Ch2: Relational Database
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Why use a database instead of flat files?
While all flat files & databases ensure : Persistency
Databases offer Persistency & Durability:
structured storage
fast search
concurrent access
flexible query language (just relational databases)
data consistency (just relational databases)
What is a database?
A: A collection of related data with implicit meaning. Can be of any size & complexity.
What is metadata?
A: Data that describes the structure and constraints of the database (e.g., data types, relationships) stored in a catalog.
What are the core tasks of a DBMS (database management system)?
A:
DBMS creates and maintains databases:
Define the database (schema)
Construct the database (populate)
Manipulate data (query, updating, generating)
Enable sharing (concurrency)
What is a transaction in a DBMS?
A: A program or process tasked by DBMS that reads from or writes to a database. DBMS ensures its ACID properties.
What is a key problem with traditional file-based systems and how does database approach solve data redundancy?
A: Data redundancy and inconsistency due to duplicate data being stored in multiple files and formats.
→ By centralizing data storage and allowing multiple applications to access a single version of the data.
What is data abstraction in the context of a DBMS, and why is it important?
A:
Data abstraction hides low-level data storage and implementation details from users (e.g., data models)
→ allows program-data independence + provides conceptual representation of the data
What is concurrency control?
A: Ensuring correct results when multiple users access or update the database at the same time, ensured by ACID properties.
What does ACID stand for?
A:
Atomicity: all or nothing
Consistency: preserves valid states
Isolation: transactions don't interfere
Durability: changes persist after committed
What is a relational data model?
A: A model where data is organized into relations (tables), each with rows (tuples) and columns (attributes), based on a schema.
What is the difference between a schema and a state?
A:
Schema: Description of structure (type pf metadata), e.g., column names, types
State: Actual content (records) at a point in time
What are the three types of data models?
A:
High-level (Conceptual) – close to user view (e.g., ER model)
Low-level (Physical) – describes storage details (specialist view)
Representational – between the two (e.g., relational model)
Who proposed the relational model and when?
A: Ted Codd in 1970 at IBM, quickly became standard bc of simplicity & mathematical foundation.
What is a tuple in a relation?
A: A row (record) representing an instance of an entity or relationship.
What is a domain in relational databases?
A: The set of valid atomic values an attribute can take (e.g., integers, strings, date).
What is a relation schema?
A: The structure of a relation, denoted as R(A1,A2,...,An), where Ai are attributes.
What does the arity (or degree) of a relation refer to?
A: The number of attributes (columns) in a relation.
What are NULL values used for?
A: Representing unknown, inapplicable, or missing attribute values-but best avoided when possible due to ambiguity.
What possible constraints on the values in a data base state:
A:
Implicit constraints (inherent)
Explicit constraints (in schema, integrity constraints)
Semantic constraints (≠ expressed explicitly in the schema)
What are the main types of relational integrity constraints?
A:
Domain constraints: w/i each tuple, the value of each attribute A must be an atomic value of domain dom(A)
Key constraints: tuple w/i a relation are unique
Null constraints: specify whether/not 0 values are permitted for an attribute
Entity Integrity: primary keys cannot be NULL — ensures each tuple is uniquely identifiable.
Referential Integrity: ensures that foreign keys point to existing tuples or are NULL
What is the difference between a superkey and a key?
A:
A superkey is any set of attributes that uniquely identifies a row
A key is a minimal superkey — the smallest such set without redundancy
What is a primary key?
A: The designated candidate key used to uniquely identify tuples in a relation.
What is a candidate key?
A: A relation can have more than 1 key, each key that could serve as the unique identifier for a tuple, is called a candidate key
What is a foreign key?
A: An attribute in one table that references the primary key in another table — enforces referential integrity.
What SQL command is used to define a table?
A: CREATE TABLE
What are the basic update operations in SQL?
A:
INSERT— add tuplesDELETE— remove tuplesUPDATE— change values in existing tuples
How is a primary key declared in SQL?
A: PRIMARY KEY (attribute_name)
What is the basic structure of a SQL SELECT query?
A:
SELECT columns FROM table WHERE condition;
How does SQL treat NULL in comparisons?
A: NULL makes conditions UNKNOWN, requiring special handling with IS NULL or three-valued logic.
What is three-valued logic in SQL?
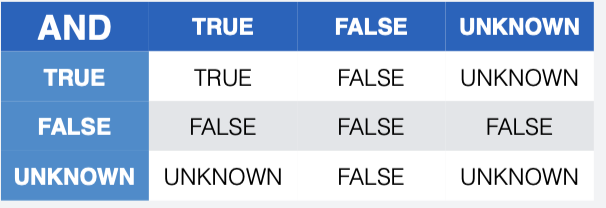
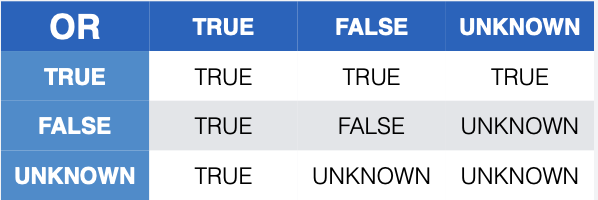
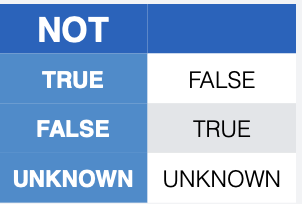
What is the purpose of the EXISTS keyword?
A: Tests if a subquery returns any tuples; returns TRUE if at least one row exists.
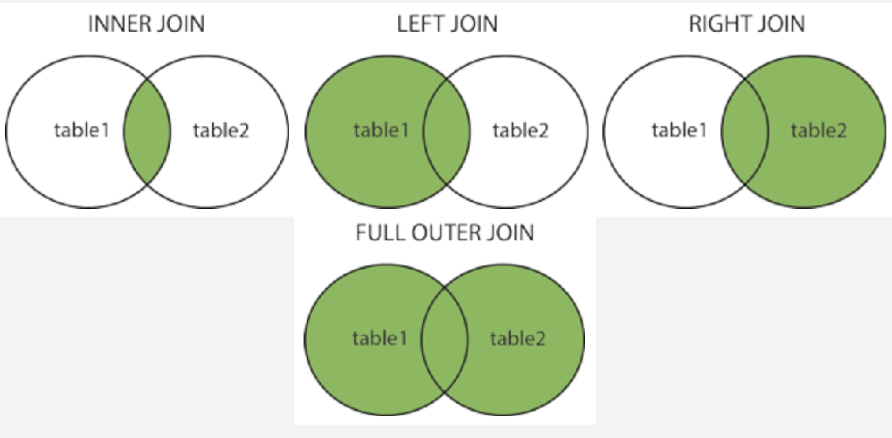
what are the different types of joined tables?