded the Qing Empire.
Qing dynasty
(1644-1911 CE), the last imperial dynasty of China which was overthrown by revolutionaries; was ruled by the Manchu people: began to isolate themselves from Western culture,
Kangxi
Qing emperor (r. 1662-1722). He oversaw the greatest expansion of the Qing Empire.
Emperor Qianlong
Emperor who reigned from 1736-1795. He was approached by Lord Macartney about liberalizing the trade restrictions; turned down the offer claiming that Europe had nothing to offer China.
Gutenberg Printing Press
a. Used to spread ideas of the Reformation and the Renaissance
b. First documented printed was the Bible
c. Led to the growth of literacy
Gunpowder Empires
Muslim empires of the Ottomans, Safavids, and the Mughals that employed cannonry and gunpowder to advance their military causes.
Ottoman Empire
A Muslim empire based in Turkey that lasted from the 1300's to 1922.
Safavid Empire
Iranian kingdom (1502-1722) established by Ismail Safavi, who declared Iran a Shi'ite state.
Mughal Empire
Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
Ghazi ideal
a model for warrior life that blended the cooperative values of nomadic culture with the willingness to serve as a holy fighter for Islam
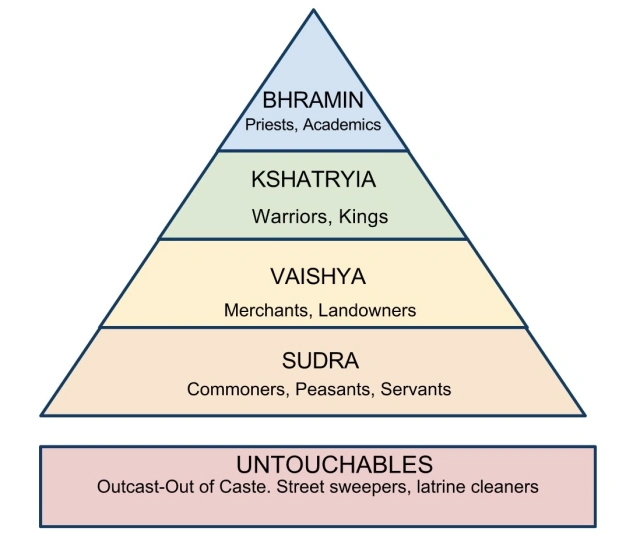
Castes
social hierarchy in hinduism which people are born and cannot change
Ivan IV of Russia
(1533-1584), known as "Ivan the Terrible", accelerated the rise of the service nobility, first to call himself tsar, crowned himself, abolished distinction between hereditary boyar property and land given temporarily for service, made service nobility entirely dependent on autocrat
Tamerlane
He is very much like Ghengis Khan; a military leader who conquered the lands of Persia; his empire was decentralized with tribal leaders.
Suleiman I
The leader of the Ottoman Turk Empire during the high Renaissance.
Ismail I
this man was a ruthless leader of the Safavid Empire who executed all Sunni Muslims in his empire
Shah Abbas I
Shah of Iran (r. 1587-1629). The most illustrious ruler of the Safavid Empire, he moved the imperial capital to Isfahan in 1598, where he erected many palaces, mosques, and public buildings. (p. 533)
Akbar
Most illustrious sultan of the Mughal Empire in India (r. 1556-1605). He expanded the empire and pursued a policy of conciliation with Hindus.
Divine Right of Kings
Doctrine that states that the right of ruling comes from God and not people's consent
English Bill of Rights
King William and Queen Mary accepted this document in 1689. It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.
absolute ruler
one who has total power
Cardinal Richelieu
(1585-1642) Minister to Louis XIII. His three point plan (1. Break the power of the nobility, 2. Humble the House of Austria, 3. Control the Protestants) helped to send France on the road to absolute monarchy.
Intendants
French government agents who collected taxes and administered justice.
Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
Ivan IV
the Terrible, beat the Mongols, Tartars, and the Poles, forced nobles into service, first ruler to take the title tsar
Romanov Dynasty
Dynasty elected in 1613 at end of Time of Troubles; ruled Russia until 1917
Peter I
Also known as Peter the Great; son of Alexis Romanov; ruled from 1689 to 1725; continued growth of absolutism and conquest; included more definite interest in changing selected aspects of economy and culture through imitation of western European models.
devshirme
'Selection' in Turkish. The system by which boys from Christian communities were taken by the Ottoman state to serve as Janissaries.
Janissaries
Infantry, originally of slave origin, armed with firearms and constituting the elite of the Ottoman army from the fifteenth century until the corps was abolished in 1826.
Daimyo
A Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai
Edo
Tokugawa capital city; modern-day Tokyo; center of the Tokugawa shogunate.
Tokugawa Ieyasu
Vassal of Toyotomi Hideyoshi; succeeded him as most powerful military figure in Japan; granted title of shogun in 1603 and established Tokugawa Shogunate; established political unity in Japan.
Period of Great Peace
Change in Samurai role; period of time in Japan in which everything was stable and peaceful
Tokugawa Shogunate
was a semi-feudal government of Japan in which one of the shoguns unified the country under his family's rule. They moved the capital to Edo, which now is called Tokyo. This family ruled from Edo 1868, when it was abolished during the Meiji Restoration.
Askia the Great
Songhai ruler, he overthrew Sunni Baru. His reign was the high point of Songhai culture.
Tax Farmers
Indirect taxes farmed out to highest bidder. Charged more than required to collect as commission. Led to very ineffecient and corrupt system. Furthermore, only peasants and lower MC ended up paying taxes becos. nobs. tax exempt. Deal with Kings - raise taxes without consent of nobs as long as nobs. not taxed. Unfair tax burden on peasants.
Tax farming
To generate money for territorial expansion rulers used new methods to get money like Tribute systems and . Under this system the government hires private individuals to go out and collect taxes for them.
tribute system
A system in which defeated peoples were forced to pay a tax in the form of goods and labor. This forced transfer of food, cloth, and other goods subsidized the development of large cities. An important component of the Aztec and Inca economies.
Zamindars
Archaic tax system of the Mughal empire where decentralized lords collected tribute for the emperor.
Taj Mahal
beautiful mausoleum at Agra built by the Mogul emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his favorite wife
Versailles
A palace built by Louis XIV outside of Paris; it was home to Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette
Boyars
Russian nobles
Serfdom
A type of labor commonly used in feudal systems in which the laborers work the land in return for protection but they are bound to the land and are not allowed to leave or to peruse their a new occupation. This was common in early Medeival Europe as well as in Russia until the mid 19th century.
Henry VIII
(1491-1547) King of England from 1509 to 1547; his desire to annul his marriage led to a conflict with the pope, England's break with the Roman Catholic Church, and its embrace of Protestantism. Henry established the Church of England in 1532.
Charles V
Holy Roman Emperor and Carlos I of Spain, tried to keep Europe religiously united, inherited Spain, the Netherlands, Southern Italy, Austria, and much of the Holy Roman Emperor from his grandparents, he sought to stop Protestantism and increase the power of Catholicism. He allied with the pope to stamp out heresy and maintain religous unity in Europe. He was preocuppied with struggles with Turkey and France and could not soley focus on the rise of Protestantism in Germany.
Philip II
(1527-1598) King of Spain from 1556 to 1598. Absolute monarch who helped lead the Counter Reformation by persecuting Protestants in his holdings. Also sent the Spanish Armada against England.
Spanish Armada
The great fleet sent from Spain against England by Philip II in 1588; defeated by the terrible winds and fire ships.
Peace of Augsburg
1555 agreement declaring that the religion of each German state would be decided by its ruler
Edict of Nantes
1598 - Granted the Huguenots liberty of conscience and worship.
Thirty Years War
Protestant rebellion against the Holy Roman Empire ends with peace of westpahlia.1618-48) A series of European wars that were partially a Catholic-Protestant religious conflict. It was primarily a batlte between France and their rivals the Hapsburg's, rulers of the Holy Roman Empire.
Peace of Westphalia
the peace treaty that ended the Thirty Years' War in 1648
indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church. It was common practice when the church needed to raise money. The practice led to the Reformation.
Holy Synod
The replacement Peter the Great created for the office of Patriarch of the Russian Orthodox Church. It was a "bureaucracy of laymen under his supervision."
Counter Reformation
the reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Reformation reaffirming the veneration of saints and the authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected)
Inquisition
A Roman Catholic tribunal for investigating and prosecuting charges of heresy - especially the one active in Spain during the 1400s.
Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism.
Council of Trent
Called by Pope Paul III to reform the church and secure reconciliation with the Protestants. Lutherans and Calvinists did not attend.
Martin Luther
95 Thesis, posted in 1517, led to religious reform in Germany, denied papal power and absolutist rule. Claimed there were only 2 sacraments: baptism and communion.
95 Theses
It was nailed to a church door in Wittenberg, Germany in 1517 and is widely seen as being the catalyst that started the Protestant Reformation. It contained Luther's list of accusations against the Roman Catholic Church.
John Calvin
1509-1564. French theologian. Developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism. Attracted Protestant followers with his teachings.
Predestination
Calvin's religious theory that God has already planned out a person's life.
Protestant Reformation
A religious movement of the 16th century that began as an attempt to reform the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the creation of Protestant churches.
Shari'ah
Islamic law
Sikhism
the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam
Empiricism
the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation