Unit 2: Tissues and integumentary system
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Tissues:
Tissues are groups of _ that are similar in structure and preform a common _ and are _ together.
The study of cells is called _ and people who have these jobs are called histologist.
cells, function, snapped, Histology,
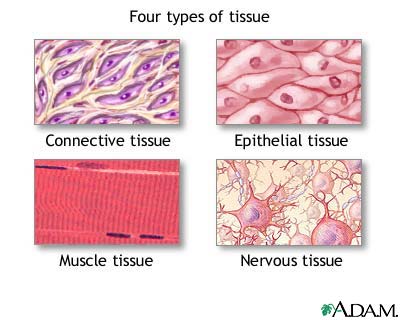
What are the 4 major types of tissue and what do they do?
Connective(support), muscle(movement), epithelial (covering), nervous(control)
Epithelial tissue
Associated with body _ and body _. As well as _ tissue.
Functions: _, _, _, and _
linings, coverings, Glandular(gland), protect, absorb, filtrate, secretion
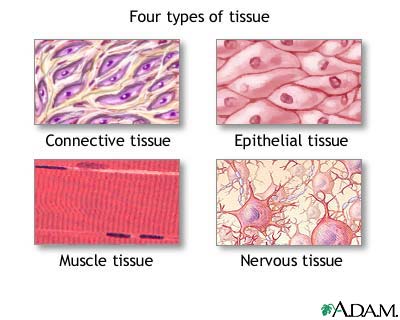
How do you name epithelial tissue (and only epithelial tissue!!!!!!)
based of the _ if cells layers
based of the _ of cells
number, shape
How do you name epithelial tissue (and only epithelial tissue!!!!!!)
Look at the number of cell layers
- What are the two cell layer names? _ and _.
- Simple- is _ cell layer.
-stratified- is _ than one layer.
-The _ layer absorbs, filtrates, and secretes
-The _ layer protects.
Shape of the cells
What are the 3 cell shapes that epithelial tissue can be made out of? _, _ and _.
-Squamous- means _
-Cuboidal- means _ shaped
-columnar- means shaped like a _
-So what will the thinnest layer of epithelial tissue be named?
Simple, stratified, one, more, simple, stratified, squamous, cuboidal, columnar, flattened, cube, column, simple squamous epithelium
Mucous membrane
_ is a specialized membrane that lines all the body cavitys that open to the _ body surface, such as the respiratory, digestive, and urinary tracts.
Often adapted for _ or _.
Wet _ absorb things better, which is why we need mucosae
mucosae, exterior, absorption, secretion, membranes
Glandular epithelia
A gland that is specialized tissue made of similar _ that make and transport a particular product of _.
What are the 4 types of glandular epithelia? _, _, _, and _.
cells, secretion, endocrine gland, exocrine gland, unicellular exocrine glands, multicellular exocrine glands
_ are a tube or vessel of the body through which fluids pass.
Glands
Endocrine gland (glandular epithelia)
An _ secreting that secretes _ directly to the _ stream.
Because these glands secretes directly they do not need ducts and are _.
internal, hormones, blood, ductless
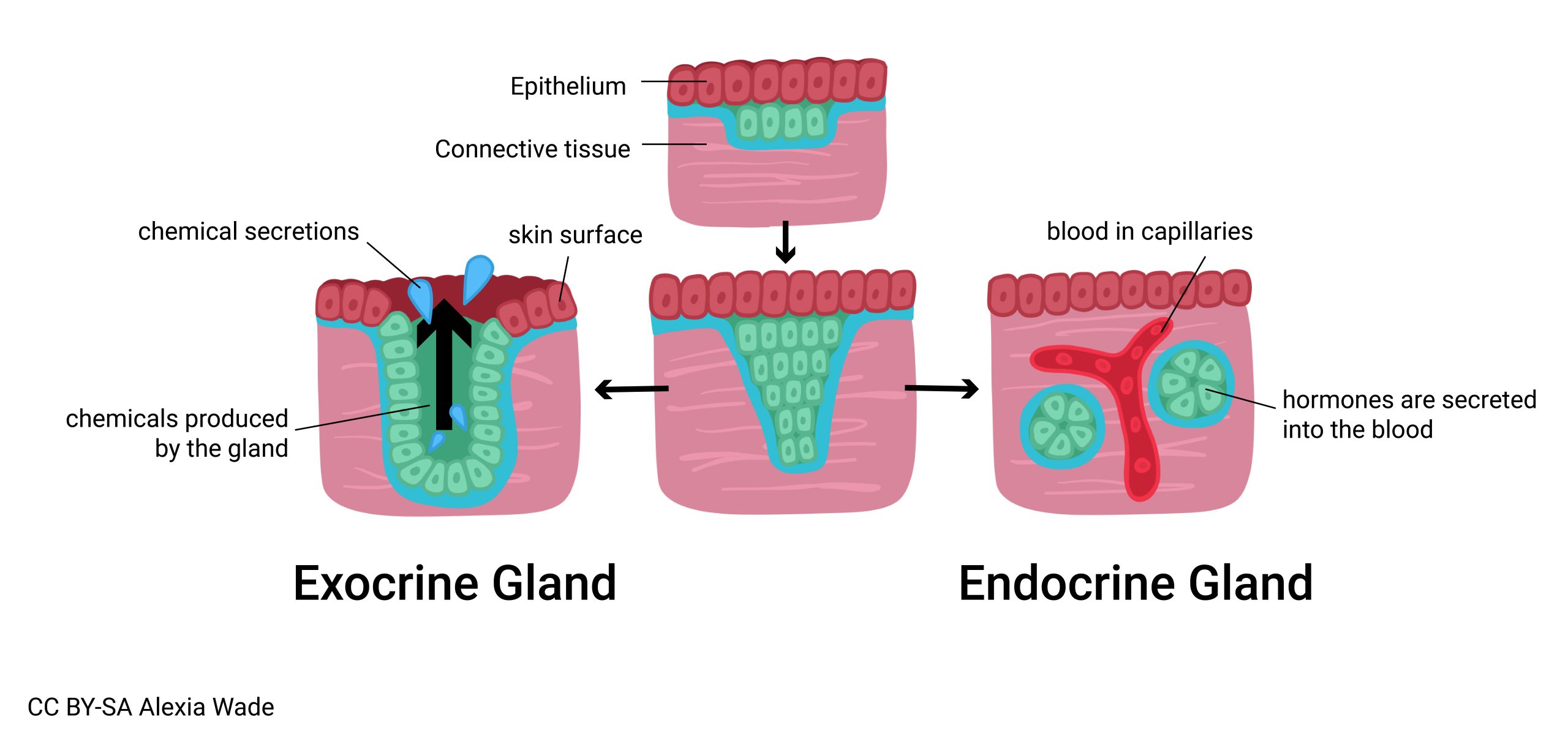
Exocrine gland (glandular epithelia)
An _ or _ gland that has _, to transports secretions
The secretions are _
internal, external, ducts, non-hormonal
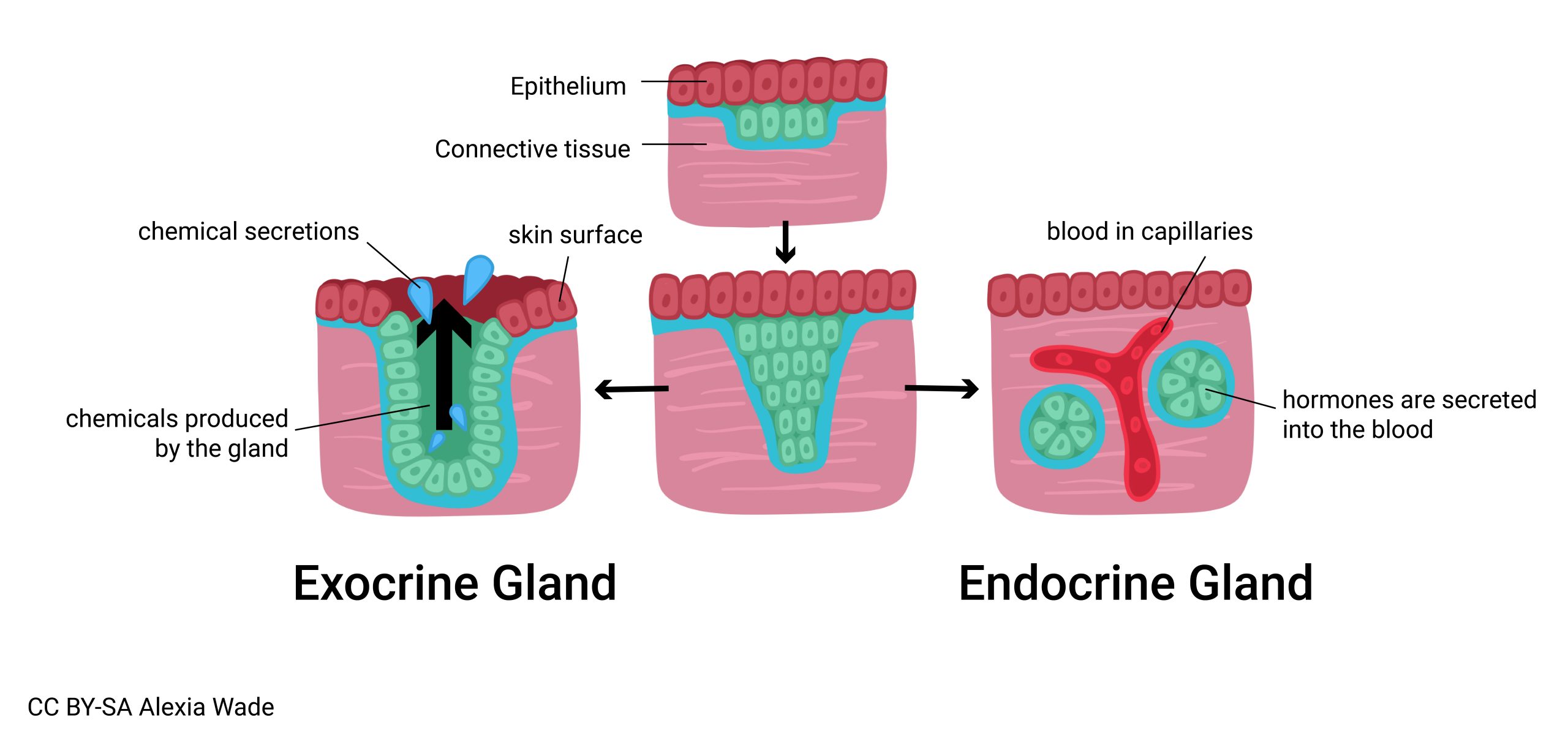
Unicellular exocrine gland (glandular epithelia)
Not a tissue or an organ but a single _.
-The cell is called a _ cell.
-The cell is located in the epithelial lining of the _ and _ tract.
-The product is a protein called _.
-Mucin and water= _
-rare
cell, goblet, intestinal, respiratory, mucin, mucus
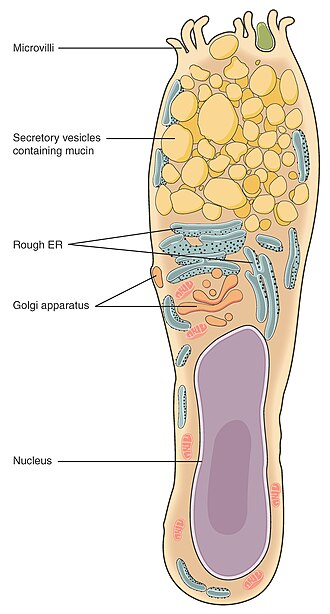
Multicellular exocrine glands (glandular epithelia)
most exocrine glands are _.
Made up of two basic parts: The _ and _.
_- specialized cells, often derived from epithelial tissues, that produce and release substances
_- specialized tubular structures formed by glandular epithelial cells that transport secretions from glands to targeted areas in the body
3 different categories of multicellular exocrine glands: _, _, and _.
multicellular, epithelium-derived duct, secretary cells, secretary cell, merocrine, apocrine, holocrine
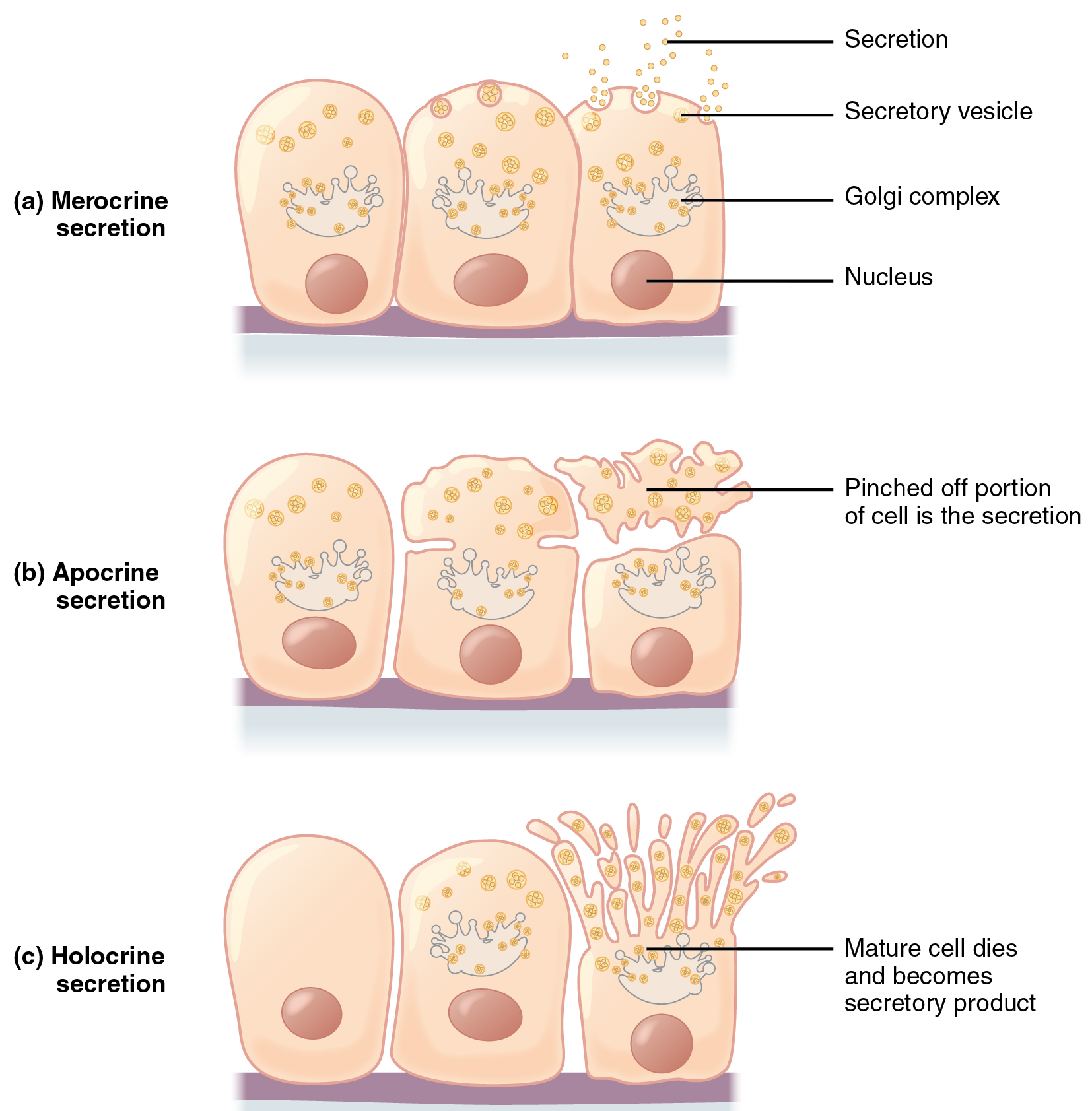
The 3 types of multicellular exocrine glands (glandular epithelia)
all of the glands secrete products differently
Merocrine gland- secrete products through _.
Apocrine gland- secrete products with _ around it (like a vesicle).
Holocrine gland- secrete products by giving up whole _ that makes the product and uses _ to replace the cell.
ducts, membrane, mitosis
Connective tissue
-found _ in the body
-in different connective tissue there is a range on how _ it is. If tissue is heavily vascularized it means it has a _ of blood going to it. If something is less vascularized it means, it has a _ blood supply. which is why it might take a longer time/never for some parts of our body to _ because the tissue isn’t living since it doesn’t have blood.
-Two basic components of connective tissue:
_ and _
-Functions: bind _ together, offers _, _, _, and water _.
Connective tissue types: “You can remember them through c2b2”. _, _, _, _
everywhere, vascularized, bunch, poor, heal, living, non-living, tissue, support, protection, transport, absorption, connective tissue proper, cartilage, blood, bone
Does all connective tissue have to be solid?
No
Parts of connective tissue
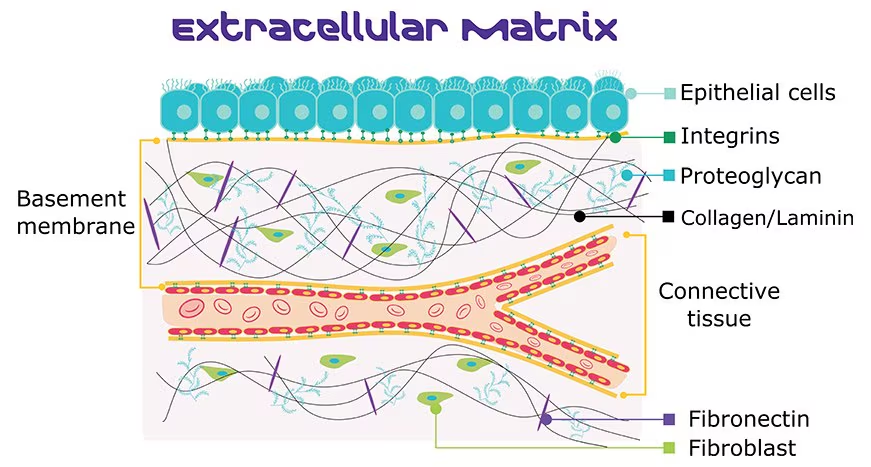
The _, is the non-cellular 3D network of proteins and polysaccharides surrounding cells in all tissues.
Living part of the connective tissue
In the extracellular matrix there is _ that make the components in the extracellular matrix. This cell is the _ component of connective tissue.
Fibroblast cells make: _ and _.
Nonliving part of the connective tissue made by the fibroblast
_ is a gel-like component of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in connective tissue that fills the spaces between cells and fibers. Its composed of _, _, and _.
_ are structural proteins that form a meshwork outside cells.
The 3 type of fibers: _, _, and _.
Extracellular matrix, fibroblast cells, living, ground substance, fibers, ground substance, water, protein, polysaccharide molecules, fibers, collogen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers
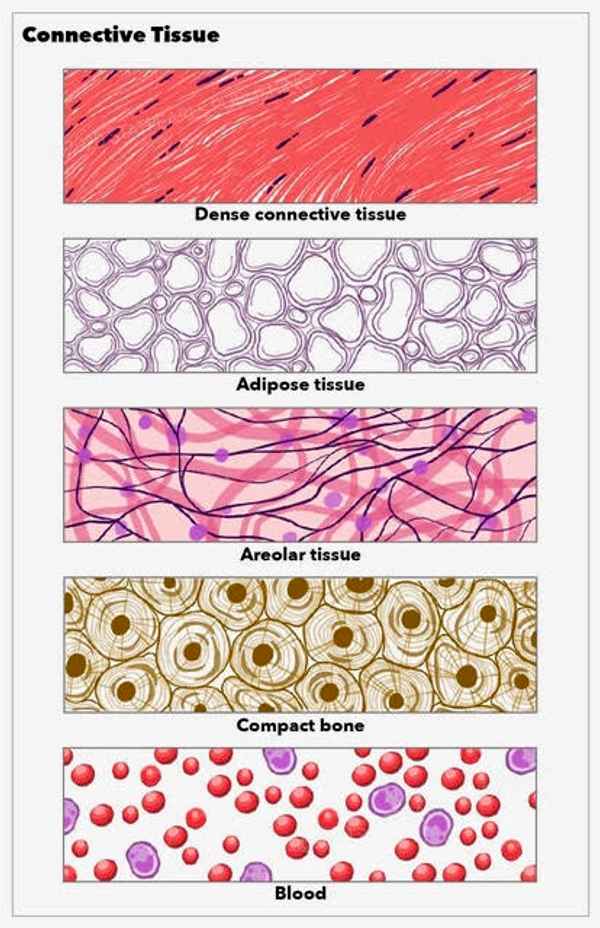
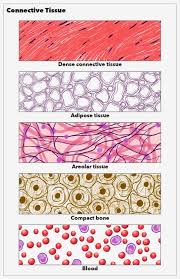
There are two types of connective tissue: _ and _
The connective tissue proper: _ and _.
-_ is dense compacted fiber that create wire like substances in the body like _
-_ is the most common connective tissue that hold together one _ to another, like epithelial tissue to muscles
Specialized connective tissue: _, _, _and _.
-_ (also known as fat tissue) is full of yellow fat ‘Gel’ with little to none fibers.
-_ little to no fibers making it more flexible, making it soft and squishy.
-_ hard tissue with lots of cells and dense fiber with little gel.
-_ the liquid connective tissue that meets the category because it has everything a connective tissue needs(ground tissue, fibers, and cells).
connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue, areolar connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue, ligaments, tissue, adipose connective tissue, hyaline cartilage, bone, blood, adipose connective tissue, hyaline cartilage, bone
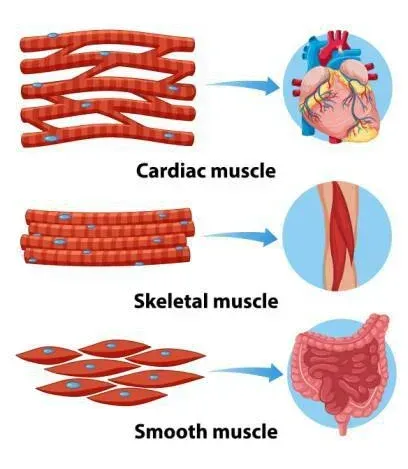
Muscular tissue
-muscular tissue, is made up of muscle _ that snap together to make muscle _.
Function of muscular tissue: Produce _.
What are the three types of muscle? _, _, and _.
_ muscle around heart the contracts in a pace and sequence
_ muscle that help peristelsis (wave-like muscle contraction) to help you swallow and get food down intestines and more
cells, fibers, movement, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac, smooth
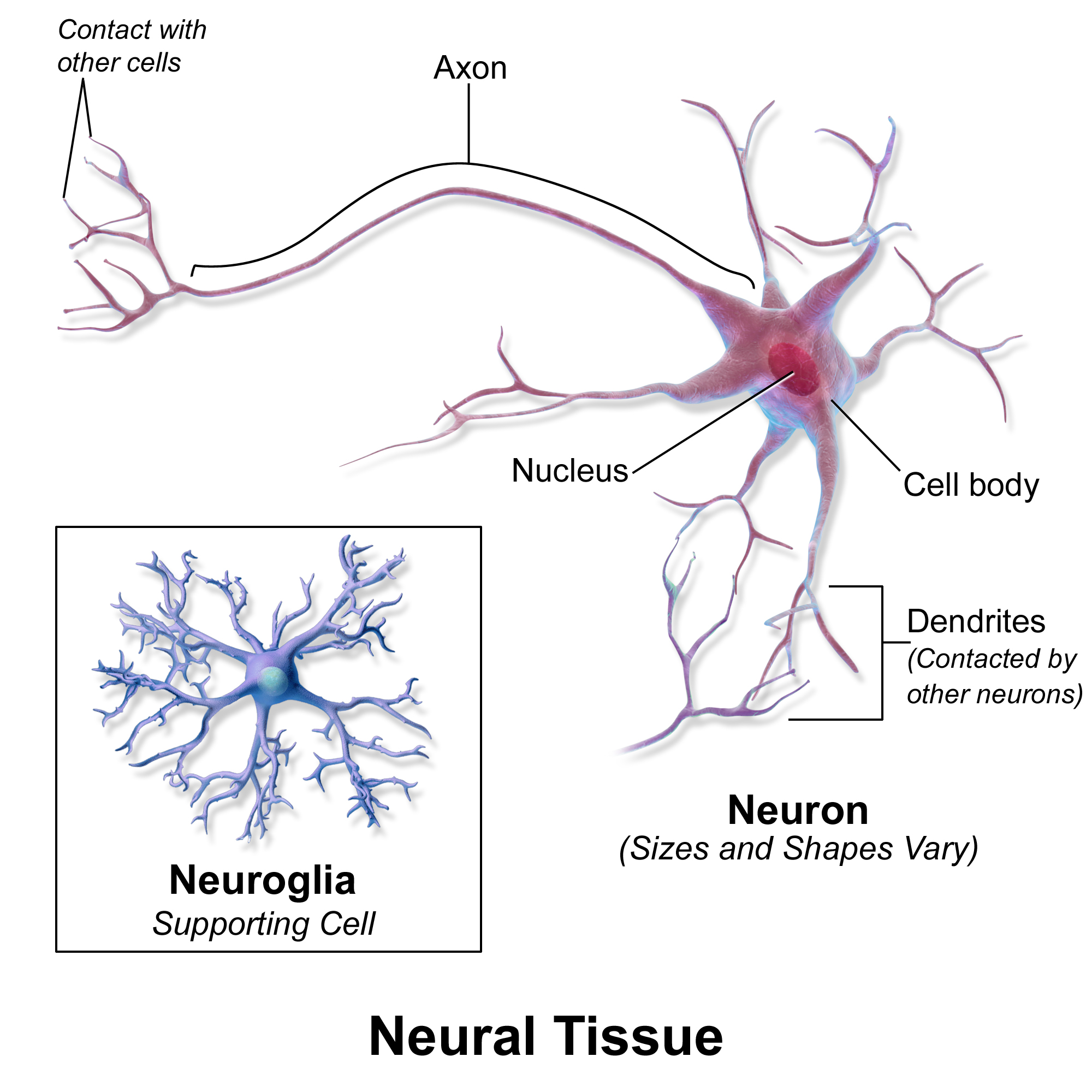
Nervous tissue
Found in: the _, _, _ nerves (nerves that branch out), _ organs
Made up of: _ and _
-_ are nerve cells
-_ help regulate and manage neuron function
Function
_ and _ center that sends and interprets sensory info and electrical currents.
brain, spinal cord, peripheral, sensory, neurons, neurological cells (support cells), neurons, neurological cells, control, processing
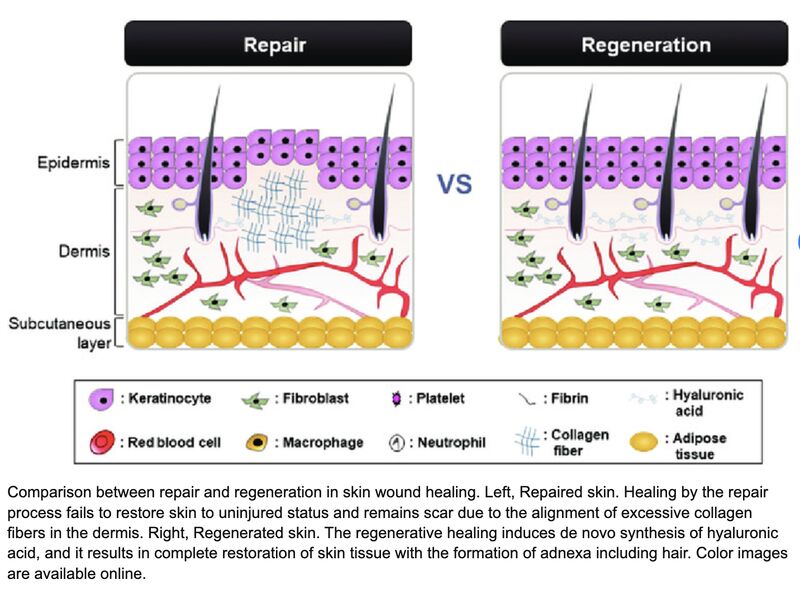
Tissue repair
What two things will hopefully happen if you damage tissue? _ or _.
The tissue repair process is regulated by the _ of tissue damaged and the _ of the injury
Fibrosis- is the repair of tissue using _. This is only done if the tissue damaged _ come back.
Regeneration- Is the _ of destroyed tissue using the _ type of cells to fully pair the normal tissue. This is done using _.
-An important _ used in tissue repair is _. It regulates cell _ and _. Fibronectin is found in _ and in the _.
regeneration, Fibrosis, type, severity, dense fibrous connective tissue(scar tissue), cannot, replacement, type, mitosis, glycoprotein, Fibronectin, attachment, repair, plasma, extracellular matrix
What is the bodys largest organ?
Skin
Integumentary system
What are the parts of the integumentary system? _, and _.
-Skin= _ = covering
-Humans get “New” skin every _ ish days because our old dead cells on our body’s surface flake _.
Humans have _ to _ kg (_ to _ pounds) of skin
-extreme thickening of skin due to friction is called _.
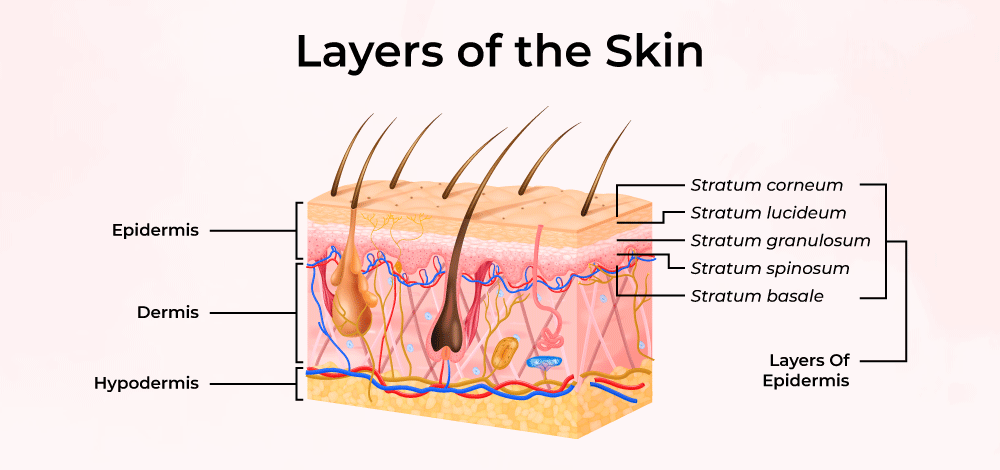
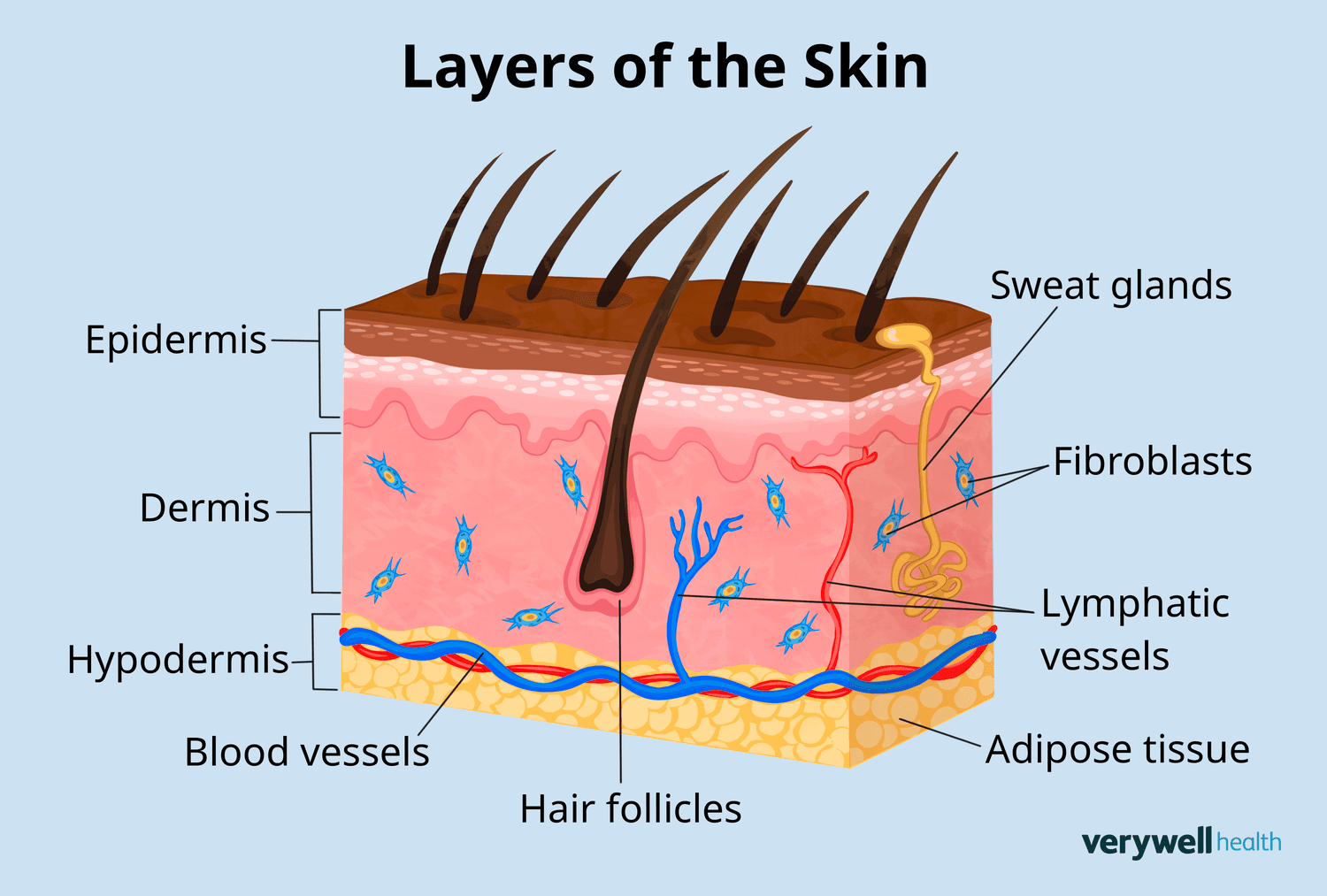
What are the 3 layers of skin(going from top to bottom): _, _, and _.
skin, derivatives(skin, hair, nails), integument, 45, off, 4,5 ,9, 11, callus, epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
Cyte= _
Cell
What is the specific type of tissue that makes the epidermis?
Sratified sqamous epithelium
Epidermis
The _ outer layer of the skin.
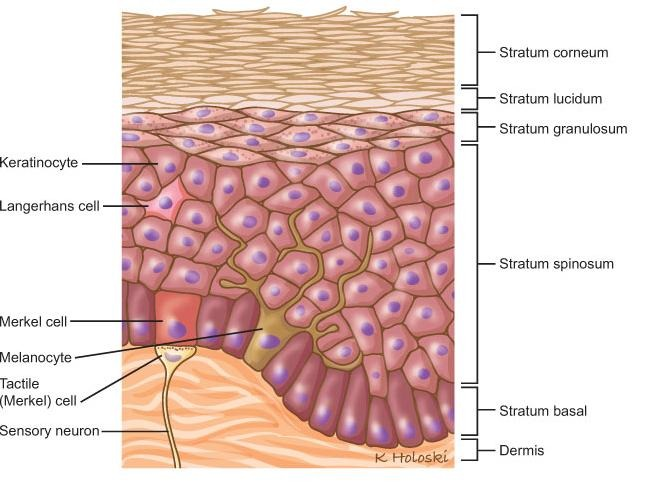
There are four cells that make up the epidermis: _, _, _, and _.
-Keratinocytes- made up of _, which are proteins. Keratinocytes make up _ of the epidermis. Keratinocytes start from the _ of the and as it moves up towards the surface over 45, they _, which leaves the outer layer of our skin to be made of _ keratinocytes cells.
-Langerhans cells- These are _ cells, which are modified _. Immune response to keep “_” out, by staying positioned randomly throughout the epidermis and when triggered it _ the germ
-Merkel cell- Extremely _. Merkel cells have “extensions sticking off of them” and are connected to a _ nerve. They help detect touch and sensory info and send it to our _.
-Melanocytes- They are _ cells, they make the pigment for our skin tone
There are 4-5 _ , of the epidermis. The layers are made out of _.
The type of skin is _ and _.
- _ : palm, fingertips, soles. Is _ strata (layers). This type of skin is 5 layers because it includes the _.
-_ : remainder of body. Is _ strata (layers), This type of skin is only 4 layers because it doesn’t include the _.
What are the 4 or 5 strata/layers of the epidermis (going deep to surface): _, _, _, _, and _.
Stratum basale- the _ layer, which is right above the dermis and is only _ layer thick. The 2 cells of this layer is _, _. In this layer _ is produced and skin is regenerated through _ mitosis.
stratum spinosum- _ granules are deposited here, which give our skin its color, and _ cells are abundant in this layer.
stratum granulosum- accumulate granules that deposit _ which makes this layer waterproof and keeps water out
stratum lucidum- a thin, clear layer of dead, flattened keratinocytes found exclusively in the _ of the palms, fingertips, and soles
stratum corneum- outermost layer, is _ -_ cells layers thick. This layer is composed of _ keratin cells, this layer is also waterproof due to _.
thin, keratinocyte, melanocytes, Merkel cells, langerhans cells, keratin, most, bottom, die, dead, immune, white blood cells, germs, catches, sensitive, sensory, brain, pigment, layers, keratinocytes, Thick skin, Thin skin, Thick skin, 5, stratum lucidum, Thin skin, 4, stratum, lucidum, stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum, bottom, 1, melanocytes, merkel cells, keratinocytes, mitosis, melanin, landgerhans cells, lipids, thick skin, 20-30, dead, glycoplipids
What is the connective tissue of the dermis?
Dense connective tissue
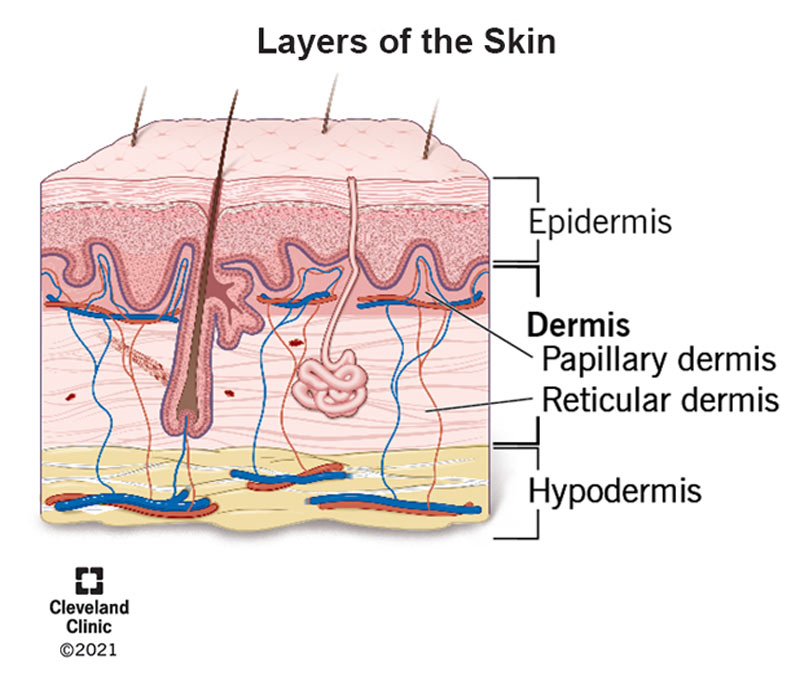
Dermis
The main thick layer of the _.
Whats are two layers of the dermis? _ layer and _ layer.
papili= _ like projection (like waves)
-Papillary layer- is _ vascularized. The _ papillae (in the upper layer of the dermis) have /_ loops and _. The nerve endings help sense pain and touch. The capillaries are connected to the _
AKA this isn’t really apart of the dermis it’s just info to better understand capillaries: The _ pumps blood. _ are blood vessels connected to the heart that pump blood out of the heart. _ are blood vessels connected to the heart that pump blood out of the heart. Since none of these should be leaking blood, the way blood travels around the body to other tissue is through /_.
- This is why _ cells are dead because they are far from the capillaries in the dermis part of skin which has blood that cells need to live.
Reticular layer- This is _ of the thickness of the dermis. Skin _ and _ comes from this layer. This is because _ binds with water, which leaves the skin _ and easy to recoil. which is why we can do the skin dehydration pinch test.
skin, papillary, reticular, finger, highly, dermis, capillary, nerve endings, dermis papillae, heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, epidermis, 80%, resilience, hydration, collagen, stretchy
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous fat)-
The _ layer of skin,
made full of * _ * and the hypodermis is basically just this ← important
Deepest, Adipose (fat) tissue
Skin color determinates - comes from 3 _ if the skin.
The 3 pigments: _, _, and _.
_ - orangish yellow pigment
_ - blackish brown, dark pigment
_- pinkish red pigment
-Our skin tone come from a unique genetic _ of the 3 pigments. Over _ genes control our skin color
-Melanocytes which make melanin is only _ layer thick which is thinner than a piece of paper
-freckles, moles, and birthmarks are local _ of pigments, which is just mistakes in depositing pigments (doesn’t hard people)
pigments, melanin, carotene, hemoglobin, carotene, melanin, hemoglobin, mixture, 100, 1, accumulation
Skin glands- /_ and /_
-sebaceous glands-
Produce /_ called sebum. A /_ for skin by keeping moisture trapped and kills /_.
The /_ ducts empty into /_ follicles
Not found on /_ and /_.
Glands are activated at /_, which is why we have teenage acnes.
This is why we want /_ soluble lotions so we can actually get hydration.
-Sweat glands Actually called sudoriferous glands-
Over the /_ surface of the body, that are /_
over /_ million per person
There are two major types: /_ and /_.
~ Eccrine glands
secrete /_. Sweat is 99% /_ and then there’s /_, /_, /_, and /_ like lactic acid and nitrogenous waste.
Nitrogenous waste is the precursor to /_ which is why we smell so bad when we sweat.
~ Apocrine glands
secrete light airbone moleucles called /_, which make us smell different to others and may make us attractive to different people.
increase during /_ activity and during /_
sebaceous glands, sweat glands, oil, lubricate, bacteria, exocrine, hair, palms, feet, puberty, lipid, entire, endocrine, eccrine glands, apocrine glands, sweat, water, salt, vitamin c, antibodies, metabolic wastes, pee, pheromones, sexual, puberty
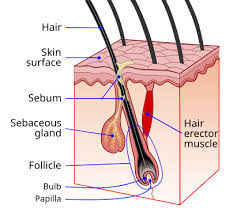
Hair
Consist of /_ that are full of keratin, keratinocytes. At the root of the hair is /_, which means at the root the cells are /_ and as it gets further is /_.
-/_ in the cell give hair its hair color and when it dies, hair is left colorless which is /_.
epithelial cells, capillaries, alive, dead, melanocytes, gray,