Cardiovascular
1/252
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 1 - Normal Animal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
253 Terms
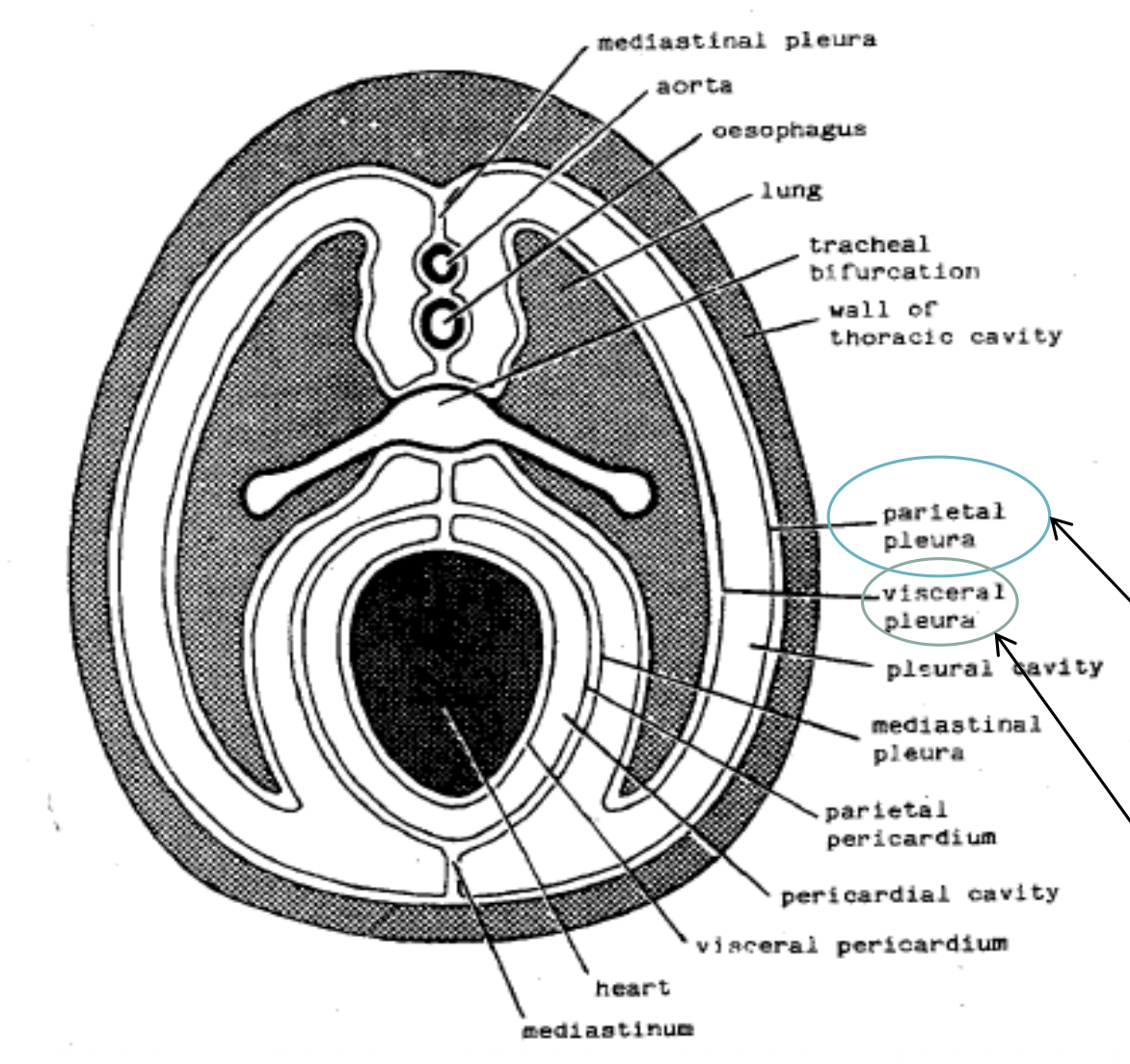
pleura
a serous membrane lining the thorax consisting of the visceral and parietal
differences with pig lungs
less obvious divisions between lobes, surface appears marbled due to connective tissue divisions visible between lobules
costochondral junction
junction between cartilage and rib bone in ribcage
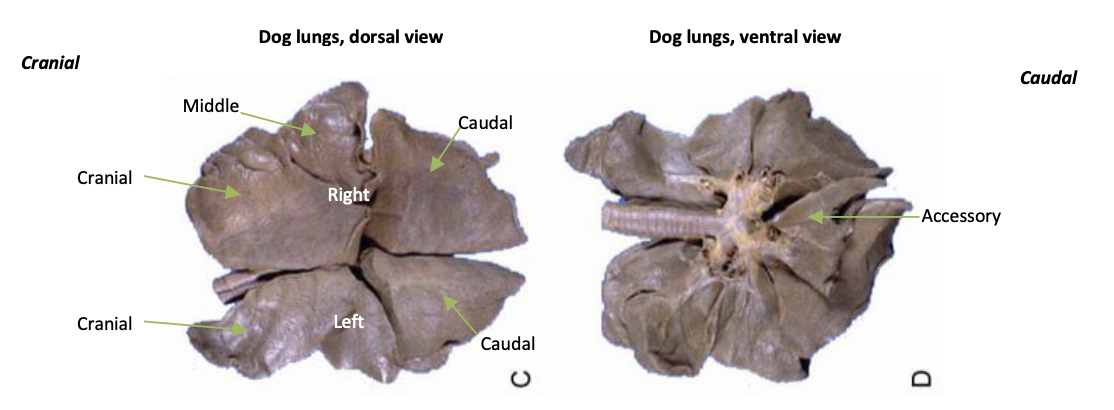
lobes of left lung
cranial and caudal
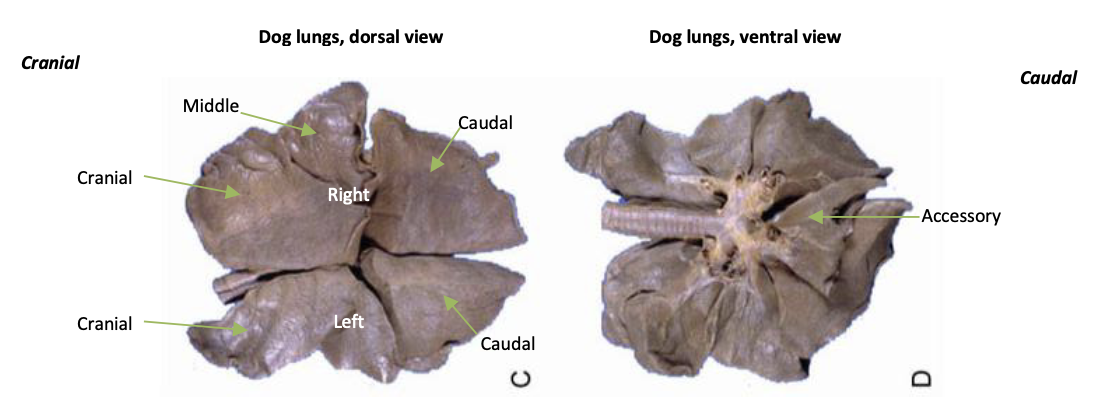
lobes of right lung
cranial, middle, caudal, accessory
pleura contained within parietal pleura
mediastinal, costal and diaphragmatic
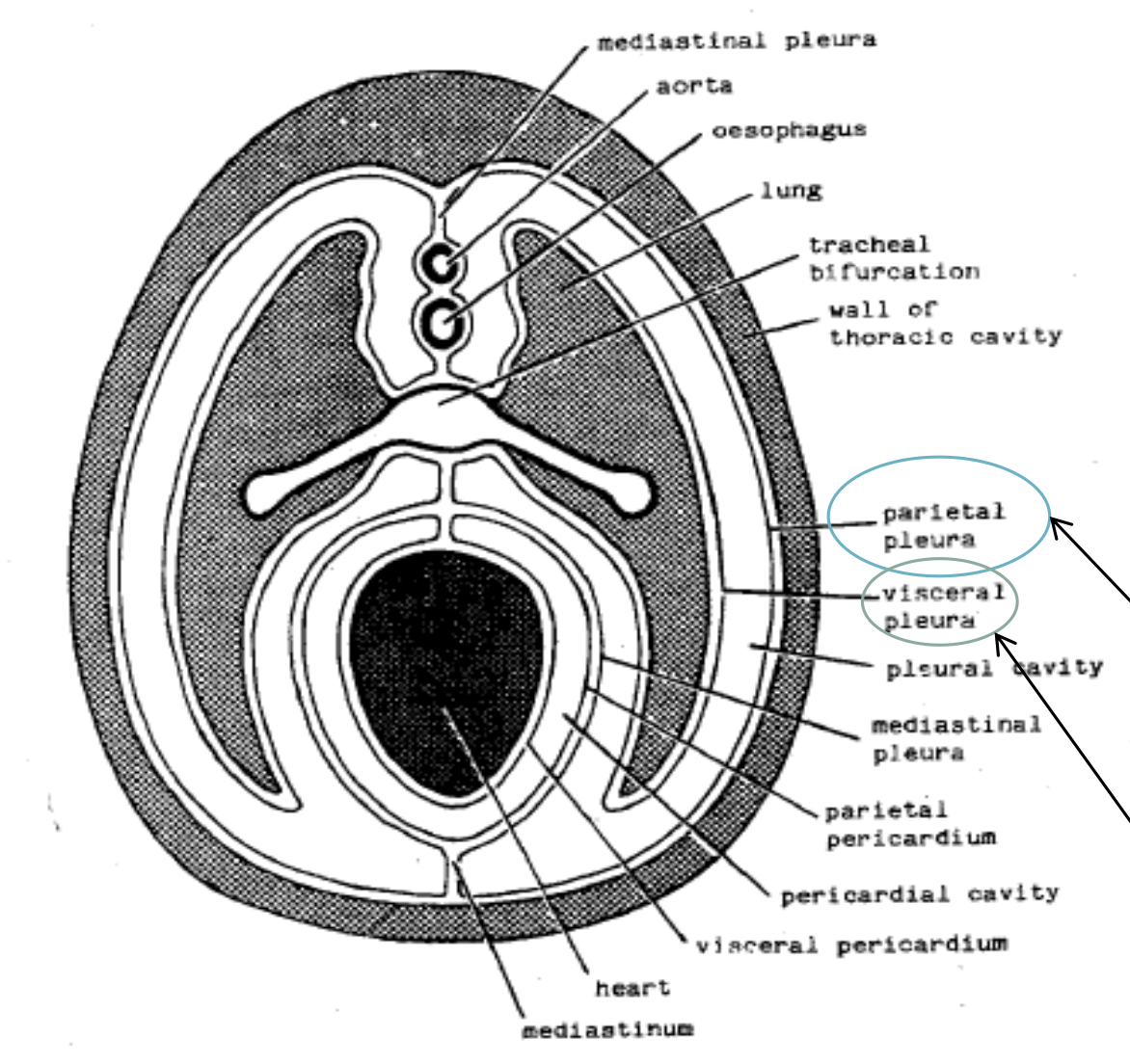
pleural cavity
the potential space between the two layers of the pleura which contains a small amount of serous fluid
function of pleural cavity
to reduce friction and help maintain negative pressure which allows the lungs to move smoothly within the chest cavity
pericardium
an invaginated sac of serous membrane containing the heart
layers of the heart wall
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium
pericardial cavity
the potential space between the two layers of the serous pericardium that encloses the heart, if fluid builds up here it restricts contraction of the heart
interatrial septum
tissue that separates the left and right atria
interventricular septum
tissue that separates the left and right ventricles
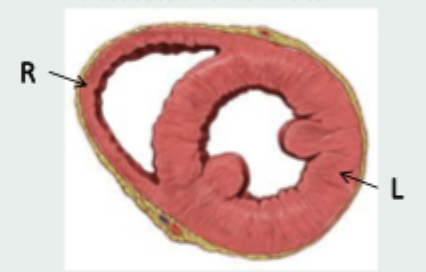
features of ventricles
left is more thick and muscular as it pumps blood around the body via the aorta, right is thinner and wraps around left and pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery
heart murmur
irregular heart sound generated by turbulence in the blood caused by anything which disturbs blood flow
auscultation of the heart
listening to the heart
annulus fibrosis
a fibrous skeleton which supports all 4 valves in the heart and also serves as an electrical insulation between atria and ventricles
features of atrioventricular valves
constructed of flaps/cusps (3 in right 2 in left) which open and close, their free edges are attached by strands of fibrous tissue (chordae tendinae) to papillary muscles in the ventricle
features of semilunar valves
each made up of 3 semilunar shaped cusps which meet tightly in the middle due to thickening of the contact areas, attached to the annulus fibrosis in artery walls
regurgitation
blood flowing in the wrong direction which can lead to congestion and heart failure
stenotic valves
valves that have become narrowed
precapillary sphincter zone
smooth muscle contained within the walls of the precapillary arterioles which regulate the blood flow into the capillary bed
arterioles
thinner branches of arteries which contain a thinner layer of smooth muscle
precapillary arterioles
further branched arterioles which have intermittent smooth muscle cells and no elastic layer, they end in capillary beds
collateral circulation
side branches of arteries which act as a safety net in case of a blockage of the main trunk as they are able to travel around it
elastic arteries
arteries mostly found near the heart which are able to withstand the high pressure output from the heart due to the high proportion of elastic tissue in their walls
anastomosis
a connection joining 2 blood vessels
retia
networks of interconnecting arteries that help to cool blood before it reaches the brain
end arteries
arteries that only have one route to a particular tissue
ischaemia
lack of blood flow to an area in the body caused by a blockage or narrowing of blood vessels
sinusoid
a modification of the capillary which has very thin walled tubular channels with relatively large diameter, found in several tissues, gaps between lining cells which allow free communication between blood plasma and surrounding tissues and movement of cells, blood moves through slowly, wider and more permeable than capillaries
muscular arteries
arteries that contain some elastic tissue and a large amount of smooth muscle, found further from the heart than elastic arteries
post-capillary venules
small blood vessels formed from capillaries with thin walls composed of a single layer of endothelium and a basement membrane, which allows for the passage of plasma proteins and white blood cells from the bloodstream into surrounding tissues
diapedesis
process by which white blood cells move out of the circulation and into tissues to fight infections
features of arteries
thick smooth muscle layer to withstand high blood pressure, narrow lumen to help maintain high pressure, elastic tissue which allows them to stretch and recoil, which helps to smooth out blood flow and maintain pressure between heartbeats, referred to as pressure reservoir
features of veins
thinner walls and wider lumen to reduce friction, valves to prevent backflow of blood, referred to as volume reservoir
thoroughfare channels/ met arterioles/ ateriovenous capillaries
direct, muscular routes in the microcirculation that allow blood to bypass a capillary bed, connecting a precapillary arteriole to a post-capillary venule (not true capillaries)
venule
more branched, smaller vein without smooth muscle
arteriovenous anastomosis
a vessel which enables a capillary bed to be shut off entirely as it directly connects an arteriole to a venule
3 basic layers that make up arteries and veins
tunica intima (internal layer with an endothelial lining), tunica media (contains varying amounts of smooth muscle and elastic tissue), tunica adventitia (layer of connective tissue)
vasa vasorum
small blood vessels that run in the tunica adventitia of larger arteries to provide them with their own blood supply
features of capillaries
contain only tunica intima consisting of a single endothelial cell, narrow intercellular clefts between overlapped ends of endothelial lining cells which forms gap junctions, tight junctions adjacent to gap junctions to form a continuous seal
fenestration
a ‘window’ in an epithelial cell, usually a circular area where the cell is reduced to a thin membrane which allows increased transport of substances, size varies depending on organ involved and substance requiring transport
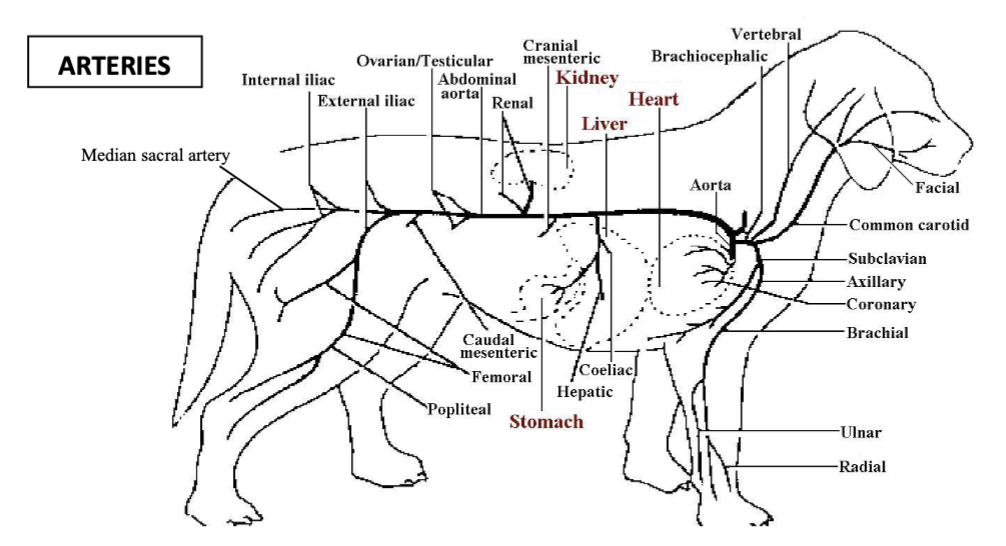
major vessels of the heart
aorta, pulmonary trunk, cranial and caudal venae cavae, pulmonary veins, coronary arteries and veins
aortic bulb
portion of the aorta immediately after the semilunar aortic valve which branches off into separate vessels
which sinus gives rise to the right coronary artery?
right aortic sinus
which sinus gives rise to the left coronary artery?
left aortic sinus
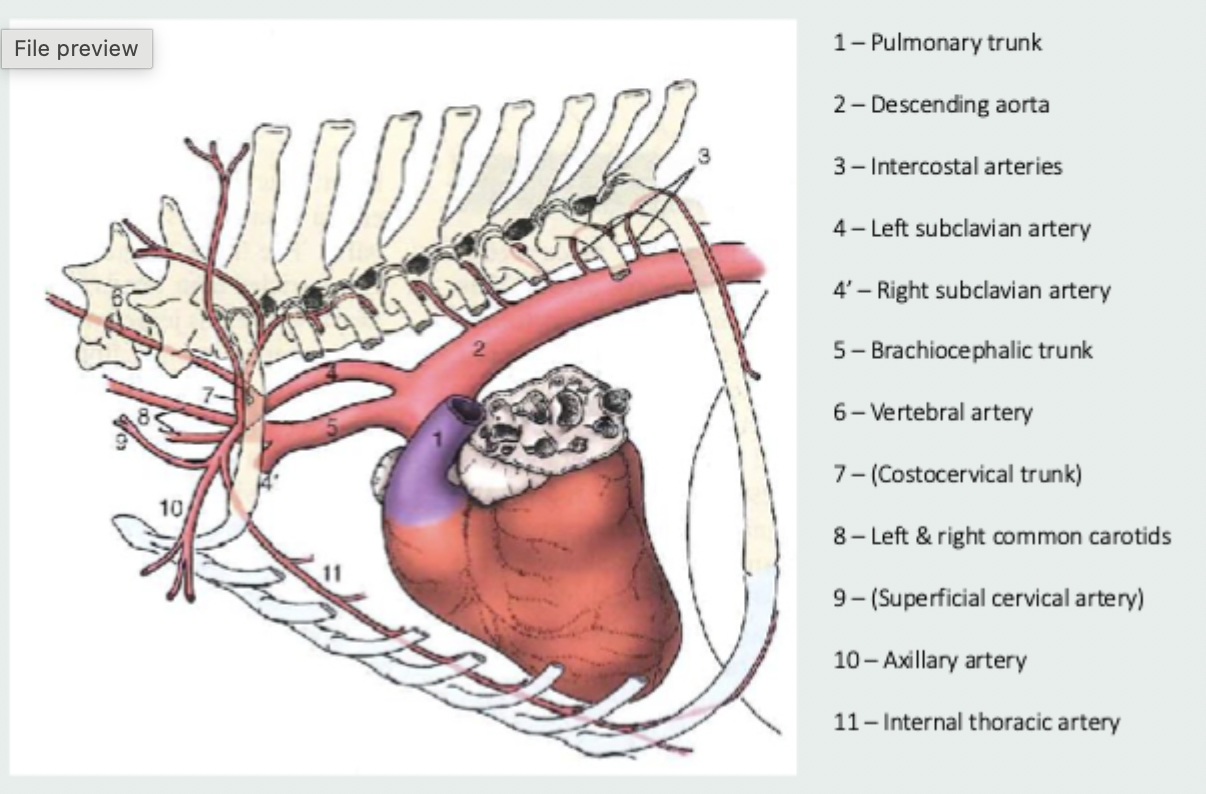
vessels which branch from the aorta after the aortic bulb
brachiocephalic trunk, subclavian arteries, common carotid arteries
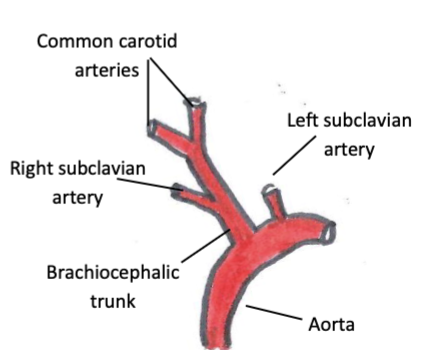
vessels that branch from the subclavian arteries
vertebral artery, costocervical trunk, internal thoracic artery, superficial cervical artery
axillary artery
smaller vessel left after the branches of the subclavian which supplies the forelimbs and chest wall
internal thoracic artery
vessel which travels ventrally and caudally in the mediastinum to supply the pleura, pericardium, thymus, pectoral muscles and cranial mammary glands and then travels below the diaphragm to the abdomen where it becomes the cranial epigastric artery
thoracic aorta
vessel which travels caudally along the dorsal thoracic cavity and supplies the vertebrae and ribcage via dorsal intercostal arteries, supplies the caudal extent of the ribcage by dorsal costoabdominal artery, supplies lung tissue and oesophagus via bronchoesophageal arteries, vessel then enters abdomen via aortic hiatus of the diaphragm
abdominal aorta
vessel which travels caudally along roof of abdomen to the left of the caudal vena cava, first branch is phrenicoabdominal arteries which supply diaphragm and cranial abdomen, second branch is lumbar arteries and then coeliac artery which splits into gastric, hepatic and splenic arteries
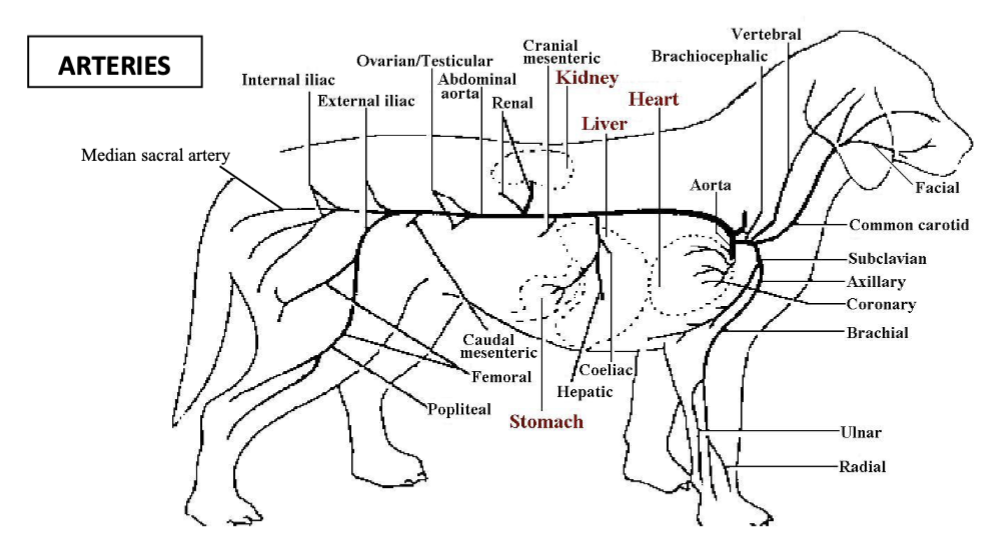
cranial mesenteric artery
vessel branched off the abdominal aorta which supplies the small intestine and some of the large intestine
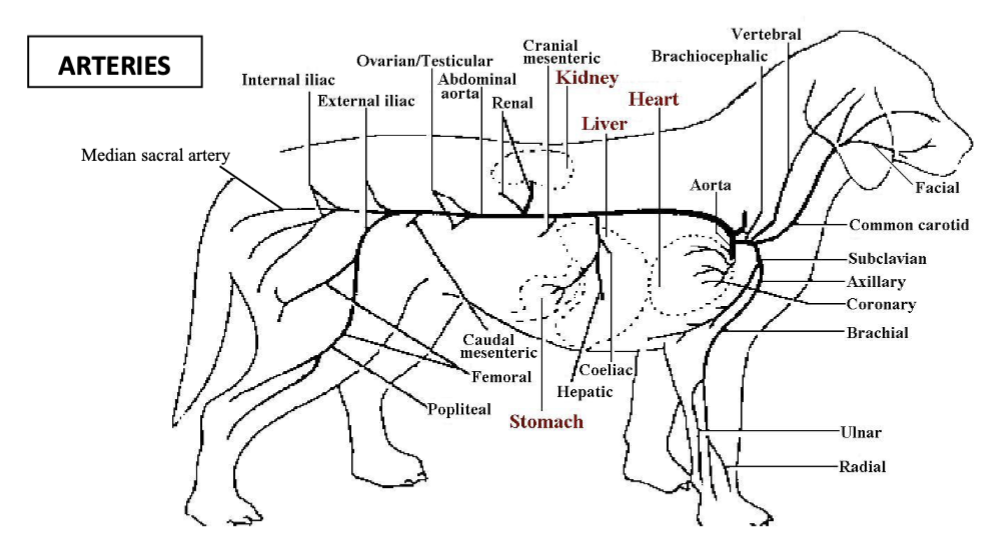
renal arteries
vessels which branch off the abdominal aorta to supply the kidneys
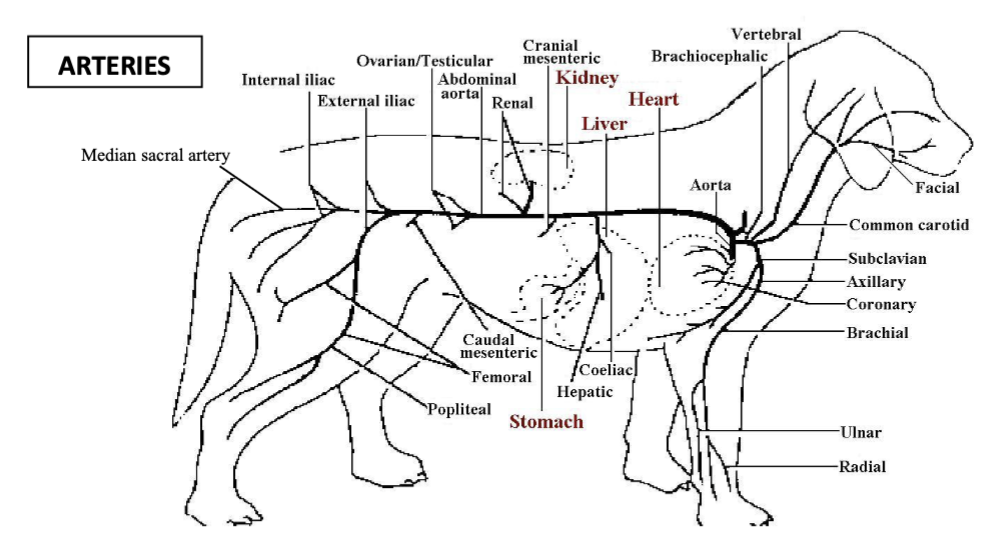
testicular/ovarian arteries
vessels which branch off the abdominal aorta to supply the gonads
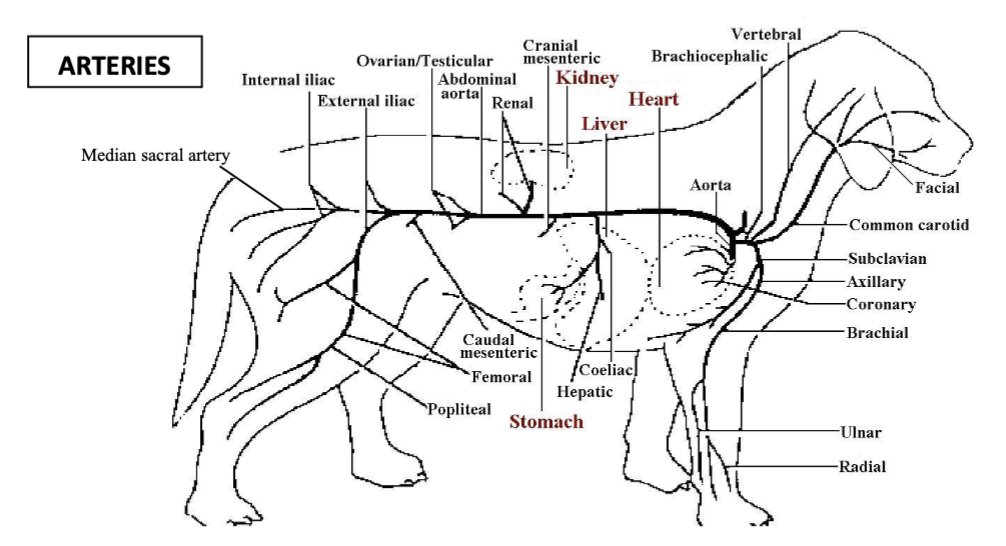
caudal mesenteric artery
vessel which branches off the abdominal aorta to supply the colon and rectum
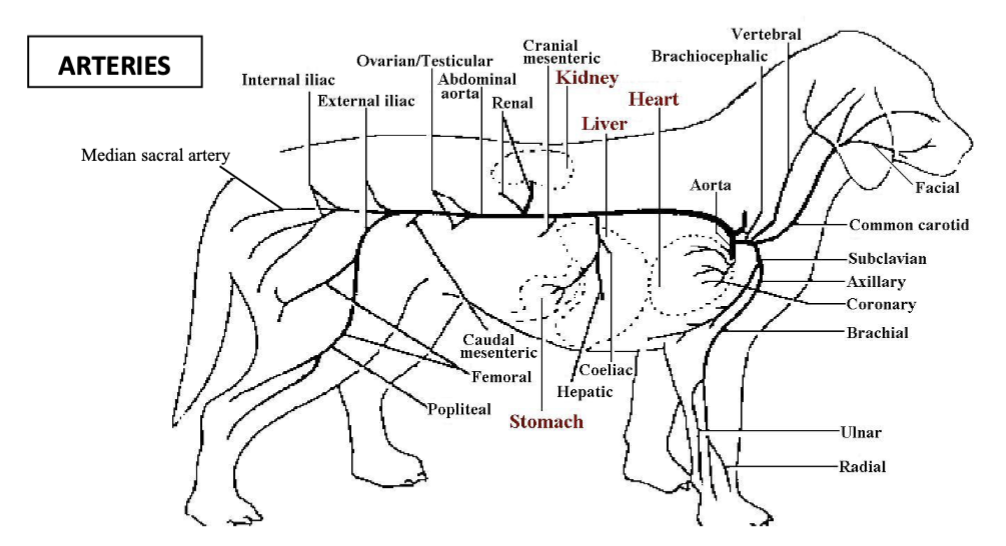
deep circumflex iliac arteries
paired vessels which branch off the abdominal artery to supply the flank
external iliac arteries
paired vessels which branch off the abdominal aorta to supply the adductors of the thigh, the groin and caudal mammary glands in the hindlimb
internal iliac artery
vessel which branches off the aorta to supply the pelvic viscera and walls, the gluteal muscles and the proximocaudal thigh
median sacral artery
the small vessel at the end of the abdominal aorta which becomes the median caudal artery to the tail
vessels which return blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium
cranial vena cava, caudal vena cava and coronary sinus
vessels which return blood from the pulmonary circulation to the left atrium
pulmonary veins
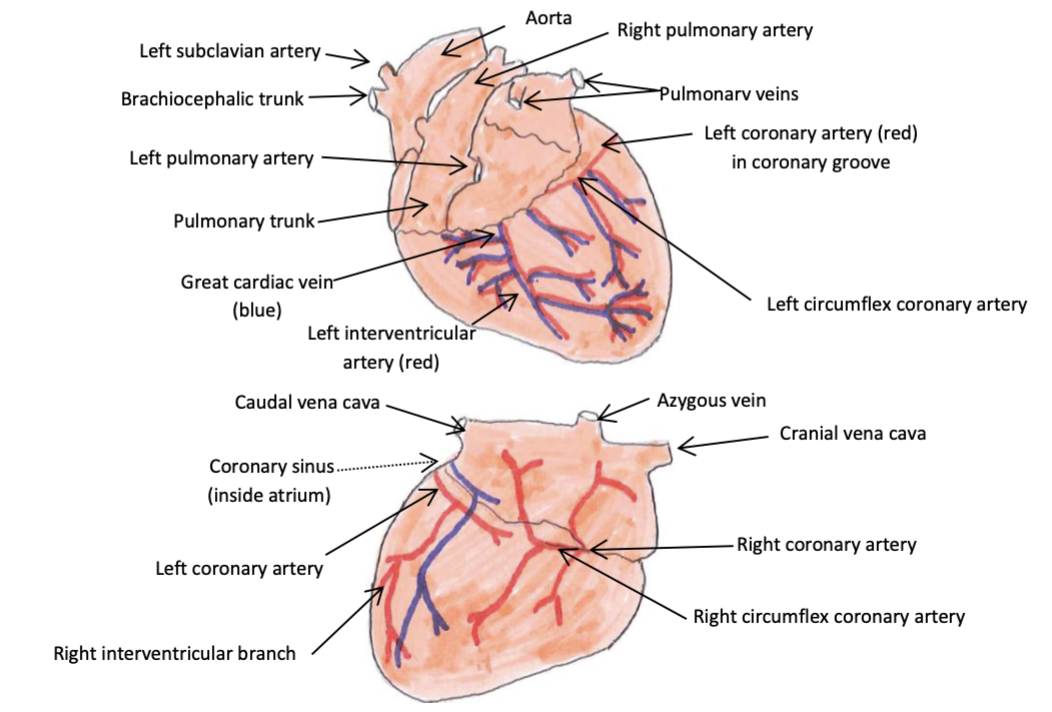
great cardiac vein
vessel which delivers deoxygenated blood to the coronary sinus from the heart wall/coronary vessels (left azygous vein in ruminants and pigs)
cranial vena cava
vessel which receives all blood returning from the body cranial to the heart as well as drainage from the thoracolumbar area and ribcage via azygous vein and internal thoracic vein
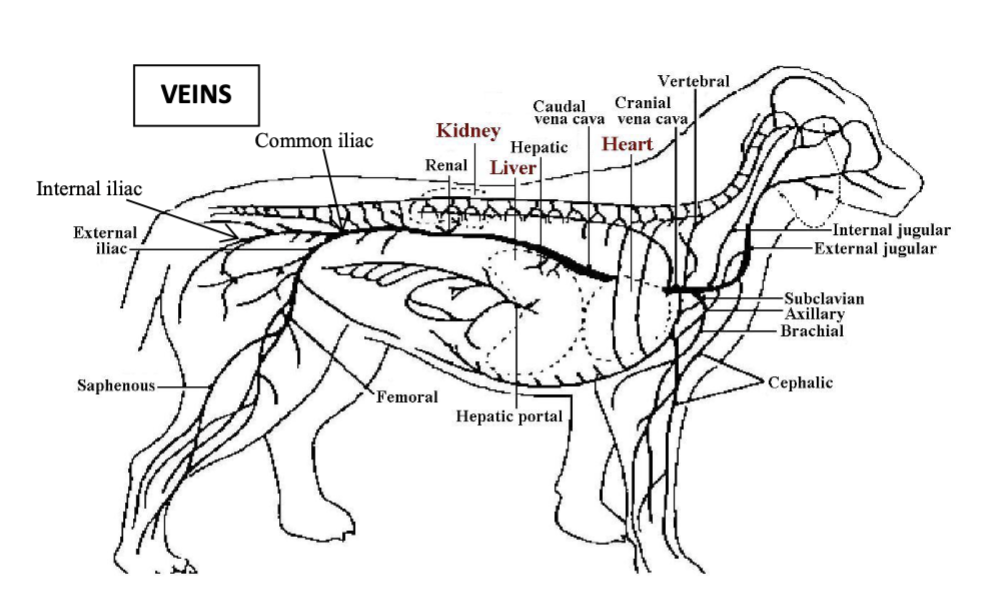
internal/external jugular vein
vessels which drain blood from the head
cephalic vein
vessel which drains blood from the cranial chest and forelimb
axillary vein
vessel which joins the subclavian vein draining the forelimb and some of the intercostal area, they combine to form the cranial vena cava
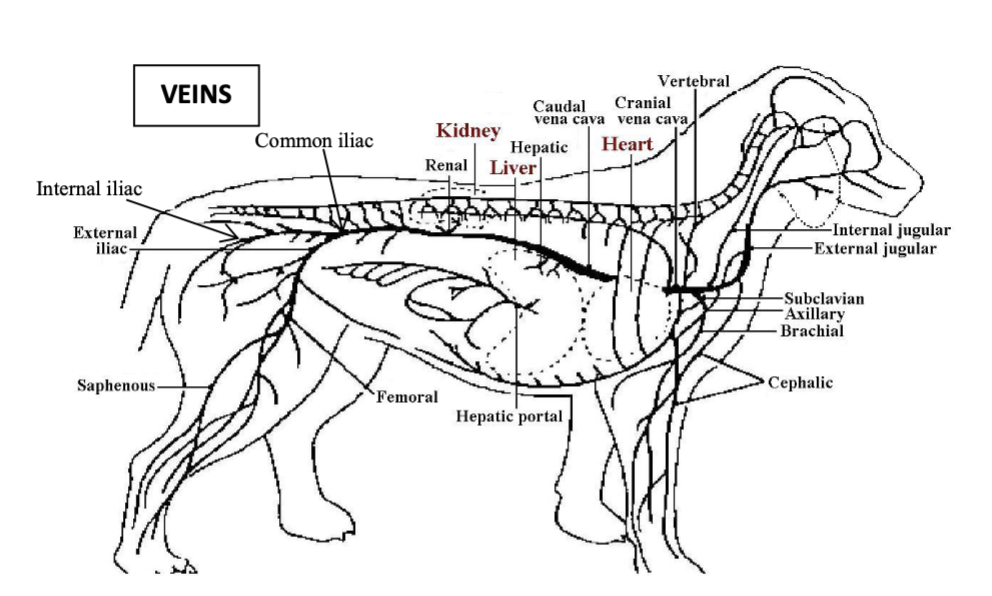
caudal vena cava
vessel which receives majority of venous return from areas caudal to the heart via iliac veins, testicular/ovarian veins, renal veins and hepatic vein
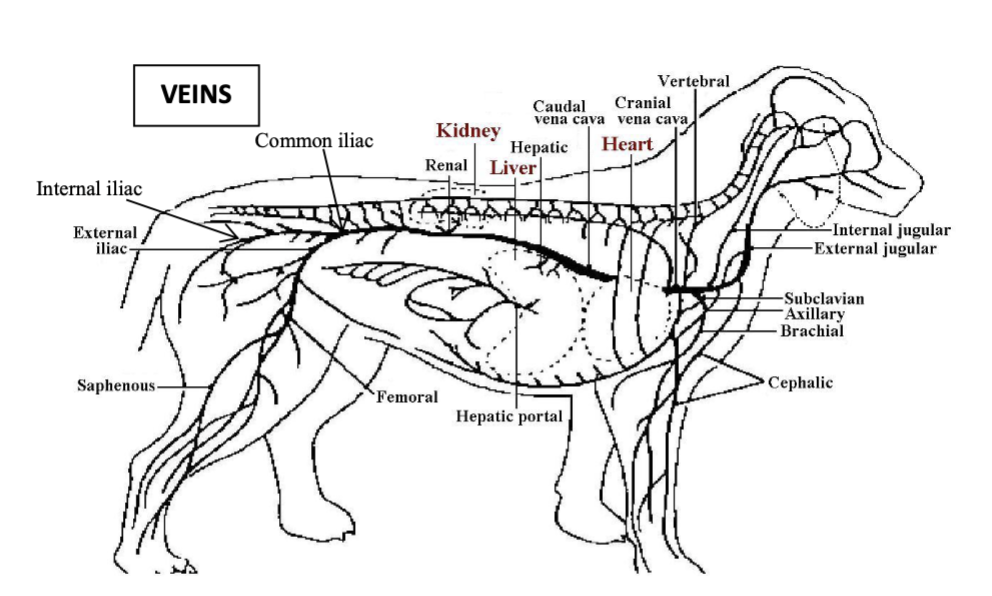
portal vein
vessel which drains most of the gastrointestinal tract
caudal vena cava journey to the right atrium
travels cranially through the diaphragm via the caval foramen and then the plica vena cava in the thorax to the right atrium
left coronary artery
larger vessel which arises from the left aortic sinus and passes between the left auricle and pulmonary trunk to reach the coronary groove where it divides into the left interventricular artery (which runs in left interventricular groove) and the circumflex artery (which runs in coronary groove)
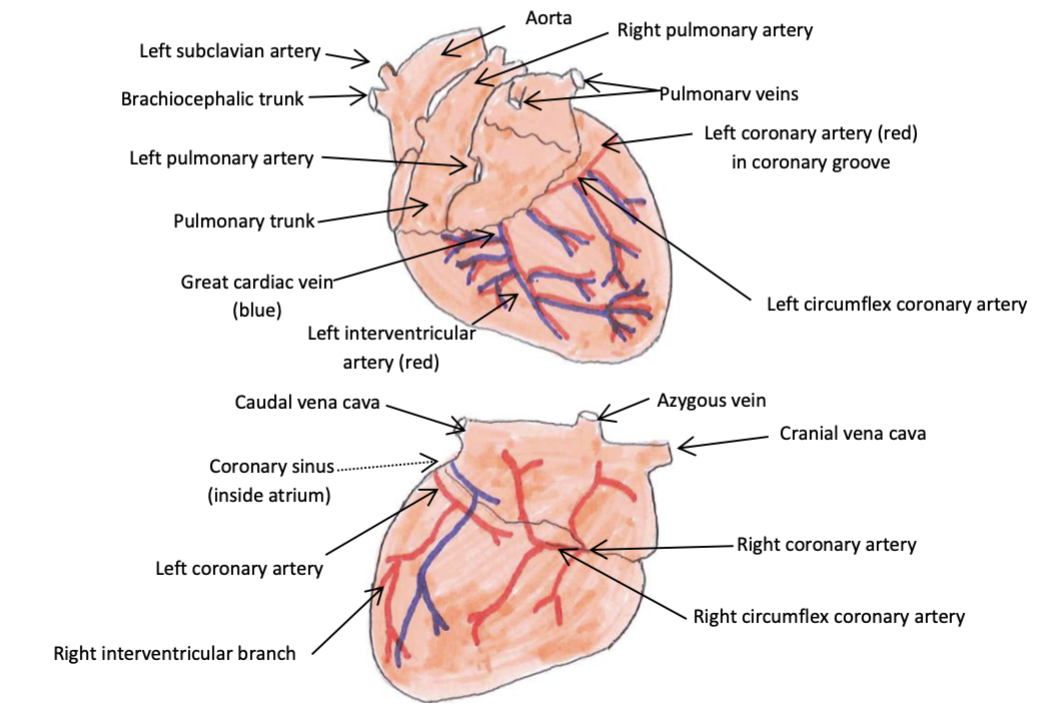
right coronary artery
smaller vessel which arises from the right aortic sinus and passes between right auricle and pulmonary trunk to reach the coronary groove where it runs round to the right side of the heart and ends in the right interventricular groove or peters out in carnivores and ruminants
rules of thumb for thoracic radiographs
take image during peak inspiration or when gently inflated via anaesthetic breathing system, keep forelimbs out of the way (drawn cranially so shoulder and humerus don’t obscure the cranial thorax), obtain orthogonal views, ensure no rotation of patient around central axis to reduce other tissues obscuring anatomy of interest, align ribs for lateral image
ventrodorsal thoracic radiograph
radiograph taken with patient in dorsal recumbency which brings lungs closer to the plate so is preferred for examination of the lungs
lateral thoracic radiograph
radiograph taken with patient in lateral recumbency, best to take both laterals as lower lung will be less inflated than upper in this position
dorsoventral thoracic radiograph
radiograph taken with patient in ventral recumbency, preferred for examination of the heart, sometimes only possible position if animal is struggling to breath or unsedated
bulk flow
movement of fluid by means of pressure difference
hydrostatic pressure
the pressure that a fluid exerts on its container
perfusion pressure
the difference in pressure between 2 points in a blood vessel, represents the pressure needed for blood to move through
transmural hydrostatic pressure
the differences between the pressure exerted by the fluid inside a vessel and outside the vessel
Fick’s law of diffusion
the rate of diffusion is equal to the concentration gradient multiplied by the area available and the diffusion coefficient, divided by the distance the substance needs to travel from the capillary to the target tissue cell
oncotic/ colloid/ protein osmotic pressre
the osmotic pressure exerted by plasma proteins
Starling’s law of capillaries
the balance of hydrostatic and oncotic pressures across a capillary wall determines the amount and direction of fluid transported across the wall
portal system
system where capillary beds exist in series, meaning one feeds into the other e.g. splanchnic circulation
cardiac output
the volume of blood pumped by one ventricle in a minute
end systolic ventricular volume (ESVV)
the volume of residual blood in the ventricle after contraction
end diastolic ventricular volume (EDVV)
volume of blood in the ventricle after diastolic filling
stroke volume
volume of blood leaving the ventricle per contraction (EDVV - ESVV)
ejection fraction
the fraction of the end diastolic volume that constitutes the stroke volume (SV/EDVV)
cardiac output equation
stroke volume x heart rate
factors affecting end diastolic ventricular volume (EDVV)
diastolic filling time, preload, compliance
preload
the filling pressure of the ventricle (equal to atrial/venous pressure/end diastolic ventricular pressure), increased by increasing volume/pressure in venous system
ways to increase preload
increase overall blood volume, reduce perfusion to non-essential tissues, increased action of respiratory and skeletal muscle pumps (compress veins and increase venous return to heart)
heterometric autoregulation
increased EDVV increases stroke volume on one side of the heart which therefore increases stroke volume on the other side
compliance
change in volume/ change in pressure, a measure of how readily ventricular walls stretch during diastolic filling
lusitropy
ability of a ventricle to relax adequately
why does cardiac output not increase in proportion to heart rate
a very high heart rate causes the length of systole and diastole to decrease which decreases diastolic filling time which decreases stroke volume
stages of the cardiac cycle
isovolumetric contraction, rapid ejection, reduced ejection, isovolumetric relaxation, rapid filling, reduced filling
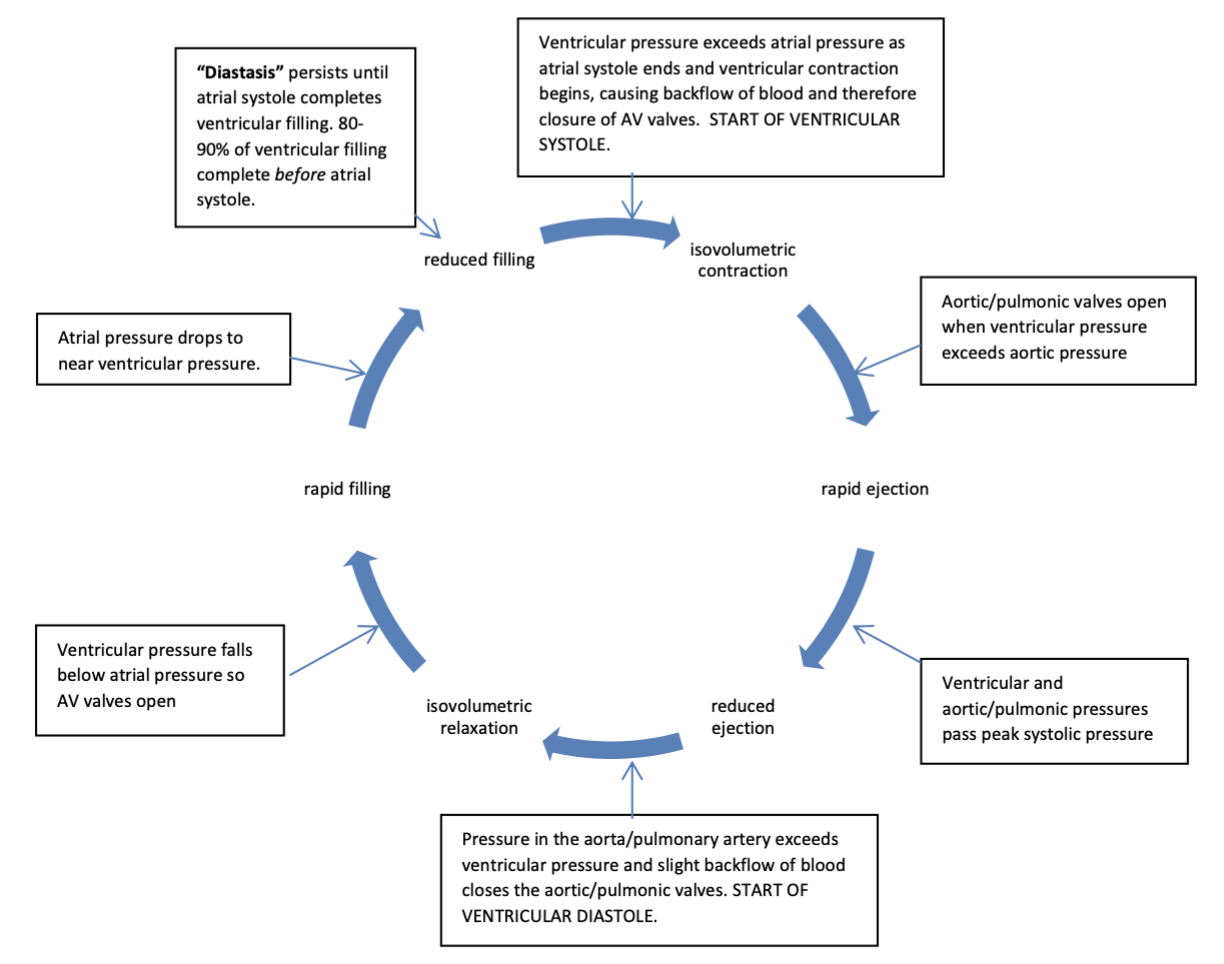
afterload
the resistance that the heart must overcome in order to force blood out into the arterial system/ the vascular resistance of the arterial system