SLE356 - Advanced Topics in Forensic Biology
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Antemortem
before death
Postmortem
after death
Perimortem
in or around time of death
Postmortem interval (PMI)
the period of time between time of death and discovery
When does decomposition begin
as soon as the death occurs
Taphonomy
The study of decompostion and what happens to a person after they die
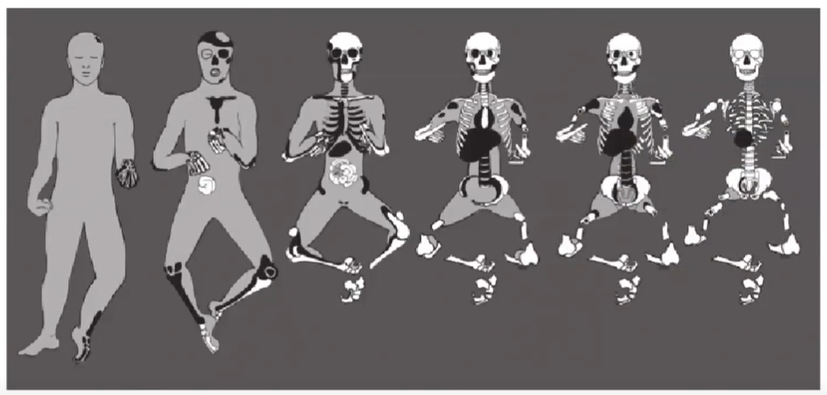
Stages of decomposition
Fresh, Putrefaction, Putrid Dry Remains
Active decompositon
bloat, putrefaction, decay
Advanced decomposition
skeletal remains
Algor mortis
Algor mortis or the coldness of death is a drop in temp caused by the lack of blood movement. It was previously used to determine PMI however it has proven to be unreliable and has the high potential for contamination
Livor Mortis
Livor Mortis also know as hypostasis or postmortem lividity is blood settling in the capillaries and veins of dependent parts of a body. It typically occurs 20-120 minutes after death.
Rigor mortis
Rigor mortis or muscle stiffening occurs in a 2-12 hour window (influence by environment) where the muscles start to contract in phases of relaxing and resetting. It starts in smaller muscles of face and those most used prior to death first, for example if they used alot of muscle right before death then those muscles would contract first. It is temperature dependent.
Cadaveric rigidity
Muscle stiffening (in some or all of the body) immediately after death
Seen in people who die in a state of extreme emotional/physical stress
Heat stiffiening
Pugilistic pose caused by exposure to extreme heat
Autolysis
Enzymes digesting cells
Bloat
Skin retains gasses and swells, it is causesd by autolysis
Putrefactive rigor
Build up of gasses in body - individual in ‘hug’ pose
Putrefaction
Soft body parts disappear form autolysis (enzymes digesting cells), microbial, insect, and animal activity
Skin slippage
Occurs in moist or wet habitats the epidermis begins to separate from underlying dermis
‘glove formation’ - when the skin separates as a relatively complete unit
Can be used for fingerprinting
Adipocere
Also known as Corpse or grave wax it is whitish, greyish, yellowish and has a soapy feel. It is caused by the breakdown of lipids and bacterial decomposition of triglycerides which produce glycerol and fatty acids and can preserve body when it is in large amounts as the lower pH slows decompostition. The odour is used to train cadaver dogs and it is most likely to occur on bodies that have been submerged, buried, sealed in containers or in peatbogs. Development is based on lipid content as well as clothing and surrounding however the rate of formation and agreement on conditions is not clear although moisture is key.
Mummification
Different from process to preserve tissue (egypt etc)
Results from exposure to dry and hot condditions
Skin becomes leathery
Common is australia
not much soft tissue left
Putris Dry Remains
Advanced stage
Gradual loss of soft tissue resulting in skeletonizarion (or in Australia, mummification)
Decay proceed more slowly
Uterus and prostate glands are fairly resistant to decay and could last for several months (in a well-sealed container)
Skeleton becomes disarticulated (nothing holding the bones together)
Skeletal remains can be seperated from natural processes such as weather and animals
How does Geographic location affect decomposiosition
Temperature and humidity
Hot/humid - increase
Cold - decrease
How does Time of year affect decomposiosition
summer vs winter
urban (faster) vs rural (slower)
How does Exposure to sunlight affect decomposiosition
Sun rays promote decay
Sun + wind = mummify
Body in fuld is avoided by invertebrates
Desiccation and UV light kill eggs
How does Wrapping and Confinement affect decomposiosition
slows
Wrappings make transport esier (tarps, carpets, shower curtains, suitcases, bins)
Insects and still permeate (some) wrappings - car boots
How does Hanging above ground affect decomposiosition
slows
No moist, dark, under-surfae for flies to lays eggs
Increased air circulation around body promotes drying out
Maggots fall off washed off by rain
How does underground Burials affect decomposiosition
slows
Soil type and chemistry
Heavy clay has lower oxygen which reduces microbial activity (slows)Burials - underground (slows)
Acidic soil reduces microbial activity (slows) but low pH dissolves tissues & bone (increases)
High calcium reduces chemical dissoution of bones but microbial decomposition continues
Depends on time of year, exposure to sun, rainfall, drainage, height of water table
Reduced blowfly, but other invertebrates will colonise
How does underwater burials affect decomposiosition
slows
Lower temperature and reduced oxygen
Decay occurs more slowly in salt water than fresh water (fewer micro-organisms)
Bodies on surface of water will decay faster than those on floor (access of insect)
Under-studied area of forensic science
How do Wounds affect decomposiosition
increases
Rapid discovery and exploitation by insects (increases)
Severe blood loss decreases the rate of decay (slows)
How does Burning affect decomposiosition
Intentional detection avoidance behaviour
Extreme high temperature necessary to completely destroy body
Extremities most affected
High fat content (increases)
Flammable clothing (increases)
Sterilised and dry skin (slows) but causes cracks to deeper tissue (increases)
How does Chemical treatment affect decomposiosition
slows
Acid can be used to destroy ecidence
Acid can also be used to preserve the body (quicklime)
How does Embalming affect decomposiosition
slows
Chemicals delay or prevent decompostition
Compromises evidence
Ways to determin PMI
Vitreous humor (fluid in the eyes)
Bone structure
Bone autofluorescence (UV light)
Chemical analyses - luminol
Radiocarbon dating
Determine of provenance
stable isotopes
Human travel, trafficking
Use of isotopes that don’t decay (carbon-12, carbon-15
Ratios can indicates diet, origin, movement
Strontium ratios (84Sr, 86Sr, 87Sr & 88Sr) vary geographically
Signature to area
Enter via diet and remain unchanged (tooth enamel) cf. strontium in metabolically active bones (where they spent the last few
Differences between various bones informative based on rate of remodelling