nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
how many nares do we have?
four
how many anterior nares are ther?
2 external nares
how many posterior nares do we have?
2 internal nares
how does the nasal cavity open into the nasopharynx?
via the 2 internal nares
what does the nasal cavity communicate with superiorly?
lacrimal sac
what does the nasal cavity communicate with superolaterally?
paranasal sinuses
what does the nasal cavity communicate with posteriorly?
the nasopharynx
where does the olfactory area reside?
the superior 1/3rd of the nasal cavity
where is the respiratory area in the nasal cavity?
inferior 2/3
air passing through the nasal cavity is __________ and _______________ before it passes through the rest of the upper respiratory tract to the lungs
warmed, moistened
functions of the nose
olfaction, respiration, filtration, humidification and eliminations of secretions from the nasal mucosa, paranasal sinuses and nasolacrimal ducts
roof boundary of nasal cavity?
olfactory area and cribiform plate of ethmoid
floor boundary of nasal cavity?
hard palate
medial wall boundary of nasal cavity?
nasal septum (which has perpendicular plate of ethmoid, septal cartilage, vomer, nasal crests of maxillary and palatine bones)
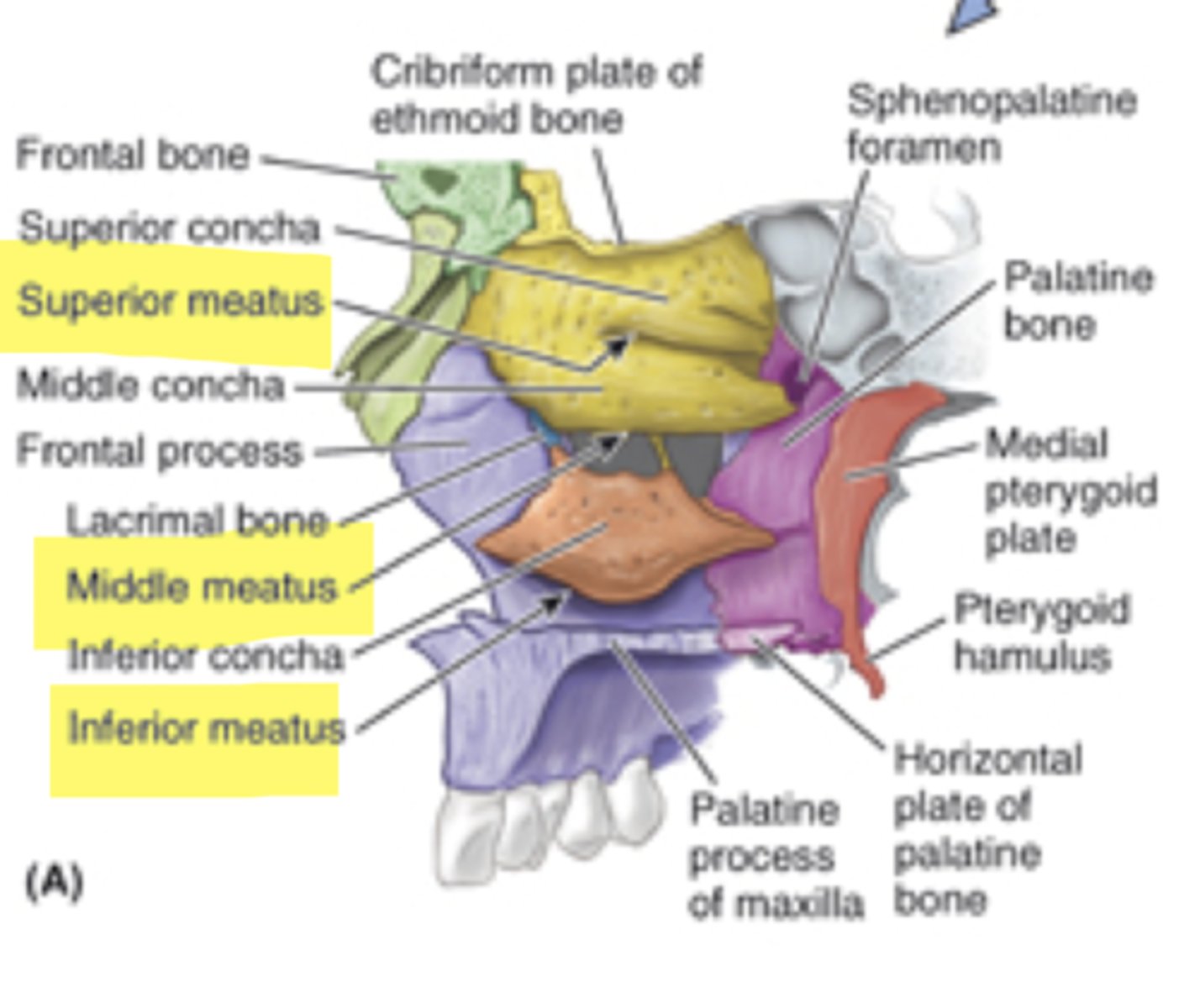
lateral wall boundary of nasal cavity?
nasal concha and their associated meatuses
where are the nasal concha located?
lateral wall
bony shelves that form meatuses above and underneath them
nasal concha
largest nasal concha and forms a separate bone
inferior nasal concha
the middle and superior nasal choncha are apart of the _______________ bone
ethmoid
how many air passages do the concha divide the nasal cavity into?
4
four air passages the nasal cavity divides into
1. sphenothemoidal recess
2. superior meatus
3. middle meatus
4. inferior meatus
what recess is superoposterior to the superior concha?
sphenoethnoidal recess
what air passage is under the superior concha?
superior meatus
what air passage is inferior to the middle concha?
middle meatus
what air passage is inferolateral to the inferior concha?
inferior meatus
opening of the sphenoidal sinus is where?
sphenoethmodial recess
opening of the posterior ethmoidal sinus is where?
superior meatus
semicircular groove in the middle meatus
semilunar hiatus
what does the semilunar hiatus form a curve around?
the ethmoid bulla
where is the semilunar hiatus and ethmoid bulla located?
middle meatus
consitutes the middle ethmoid air cells (sinus)
ethmoid bulla
what openings are within the semilunar hiatus?
opening of the frontal sinus, anterior ethmoidal air cells and maxillary sinus
what opening is in the inferior meatus?
nasolacrimal duct
what drains into the nasolacrimal duct?
lacrimal sac
the nasal cavity recieves arterial supply from five arties which anastomose at an anterior area in the nasal septum called the ......
kisselbach area (kisselbach plexus)
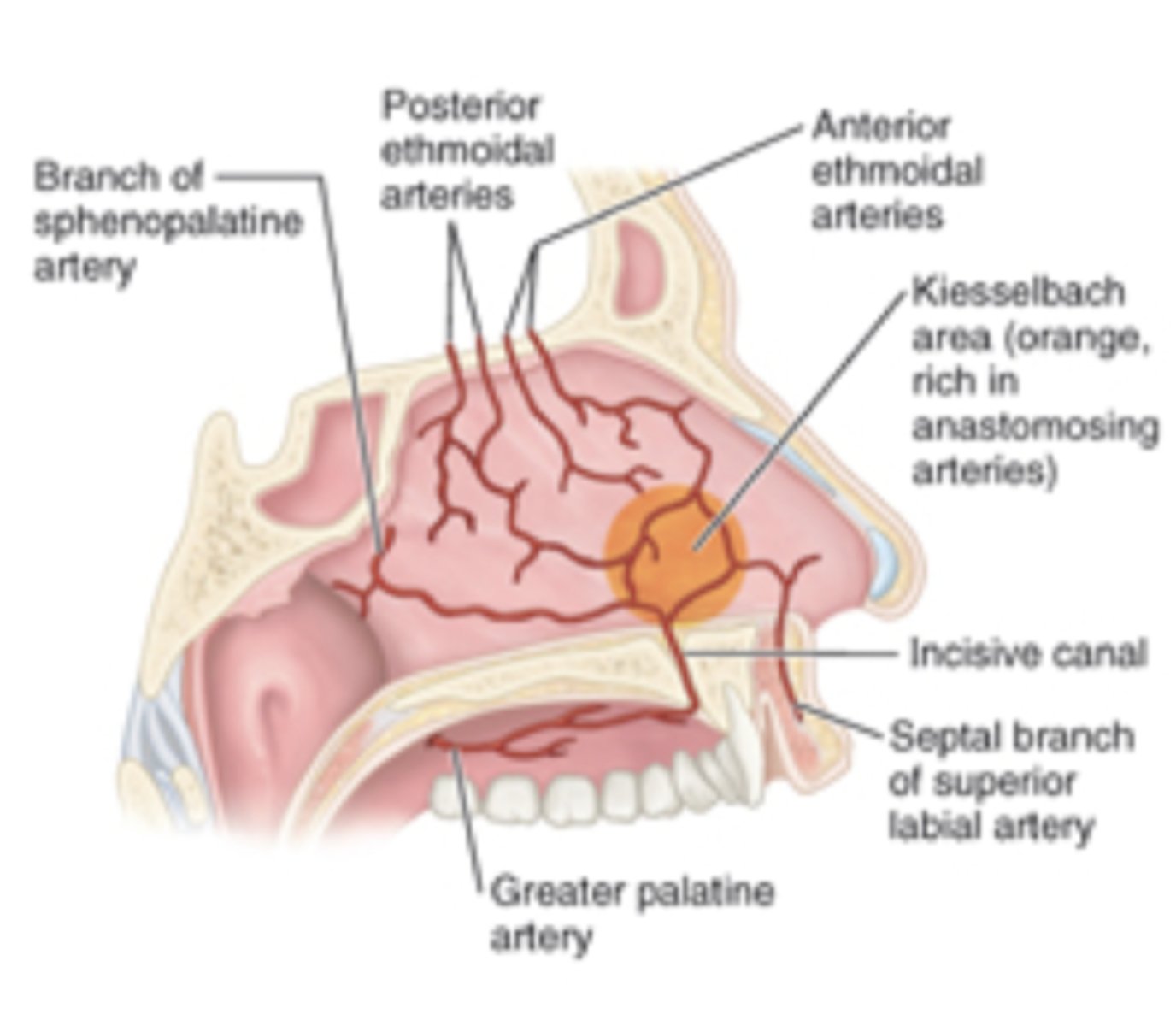
place of heavy source of bleeding from the nose
kisselbach plexus
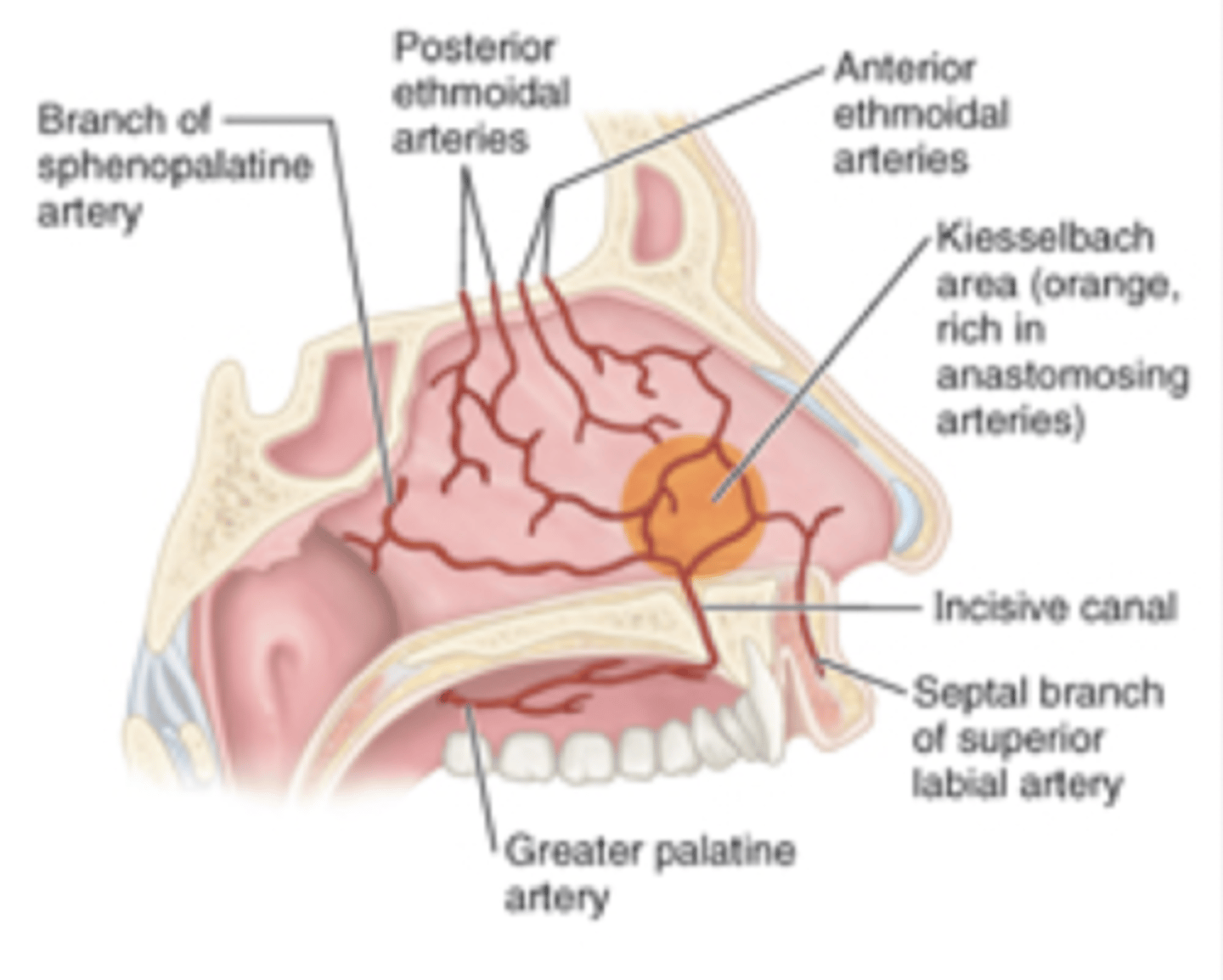
epistaxis
nose bleed
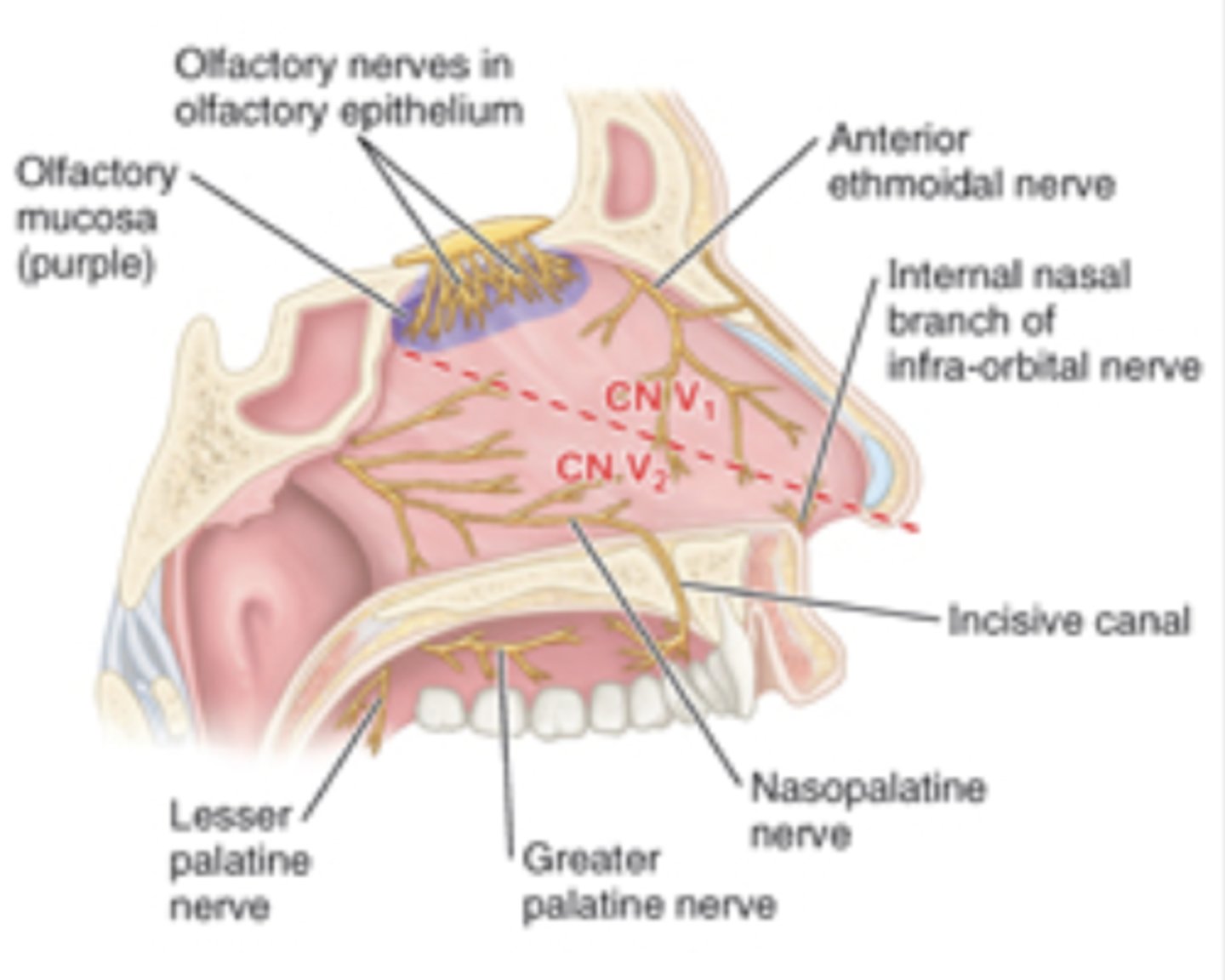
nerve that provides sensory supply to the anterosuperior half of the nasal cavity
opthalamic division of trigeminal nerve (CNV 1)
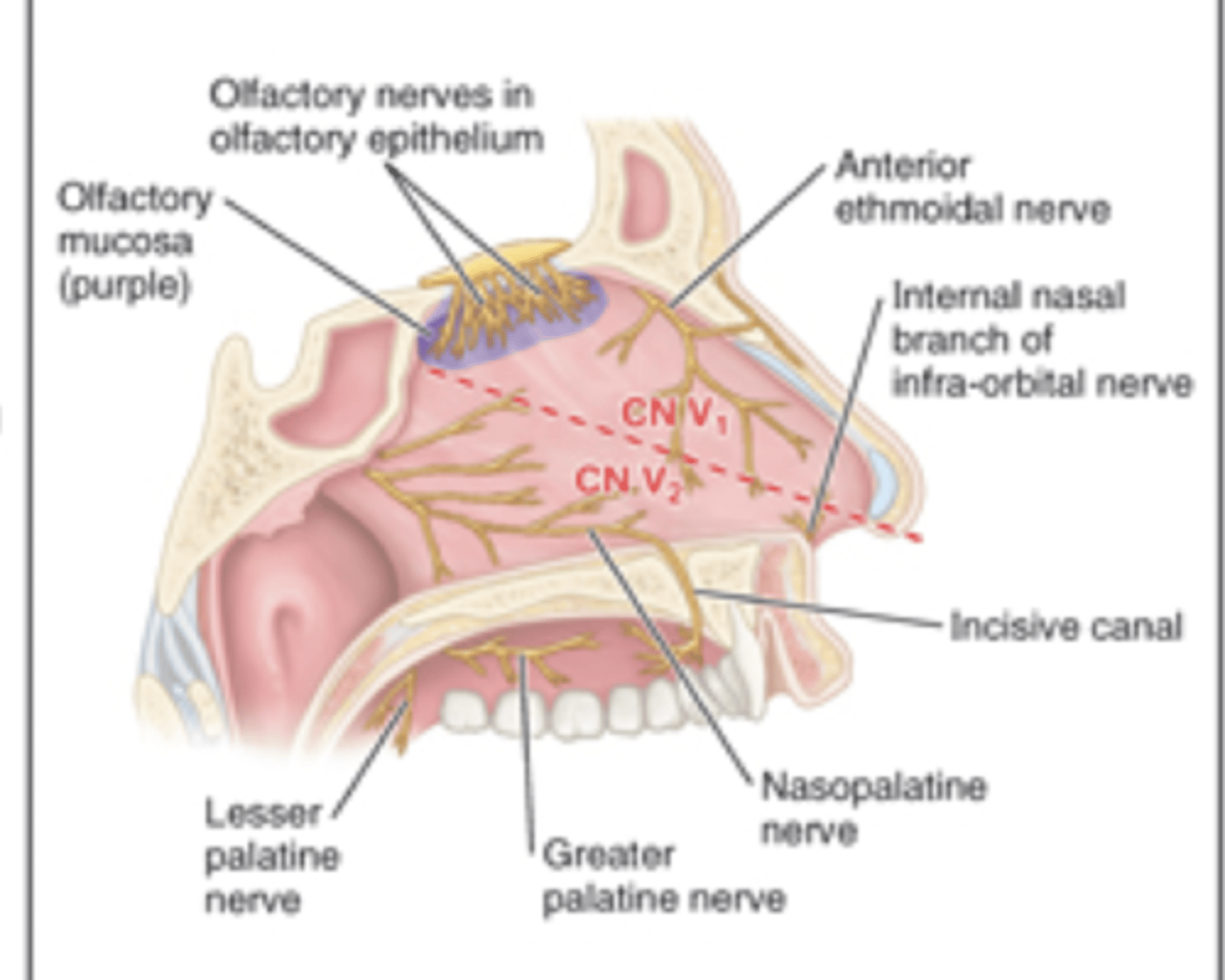
nerve that supplies sensory supply to the inferoposterior half of the nasal cavity
maxillary division of trigeminal nerve (CNV 2)
air-filled cavities lined with mucous membrane, named according to the bones they are located in
paranasal sinuses
function of paranasal sinuses
lighten the weight of the skull, facilitate voice resonance, passage for warming and moistening air
name the paranasal sinuses
frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid and maxillary sinues
true or false: all paranasal sinuses are paired
true
location of the frontal sinuses
located posterior to the superciliary arches of the forehead
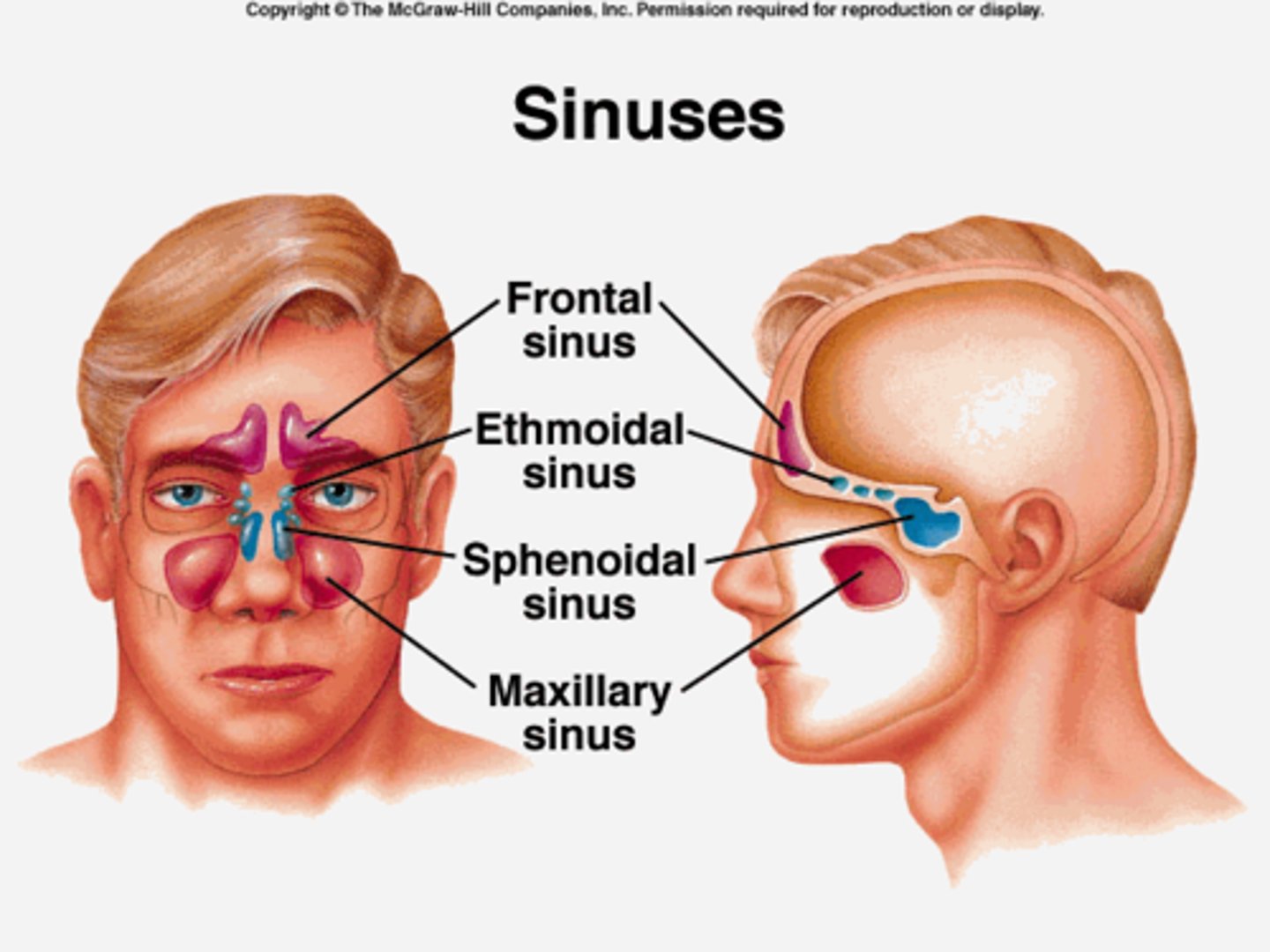
where do the frontal nasal sinuses drain into?
drain via the frontonasal duct into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus
interconnected small cavities that are located in the ethmoid bone between the nasal cavity and orbit
ethmoid sinuses
where do posterior ethmoid cells drain into?
superior meatus
where do the anterior and middle ethmoid cells drain into?
the middle meatus
what cells make up the ethmoid bulla
middle ethmoid cells
what cells open into the semilunar hiatus?
anterior ethmoid cells
sinuses that occupy the body of sphenoid bone
sphenoid sinuses
what structures are the sphenoid sinuses related to?
optic nerves
optic chiasm
pituitary gland
cavernous sinus
internal carotid arteries
where do the sphenoid sinsues drain into?
the sphenoethmoidal recess
largest paranasal sinus
maxillary sinus
pyramidally shaped paransal sinuses that occupy the body of the maxilla
maxillary sinuses
base of the maxillary sinus
formed by the inferior part of the lateral nasal wall
apex of the maxillary sinus
extends laterally into the zygomatic bone
roof of the maxillary sinus
formed by the floor of the orbit
floor of the maxillary sinus
formed by the alveolar bone of the maxilla
opening of the maxillary sinus
maxillary ostium
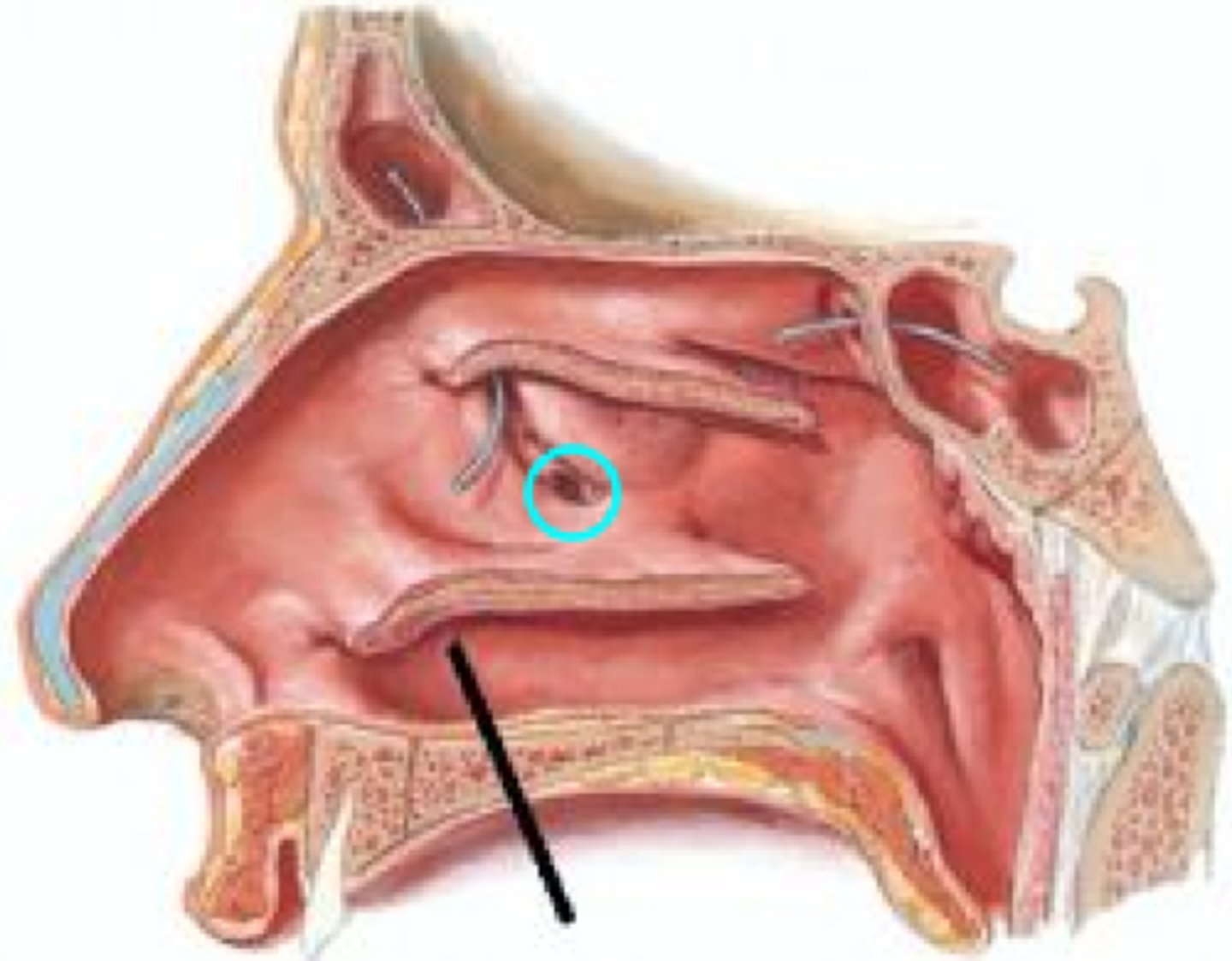
where does the maxillary sinus drain into?
the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus
location of the maxillary ostium
superior part of the maxillary sinus
why is drainage of the maxillary sinus problematic?
because the ostium is in the superior of part sinus, it has to drain against gravity and makes the maxillary sinus prone to lingering infections
sinuses tend to ______________ with age
pneumatize
sinus increase in size
pneumatization
maxillary antrum
maxillary sinus
sinus that may pneumatize to the extent that the roots of the maxillary posterior teeth would form conical projections into the sinus
maxillary sinus
which maxillary teeth are most effected by maxillary pneumatization?
first and second molars
why do maxillary teeth need special consideration with extraction?
because there is only a thin shell of bone around the maxillary sinus during pnenumatization, which could reamin attached to the root of the tooth and break away when pulling the tooth out.
when is an oro-antral communication made?
when a maxillary molar is pulled out and the bone is still connected, it could expose the maxillary sinus.
how could a root of a tooth be forced into the maxillary sinus?
tooth elevators that are used to luxate teeth are wedged into the pdl space around the roots, but can force the root into the maxillary sinus
true or false: you need surgery to remove a root from the maxillary sinus
true