2 thyroid gland function Bone mineralization
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Typical effects of thyroid hormones in the body
energymetabolism: consume O2 in tissue producing heat
Growth and development of body
metabolism: sugar → energy (SYMPTOMS OF VERY ACTIVE PERSON) weight loss, warm, energetic, agitation, sleep disorder, tremor
nervous system: Development
Myocardium: Stimulates B adrenergic receptors increaseing O2 consumption
T3 is 10 times more potent then T4
Terminology
-thi- = thyroid homrone antagonist
HYPOthyroidism: Decreased thyroid function and reduced hormone levels. → Hormone replacement therapy. Caused by autoimmune thyroiditis, hyperthyroidism, thyroid gland surgery, medications (lithium, amiodarone)
Hyperthyroidism: Increased thyroid function and increased hormone levels. caused by graves (bazedovs) diease, nodular toxic goiter. The characteristic symptoms of hyperthyroidism are the opposite of those of hypothyroidism. Surgical treatment, radioactive iodine therapy or thyrostatic drug therapy applied as a cure. More energy heat/weight loss/tachycardia
Toxicology of thyroid hormone preparations
overdose of thyroid horomes
Mild/moderate intoxication cause tachycardia, tremor, anxiety, feeling of heat, agitiation, sleep disorders
severe intoxication cause: supraventricular tachycardia, hyperthermia, hypertension, seuzure, coma
Treatment: symptomatic (beta blockers)
Levothyroxine
Synthetic form of T4
Converts to T3 → stimulates intracellular thyroid receptors → nuclear DNA → gene expression → protein syntheisis
Indicaiton: hypothyroidism, autoimmune (hashimoto) thyroiditis. Replacement therapy after thyroidectomy
SE: Tachycardia, Malabsorbiton if combined with other drugs, Toxic if overdoed
Thiamazole (methimazole)
Antithyroid agent
Inhibit thyroid peroxidase (interfering with iodine and tyronine structure) reducing synthesis of (MIT,DIT) T3/T4
Indication: hyperthyroism (graves/bazedovs diease)
SE: Dont give to pregnant, allergic skin reaction, agranulocytosis
thia - thyroid → antagonist
Propylthiouracil
Antithyroid agent
Inhibits thyroid peroxidase → inhibit T3 / T4 synthesis
Inhibit iodothyonine deiodinase → inhibit T4 to T3 convertion
Indication: hyperthyroism (graves/bazedovs diease)
SE: Dont give to pregnant, allergic skin reaction, agranulocytosis
can be used during 1 trimester
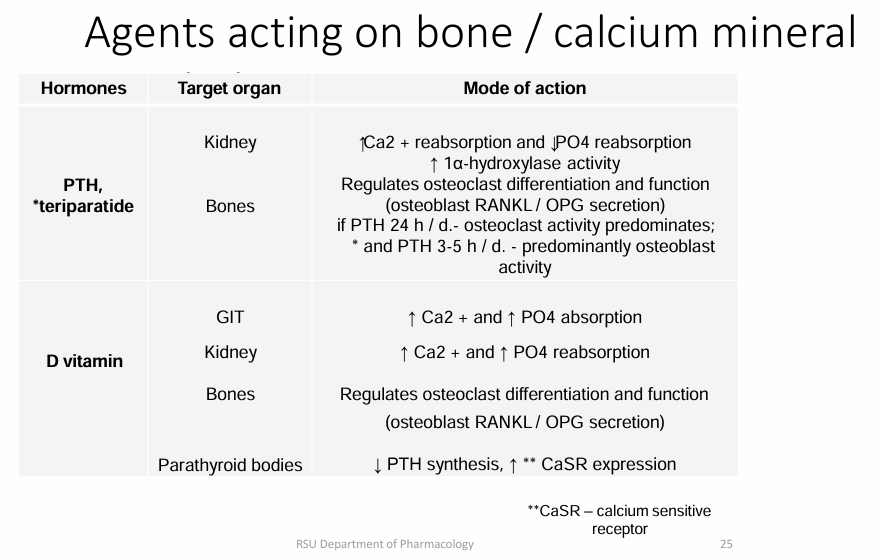
bone mineral metabolism
important minerals: Ca2+ and phosphates
Regulated by: PRH (paraphyroid hormone) and Vitamin D
Bone remodling receptor/signal: RANK and OGG (by osteoblast)
Terminology
Osteoporosis is a chronic, progressive, multifactorial skeletal disease. Decreased bone mineral density BMD or bone mass loss (brittle bones).
Osteoporosis: Treatment drugs: bisphosphonates, RANKLinhibitors, * estrogens / androgens ( All are antiresorptives → reduce bone resorption)
secondary osteoporosis caused by prologed use of medications (glucocorticoids, loop diuretics, proton pump inhibitors). Inadequate bone mineralization. called rickets in children. called osteomalacia (soft bones) in adults.
Renal osteoporosis: Cronic renal disase (GFR<30) → bad vitaminD/Ca absorbtion (hypocalcaemia). → Bone demineralization → Decreased Ca levels causes increased phosphate levels (hyperphosphatemia)
Bisphosphonates (BP): BPbinds to bone hydroxyapatite crystals and inhibits bone resorption. In combination with calcium, BP provides sustained osteoclast inhibition and apoptosis
PTH FORM BONES: Calcitrol, Teriparatide
Reduce bone broken down and reabsorbed: alendronic/zolendronic acid, Denosumab
Alendronic acid, Zoledronic acid
Bisphosphonates
Anti BONE reabsorbtive (less bone is reabsorbed)
Drug combination:
NSAID → GIT irritation
antacids → intefere absorption
weekly, take in morning 30 min before first meal with water, have to be vertical (cause GI trackt irritation)
Indication: osteoprosis (postmenopause, andropause)
bone tumor metastases (oncogenic hypercalcaemia)
secondary osteoporosis (glucocorticoid indused osteoporisis)
SE: hypocalcaemia (arrhythmia, neurological symptoms seizures, tetany)
Denosumab
RANKLinhibitors
(suppresses osteoclast formation) (osteoclast break down bone)
Indication: osteoprosis (postmenopause, andropause)
bone tumor metastases (oncogenic hypercalcaemia)
secondary osteoporosis (glucocorticoid indused osteoporisis)
SE: hypocalcaemia (arrhythmia, neurological symptoms seizures, tetany)
Teriparatide
Osteoanabolic agents
parathyroid hormone (PTH) analogues/agonist
promote bone formation
Indication:
Severe osteoporosis (in post-menopause, andropause)
Secondary osteoporosis (glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis)
Contraindicaiton: hypercalcemia
Calcitriol
Active vitamin D form. non selective intracellular vitamin D receptor agonist
Regulates bone mineralization/orestoclast differentiation/Ca & phosphate homeostasis
reducaes PTH synthesis
↑ Ca2+and↑PO4 absorption
Indication: Prevents rickets (secondary osteoporosis in children), osteoporosis, renal osterodystorphy, hypocalcaemia
Side effect: hypercalcaemia, calcification of organs
Precursor of Vitamin D (Ergocalciferol, Cholecalciferol)
Cinacalcet
Allosteric modulator of Calcium sensitive receptor for parathyroid cells (CaSR). By increasing the sensitivity of CaSR to extracellular Ca2+, decreases PTH secretion- an antiparathyroid agent
Antisecretory action
Indication: Primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism
SE: hypocalcaemia