LABORATORY 7 HISTOLOGY II -- MUSCLE TISSUE, NERVOUS TISSUE, MEMBRANES, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
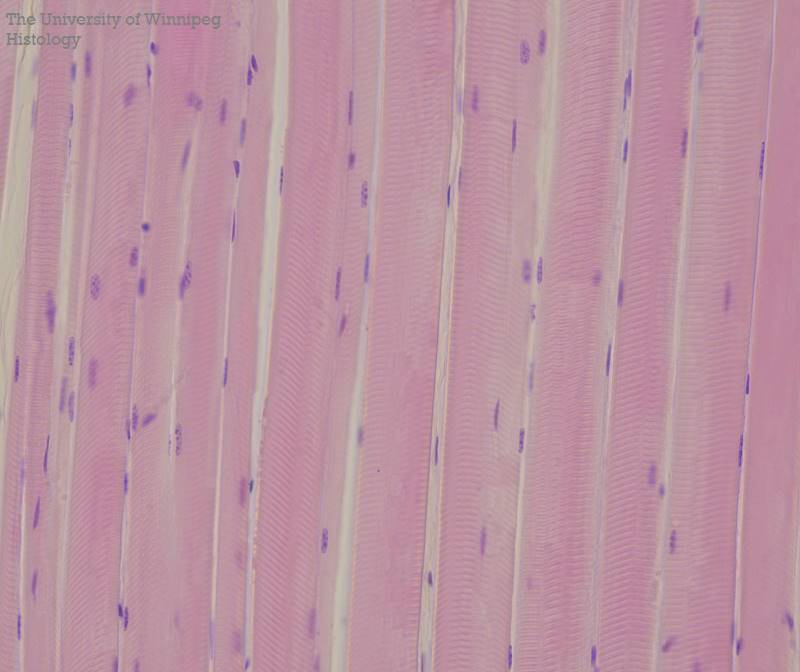
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Associated with movement and is under voluntary control.
located in skeletal muscules
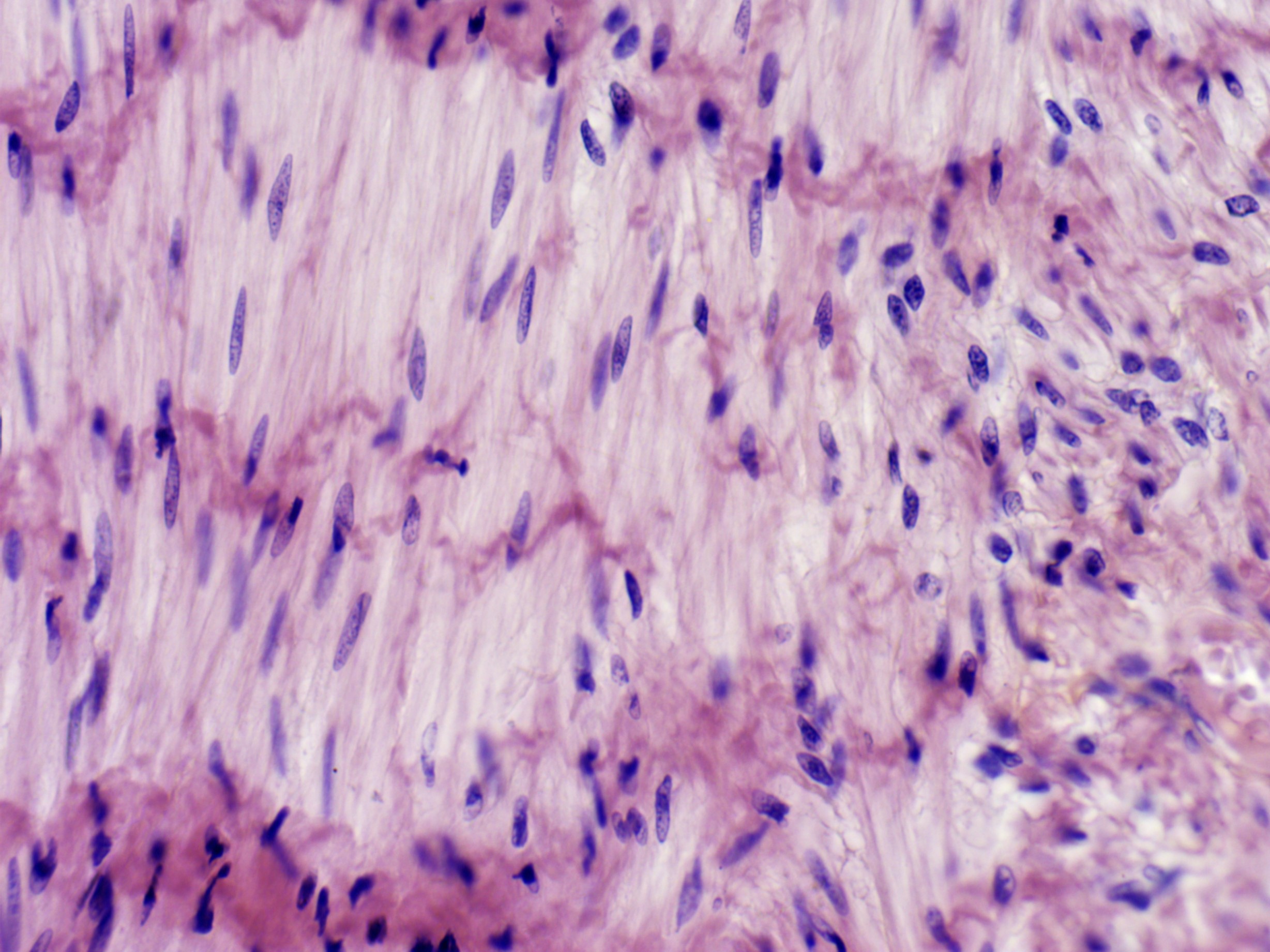
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Found in organs and structures like the digestive tract, and operates involuntarily.
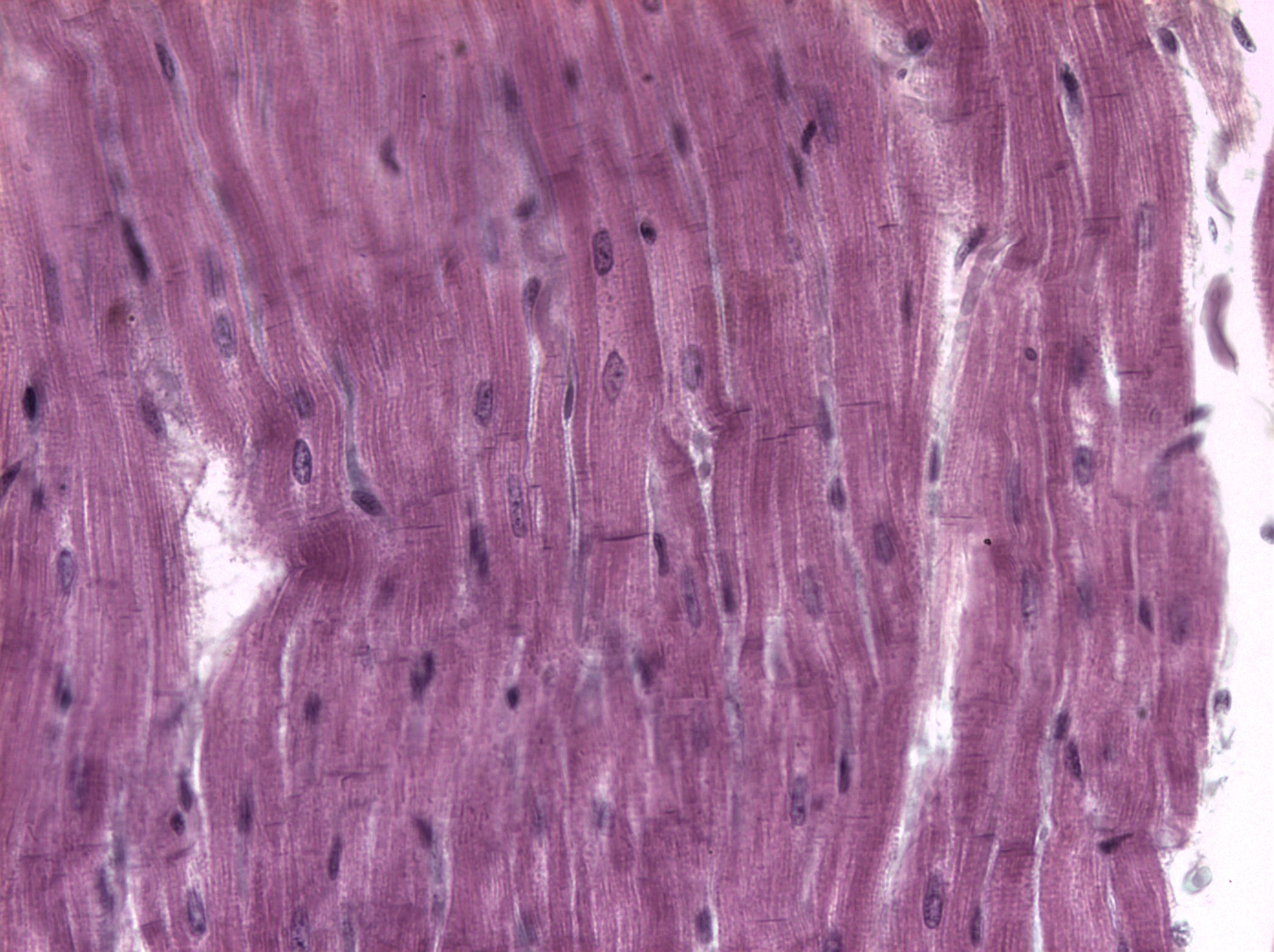
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Found in the heart, has unique characteristics, and operates involuntarily.
Axon
Conducts electrical signals away from the neuron's cell body
Cytoplasm
Houses cellular organelles; site of various cellular activities
Neurofibrils
Provide structural support; aid in substance transport
Telodendrites
Form synaptic connections with other cells.
Nucleus
Contains DNA; controls cellular activities
Nissl Bodies
involved in protein sysnthesis
Dendrites
Receive signals; transmit them toward the cell body
Nucleolus
involved in ribosome production
Nodes of Ranvier
They help nerve impulses travel faster by allowing them to jump from node to node.
myelin sheath
protective coating around a neuron's communication line (axon). It helps the electrical signals travel faster
main types of tissues in the human body
Epithelial Tissue: Forms protective coverings and linings, often on body surfaces and organs.
Connective Tissue: Provides support, connects, and protects various body structures.
Muscle Tissue: Responsible for body movements, posture, and heat generation.
Nervous Tissue: Facilitates communication and coordination through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters in the nervous system.
three types of body membrane
mucous membrane
Serous membranes
cutaneous membrane
mucous membrane
Location: Line body cavities open to the exterior.
Function: Moist membranes with various epithelia; contain goblet cells or mucous glands.
example: reproductive tract
function and body location of nervous tissue
Function of Nervous Tissue: Nervous tissue acts like the body's communication system, receiving and sending electrical signals to control actions and respond to stimuli.
Body Location: Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body, forming a network that helps coordinate functions and reactions. It's like the body's messaging and control center.
Serous membrane
protective layers that cover the inside of certain body spaces. They are found in closed areas like the heart, lungs, and the abdominal region.
cutaneous membrane
fancy name for our skin. It's the outer layer exposed to the air, and it's what we feel when we touch ourselves. It's a dry layer and is part of the system that includes our skin, hair, and nails.
state the three layers of the skin
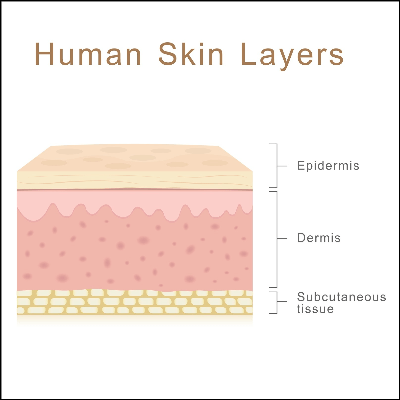
what is the epithelium of the outer layer of skin
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
where is the epidermis thickest
palms of the hand
where is the epidermis thinnest
eyelids
what are the two layers within the dermis
the thin superficial papillary layer is the areolar connective tissue and it connects the skin to the tissues below.
deepest and thickest layer of the two is the irregular dense connective tissue and support the skin and body to prevent ripping
state the associated structure of the epidermis